최소 단어 이상 선택하여야 합니다.
최대 10 단어까지만 선택 가능합니다.
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
NTIS 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
DataON 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Edison 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Kafe 바로가기
| 주관연구기관 | 경상대학교 GyeongSang National University |
|---|---|
| 연구책임자 | 장기철 |
| 보고서유형 | 최종보고서 |
| 발행국가 | 대한민국 |
| 언어 | 한국어 |
| 발행년월 | 2013-03 |
| 과제시작연도 | 2012 |
| 주관부처 | 교육과학기술부 |
| 연구관리전문기관 | 한국연구재단 National Research Foundation of Korea |
| 등록번호 | TRKO201300034890 |
| 과제고유번호 | 1345172450 |
| DB 구축일자 | 2013-12-21 |
| 키워드 | 면역반응:항 염작용:콜린성 항염작용:대식세포:패혈증:일산화탄소:7-알파 니코틴수용체:햄옥시게나제:신호전달immune response,anti-inflammation,cholinergic,macrophages,sepsis,heme oxygenase,a7 nicotinic receptor,signal transduction,MAPK |
연구의 목적 및 내용
2000년도에 들어서면서 CNS를 통한 염증과 면역에 대한 연구가 활발하게 진행되면서 cholinergic nerve 자극에 의한 항염작용이 있음이 알려졌다. 즉, a7nicotinic acetylcholine recetor (a7nAChR)를 통해 NF-kB가 억제되어 항염작용을 나타내는데 이를 처음 발견한 Tracey group에서 이러한 기전을 “cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway (CAP)"라고 명명하였다. 본인은 이 CAP의 target 단백으로 heme oxyge
연구의 목적 및 내용
2000년도에 들어서면서 CNS를 통한 염증과 면역에 대한 연구가 활발하게 진행되면서 cholinergic nerve 자극에 의한 항염작용이 있음이 알려졌다. 즉, a7nicotinic acetylcholine recetor (a7nAChR)를 통해 NF-kB가 억제되어 항염작용을 나타내는데 이를 처음 발견한 Tracey group에서 이러한 기전을 “cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway (CAP)"라고 명명하였다. 본인은 이 CAP의 target 단백으로 heme oxygenase (HO)-1일 가능성에 대한 가설을 세우고 a7nAChR의 agonist인 nicotine을 사용하여 전신성염증반응인 패혈증 모델에서 nicotine은 HO-1을 유도하여 항염작용을 나타내는지에 대한 연구를 수행하고자하였다. 따라서 1) 면역세포인 RAW264.7 cell에서 nicotine에 의한 HO-1의 발현 기전 확립, 2) 이에 대한 back-up 실험으로 nicotine에 의한 HO-1발현에 si-a7nAChR mRNA transfection, 3) HO-1 KO 동물등을 사용하여 본인의 가설을 입증하고자 하였으며 특히 패혈증에서 중요한 late phase cytokine인 high mobility group box-1 (HMGB1)의 억제를 통한 HO-1의 역할에 초점을 맞추었다.
연구결과
연구결과는 본인의 가설대로 nicotine은 CAP을 나타냄에 있어서 a7nAChR를 통해 Ca2+의 유입을 촉진하였고 이것은 Ca2+-dependent protein kinase인 PKC를 활성화로 이어졌으며 이어서 활성화된 PKC는 membrane의 NADPH Oxidase를 통해 reactive oxygene species(ROS)를 생성하였다. 이 증가된 ROS의 반응으로 RAW264.7 세포는 HO-1을 유도하였다. 이를 검증하기위해 PKC 억제제, NOX 억제제, ROS scavenger존재 하에서 nicotine이 HO-1을 발현 시키는지를 확인 하였다. 또한 이러한 HO-1의 발현이 α7nAChR수용체를 경유한것인지를 확인하기위해 si-RNA 기법을 사용한 si-α7nAChR를 transfection 시킨 세포에서 nicotine에 의한 HO-1의 발현이 줄어들었다. Nicotine에 의해 유도된 HO-1은 LPS로 처리된 세포의 HMGB1유리를 억제하였다.
HO-1차단제 존재 시 LPS를 처리한 RAW 264.7세포의 HMGB1유리와 염증성 cytokine양을 줄였다.
한편 nicotine 투여동물 조직(간, 폐등)에서 HO-1발현이 증가 하였으며 조직과 혈액의 HMGB1이 줄어들었음을 확인하였다. siHO-1RNA로 transfection시킨 RAW 264.7세포에서 LPS에 의한 HMGB1 유리도 nicotinexn여로 줄어 들었다. 또한 rHMGB1투여로 실험용 동물의 사망이 nicotine 투여로 생존률이 증가 함을 확인하였다. 마지막으로 HO-1-/- 동물에서 nicotine에 의한 HO-1의 발현이 안 됨을 확인하고 nicotine에 의한 항염작용이 소실되는지를 여러 염증 marker와 생존률등을 HO-1+/+동물과 비교함으로서 콜린성 항염작용에 대한 HO-1가설을 증명하였으며 그밖에 여러 약물을 사용하여 HO-1은 여러 질환모델(패혈증, 뇌 허혈조직손상, 상처치유동물모델등)에서 HMGB1의 negative regulator임을 증명하였다.
연구결과의 활용계획
본 연구를 통해 적어도 nicotinic 수용체를 통한 항염작용에 HO-1/CO가 cholinergicanti-inflammation pathway에 적어도 target이 됨을 in vitro와 in vivo에서 증명하였다. 이러한 연구의 중요성은 생체 내에서 heme을 함유하고 있는 효소들(HO-2, cytochrome c, hemoglobin, myoglobin, catalase, peroxidase등)이 choline 성 신경의 활성으로 HO-1이 유도되면 이 활성으로부터 유리될 수 있는 CO에 대한 연구와 이들 효소를 활성화 시킬 수 있는 약물의 개발도 가능할 수 있으므로 그 파급효과는 기대 이상으로 클 수 있을 것으로 생각된다. 활용분야는 염증과 관련한 질환에 적용 가능하므로 동맥경화증, 패혈증, 당뇨병, 심지어 암의 예방 및 치료도 가능할 수 있을것으로 생각됨.
Purpose&contents
Cholinergic modalities through vagus nerve- and/or α7nAChR-mediated mechanism have been shown to suppress excessive inflammation in several experimental models of diseases, including endotoxemic shock, sepsis, ischemia-reperfusion injury, hemorrhagic shock, colitis, postopertive
Purpose&contents
Cholinergic modalities through vagus nerve- and/or α7nAChR-mediated mechanism have been shown to suppress excessive inflammation in several experimental models of diseases, including endotoxemic shock, sepsis, ischemia-reperfusion injury, hemorrhagic shock, colitis, postopertive ileus and pancreatitis. However, the signal pathway and target molecule(s) for this are not elucidated. The purpose of the present study is to investigate the hypothesis that heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), may be responsible for suppression of the inflammation mediated by nicotine through α7nAChR. To test this hypothesis, HO-1 induction was investigated using nicotine, a well known α7nAChR agonist, in RAW 264.7 cells and survival was measured in CLP-induced septic mice. In particular, we focused on the issue of HO-1 which regulates high mobility group box-1 (HMGB1), a late phase cytokine in sepsis.
Result
We found that nicotine through activation of α7nAchR induced HO-1 protein in macrophages in vitro. Results showed that when nicotine actives a7nAChR, it causes to increase Ca2+ influx from the outside. The increased intracellular Ca2+ concentration activates Ca2+-dependent protein kinase which sequentially generates ROS(reactive oxigen species) through activation of NADPH Oxidase. This conclusion ws beased on the results that pharmacological inhibitors of each step was significantly antagonisted the action of nicotine. Following ROS generation, the cell may prepare to protect the cell from the oxidative stress. This motivation leads to induction of HO-1 via p38 MAPK. Importantly, we verified that silencing of functional receptor protein using transfection of si-a7nAChR resulted in diminishing HO-1 induction effect of nicotine. The reduction of proinflammatory cytokines by nicotine in LPS-treated cells was antagonised by HO-1 inhibitor indicating that anti-inflammatory efect of nicotine is mediatedat least by HO-1. We recently reported that CO inhibits high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), a pro-inflammatory cytokine, in LPS-induced endotoxemic rats. Therefore, we investigated whether HMGB1 is responsible for action of nicotine to ameliorate not only tissue injury but increase survival rate in animals treated with LPS or CLP (cecal ligation and puncture). As expected, HO-1 induction by nicotine significantly reduced the production of HMGB1 in LPS-sctivated cells and in blod of CLP-induced or LPS-treated septic animals. Finally, we confirmed our hypothesis using HO-1 knock out animals that HO-1 plays an important role for cholinergic anti-inflammatory action. Through this research, we learned that HO-1 is at east one of target protines for cholinergic antiinflammatory signal. Furthermore, we found a valuable lesson that HO-1 can be a negative regulator of HMGB1. This suggests that HO-1 can be a drug target for many diseases in which HMGB1 is major cause of pathophysiology such as sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis, and ischemic reperfusion injury so on.
Expected Contribution
From this project, we broadened our knowledge about the role of HO-1 in which HO-1/CO controls anti-inflammatory action through cholinergic system. In addition, we published our results performed though this project more than 8 papers in SCI journal. From this project we anticipate to give fundamental knowledge to pharmaceutical industry to develop new type of anti-inflammatory drugs.
 표
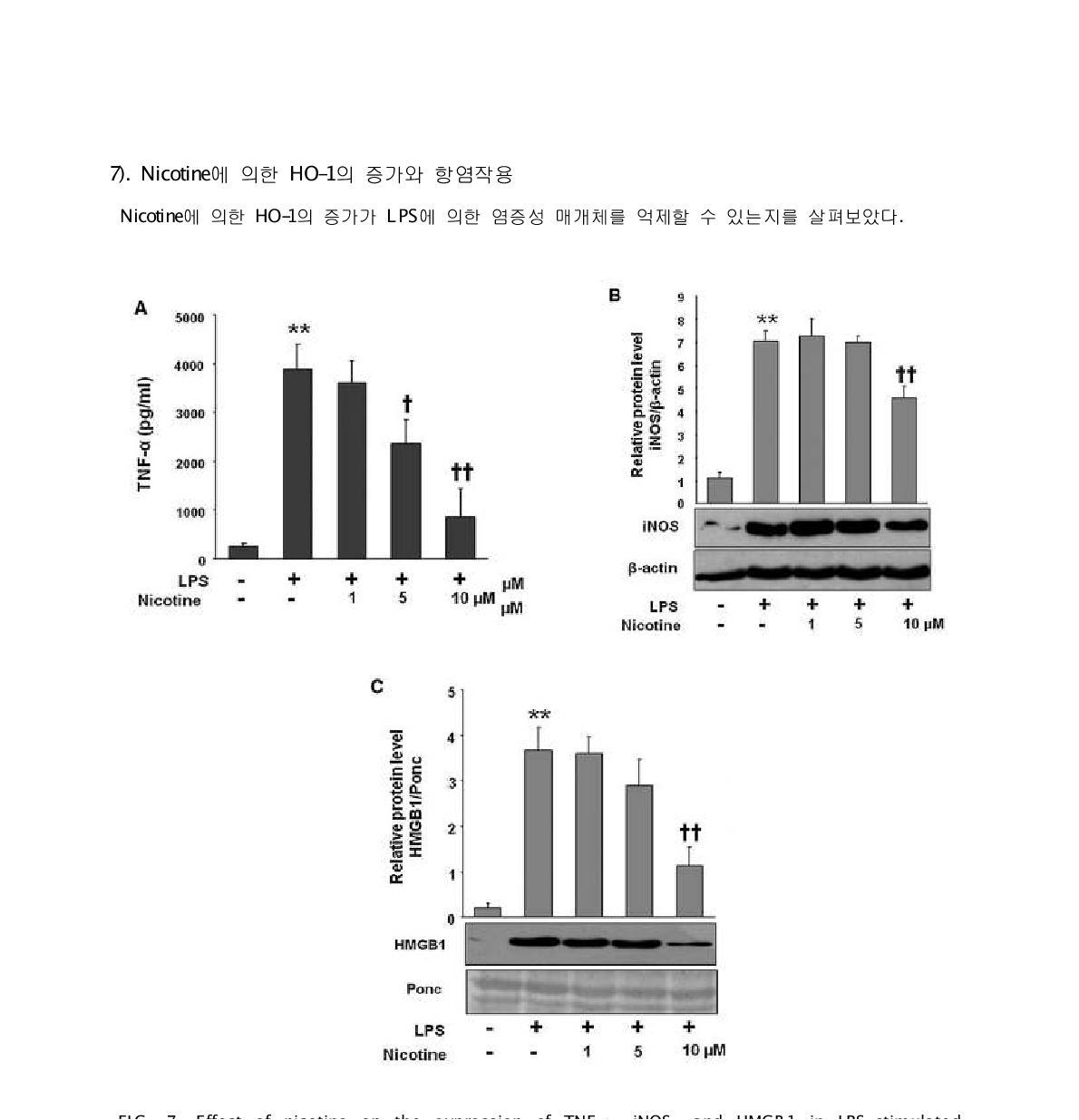
Effect of nicotine on the expression of TNF-α, iNOS, and HMGB1 in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Cells were stimulated with LPS (1 mg=ml) in the presence or absence of nicotine (1, 5, 10 μM) for 24 h. After incubation culture medium samples were subjected to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for (A) TNF-a detection, lysates were subjected to Western blot for (B) iNOS and (C) HMGB1, respectively. Blot bands are representative of three independent experiments. Data are presented as meanSD of three independent experiments. Significance compared to control, **p<0.01; significance compared with LPS alone {p<0.05 or {{p<0.01. HMGB1, high mobility group box 1; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
표
Effect of nicotine on the expression of TNF-α, iNOS, and HMGB1 in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Cells were stimulated with LPS (1 mg=ml) in the presence or absence of nicotine (1, 5, 10 μM) for 24 h. After incubation culture medium samples were subjected to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for (A) TNF-a detection, lysates were subjected to Western blot for (B) iNOS and (C) HMGB1, respectively. Blot bands are representative of three independent experiments. Data are presented as meanSD of three independent experiments. Significance compared to control, **p<0.01; significance compared with LPS alone {p<0.05 or {{p<0.01. HMGB1, high mobility group box 1; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
 표
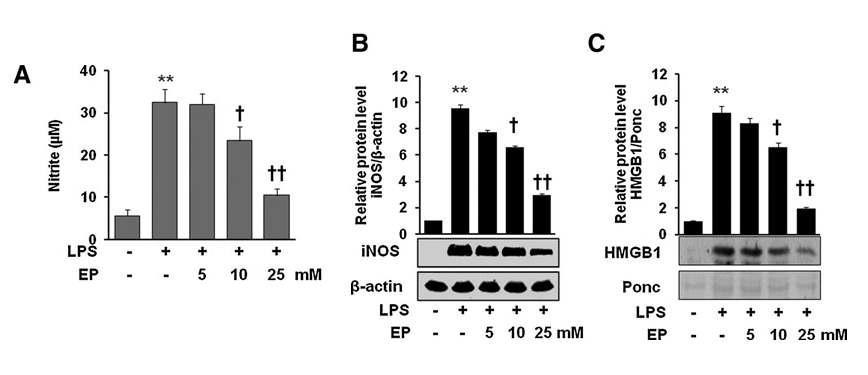
Effect of EP on the expression of iNOS/NO and HMGB1 release in LPS-stimulated macrophages (A– C). Cells were pretreated with EP for 1 h at doses 5, 10, and 25mM. Then, the cells were stimulated with LPS (1 mg/ml) for 16 h. The culture medium was collected and subjected to NO assay (A) and HMGB1 analysis (C). Cells were lysed and harvested and subjected to western blot for iNOS detection (B) as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
표
Effect of EP on the expression of iNOS/NO and HMGB1 release in LPS-stimulated macrophages (A– C). Cells were pretreated with EP for 1 h at doses 5, 10, and 25mM. Then, the cells were stimulated with LPS (1 mg/ml) for 16 h. The culture medium was collected and subjected to NO assay (A) and HMGB1 analysis (C). Cells were lysed and harvested and subjected to western blot for iNOS detection (B) as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
 표
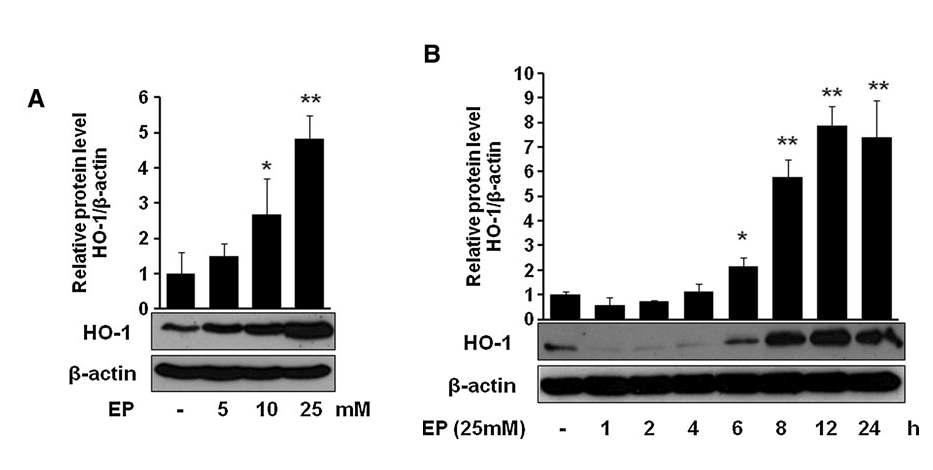
Effect of EP on the expression of HO-1 in macrophages. Cells were treated with EP at doses 5, 10, and 25mM for 8 h (A) or at dose 25mM for 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 h (B). After incubation, cells were harvested and subjected to western blot as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are presented as mean ±SD of three independent experiments. Significance compared with control, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01. HO-1, heme oxygenase-1.
표
Effect of EP on the expression of HO-1 in macrophages. Cells were treated with EP at doses 5, 10, and 25mM for 8 h (A) or at dose 25mM for 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 h (B). After incubation, cells were harvested and subjected to western blot as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are presented as mean ±SD of three independent experiments. Significance compared with control, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01. HO-1, heme oxygenase-1.
 표
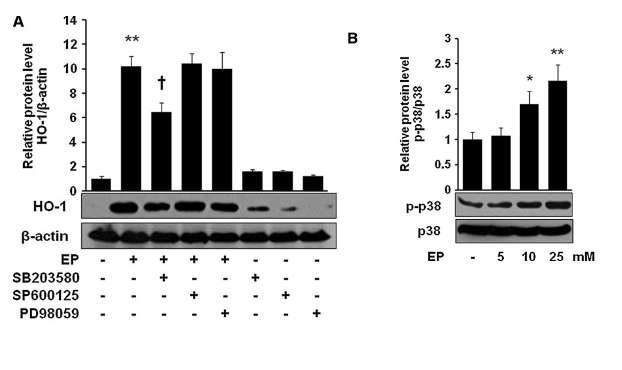
EP induces HO-1 through p38 MAPK. Cells were pretreated with SB203580 (10 μM), SP600125 (10 μM), and PD98059 (10 μM) for 1 h, and then cells were treated with EP (25mM) for 8 h (A, for HO-1) and for 6 h (B, for p-p38). After incubation, cells were harvested and subjected to western blot as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are presented as – SD of three independent experiments.
표
EP induces HO-1 through p38 MAPK. Cells were pretreated with SB203580 (10 μM), SP600125 (10 μM), and PD98059 (10 μM) for 1 h, and then cells were treated with EP (25mM) for 8 h (A, for HO-1) and for 6 h (B, for p-p38). After incubation, cells were harvested and subjected to western blot as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are presented as – SD of three independent experiments.
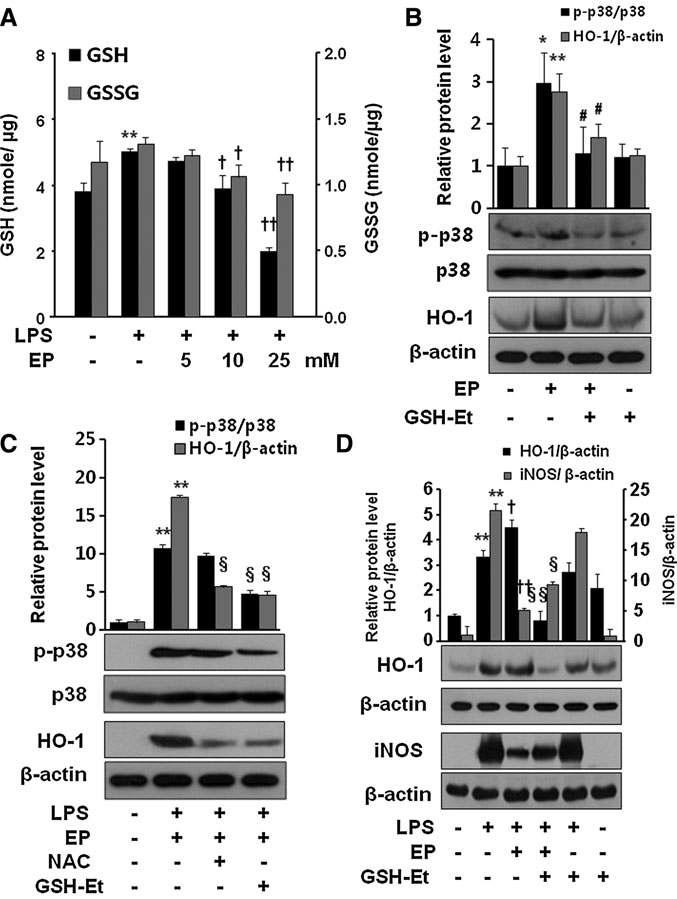 표
Effect of EP on intracellular GSH levels and p38 phosphorylation in RAW 264.7 cells. The cells were incubated for 24 h without or with LPS, or LPS with different concentrations of EP (5, 10, and 25mM). Intracellular levels of reduced (GSH) and oxidized (GSSG) glutathione were assayed (A) as described in the Materials and Methods section. To see the effect of EP on p38 phosphorylation and HO-1 expression, cells were incubated with EP (25mM) in the presence or absence of GSH-Et (10μM) for 8 h (B). To check the expression of HO-1 and p38 phosphorylation by NAC and GSH-Et, cells were incubated for 8 h in the presence of LPS + EP (C). To see whether GSH-Et reverses the EP effect on LPS-activated iNOS and HO-1 expression, cells were treated with EP (25mM) or EP with GSH-Et (10μM) for 8 h (HO-1) or for 16 h (HMGB1) in the presence of LPS (D). After incubation, cells were harvested and subjected to western blot as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are presented as means ± SD of three independent experiments. Significance compared with control, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01; significance compared with LPS, {p < 0.05 and {{p < 0.01; significance compared with EP, #p < 0.05; significance compared with LPS + EP, xp < 0.05 and xxp < 0.01. GSH-Et, glutathione ethyl ester; NAC, N-acetyl cysteine.
표
Effect of EP on intracellular GSH levels and p38 phosphorylation in RAW 264.7 cells. The cells were incubated for 24 h without or with LPS, or LPS with different concentrations of EP (5, 10, and 25mM). Intracellular levels of reduced (GSH) and oxidized (GSSG) glutathione were assayed (A) as described in the Materials and Methods section. To see the effect of EP on p38 phosphorylation and HO-1 expression, cells were incubated with EP (25mM) in the presence or absence of GSH-Et (10μM) for 8 h (B). To check the expression of HO-1 and p38 phosphorylation by NAC and GSH-Et, cells were incubated for 8 h in the presence of LPS + EP (C). To see whether GSH-Et reverses the EP effect on LPS-activated iNOS and HO-1 expression, cells were treated with EP (25mM) or EP with GSH-Et (10μM) for 8 h (HO-1) or for 16 h (HMGB1) in the presence of LPS (D). After incubation, cells were harvested and subjected to western blot as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are presented as means ± SD of three independent experiments. Significance compared with control, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01; significance compared with LPS, {p < 0.05 and {{p < 0.01; significance compared with EP, #p < 0.05; significance compared with LPS + EP, xp < 0.05 and xxp < 0.01. GSH-Et, glutathione ethyl ester; NAC, N-acetyl cysteine.
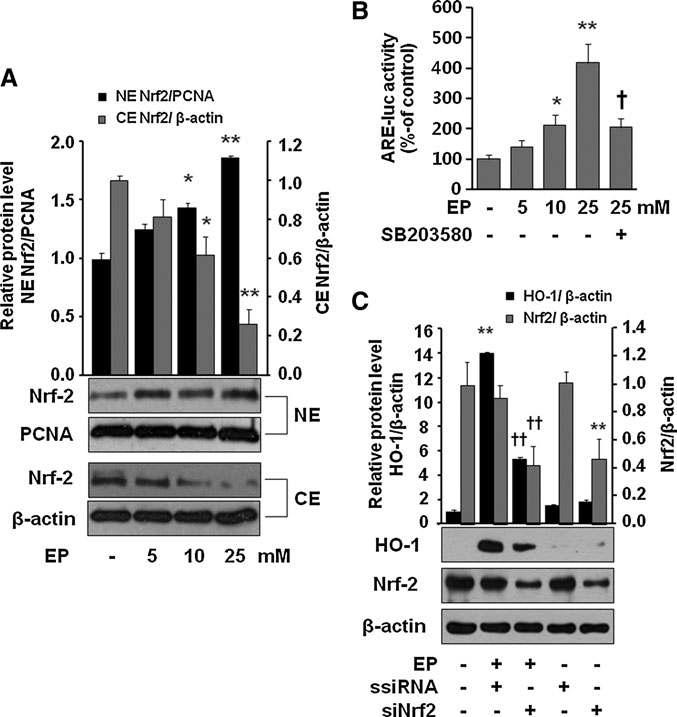 표
Involvement of Nrf2 in EP mediated HO-1 expression. Cells were treated for 1 h with EP at 5, 10, and 25mM, and then harvested and subjectedto cytosol/nuclear fractionation (A). Cells were transiently transfected with the ARE-luc vector (B). After incubation, cells were treated with EP (5,10, and 25mM) or EP (25 mM) + SB203580 (10 μM, which was pretreated 1 h before addition of EP) for 1 h. After incubation, cells were subjected to luciferase assay as described in the Materials and Methods section. Cells were transfected with scramble (siRNA) or siNrf2 (C) as described in the Materials and Methods section. After 8-h incubation with EP (25 mM), cells were harvested and subjected to western blot for HO-1 expression. Transfection efficiency was confirmed by checking Nrf2 expression. Data are presented as – SD of three independent experiments. Significance compared with control, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01; significance compared with EP alone or EP + ssiRNA, {p < 0.05 and {{p < 0.01. ARE, antioxidant redox element; Nrf2, NF-E2-related factor 2.
표
Involvement of Nrf2 in EP mediated HO-1 expression. Cells were treated for 1 h with EP at 5, 10, and 25mM, and then harvested and subjectedto cytosol/nuclear fractionation (A). Cells were transiently transfected with the ARE-luc vector (B). After incubation, cells were treated with EP (5,10, and 25mM) or EP (25 mM) + SB203580 (10 μM, which was pretreated 1 h before addition of EP) for 1 h. After incubation, cells were subjected to luciferase assay as described in the Materials and Methods section. Cells were transfected with scramble (siRNA) or siNrf2 (C) as described in the Materials and Methods section. After 8-h incubation with EP (25 mM), cells were harvested and subjected to western blot for HO-1 expression. Transfection efficiency was confirmed by checking Nrf2 expression. Data are presented as – SD of three independent experiments. Significance compared with control, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01; significance compared with EP alone or EP + ssiRNA, {p < 0.05 and {{p < 0.01. ARE, antioxidant redox element; Nrf2, NF-E2-related factor 2.
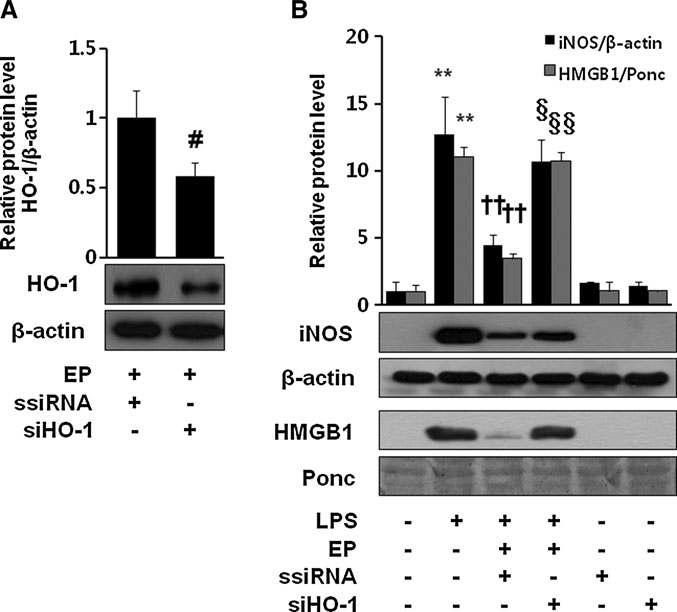 표
Importance of HO-1 in the anti-inflammatory action of EP. Cells were transfected with ssiRNA or siHO-1 RNA, which were subjected to western blot to confirm siHO-1 efficiency by EP (25mM) for 8 h (A). Cells were stimulated with LPS (1μg/ml) in the presence or absence of EP (25mM) for 16 h. Then, cell extract and culture medium samples were subjected to western blot for iNOS and HMGB1, respectively (B). Significance compared with control, **p < 0.01; significance compared with LPS,
표
Importance of HO-1 in the anti-inflammatory action of EP. Cells were transfected with ssiRNA or siHO-1 RNA, which were subjected to western blot to confirm siHO-1 efficiency by EP (25mM) for 8 h (A). Cells were stimulated with LPS (1μg/ml) in the presence or absence of EP (25mM) for 16 h. Then, cell extract and culture medium samples were subjected to western blot for iNOS and HMGB1, respectively (B). Significance compared with control, **p < 0.01; significance compared with LPS,
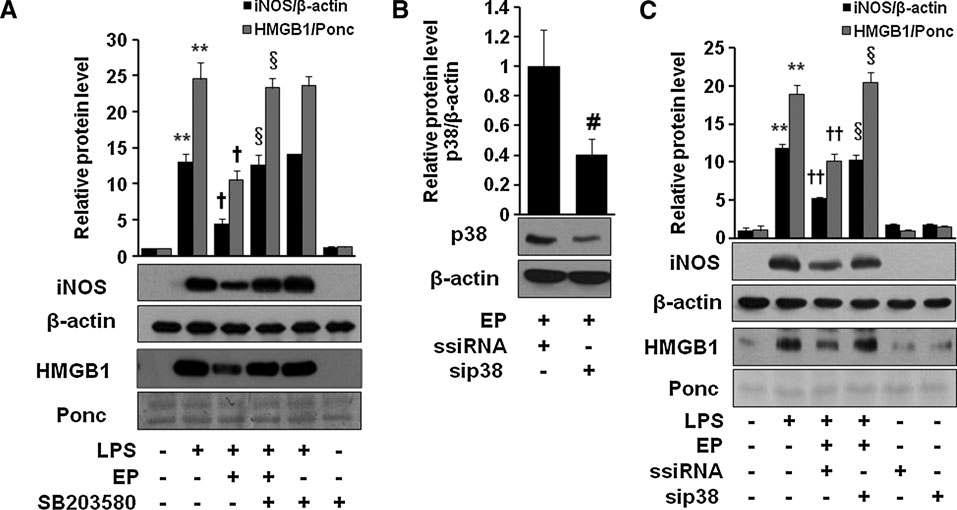 표
SB203580 and p38-siRNA reverse anti-inflammatory effect of EP in macrophages. Cells were incubated with EP (25mM) with or without SB203580 (10 μM) for 1 h and stimulated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 16 h (A), or cells were transfected with p38-siRNA or ssiRNA (B, C), which were incubated with EP (25mM) for 1 h and stimulated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 16 h. Cell extract and culture medium samples were subjected to western blot for iNOS and HMGB1 analysis, respectively. Data are presented as means± SD of three independent experiments.
표
SB203580 and p38-siRNA reverse anti-inflammatory effect of EP in macrophages. Cells were incubated with EP (25mM) with or without SB203580 (10 μM) for 1 h and stimulated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 16 h (A), or cells were transfected with p38-siRNA or ssiRNA (B, C), which were incubated with EP (25mM) for 1 h and stimulated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 16 h. Cell extract and culture medium samples were subjected to western blot for iNOS and HMGB1 analysis, respectively. Data are presented as means± SD of three independent experiments.
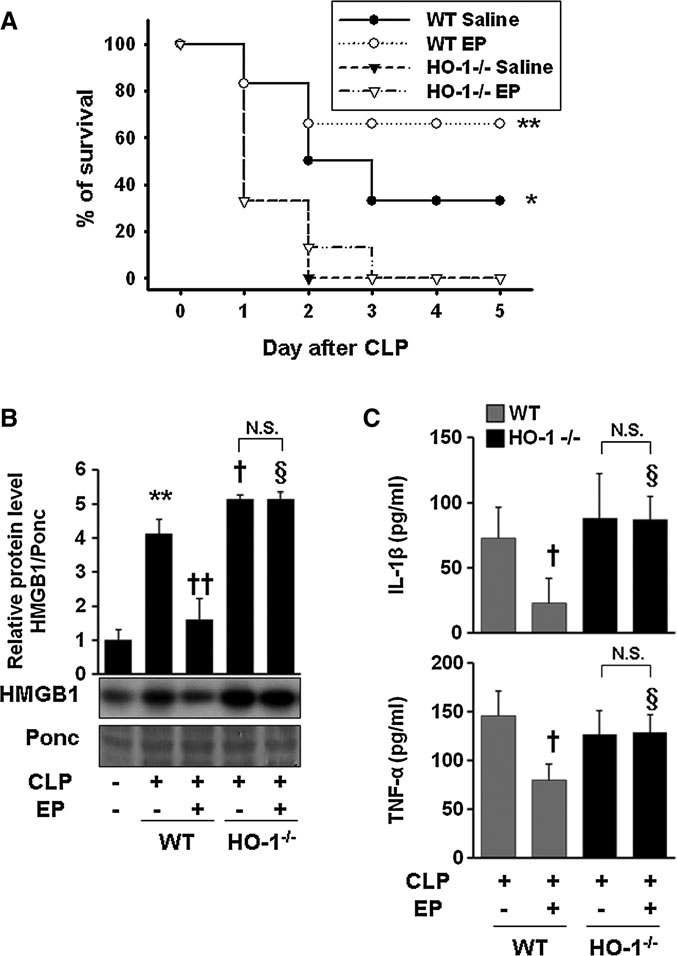 표
EP fails to increase the survival rate in the CLP-induced sepsis model of HO-1- / - mice. BALB/c WT (n = 12) and HO-1-/ - mice (n = 12) were subjected to CLP with EP (n = 6, 40 mg/kg i.p.) or an equal volume of vehicle (n = 6, saline) treatment at 0 and 24 h, after onset of sepsis. Survival was monitored daily for up to 5 days (A). To determine serum HMGB1 levels, WT and HO-1-/- mice were treated with EP (40 mg/kg i.p., n = 5) or an equal volume of vehicle (n = 4, saline) at 0 and 12 h after onset of sepsis (CLP). Twenty-four hours later, blood was collected by cardiac puncture and subjected to HMGB1 (B) and ELISA (C) analysis. The Kaplan– Meier program was utilized to compare the differences in mortality rates between groups.
표
EP fails to increase the survival rate in the CLP-induced sepsis model of HO-1- / - mice. BALB/c WT (n = 12) and HO-1-/ - mice (n = 12) were subjected to CLP with EP (n = 6, 40 mg/kg i.p.) or an equal volume of vehicle (n = 6, saline) treatment at 0 and 24 h, after onset of sepsis. Survival was monitored daily for up to 5 days (A). To determine serum HMGB1 levels, WT and HO-1-/- mice were treated with EP (40 mg/kg i.p., n = 5) or an equal volume of vehicle (n = 4, saline) at 0 and 12 h after onset of sepsis (CLP). Twenty-four hours later, blood was collected by cardiac puncture and subjected to HMGB1 (B) and ELISA (C) analysis. The Kaplan– Meier program was utilized to compare the differences in mortality rates between groups.
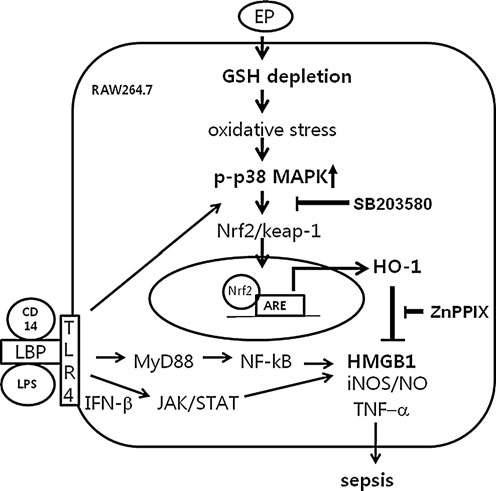 표
Possible mechanism by which EP reduces HMGB1 in sepsis. EP depletes intracellular GSH levels that change redox states of the cell, which, in turn, stimulates p38 MAPK. The activation of p38 MAPK by phosphorylation triggers to activate Nrf2, which dissociates from keap1 and then moves into the nucleus, where it binds to ARE binding sites to induce the HO-1 gene. Thus, SB203580, p38 inhibitor, inhibits EP-mediated HO-1 induction. On the other hand, LPS binds to LPS binding protein (LBP) along with CD14, a recognition molecule for LPS, which activates toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). The activated TLR4 stimulates p38 MAPK, which then induces HO-1. However, LPS activates NF-jB through MyD88-dependent signal pathways, and IFN-b, generated by LPS through TRIF-dependent signal pathways, activates the JAK/STAT signal pathway to induce inflammatory gene expression, such as iNOS, TNF-a, IL-1b, and release of HMGB1. The induction of HO-1 by EP inhibits these inflammatory cytokines and release of HMGB1 and NO production in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells. ZnPPIX, a HO-1 inhibitor, reverses the anti-inflammatory effect of EP (data not shown). Administration of EP also inhibits iNOS expression and circulating TNF-a, IL-1b, and HMGB1 in CLP-induced septic mice, which are dependent on HO-1 induction via activation of p38 MAPK. The schema describes possible signal pathways by which EP activates HO-1 induction in RAW 264.7 cells. IL-1, interleukin-1; NF-jB, nuclear factor kappa B; STAT1, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
표
Possible mechanism by which EP reduces HMGB1 in sepsis. EP depletes intracellular GSH levels that change redox states of the cell, which, in turn, stimulates p38 MAPK. The activation of p38 MAPK by phosphorylation triggers to activate Nrf2, which dissociates from keap1 and then moves into the nucleus, where it binds to ARE binding sites to induce the HO-1 gene. Thus, SB203580, p38 inhibitor, inhibits EP-mediated HO-1 induction. On the other hand, LPS binds to LPS binding protein (LBP) along with CD14, a recognition molecule for LPS, which activates toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). The activated TLR4 stimulates p38 MAPK, which then induces HO-1. However, LPS activates NF-jB through MyD88-dependent signal pathways, and IFN-b, generated by LPS through TRIF-dependent signal pathways, activates the JAK/STAT signal pathway to induce inflammatory gene expression, such as iNOS, TNF-a, IL-1b, and release of HMGB1. The induction of HO-1 by EP inhibits these inflammatory cytokines and release of HMGB1 and NO production in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells. ZnPPIX, a HO-1 inhibitor, reverses the anti-inflammatory effect of EP (data not shown). Administration of EP also inhibits iNOS expression and circulating TNF-a, IL-1b, and HMGB1 in CLP-induced septic mice, which are dependent on HO-1 induction via activation of p38 MAPK. The schema describes possible signal pathways by which EP activates HO-1 induction in RAW 264.7 cells. IL-1, interleukin-1; NF-jB, nuclear factor kappa B; STAT1, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
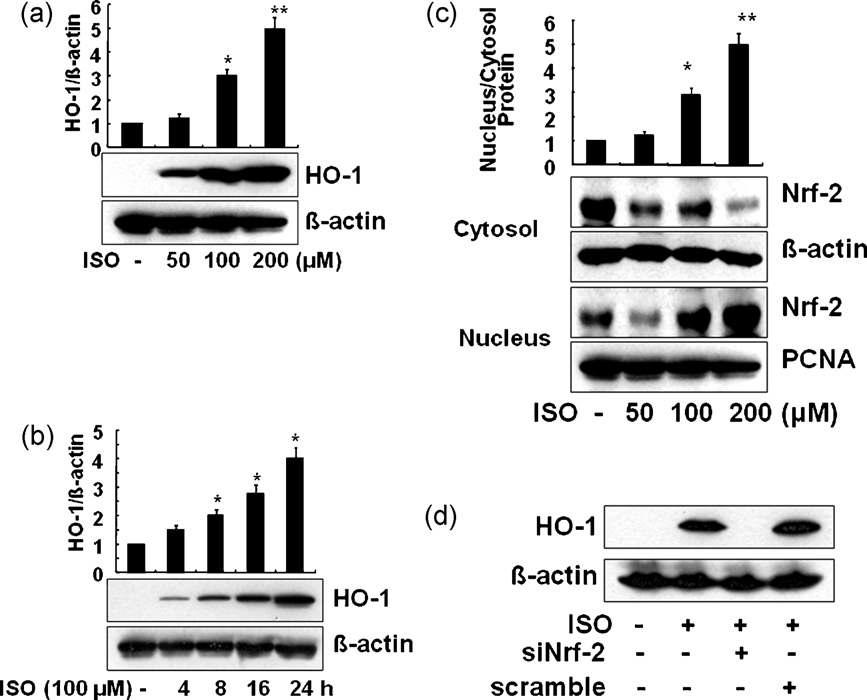 표
Isoproterenol induces HO-1 in a concentra tion and time-dependent manner via Nrf-2 activ ation. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with isoprot erenol (ISO) for 8 h at different concentrations (a). Cells were incubated for the indicated perio d of time with a fixed dose of ISO (100 mM) (b), and then Western blot analysis was perfor med. To determine whether Nrf-2 translocation i s involved in HO-1 induction by isoproterenol, c ytosol and nuclear fraction were separated after 3 h of treatment with the indicated concentratio ns of isoproterenol. Western blot analysis was p erformed with anti-Nrf-2 antibody (c). Using Nrf -2 siRNA-transfected cells, HO-1 induction was i nvestigated in the presence and absence of ISO (d). Representative blot shown is from one of t he three independent experiments with similar r esults. Data are expressed as mean ±SEM of th ree independent experiments.
표
Isoproterenol induces HO-1 in a concentra tion and time-dependent manner via Nrf-2 activ ation. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with isoprot erenol (ISO) for 8 h at different concentrations (a). Cells were incubated for the indicated perio d of time with a fixed dose of ISO (100 mM) (b), and then Western blot analysis was perfor med. To determine whether Nrf-2 translocation i s involved in HO-1 induction by isoproterenol, c ytosol and nuclear fraction were separated after 3 h of treatment with the indicated concentratio ns of isoproterenol. Western blot analysis was p erformed with anti-Nrf-2 antibody (c). Using Nrf -2 siRNA-transfected cells, HO-1 induction was i nvestigated in the presence and absence of ISO (d). Representative blot shown is from one of t he three independent experiments with similar r esults. Data are expressed as mean ±SEM of th ree independent experiments.
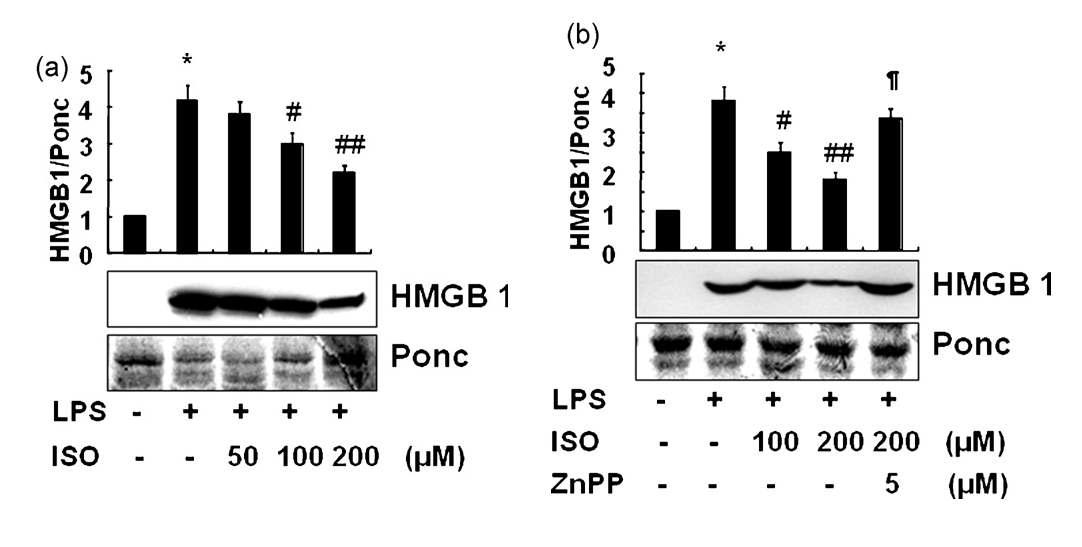 표
soproterenol reduces HMGB1 release in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells by HO-1 induction. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of isoproterenol (ISO) 1 h prior to addition of 1 μg/ml LPS. After a 16-h incubation period, detection of HMGB1 released into the medium was performed by Western blot analysis (a). Ponceau S (ponc) band was used as a loading control. To understand whether the reduced HMGB1 release is due to increased HO-1 activity in the presence of ISO, ZnPPIX (5 μM), an HO-1 inhibitor, was coadministered with ISO and HMGB1 detected after 16 h of incubation with LPS (b). Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Data are given as mean ±SEM of three independent experiments.
표
soproterenol reduces HMGB1 release in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells by HO-1 induction. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of isoproterenol (ISO) 1 h prior to addition of 1 μg/ml LPS. After a 16-h incubation period, detection of HMGB1 released into the medium was performed by Western blot analysis (a). Ponceau S (ponc) band was used as a loading control. To understand whether the reduced HMGB1 release is due to increased HO-1 activity in the presence of ISO, ZnPPIX (5 μM), an HO-1 inhibitor, was coadministered with ISO and HMGB1 detected after 16 h of incubation with LPS (b). Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Data are given as mean ±SEM of three independent experiments.
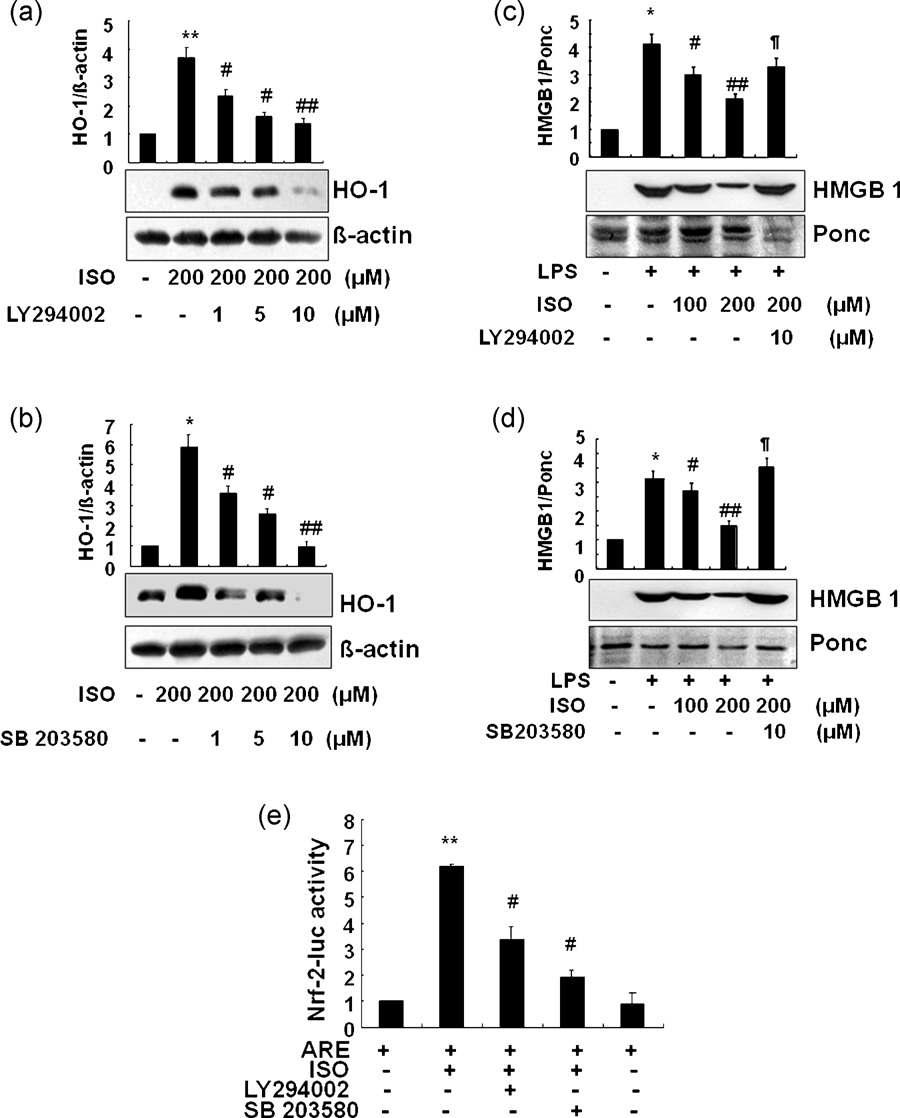 표
Isoproterenol induces HO-1 expression via a PI3K- and p38 MAPK-dependent pathway. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated 30 min prior to addition of isoproterenol (ISO,200 μM) with different concentrations of LY294002, a PI3K inhibitor (a) or SB203580, a p38 MAPK inhibitor (b) to identify the signaling pathway involved in HO-1 induction. HO-1 protein was detected after 8 h of incubation with ISO. To confirm that these signaling molecules are involved in inhibition of HMGB1 release (c and d) due to HO-1 induction, RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of ISO 1 h prior to addition of 1 mg/ml LPS. LY294002 (10 μM) or SB 203580 (10 μM) was administered 30 min prior to treatment with ISO. Cells were incubated for 16 h after LPS addition for the purpose of detecting HMGB1. To further confirm that ISO-induced HO-1 expression is related to Nrf-2, which is also sensitive to PI3K and p38 MAPK, Nrf-2 luciferase activity was measured in the presence or absence of LY294002 or SB 203580 (e). Cells transfected with the Nrf-2 luciferase gene were incubated for 1 h with ISO (200 μM) with or without the inhibitors (each at 10 μM). Intensity is represented as fold increase in activity. Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Data are given as mean SEM of three independent experiments.
표
Isoproterenol induces HO-1 expression via a PI3K- and p38 MAPK-dependent pathway. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated 30 min prior to addition of isoproterenol (ISO,200 μM) with different concentrations of LY294002, a PI3K inhibitor (a) or SB203580, a p38 MAPK inhibitor (b) to identify the signaling pathway involved in HO-1 induction. HO-1 protein was detected after 8 h of incubation with ISO. To confirm that these signaling molecules are involved in inhibition of HMGB1 release (c and d) due to HO-1 induction, RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of ISO 1 h prior to addition of 1 mg/ml LPS. LY294002 (10 μM) or SB 203580 (10 μM) was administered 30 min prior to treatment with ISO. Cells were incubated for 16 h after LPS addition for the purpose of detecting HMGB1. To further confirm that ISO-induced HO-1 expression is related to Nrf-2, which is also sensitive to PI3K and p38 MAPK, Nrf-2 luciferase activity was measured in the presence or absence of LY294002 or SB 203580 (e). Cells transfected with the Nrf-2 luciferase gene were incubated for 1 h with ISO (200 μM) with or without the inhibitors (each at 10 μM). Intensity is represented as fold increase in activity. Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Data are given as mean SEM of three independent experiments.
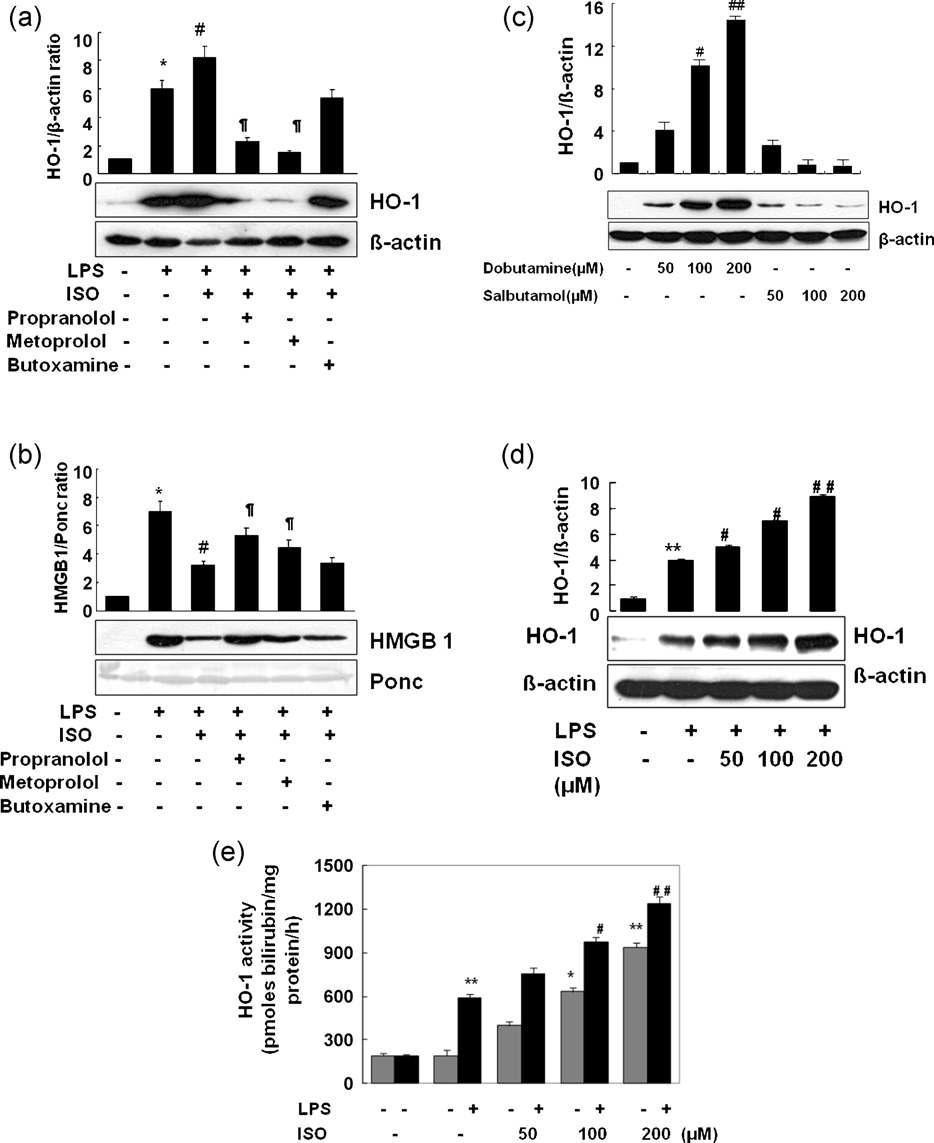 표
β1-Adrenoceptor activation induces HO-1 expression and activity in macrophage cells. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with isoproterenol (ISO, 100 μM), ISO + propranolol (100 μM), a non-selective β-AR antagonist, ISO + metoprolol (100 μM), a selective β1-AR antagonist, or ISO + butoxamine (100 μM), a selective β2-AR antagonist 30 min prior to addition of LPS (1 μg/ml). After incubation for 8 h (HO-1, a) or 16 h (HMGB1, b), cells were harvested and subjected to Western blot analysis as described in Section 2. To confirm that HO-1 induction by isoproterenol is mediated by the b1-AR, different concentrations of dobutamine, a β1-selective AR agonist, and salbutamol, a β2-selective AR agonist, were administered for 8 h to RAW 264.7 cells (c). Cells were incubated with LPS (1 μg/ml) or LPS + ISO (50, 100, and 200 μM) for 8 h and HO-1 expression and activity were measured as described in Section 2. Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Data are given as mean SEM of three independent experiments.
표
β1-Adrenoceptor activation induces HO-1 expression and activity in macrophage cells. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with isoproterenol (ISO, 100 μM), ISO + propranolol (100 μM), a non-selective β-AR antagonist, ISO + metoprolol (100 μM), a selective β1-AR antagonist, or ISO + butoxamine (100 μM), a selective β2-AR antagonist 30 min prior to addition of LPS (1 μg/ml). After incubation for 8 h (HO-1, a) or 16 h (HMGB1, b), cells were harvested and subjected to Western blot analysis as described in Section 2. To confirm that HO-1 induction by isoproterenol is mediated by the b1-AR, different concentrations of dobutamine, a β1-selective AR agonist, and salbutamol, a β2-selective AR agonist, were administered for 8 h to RAW 264.7 cells (c). Cells were incubated with LPS (1 μg/ml) or LPS + ISO (50, 100, and 200 μM) for 8 h and HO-1 expression and activity were measured as described in Section 2. Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Data are given as mean SEM of three independent experiments.
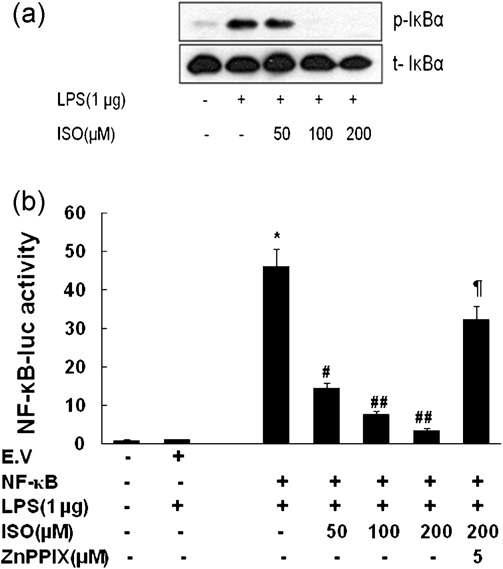 표
Inhibition of inflammatory cytokines is related to NF-kB activity. The involvement of NF-kB activity in the anti-inflammatory action of isoproterenol (ISO), phosphorylation of IkBa (a) and NF-kB luciferase activity (b) were measured. Cells were incubated after 1 h of incubation with LPS (1 mg/ml) in the absence or presence of different concentrations of ISO or ISO (200 μM) + ZnPPIX. Then Western blot analysis was performed using phosphor-IkBa and IkBa antibodies and NF-kB driven luciferase activity was measured in cells transfected with NF-kB as described in Section 2. Activity was presented as fold increase. Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Data are given as mean ±SEM of three independent experiments.
표
Inhibition of inflammatory cytokines is related to NF-kB activity. The involvement of NF-kB activity in the anti-inflammatory action of isoproterenol (ISO), phosphorylation of IkBa (a) and NF-kB luciferase activity (b) were measured. Cells were incubated after 1 h of incubation with LPS (1 mg/ml) in the absence or presence of different concentrations of ISO or ISO (200 μM) + ZnPPIX. Then Western blot analysis was performed using phosphor-IkBa and IkBa antibodies and NF-kB driven luciferase activity was measured in cells transfected with NF-kB as described in Section 2. Activity was presented as fold increase. Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Data are given as mean ±SEM of three independent experiments.
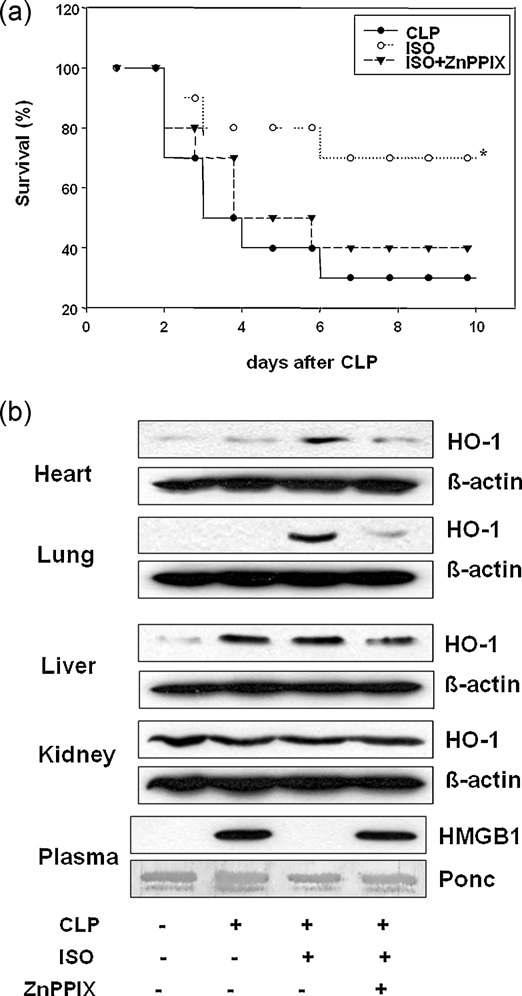 표
Isoproterenol improves survival rate and reduces serum HMGB1 in CLP-induced septic mice in an HO-1 sensitive manner. Health male Balb/c mice were injected with isoproterenol (ISO, 10 mg/kg, i.p. n = 14) 1 h before CLP (n = 14). Survival was monitored daily for 10 days (a). ISO significantly increased survival rate (p < 0.038). In separate experiments, mice were treated with saline (n = 2), CLP (n = 6), CLP + ISO (n = 6), CLP + ISO + ZnPPIX (n = 6) and 24 h later tissue (heart, lung, iver, and kidney) HO-1 protein levels and serum HMGB1 levels were measured by Western blot methods (b).
표
Isoproterenol improves survival rate and reduces serum HMGB1 in CLP-induced septic mice in an HO-1 sensitive manner. Health male Balb/c mice were injected with isoproterenol (ISO, 10 mg/kg, i.p. n = 14) 1 h before CLP (n = 14). Survival was monitored daily for 10 days (a). ISO significantly increased survival rate (p < 0.038). In separate experiments, mice were treated with saline (n = 2), CLP (n = 6), CLP + ISO (n = 6), CLP + ISO + ZnPPIX (n = 6) and 24 h later tissue (heart, lung, iver, and kidney) HO-1 protein levels and serum HMGB1 levels were measured by Western blot methods (b).
![Model for the anti-inflammatory action of isoproterenol through HO-1 induction in RAW 264.7 cells. Activation of the b1-AR by isoproterenol leads to an increase in cAMP, which then activates protein kinase A (PKA) (Sun et al. [17]), and also stimulates PI3K and p38MAPK activity. Activated PI3K and p38MAPK make it possible for Nrf2 to move to nucleus, where binding of Nrf2 to the ARE promoter site, leads to the upregulation of HO-1 gene expression. Therefore, the non-selective b-AR blocker, propranolol, or the β1-selective AR blocker, metoprolol inhibits but the β1-selective AR agonist dobutamine, activates HO-1 induction. Likewise, the PI3K inhibitor, LY294002, or p38MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, inhibits HO-1 induction. It is not yet known whether cAMP activates PI3K, p38 MAPK, or Nrf2 translocation to induce HO-1 in RAW 264.7 cells. However, H89, a PKA inhibitor blocked ISO-induced HO-1 upregulation. The increased HO-1 expression induced by ISO inhibits NF-kB activity, which can be activated by LPS through TLR4; thus production of pro-inflammatory cytokines dependent on NF-kB, such as TNF-α, IL- 1β, NO and HMGB1 can be reduced. It should be noted, however, that LPS also induces HO-1 by production of ROS via TLR4, but it also activates NF-kB which could tilt the balance toward to pro-inflammation. Model for the anti-inflammatory action of isoproterenol through HO-1 induction in RAW 264.7 cells. Activation of the b1-AR by isoproterenol leads to an increase in cAMP, which then activates protein kinase A (PKA) (Sun et al. [17]), and also stimulates PI3K and p38MAPK activity. Activated PI3K and p38MAPK make it possible for Nrf2 to move to nucleus, where binding of Nrf2 to the ARE promoter site, leads to the upregulation of HO-1 gene expression. Therefore, the non-selective b-AR blocker, propranolol, or the β1-selective AR blocker, metoprolol inhibits but the β1-selective AR agonist dobutamine, activates HO-1 induction. Likewise, the PI3K inhibitor, LY294002, or p38MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, inhibits HO-1 induction. It is not yet known whether cAMP activates PI3K, p38 MAPK, or Nrf2 translocation to induce HO-1 in RAW 264.7 cells. However, H89, a PKA inhibitor blocked ISO-induced HO-1 upregulation. The increased HO-1 expression induced by ISO inhibits NF-kB activity, which can be activated by LPS through TLR4; thus production of pro-inflammatory cytokines dependent on NF-kB, such as TNF-α, IL- 1β, NO and HMGB1 can be reduced. It should be noted, however, that LPS also induces HO-1 by production of ROS via TLR4, but it also activates NF-kB which could tilt the balance toward to pro-inflammation.](https://nrms.kisti.re.kr/bitextimages/TRKO201300034890/TRKO201300034890_39_image_24.jpg) 표
Model for the anti-inflammatory action of isoproterenol through HO-1 induction in RAW 264.7 cells. Activation of the b1-AR by isoproterenol leads to an increase in cAMP, which then activates protein kinase A (PKA) (Sun et al. [17]), and also stimulates PI3K and p38MAPK activity. Activated PI3K and p38MAPK make it possible for Nrf2 to move to nucleus, where binding of Nrf2 to the ARE promoter site, leads to the upregulation of HO-1 gene expression. Therefore, the non-selective b-AR blocker, propranolol, or the β1-selective AR blocker, metoprolol inhibits but the β1-selective AR agonist dobutamine, activates HO-1 induction. Likewise, the PI3K inhibitor, LY294002, or p38MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, inhibits HO-1 induction. It is not yet known whether cAMP activates PI3K, p38 MAPK, or Nrf2 translocation to induce HO-1 in RAW 264.7 cells. However, H89, a PKA inhibitor blocked ISO-induced HO-1 upregulation. The increased HO-1 expression induced by ISO inhibits NF-kB activity, which can be activated by LPS through TLR4; thus production of pro-inflammatory cytokines dependent on NF-kB, such as TNF-α, IL- 1β, NO and HMGB1 can be reduced. It should be noted, however, that LPS also induces HO-1 by production of ROS via TLR4, but it also activates NF-kB which could tilt the balance toward to pro-inflammation.
표
Model for the anti-inflammatory action of isoproterenol through HO-1 induction in RAW 264.7 cells. Activation of the b1-AR by isoproterenol leads to an increase in cAMP, which then activates protein kinase A (PKA) (Sun et al. [17]), and also stimulates PI3K and p38MAPK activity. Activated PI3K and p38MAPK make it possible for Nrf2 to move to nucleus, where binding of Nrf2 to the ARE promoter site, leads to the upregulation of HO-1 gene expression. Therefore, the non-selective b-AR blocker, propranolol, or the β1-selective AR blocker, metoprolol inhibits but the β1-selective AR agonist dobutamine, activates HO-1 induction. Likewise, the PI3K inhibitor, LY294002, or p38MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, inhibits HO-1 induction. It is not yet known whether cAMP activates PI3K, p38 MAPK, or Nrf2 translocation to induce HO-1 in RAW 264.7 cells. However, H89, a PKA inhibitor blocked ISO-induced HO-1 upregulation. The increased HO-1 expression induced by ISO inhibits NF-kB activity, which can be activated by LPS through TLR4; thus production of pro-inflammatory cytokines dependent on NF-kB, such as TNF-α, IL- 1β, NO and HMGB1 can be reduced. It should be noted, however, that LPS also induces HO-1 by production of ROS via TLR4, but it also activates NF-kB which could tilt the balance toward to pro-inflammation.
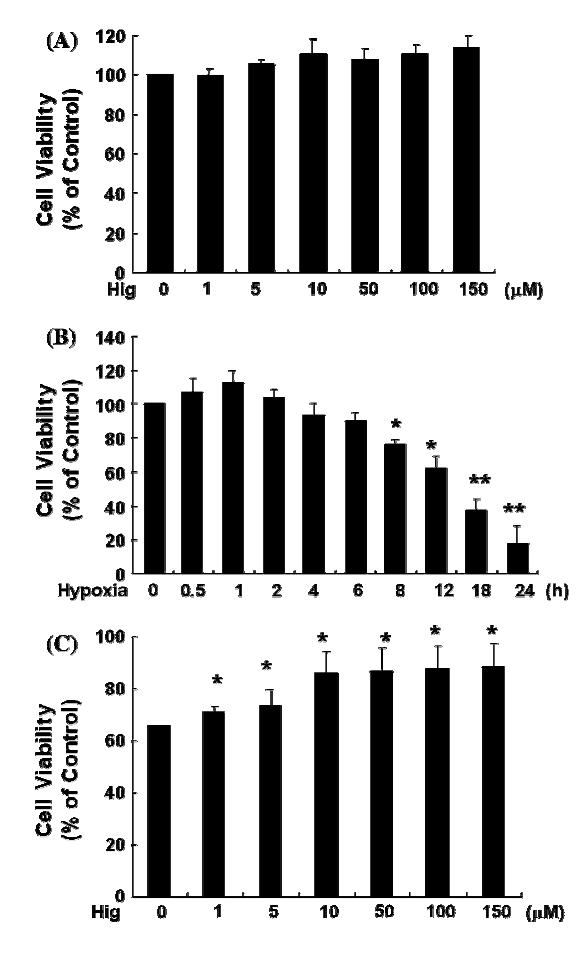 표
Cell viability of higenamine in C6 cells. Cell proliferation was tested using MTT. a Under normoxia, C6 cells were treated with different concentrations of higenamine (lM), and incubated for 24 h in CO2 incubator. b Cells were moved to hypoxic chamber and cell proliferation was measured after incubation of indicated time. c The indicated dose of higenamine (lM) was treated and incubated for12 h under hypoxic chamber as described in ‘‘Materials and methods’’
표
Cell viability of higenamine in C6 cells. Cell proliferation was tested using MTT. a Under normoxia, C6 cells were treated with different concentrations of higenamine (lM), and incubated for 24 h in CO2 incubator. b Cells were moved to hypoxic chamber and cell proliferation was measured after incubation of indicated time. c The indicated dose of higenamine (lM) was treated and incubated for12 h under hypoxic chamber as described in ‘‘Materials and methods’’
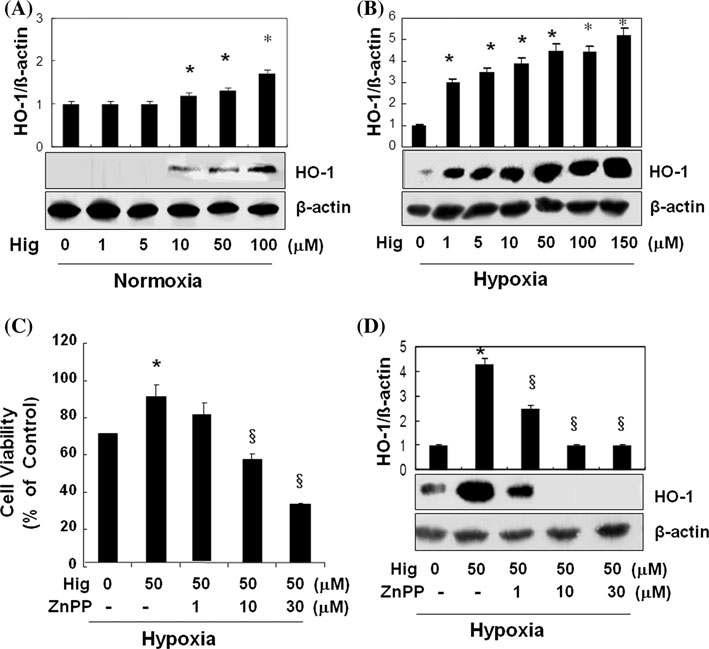 표
Higenamine increases HO-1 and it protects hypoxic injury in C6 cells. Higenamine was treated as indicated dose and incubated for 8 h under a normoxic or b hypoxic condition and after that protein was extracted for western analysis with anti-HO-1 antibody. c A fixed concentration of higenamine (50 μM) was treated in the presence or absence of ZnPPIX (1, 10, and 30 μM). After incubation for 12 h under hypoxic condition, cell proliferation was tested with MTT. d Cells were treated with a fixed concentration of higenamine (50 μM) in the presence or absence of increasing concentration of ZnPPIX (1,10,30 μM), which was incubated for 12 h under hypoxia and proteins were extracted for western analysis using anti-HO-1 antibody. Results are means ± SE of three to four independent experiments. *P<0.05 compared to control. §P <0.05 compared to higenamine.
표
Higenamine increases HO-1 and it protects hypoxic injury in C6 cells. Higenamine was treated as indicated dose and incubated for 8 h under a normoxic or b hypoxic condition and after that protein was extracted for western analysis with anti-HO-1 antibody. c A fixed concentration of higenamine (50 μM) was treated in the presence or absence of ZnPPIX (1, 10, and 30 μM). After incubation for 12 h under hypoxic condition, cell proliferation was tested with MTT. d Cells were treated with a fixed concentration of higenamine (50 μM) in the presence or absence of increasing concentration of ZnPPIX (1,10,30 μM), which was incubated for 12 h under hypoxia and proteins were extracted for western analysis using anti-HO-1 antibody. Results are means ± SE of three to four independent experiments. *P<0.05 compared to control. §P <0.05 compared to higenamine.
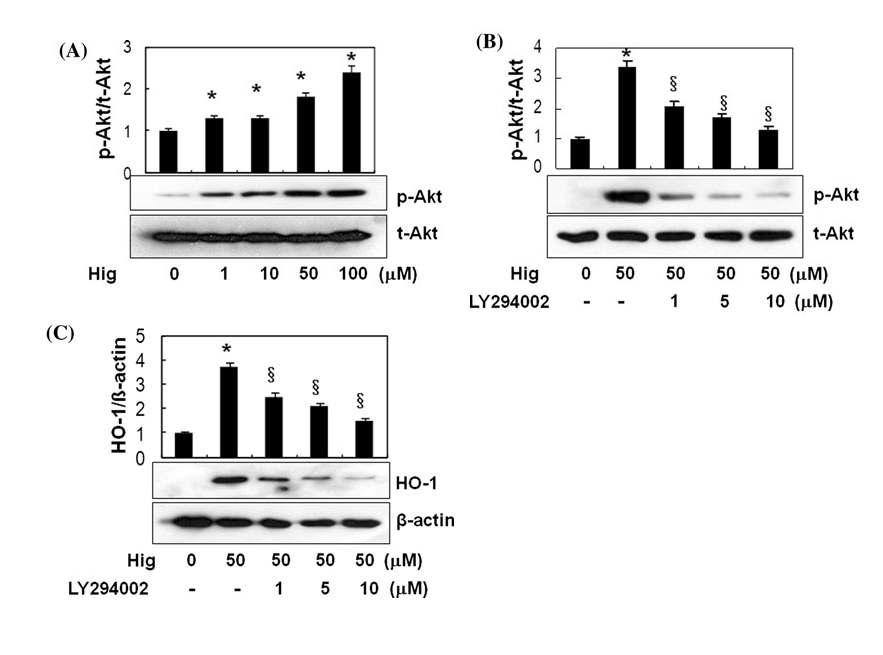 표
Phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase/Akt pathway-dependent HO-1 induction by higenamine. Cells were treated with indicated concentration of higneamine and incubated for 15 min and phosphorylation of Akt (a) was examined by western analysis using anti-Akt or p-Akt antibodies. Loading control was shown as t-Akt level in each lane. A fixed concentration of higenamine (50 lM) was treated in the presence or absence of LY 294002 and the levels of p-Akt (b) and HO-1 (c) were analyzed using corresponding antibodies, respectively. Results are means ± SE of three independent experiments.
표
Phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase/Akt pathway-dependent HO-1 induction by higenamine. Cells were treated with indicated concentration of higneamine and incubated for 15 min and phosphorylation of Akt (a) was examined by western analysis using anti-Akt or p-Akt antibodies. Loading control was shown as t-Akt level in each lane. A fixed concentration of higenamine (50 lM) was treated in the presence or absence of LY 294002 and the levels of p-Akt (b) and HO-1 (c) were analyzed using corresponding antibodies, respectively. Results are means ± SE of three independent experiments.
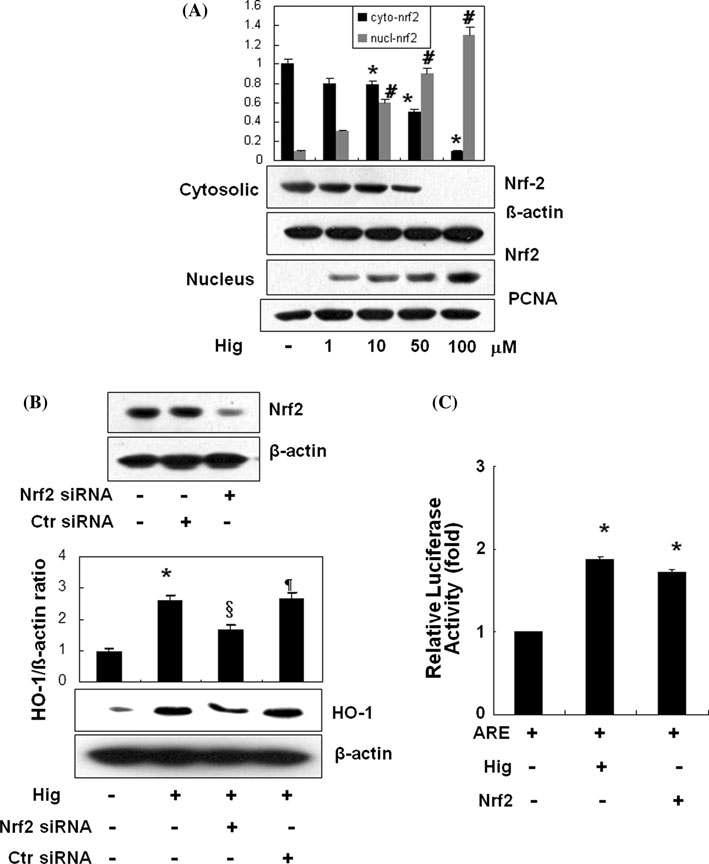 표
Higenamine translocates Nrf-2 and activates ARE element. Cells were treated with higenamine as indicated concentration and incubated for 1 h and proteins were extracted from cytosol fraction and nuclear fraction as described in the ‘‘Materials and methods’’ section. a Then western blot analysis was performed using anti-Nrf2 antibody. The internal loading control for cytosol and nuclear were used b-actin and PCNA, respectively. b Transfection efficiency of siNrf-2 RNA was checked by western analysis and the expression of HO-1 by higenamine was examined in scrambled siRNA- and Nrf2- siRNA-transfected cells by western analysis. c ARE activity was measured in cells transfected with luciferase reporter plasmid construct harboring the ARE promoter after 2 h treatment with higenamine (50 μM). Results are means ± SE of three independent experiments.
표
Higenamine translocates Nrf-2 and activates ARE element. Cells were treated with higenamine as indicated concentration and incubated for 1 h and proteins were extracted from cytosol fraction and nuclear fraction as described in the ‘‘Materials and methods’’ section. a Then western blot analysis was performed using anti-Nrf2 antibody. The internal loading control for cytosol and nuclear were used b-actin and PCNA, respectively. b Transfection efficiency of siNrf-2 RNA was checked by western analysis and the expression of HO-1 by higenamine was examined in scrambled siRNA- and Nrf2- siRNA-transfected cells by western analysis. c ARE activity was measured in cells transfected with luciferase reporter plasmid construct harboring the ARE promoter after 2 h treatment with higenamine (50 μM). Results are means ± SE of three independent experiments.
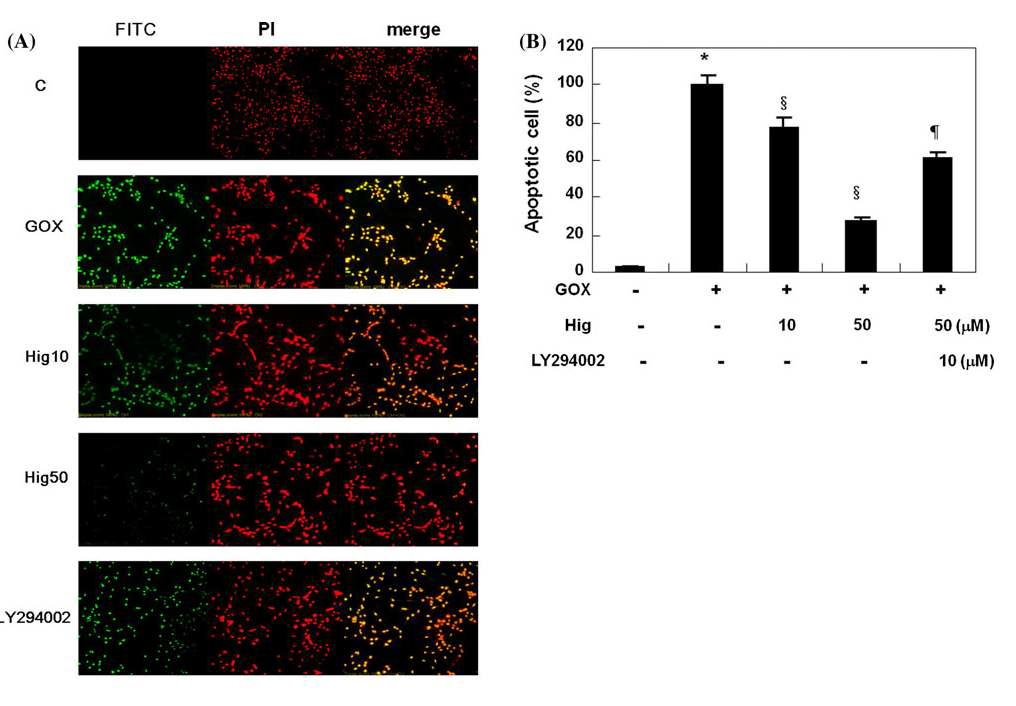 표
Higenamine inhibits ROS-induced apoptosis with PI3K-sensitive manner. Cells were pretreated with higenamine (10 and 50 lM) for 8 h before exposure to GOX (20 mU/ml) and, 8 h later, a TUNEL assay was performed as described in ‘‘Materials and methods’’ section. In a, 1, control; 2, GOX 20 mU/ml; 3, GOX 20 mU/ml with higenamine 10 lM; 4, GOX 20 mU/ml with higenamine 50 μM; 5, GOX 20 mU/ml with higenamine 50 μM + LY 294002 (10 μM). b Apoptotic cell reactions were analyzed. Results are means ± SE of three independent experiments.
표
Higenamine inhibits ROS-induced apoptosis with PI3K-sensitive manner. Cells were pretreated with higenamine (10 and 50 lM) for 8 h before exposure to GOX (20 mU/ml) and, 8 h later, a TUNEL assay was performed as described in ‘‘Materials and methods’’ section. In a, 1, control; 2, GOX 20 mU/ml; 3, GOX 20 mU/ml with higenamine 10 lM; 4, GOX 20 mU/ml with higenamine 50 μM; 5, GOX 20 mU/ml with higenamine 50 μM + LY 294002 (10 μM). b Apoptotic cell reactions were analyzed. Results are means ± SE of three independent experiments.
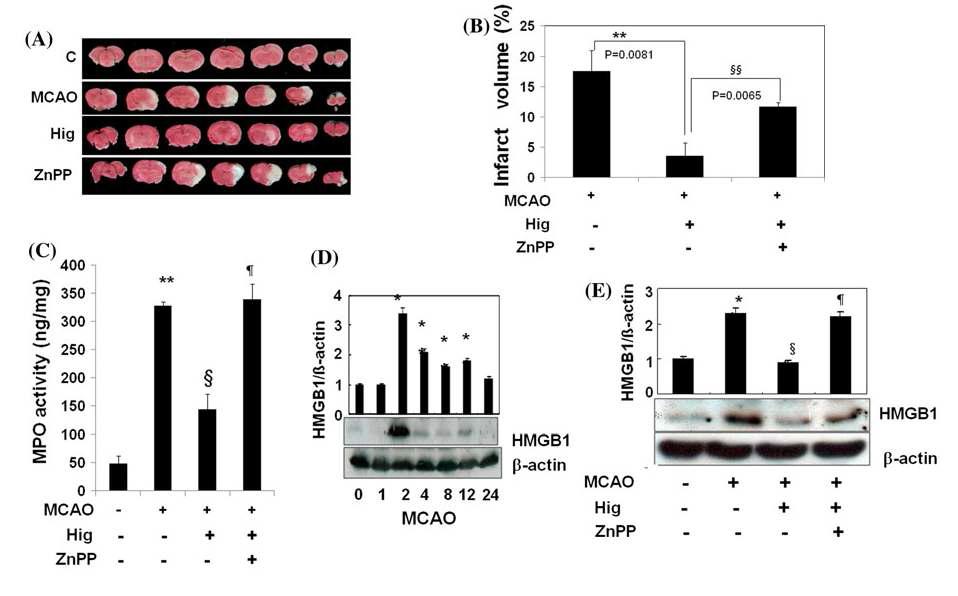 표
Higenamine reduces inflammation and infarct volume in MCAO rats due to HO-1 induction. Higenamine (10 mg/kg, i.p, n = 12) was administered in rats 24 h prior to MCA occlusion. In ZnPPIXtreated animal study, ZnPPIX (10 mg/kg, i.p, n = 10) was administered 1 h before higenamine treatment. After the treatment, TTC staining was performed as described in ‘'‘'Materials and methods’'’' section. A typical slide was shown in a, in which (1) sham (n = 6), (2) MCAO (n = 16), (3) MCAO + higenamine (n = 12, 10 mg/kg), and (4) MCAO + higenamine (10 mg/ kg) + ZnPPIX (10 mg/kg) (n = 10). b Percent change of infarct volume by each treatment in MCAO rats was shown. c MPO activity and d, e HMGB1 expression were measured from brain tissues taken out 24 h after the MCA occluded rats, respectively. Results are means ± SE of four independent experiments.
표
Higenamine reduces inflammation and infarct volume in MCAO rats due to HO-1 induction. Higenamine (10 mg/kg, i.p, n = 12) was administered in rats 24 h prior to MCA occlusion. In ZnPPIXtreated animal study, ZnPPIX (10 mg/kg, i.p, n = 10) was administered 1 h before higenamine treatment. After the treatment, TTC staining was performed as described in ‘'‘'Materials and methods’'’' section. A typical slide was shown in a, in which (1) sham (n = 6), (2) MCAO (n = 16), (3) MCAO + higenamine (n = 12, 10 mg/kg), and (4) MCAO + higenamine (10 mg/ kg) + ZnPPIX (10 mg/kg) (n = 10). b Percent change of infarct volume by each treatment in MCAO rats was shown. c MPO activity and d, e HMGB1 expression were measured from brain tissues taken out 24 h after the MCA occluded rats, respectively. Results are means ± SE of four independent experiments.
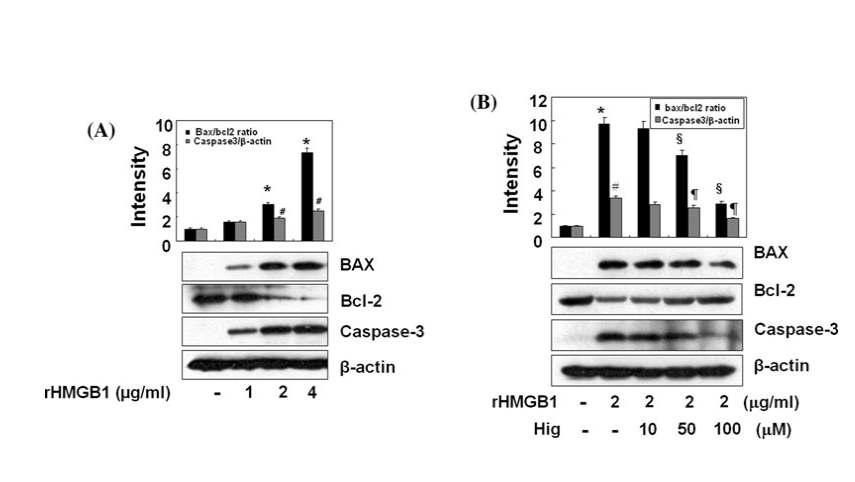 표
Higenamine reduces rHMGB1-induced apoptosis in C6 cells. Cells were treated with rHMGB1 (1, 2, and 4 lg/ml) and incubated for 4 h (for Bax, Bcl-2) and 6 h (for cleaved caspase-3), respectively. The extracted proteins were subjected to western blot analysis with corresponding antibodies (a). Different concentrations of higenmine were treated 1 h prior to application of rHMGB1 (2 lg/ml) in C6 cells. After indicated time of incubation, cells were harvested and western blot analysis was performed as described above (b). Results are means ± SE of three independent experiments.
표
Higenamine reduces rHMGB1-induced apoptosis in C6 cells. Cells were treated with rHMGB1 (1, 2, and 4 lg/ml) and incubated for 4 h (for Bax, Bcl-2) and 6 h (for cleaved caspase-3), respectively. The extracted proteins were subjected to western blot analysis with corresponding antibodies (a). Different concentrations of higenmine were treated 1 h prior to application of rHMGB1 (2 lg/ml) in C6 cells. After indicated time of incubation, cells were harvested and western blot analysis was performed as described above (b). Results are means ± SE of three independent experiments.
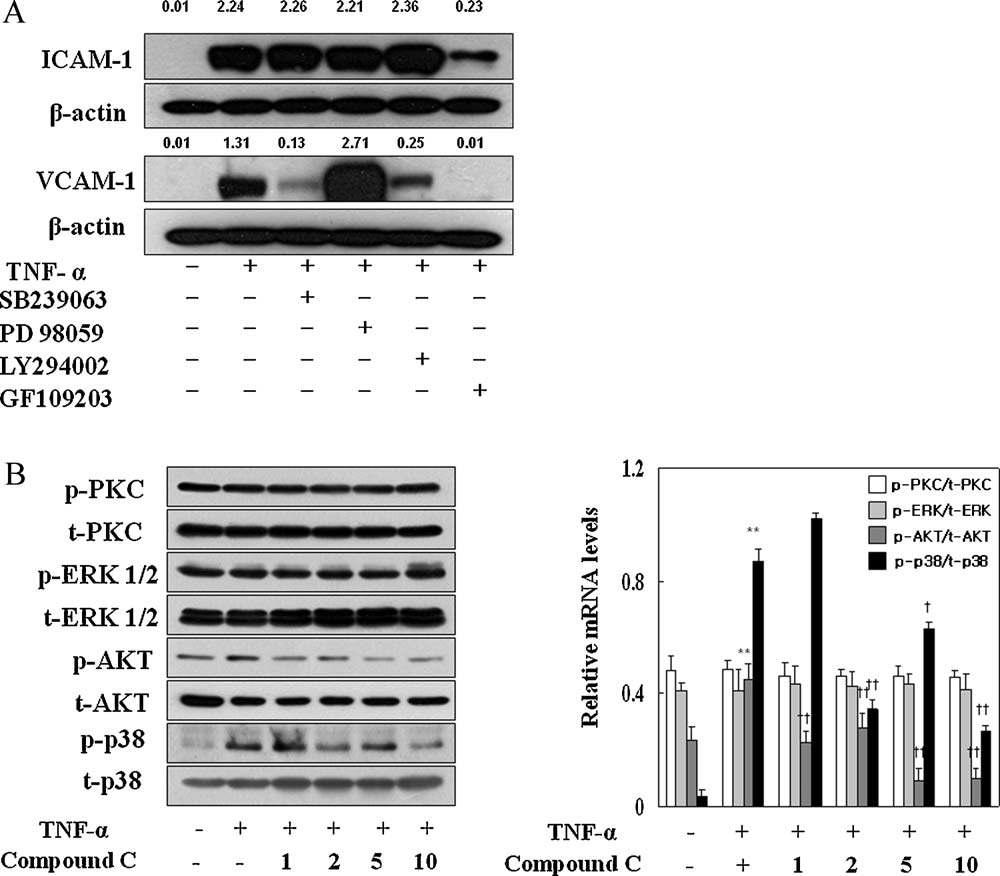 표
Signals involved in preferential inhibition of VCAM-1 over ICAM-1 expression in response to TNF-in cultured endothelial cells and inhibition of phosphorylation of Akt and p38 MAP kinases by compound C. Cells were pretreated signal inhibitors 30 min prior to TNF-and incubated for 6 h to see which signals are involved in inhibition of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 (A). Cells were treated with indicated concentrations of compound C 30min prior to TNF-and then incubated for 30 min (B). Proteins were extracted and subjected to western blot analysis using corresponding antibodies. Data represent one of typical blots with similar results of triplicates. The intensity ratio was depicted as Arabic numbers on the top of each band when histogram was not presented.
표
Signals involved in preferential inhibition of VCAM-1 over ICAM-1 expression in response to TNF-in cultured endothelial cells and inhibition of phosphorylation of Akt and p38 MAP kinases by compound C. Cells were pretreated signal inhibitors 30 min prior to TNF-and incubated for 6 h to see which signals are involved in inhibition of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 (A). Cells were treated with indicated concentrations of compound C 30min prior to TNF-and then incubated for 30 min (B). Proteins were extracted and subjected to western blot analysis using corresponding antibodies. Data represent one of typical blots with similar results of triplicates. The intensity ratio was depicted as Arabic numbers on the top of each band when histogram was not presented.
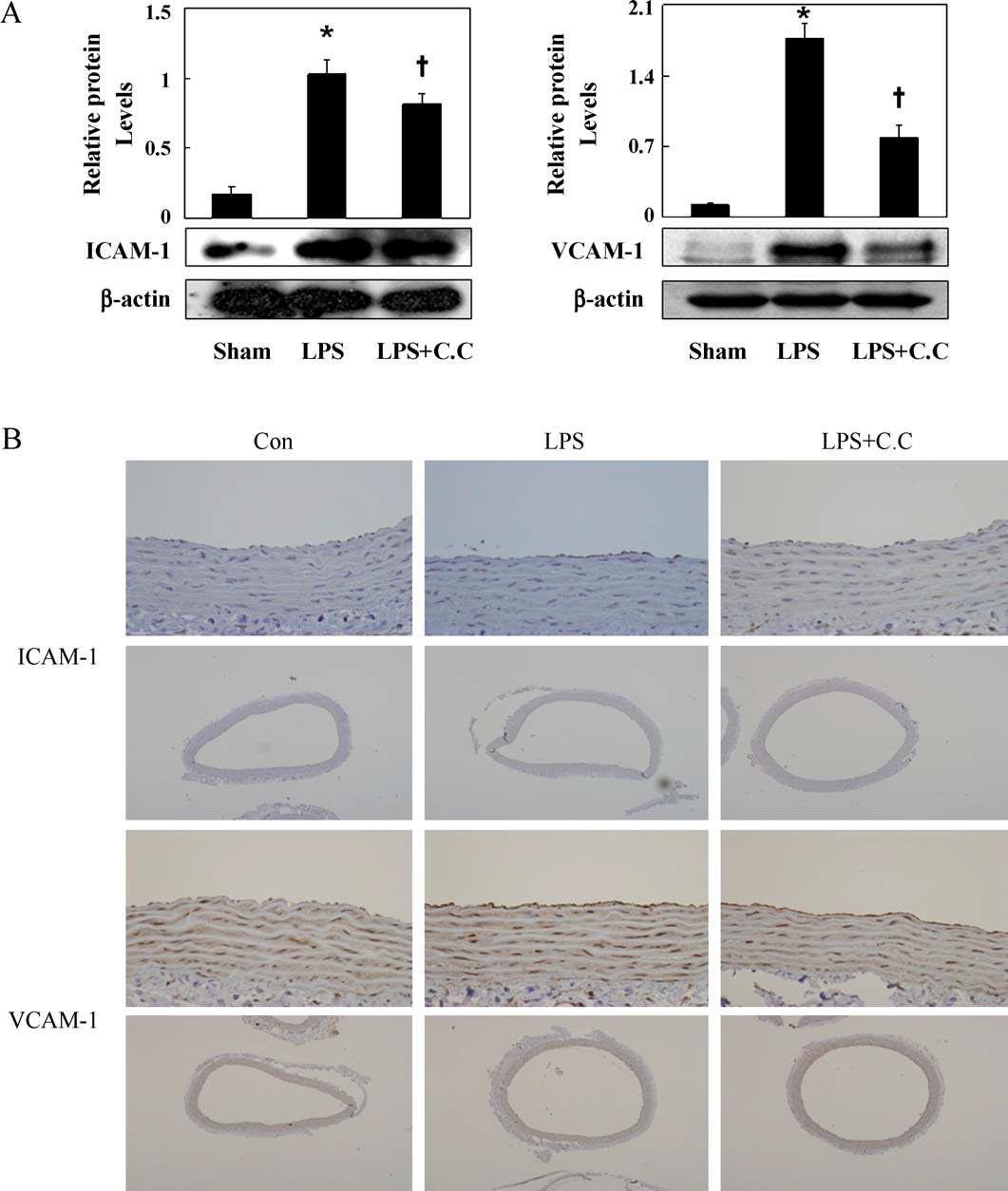 표
Effect of compound C treatment on VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression in the aorta of LPS-treated rats. Compound C (0.2 mg/kg) was administrated (i.v.) 30 min before LPS (10 mg/kg) injection. Six hours later rats were anesthetized and thoracic aortas were collected for western blotting and immunohistochemistry, respectively. Relative protein levels (ICAM-1 or VCAM-1/-actin) in sham (n = 3), LPS (n = 3), and LPS with compound C (LPS + C.C., n = 3) were shown in A. Representative images of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 immunoreactivity (B) for aortic sections of control (CTL), LPS, and LPS with compound C (LPS + C.C.). Of note, the increased VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 immunoreactivity in the aortic endothelium of LPS-treated rats were decreased by compound C.
표
Effect of compound C treatment on VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression in the aorta of LPS-treated rats. Compound C (0.2 mg/kg) was administrated (i.v.) 30 min before LPS (10 mg/kg) injection. Six hours later rats were anesthetized and thoracic aortas were collected for western blotting and immunohistochemistry, respectively. Relative protein levels (ICAM-1 or VCAM-1/-actin) in sham (n = 3), LPS (n = 3), and LPS with compound C (LPS + C.C., n = 3) were shown in A. Representative images of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 immunoreactivity (B) for aortic sections of control (CTL), LPS, and LPS with compound C (LPS + C.C.). Of note, the increased VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 immunoreactivity in the aortic endothelium of LPS-treated rats were decreased by compound C.
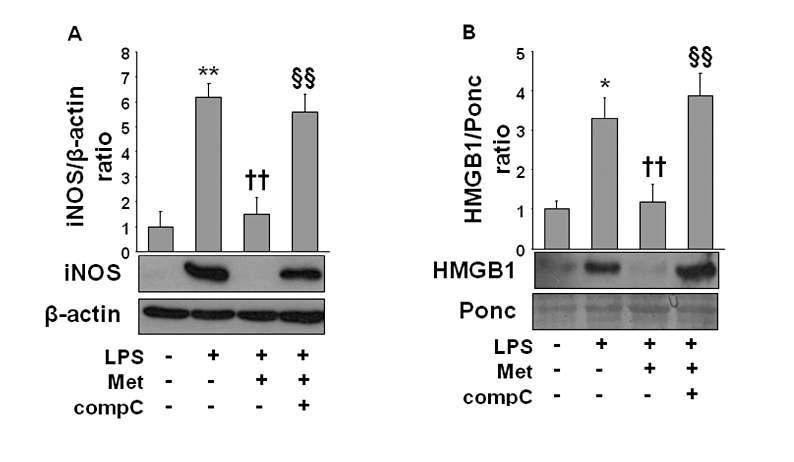 표
Pharmacological inhibition of AMPK reversed metformin-mediated anti-inflammatory effect in LPS-activated macrophages. Cells were treated with metformin (10 mM) in the presence or absence of compound C (comp C; 12 μM) for 1 h. Then cells were stimulated with LPS (1 μg·mL−1) for the next 24 h. After incubation, cells were lysed and subjected to Western blot (A); culture medium samples were extracted for HMGB1 detection by HMGB1 analysis (B) as described in Methods. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
표
Pharmacological inhibition of AMPK reversed metformin-mediated anti-inflammatory effect in LPS-activated macrophages. Cells were treated with metformin (10 mM) in the presence or absence of compound C (comp C; 12 μM) for 1 h. Then cells were stimulated with LPS (1 μg·mL−1) for the next 24 h. After incubation, cells were lysed and subjected to Western blot (A); culture medium samples were extracted for HMGB1 detection by HMGB1 analysis (B) as described in Methods. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
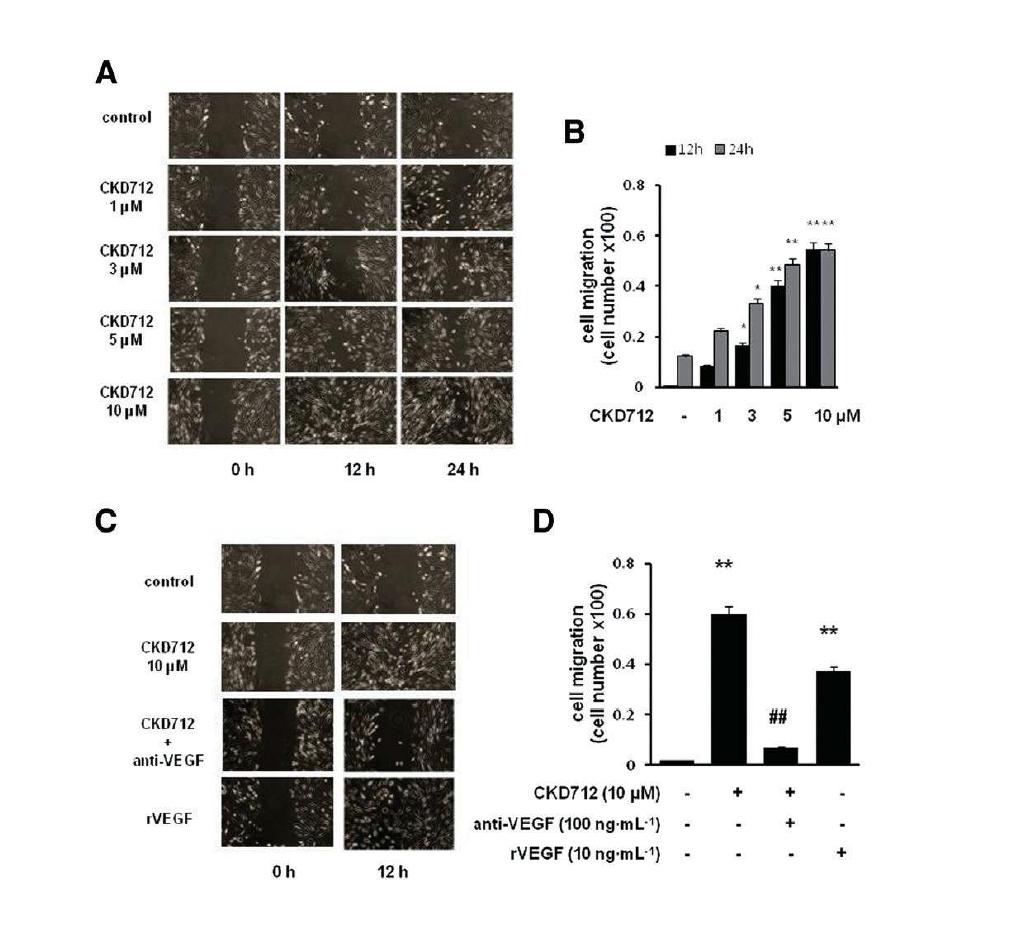 표
Involvement of VEGF in CKD712-mediated cell migration and its effect on the migration of HDFs. Confluent cells were treated with mitomycin C (8 mg·mL-1) for 2 h. After washing with PBS, the cells were wounded by scraping, and fresh medium was added. (A,B) Cells were treated with CKD712 at the indicated concentrations for 12 or 24 h and then cell migration was assessed. (C, D) Cell migration was also assessed in HDF cells stimulated with recombinant VEGF (10 ng·mL-1) or with CKD712 (10 mM) in presence or absence of anti-VEGF antibody (100 ng·mL-1). Representative photographs from three independent experiments are shown with similar results.
표
Involvement of VEGF in CKD712-mediated cell migration and its effect on the migration of HDFs. Confluent cells were treated with mitomycin C (8 mg·mL-1) for 2 h. After washing with PBS, the cells were wounded by scraping, and fresh medium was added. (A,B) Cells were treated with CKD712 at the indicated concentrations for 12 or 24 h and then cell migration was assessed. (C, D) Cell migration was also assessed in HDF cells stimulated with recombinant VEGF (10 ng·mL-1) or with CKD712 (10 mM) in presence or absence of anti-VEGF antibody (100 ng·mL-1). Representative photographs from three independent experiments are shown with similar results.
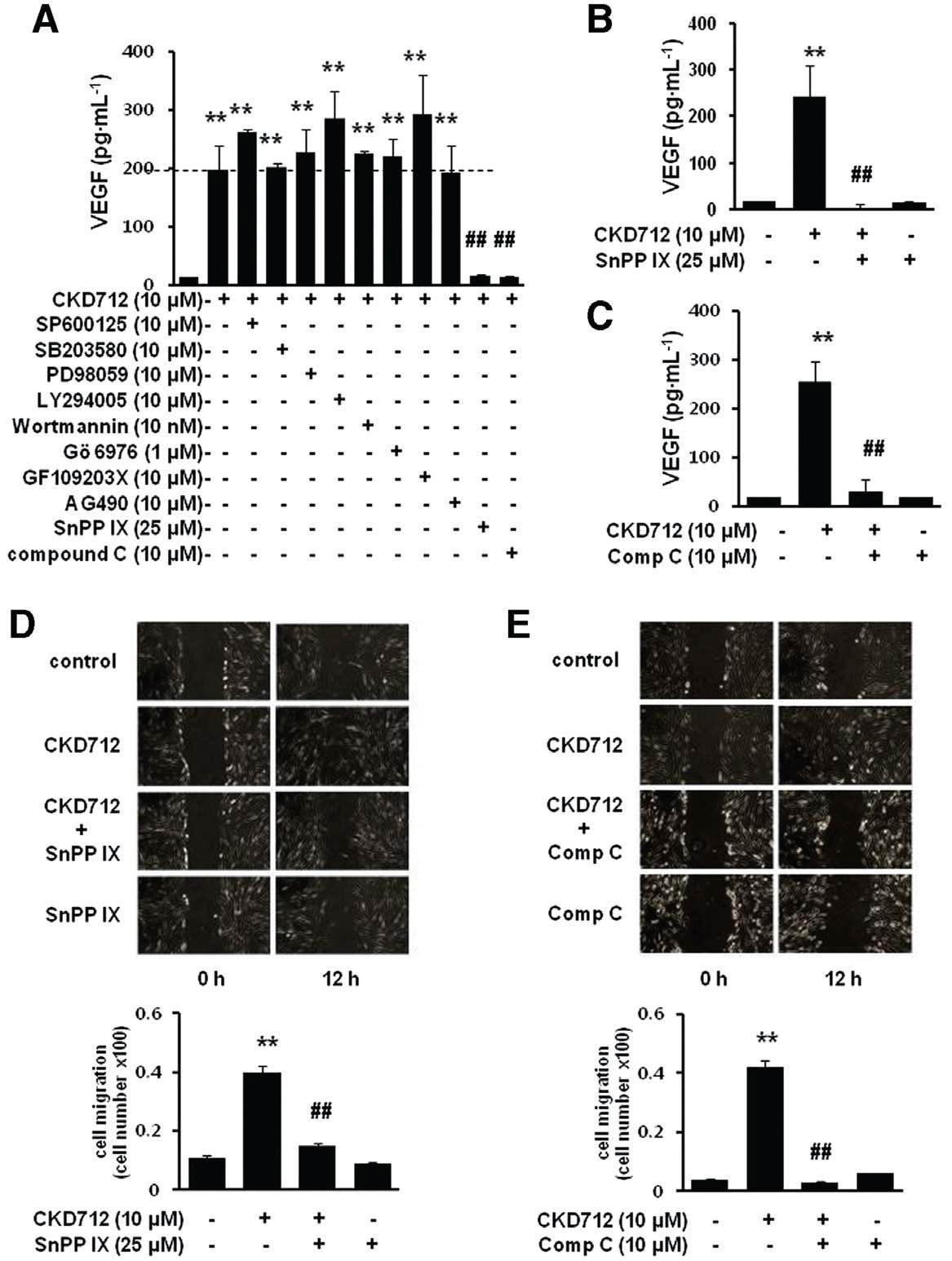 표
Dependence on HO-1/AMPK signalling of the production of VEGF by CKD712 and the effect of SnPPIX and compound C on the cell migration induced by CKD712. The cells were pretreated with various inhibitors and then treated with CKD712. After incubation, samples of the culture media were collected and subjected to ELISA for VEGF (A– C). Confluent cells were treated with mitomycin C (8 mg·mL-1) for 2 h. After washing with PBS, the cells were wounded by scraping, and fresh medium was added. The cells were incubated with CKD712 (10 mM) in the presence or absence of SnPPIX (25 mM) (D) or compound C (10 mM) (E) for 12 h. The data are presented as the mean SD of three independent experiments.
표
Dependence on HO-1/AMPK signalling of the production of VEGF by CKD712 and the effect of SnPPIX and compound C on the cell migration induced by CKD712. The cells were pretreated with various inhibitors and then treated with CKD712. After incubation, samples of the culture media were collected and subjected to ELISA for VEGF (A– C). Confluent cells were treated with mitomycin C (8 mg·mL-1) for 2 h. After washing with PBS, the cells were wounded by scraping, and fresh medium was added. The cells were incubated with CKD712 (10 mM) in the presence or absence of SnPPIX (25 mM) (D) or compound C (10 mM) (E) for 12 h. The data are presented as the mean SD of three independent experiments.
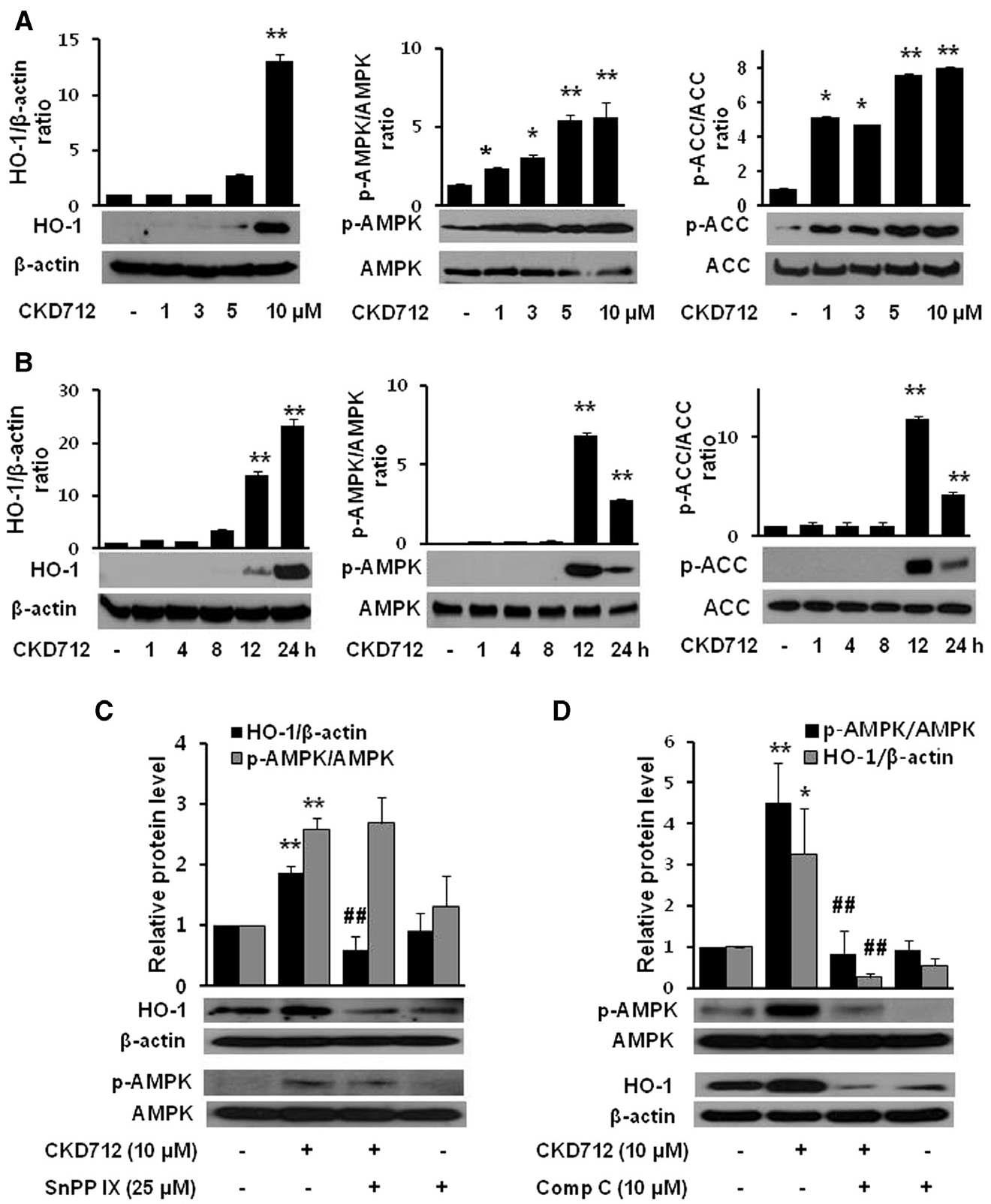 표
Effect of CKD712 on the HO-1/AMPK protein levels in HDFs. The cells were treated with CKD712 (1, 3, 5 and 10 mM) for 12 h (A) or incubated with CKD712 (10 mM) for different time periods (1, 4, 8, 12 and 24 h) (B). After incubation, the cells were harvested for Western blotting to detect HO-1, p-AMPK and p-ACC. The cells were treated with CKD712 (10 mM), with or without SnPPIX (25 mM) or compound C (10 mM) and incubated for 12 h (C) or 24 h (D). After incubation, the cells were lysed and analysed by Western blotting. The bands of the blots are representative of three independent experiments, with similar results. The data are presented as the mean SD of three independent experiments.
표
Effect of CKD712 on the HO-1/AMPK protein levels in HDFs. The cells were treated with CKD712 (1, 3, 5 and 10 mM) for 12 h (A) or incubated with CKD712 (10 mM) for different time periods (1, 4, 8, 12 and 24 h) (B). After incubation, the cells were harvested for Western blotting to detect HO-1, p-AMPK and p-ACC. The cells were treated with CKD712 (10 mM), with or without SnPPIX (25 mM) or compound C (10 mM) and incubated for 12 h (C) or 24 h (D). After incubation, the cells were lysed and analysed by Western blotting. The bands of the blots are representative of three independent experiments, with similar results. The data are presented as the mean SD of three independent experiments.
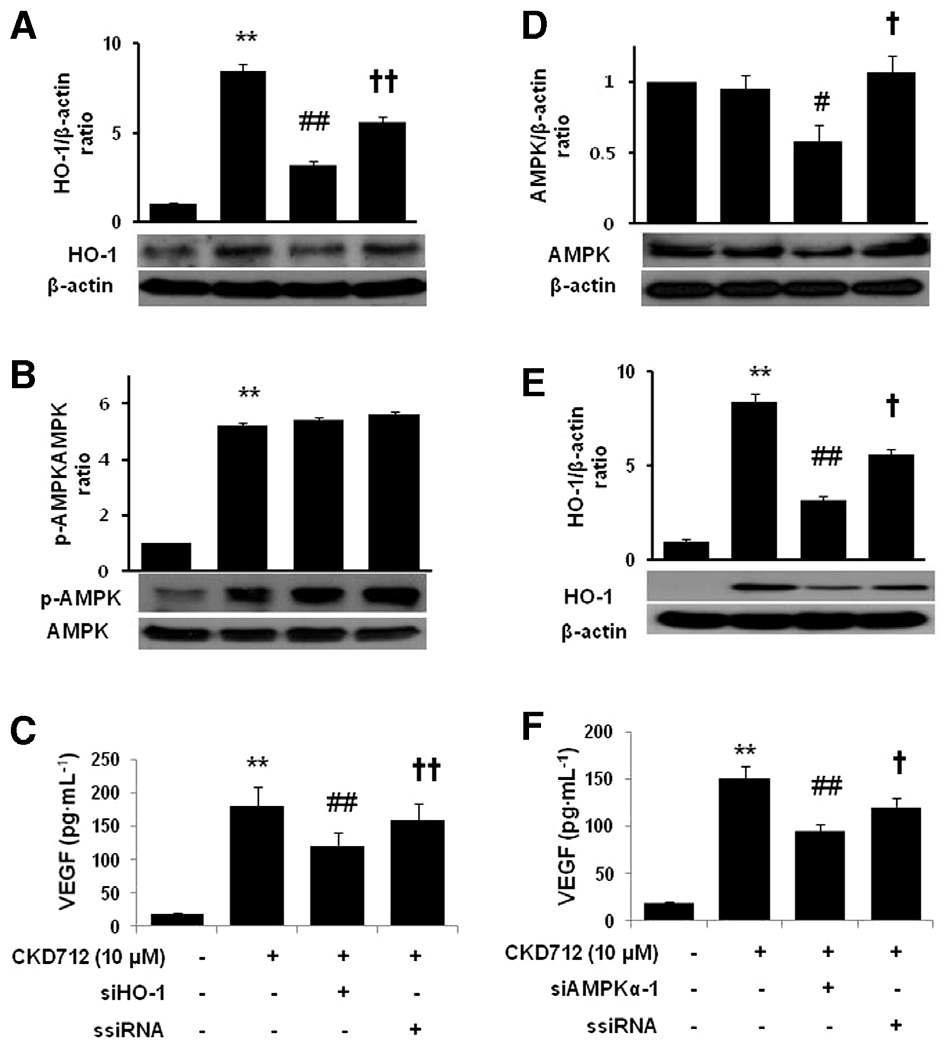 표
Effect of siRNA transfection on the CKD712-mediated expression of HO-1 and AMPK and VEGF production in HDFs. After transfection with HO-1- or AMPK-siRNA, the cells were treated with CKD712 (10 mM) for 24 h (A) or 12 h (B). Then cells were harvested and analysed by Western blotting for HO-1 (A, E) or AMPK (B, D). The cells were treated with CKD712 (10 mM) for 12 h, and culture medium samples were collected and subjected to ELISA for VEGF (C, F). The data are presented as the mean SD of three independent experiments.
표
Effect of siRNA transfection on the CKD712-mediated expression of HO-1 and AMPK and VEGF production in HDFs. After transfection with HO-1- or AMPK-siRNA, the cells were treated with CKD712 (10 mM) for 24 h (A) or 12 h (B). Then cells were harvested and analysed by Western blotting for HO-1 (A, E) or AMPK (B, D). The cells were treated with CKD712 (10 mM) for 12 h, and culture medium samples were collected and subjected to ELISA for VEGF (C, F). The data are presented as the mean SD of three independent experiments.
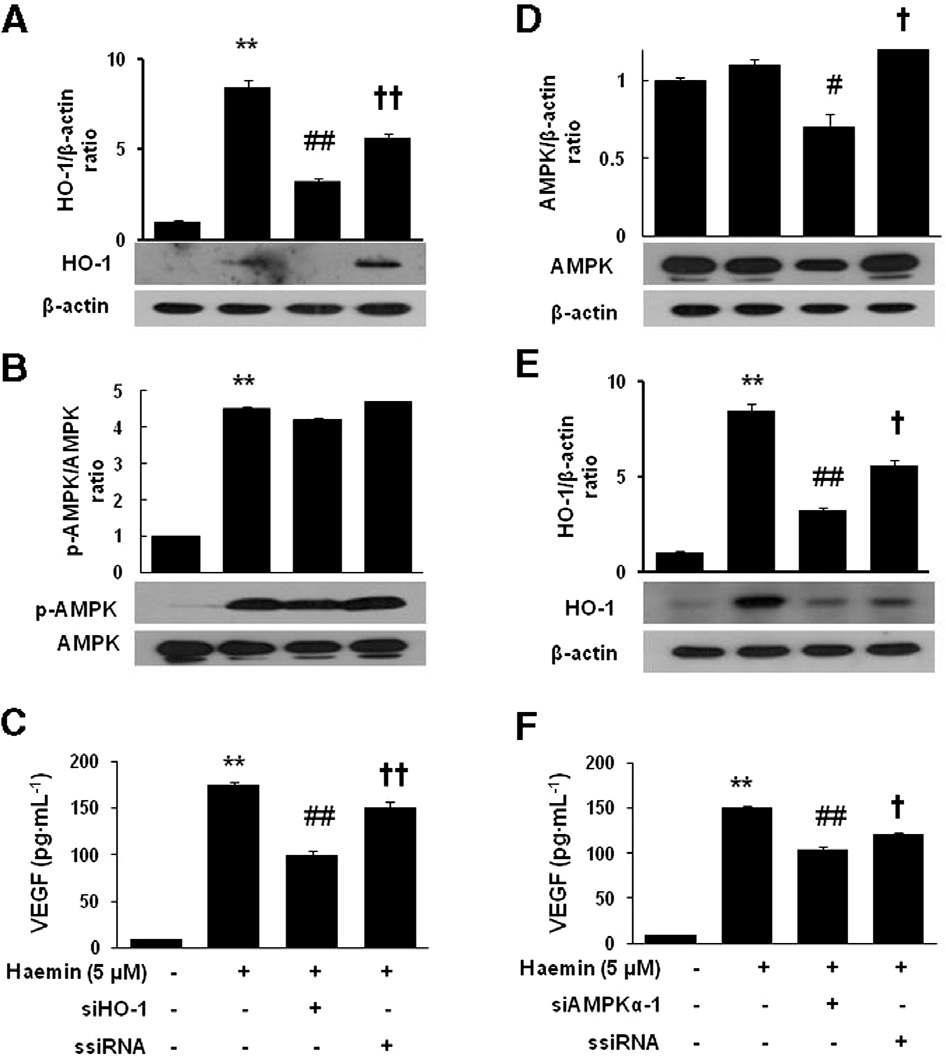 표
Effect of siRNA transfection on the expression of HO-1, AMPK and VEGF production induced by haemin in HDFs. After transfection with the corresponding siRNA, the cells were treated with haemin (15 mM) for 24 h (A) or 12 h (B). The cells were harvested and analysed by Western blotting for HO-1 (A, E) or for AMPK (B, D). The cells were treated with haemin (15 mM) for 12 h, and culture medium samples were collected and subjected to ELISA for VEGF (C, F). The data are presented as the mean SD of three independent experiments.
표
Effect of siRNA transfection on the expression of HO-1, AMPK and VEGF production induced by haemin in HDFs. After transfection with the corresponding siRNA, the cells were treated with haemin (15 mM) for 24 h (A) or 12 h (B). The cells were harvested and analysed by Western blotting for HO-1 (A, E) or for AMPK (B, D). The cells were treated with haemin (15 mM) for 12 h, and culture medium samples were collected and subjected to ELISA for VEGF (C, F). The data are presented as the mean SD of three independent experiments.
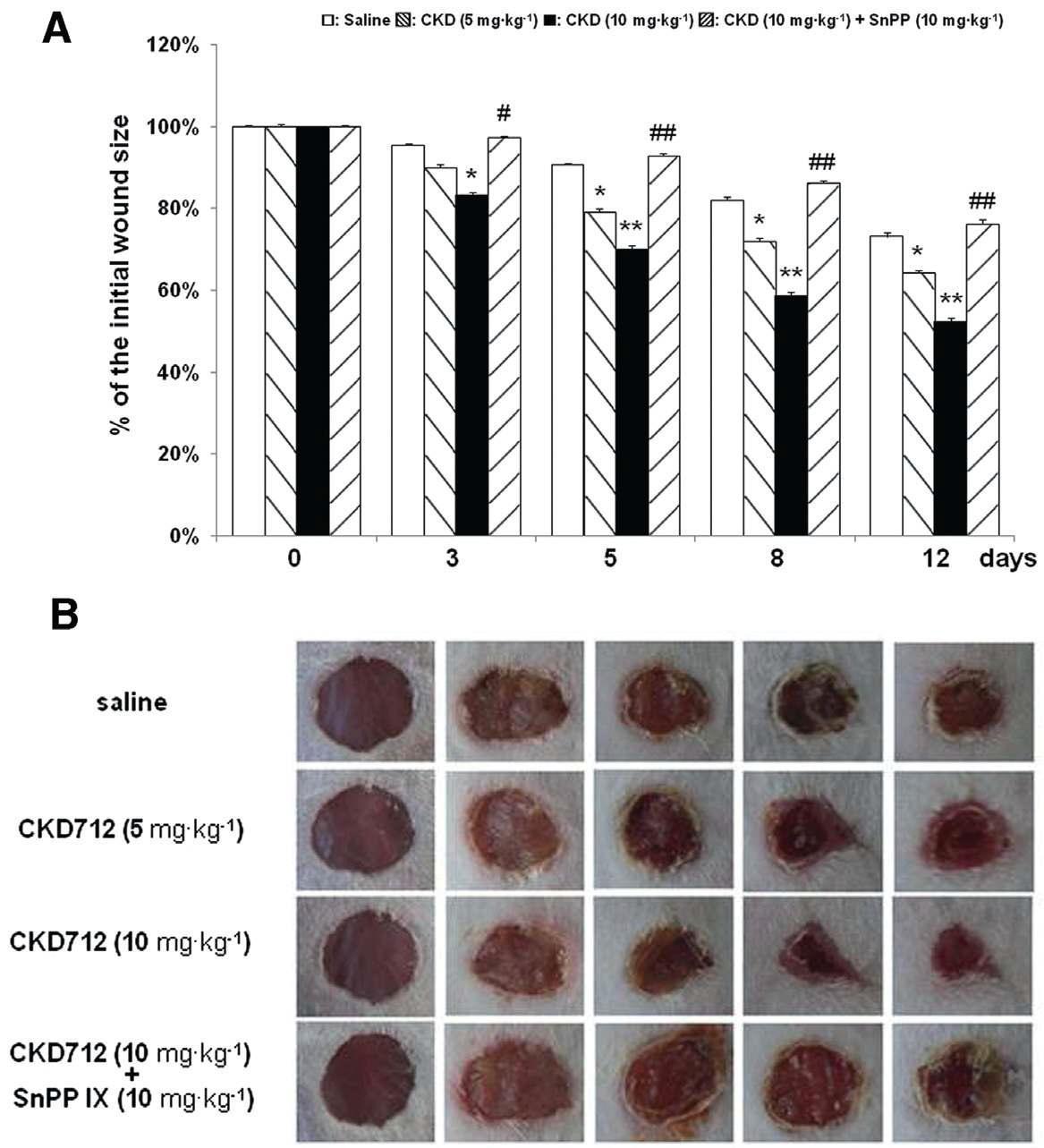 표
The wound closure induced by CKD712 is antagonized by SnPPIX in an animal wound model. Two full-thickness 5-mm punch wounds were inflicted on the dorsal surface of each mouse, and the mice were injected (i.p) with saline, CKD712 (5 mg·kg-1), CKD712 (10 mg·kg-1) or CKD712 (10 mg·kg-1 plus SnPPIX (10 mg·kg-1). The time course of the changes in the wound size with different treatments in mice (A). Images of a representative mouse from each group taken on post-injury days 0, 3, 5, 8 and 12 are shown (B). The wound sizes at the indicated time points in topically treated mice.
표
The wound closure induced by CKD712 is antagonized by SnPPIX in an animal wound model. Two full-thickness 5-mm punch wounds were inflicted on the dorsal surface of each mouse, and the mice were injected (i.p) with saline, CKD712 (5 mg·kg-1), CKD712 (10 mg·kg-1) or CKD712 (10 mg·kg-1 plus SnPPIX (10 mg·kg-1). The time course of the changes in the wound size with different treatments in mice (A). Images of a representative mouse from each group taken on post-injury days 0, 3, 5, 8 and 12 are shown (B). The wound sizes at the indicated time points in topically treated mice.
 표
Effect of nicotine on the expression of TNF-α, iNOS, and HMGB1 in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Cells were stimulated with LPS (1 mg=ml) in the presence or absence of nicotine (1, 5, 10 μM) for 24 h. After incubation culture medium samples were subjected to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for (A) TNF-a detection, lysates were subjected to Western blot for (B) iNOS and (C) HMGB1, respectively. Blot bands are representative of three independent experiments. Data are presented as meanSD of three independent experiments. Significance compared to control, **p<0.01; significance compared with LPS alone {p<0.05 or {{p<0.01. HMGB1, high mobility group box 1; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
표
Effect of nicotine on the expression of TNF-α, iNOS, and HMGB1 in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Cells were stimulated with LPS (1 mg=ml) in the presence or absence of nicotine (1, 5, 10 μM) for 24 h. After incubation culture medium samples were subjected to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for (A) TNF-a detection, lysates were subjected to Western blot for (B) iNOS and (C) HMGB1, respectively. Blot bands are representative of three independent experiments. Data are presented as meanSD of three independent experiments. Significance compared to control, **p<0.01; significance compared with LPS alone {p<0.05 or {{p<0.01. HMGB1, high mobility group box 1; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
 표
Effect of EP on the expression of iNOS/NO and HMGB1 release in LPS-stimulated macrophages (A– C). Cells were pretreated with EP for 1 h at doses 5, 10, and 25mM. Then, the cells were stimulated with LPS (1 mg/ml) for 16 h. The culture medium was collected and subjected to NO assay (A) and HMGB1 analysis (C). Cells were lysed and harvested and subjected to western blot for iNOS detection (B) as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
표
Effect of EP on the expression of iNOS/NO and HMGB1 release in LPS-stimulated macrophages (A– C). Cells were pretreated with EP for 1 h at doses 5, 10, and 25mM. Then, the cells were stimulated with LPS (1 mg/ml) for 16 h. The culture medium was collected and subjected to NO assay (A) and HMGB1 analysis (C). Cells were lysed and harvested and subjected to western blot for iNOS detection (B) as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
 표
Effect of EP on the expression of HO-1 in macrophages. Cells were treated with EP at doses 5, 10, and 25mM for 8 h (A) or at dose 25mM for 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 h (B). After incubation, cells were harvested and subjected to western blot as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are presented as mean ±SD of three independent experiments. Significance compared with control, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01. HO-1, heme oxygenase-1.
표
Effect of EP on the expression of HO-1 in macrophages. Cells were treated with EP at doses 5, 10, and 25mM for 8 h (A) or at dose 25mM for 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 h (B). After incubation, cells were harvested and subjected to western blot as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are presented as mean ±SD of three independent experiments. Significance compared with control, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01. HO-1, heme oxygenase-1.
 표
EP induces HO-1 through p38 MAPK. Cells were pretreated with SB203580 (10 μM), SP600125 (10 μM), and PD98059 (10 μM) for 1 h, and then cells were treated with EP (25mM) for 8 h (A, for HO-1) and for 6 h (B, for p-p38). After incubation, cells were harvested and subjected to western blot as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are presented as – SD of three independent experiments.
표
EP induces HO-1 through p38 MAPK. Cells were pretreated with SB203580 (10 μM), SP600125 (10 μM), and PD98059 (10 μM) for 1 h, and then cells were treated with EP (25mM) for 8 h (A, for HO-1) and for 6 h (B, for p-p38). After incubation, cells were harvested and subjected to western blot as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are presented as – SD of three independent experiments.
 표
Effect of EP on intracellular GSH levels and p38 phosphorylation in RAW 264.7 cells. The cells were incubated for 24 h without or with LPS, or LPS with different concentrations of EP (5, 10, and 25mM). Intracellular levels of reduced (GSH) and oxidized (GSSG) glutathione were assayed (A) as described in the Materials and Methods section. To see the effect of EP on p38 phosphorylation and HO-1 expression, cells were incubated with EP (25mM) in the presence or absence of GSH-Et (10μM) for 8 h (B). To check the expression of HO-1 and p38 phosphorylation by NAC and GSH-Et, cells were incubated for 8 h in the presence of LPS + EP (C). To see whether GSH-Et reverses the EP effect on LPS-activated iNOS and HO-1 expression, cells were treated with EP (25mM) or EP with GSH-Et (10μM) for 8 h (HO-1) or for 16 h (HMGB1) in the presence of LPS (D). After incubation, cells were harvested and subjected to western blot as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are presented as means ± SD of three independent experiments. Significance compared with control, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01; significance compared with LPS, {p < 0.05 and {{p < 0.01; significance compared with EP, #p < 0.05; significance compared with LPS + EP, xp < 0.05 and xxp < 0.01. GSH-Et, glutathione ethyl ester; NAC, N-acetyl cysteine.
표
Effect of EP on intracellular GSH levels and p38 phosphorylation in RAW 264.7 cells. The cells were incubated for 24 h without or with LPS, or LPS with different concentrations of EP (5, 10, and 25mM). Intracellular levels of reduced (GSH) and oxidized (GSSG) glutathione were assayed (A) as described in the Materials and Methods section. To see the effect of EP on p38 phosphorylation and HO-1 expression, cells were incubated with EP (25mM) in the presence or absence of GSH-Et (10μM) for 8 h (B). To check the expression of HO-1 and p38 phosphorylation by NAC and GSH-Et, cells were incubated for 8 h in the presence of LPS + EP (C). To see whether GSH-Et reverses the EP effect on LPS-activated iNOS and HO-1 expression, cells were treated with EP (25mM) or EP with GSH-Et (10μM) for 8 h (HO-1) or for 16 h (HMGB1) in the presence of LPS (D). After incubation, cells were harvested and subjected to western blot as described in the Materials and Methods section. Data are presented as means ± SD of three independent experiments. Significance compared with control, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01; significance compared with LPS, {p < 0.05 and {{p < 0.01; significance compared with EP, #p < 0.05; significance compared with LPS + EP, xp < 0.05 and xxp < 0.01. GSH-Et, glutathione ethyl ester; NAC, N-acetyl cysteine.
 표
Involvement of Nrf2 in EP mediated HO-1 expression. Cells were treated for 1 h with EP at 5, 10, and 25mM, and then harvested and subjectedto cytosol/nuclear fractionation (A). Cells were transiently transfected with the ARE-luc vector (B). After incubation, cells were treated with EP (5,10, and 25mM) or EP (25 mM) + SB203580 (10 μM, which was pretreated 1 h before addition of EP) for 1 h. After incubation, cells were subjected to luciferase assay as described in the Materials and Methods section. Cells were transfected with scramble (siRNA) or siNrf2 (C) as described in the Materials and Methods section. After 8-h incubation with EP (25 mM), cells were harvested and subjected to western blot for HO-1 expression. Transfection efficiency was confirmed by checking Nrf2 expression. Data are presented as – SD of three independent experiments. Significance compared with control, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01; significance compared with EP alone or EP + ssiRNA, {p < 0.05 and {{p < 0.01. ARE, antioxidant redox element; Nrf2, NF-E2-related factor 2.
표
Involvement of Nrf2 in EP mediated HO-1 expression. Cells were treated for 1 h with EP at 5, 10, and 25mM, and then harvested and subjectedto cytosol/nuclear fractionation (A). Cells were transiently transfected with the ARE-luc vector (B). After incubation, cells were treated with EP (5,10, and 25mM) or EP (25 mM) + SB203580 (10 μM, which was pretreated 1 h before addition of EP) for 1 h. After incubation, cells were subjected to luciferase assay as described in the Materials and Methods section. Cells were transfected with scramble (siRNA) or siNrf2 (C) as described in the Materials and Methods section. After 8-h incubation with EP (25 mM), cells were harvested and subjected to western blot for HO-1 expression. Transfection efficiency was confirmed by checking Nrf2 expression. Data are presented as – SD of three independent experiments. Significance compared with control, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01; significance compared with EP alone or EP + ssiRNA, {p < 0.05 and {{p < 0.01. ARE, antioxidant redox element; Nrf2, NF-E2-related factor 2.
 표
Importance of HO-1 in the anti-inflammatory action of EP. Cells were transfected with ssiRNA or siHO-1 RNA, which were subjected to western blot to confirm siHO-1 efficiency by EP (25mM) for 8 h (A). Cells were stimulated with LPS (1μg/ml) in the presence or absence of EP (25mM) for 16 h. Then, cell extract and culture medium samples were subjected to western blot for iNOS and HMGB1, respectively (B). Significance compared with control, **p < 0.01; significance compared with LPS,
표
Importance of HO-1 in the anti-inflammatory action of EP. Cells were transfected with ssiRNA or siHO-1 RNA, which were subjected to western blot to confirm siHO-1 efficiency by EP (25mM) for 8 h (A). Cells were stimulated with LPS (1μg/ml) in the presence or absence of EP (25mM) for 16 h. Then, cell extract and culture medium samples were subjected to western blot for iNOS and HMGB1, respectively (B). Significance compared with control, **p < 0.01; significance compared with LPS,
 표
SB203580 and p38-siRNA reverse anti-inflammatory effect of EP in macrophages. Cells were incubated with EP (25mM) with or without SB203580 (10 μM) for 1 h and stimulated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 16 h (A), or cells were transfected with p38-siRNA or ssiRNA (B, C), which were incubated with EP (25mM) for 1 h and stimulated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 16 h. Cell extract and culture medium samples were subjected to western blot for iNOS and HMGB1 analysis, respectively. Data are presented as means± SD of three independent experiments.
표
SB203580 and p38-siRNA reverse anti-inflammatory effect of EP in macrophages. Cells were incubated with EP (25mM) with or without SB203580 (10 μM) for 1 h and stimulated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 16 h (A), or cells were transfected with p38-siRNA or ssiRNA (B, C), which were incubated with EP (25mM) for 1 h and stimulated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 16 h. Cell extract and culture medium samples were subjected to western blot for iNOS and HMGB1 analysis, respectively. Data are presented as means± SD of three independent experiments.
 표
EP fails to increase the survival rate in the CLP-induced sepsis model of HO-1- / - mice. BALB/c WT (n = 12) and HO-1-/ - mice (n = 12) were subjected to CLP with EP (n = 6, 40 mg/kg i.p.) or an equal volume of vehicle (n = 6, saline) treatment at 0 and 24 h, after onset of sepsis. Survival was monitored daily for up to 5 days (A). To determine serum HMGB1 levels, WT and HO-1-/- mice were treated with EP (40 mg/kg i.p., n = 5) or an equal volume of vehicle (n = 4, saline) at 0 and 12 h after onset of sepsis (CLP). Twenty-four hours later, blood was collected by cardiac puncture and subjected to HMGB1 (B) and ELISA (C) analysis. The Kaplan– Meier program was utilized to compare the differences in mortality rates between groups.
표
EP fails to increase the survival rate in the CLP-induced sepsis model of HO-1- / - mice. BALB/c WT (n = 12) and HO-1-/ - mice (n = 12) were subjected to CLP with EP (n = 6, 40 mg/kg i.p.) or an equal volume of vehicle (n = 6, saline) treatment at 0 and 24 h, after onset of sepsis. Survival was monitored daily for up to 5 days (A). To determine serum HMGB1 levels, WT and HO-1-/- mice were treated with EP (40 mg/kg i.p., n = 5) or an equal volume of vehicle (n = 4, saline) at 0 and 12 h after onset of sepsis (CLP). Twenty-four hours later, blood was collected by cardiac puncture and subjected to HMGB1 (B) and ELISA (C) analysis. The Kaplan– Meier program was utilized to compare the differences in mortality rates between groups.
 표
Possible mechanism by which EP reduces HMGB1 in sepsis. EP depletes intracellular GSH levels that change redox states of the cell, which, in turn, stimulates p38 MAPK. The activation of p38 MAPK by phosphorylation triggers to activate Nrf2, which dissociates from keap1 and then moves into the nucleus, where it binds to ARE binding sites to induce the HO-1 gene. Thus, SB203580, p38 inhibitor, inhibits EP-mediated HO-1 induction. On the other hand, LPS binds to LPS binding protein (LBP) along with CD14, a recognition molecule for LPS, which activates toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). The activated TLR4 stimulates p38 MAPK, which then induces HO-1. However, LPS activates NF-jB through MyD88-dependent signal pathways, and IFN-b, generated by LPS through TRIF-dependent signal pathways, activates the JAK/STAT signal pathway to induce inflammatory gene expression, such as iNOS, TNF-a, IL-1b, and release of HMGB1. The induction of HO-1 by EP inhibits these inflammatory cytokines and release of HMGB1 and NO production in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells. ZnPPIX, a HO-1 inhibitor, reverses the anti-inflammatory effect of EP (data not shown). Administration of EP also inhibits iNOS expression and circulating TNF-a, IL-1b, and HMGB1 in CLP-induced septic mice, which are dependent on HO-1 induction via activation of p38 MAPK. The schema describes possible signal pathways by which EP activates HO-1 induction in RAW 264.7 cells. IL-1, interleukin-1; NF-jB, nuclear factor kappa B; STAT1, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
표
Possible mechanism by which EP reduces HMGB1 in sepsis. EP depletes intracellular GSH levels that change redox states of the cell, which, in turn, stimulates p38 MAPK. The activation of p38 MAPK by phosphorylation triggers to activate Nrf2, which dissociates from keap1 and then moves into the nucleus, where it binds to ARE binding sites to induce the HO-1 gene. Thus, SB203580, p38 inhibitor, inhibits EP-mediated HO-1 induction. On the other hand, LPS binds to LPS binding protein (LBP) along with CD14, a recognition molecule for LPS, which activates toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). The activated TLR4 stimulates p38 MAPK, which then induces HO-1. However, LPS activates NF-jB through MyD88-dependent signal pathways, and IFN-b, generated by LPS through TRIF-dependent signal pathways, activates the JAK/STAT signal pathway to induce inflammatory gene expression, such as iNOS, TNF-a, IL-1b, and release of HMGB1. The induction of HO-1 by EP inhibits these inflammatory cytokines and release of HMGB1 and NO production in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells. ZnPPIX, a HO-1 inhibitor, reverses the anti-inflammatory effect of EP (data not shown). Administration of EP also inhibits iNOS expression and circulating TNF-a, IL-1b, and HMGB1 in CLP-induced septic mice, which are dependent on HO-1 induction via activation of p38 MAPK. The schema describes possible signal pathways by which EP activates HO-1 induction in RAW 264.7 cells. IL-1, interleukin-1; NF-jB, nuclear factor kappa B; STAT1, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
 표
Isoproterenol induces HO-1 in a concentra tion and time-dependent manner via Nrf-2 activ ation. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with isoprot erenol (ISO) for 8 h at different concentrations (a). Cells were incubated for the indicated perio d of time with a fixed dose of ISO (100 mM) (b), and then Western blot analysis was perfor med. To determine whether Nrf-2 translocation i s involved in HO-1 induction by isoproterenol, c ytosol and nuclear fraction were separated after 3 h of treatment with the indicated concentratio ns of isoproterenol. Western blot analysis was p erformed with anti-Nrf-2 antibody (c). Using Nrf -2 siRNA-transfected cells, HO-1 induction was i nvestigated in the presence and absence of ISO (d). Representative blot shown is from one of t he three independent experiments with similar r esults. Data are expressed as mean ±SEM of th ree independent experiments.
표
Isoproterenol induces HO-1 in a concentra tion and time-dependent manner via Nrf-2 activ ation. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with isoprot erenol (ISO) for 8 h at different concentrations (a). Cells were incubated for the indicated perio d of time with a fixed dose of ISO (100 mM) (b), and then Western blot analysis was perfor med. To determine whether Nrf-2 translocation i s involved in HO-1 induction by isoproterenol, c ytosol and nuclear fraction were separated after 3 h of treatment with the indicated concentratio ns of isoproterenol. Western blot analysis was p erformed with anti-Nrf-2 antibody (c). Using Nrf -2 siRNA-transfected cells, HO-1 induction was i nvestigated in the presence and absence of ISO (d). Representative blot shown is from one of t he three independent experiments with similar r esults. Data are expressed as mean ±SEM of th ree independent experiments.
 표
soproterenol reduces HMGB1 release in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells by HO-1 induction. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of isoproterenol (ISO) 1 h prior to addition of 1 μg/ml LPS. After a 16-h incubation period, detection of HMGB1 released into the medium was performed by Western blot analysis (a). Ponceau S (ponc) band was used as a loading control. To understand whether the reduced HMGB1 release is due to increased HO-1 activity in the presence of ISO, ZnPPIX (5 μM), an HO-1 inhibitor, was coadministered with ISO and HMGB1 detected after 16 h of incubation with LPS (b). Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Data are given as mean ±SEM of three independent experiments.
표
soproterenol reduces HMGB1 release in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells by HO-1 induction. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of isoproterenol (ISO) 1 h prior to addition of 1 μg/ml LPS. After a 16-h incubation period, detection of HMGB1 released into the medium was performed by Western blot analysis (a). Ponceau S (ponc) band was used as a loading control. To understand whether the reduced HMGB1 release is due to increased HO-1 activity in the presence of ISO, ZnPPIX (5 μM), an HO-1 inhibitor, was coadministered with ISO and HMGB1 detected after 16 h of incubation with LPS (b). Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Data are given as mean ±SEM of three independent experiments.
 표
Isoproterenol induces HO-1 expression via a PI3K- and p38 MAPK-dependent pathway. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated 30 min prior to addition of isoproterenol (ISO,200 μM) with different concentrations of LY294002, a PI3K inhibitor (a) or SB203580, a p38 MAPK inhibitor (b) to identify the signaling pathway involved in HO-1 induction. HO-1 protein was detected after 8 h of incubation with ISO. To confirm that these signaling molecules are involved in inhibition of HMGB1 release (c and d) due to HO-1 induction, RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of ISO 1 h prior to addition of 1 mg/ml LPS. LY294002 (10 μM) or SB 203580 (10 μM) was administered 30 min prior to treatment with ISO. Cells were incubated for 16 h after LPS addition for the purpose of detecting HMGB1. To further confirm that ISO-induced HO-1 expression is related to Nrf-2, which is also sensitive to PI3K and p38 MAPK, Nrf-2 luciferase activity was measured in the presence or absence of LY294002 or SB 203580 (e). Cells transfected with the Nrf-2 luciferase gene were incubated for 1 h with ISO (200 μM) with or without the inhibitors (each at 10 μM). Intensity is represented as fold increase in activity. Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Data are given as mean SEM of three independent experiments.
표
Isoproterenol induces HO-1 expression via a PI3K- and p38 MAPK-dependent pathway. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated 30 min prior to addition of isoproterenol (ISO,200 μM) with different concentrations of LY294002, a PI3K inhibitor (a) or SB203580, a p38 MAPK inhibitor (b) to identify the signaling pathway involved in HO-1 induction. HO-1 protein was detected after 8 h of incubation with ISO. To confirm that these signaling molecules are involved in inhibition of HMGB1 release (c and d) due to HO-1 induction, RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of ISO 1 h prior to addition of 1 mg/ml LPS. LY294002 (10 μM) or SB 203580 (10 μM) was administered 30 min prior to treatment with ISO. Cells were incubated for 16 h after LPS addition for the purpose of detecting HMGB1. To further confirm that ISO-induced HO-1 expression is related to Nrf-2, which is also sensitive to PI3K and p38 MAPK, Nrf-2 luciferase activity was measured in the presence or absence of LY294002 or SB 203580 (e). Cells transfected with the Nrf-2 luciferase gene were incubated for 1 h with ISO (200 μM) with or without the inhibitors (each at 10 μM). Intensity is represented as fold increase in activity. Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Data are given as mean SEM of three independent experiments.
 표
β1-Adrenoceptor activation induces HO-1 expression and activity in macrophage cells. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with isoproterenol (ISO, 100 μM), ISO + propranolol (100 μM), a non-selective β-AR antagonist, ISO + metoprolol (100 μM), a selective β1-AR antagonist, or ISO + butoxamine (100 μM), a selective β2-AR antagonist 30 min prior to addition of LPS (1 μg/ml). After incubation for 8 h (HO-1, a) or 16 h (HMGB1, b), cells were harvested and subjected to Western blot analysis as described in Section 2. To confirm that HO-1 induction by isoproterenol is mediated by the b1-AR, different concentrations of dobutamine, a β1-selective AR agonist, and salbutamol, a β2-selective AR agonist, were administered for 8 h to RAW 264.7 cells (c). Cells were incubated with LPS (1 μg/ml) or LPS + ISO (50, 100, and 200 μM) for 8 h and HO-1 expression and activity were measured as described in Section 2. Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Data are given as mean SEM of three independent experiments.
표
β1-Adrenoceptor activation induces HO-1 expression and activity in macrophage cells. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with isoproterenol (ISO, 100 μM), ISO + propranolol (100 μM), a non-selective β-AR antagonist, ISO + metoprolol (100 μM), a selective β1-AR antagonist, or ISO + butoxamine (100 μM), a selective β2-AR antagonist 30 min prior to addition of LPS (1 μg/ml). After incubation for 8 h (HO-1, a) or 16 h (HMGB1, b), cells were harvested and subjected to Western blot analysis as described in Section 2. To confirm that HO-1 induction by isoproterenol is mediated by the b1-AR, different concentrations of dobutamine, a β1-selective AR agonist, and salbutamol, a β2-selective AR agonist, were administered for 8 h to RAW 264.7 cells (c). Cells were incubated with LPS (1 μg/ml) or LPS + ISO (50, 100, and 200 μM) for 8 h and HO-1 expression and activity were measured as described in Section 2. Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Data are given as mean SEM of three independent experiments.
 표
Inhibition of inflammatory cytokines is related to NF-kB activity. The involvement of NF-kB activity in the anti-inflammatory action of isoproterenol (ISO), phosphorylation of IkBa (a) and NF-kB luciferase activity (b) were measured. Cells were incubated after 1 h of incubation with LPS (1 mg/ml) in the absence or presence of different concentrations of ISO or ISO (200 μM) + ZnPPIX. Then Western blot analysis was performed using phosphor-IkBa and IkBa antibodies and NF-kB driven luciferase activity was measured in cells transfected with NF-kB as described in Section 2. Activity was presented as fold increase. Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Data are given as mean ±SEM of three independent experiments.
표
Inhibition of inflammatory cytokines is related to NF-kB activity. The involvement of NF-kB activity in the anti-inflammatory action of isoproterenol (ISO), phosphorylation of IkBa (a) and NF-kB luciferase activity (b) were measured. Cells were incubated after 1 h of incubation with LPS (1 mg/ml) in the absence or presence of different concentrations of ISO or ISO (200 μM) + ZnPPIX. Then Western blot analysis was performed using phosphor-IkBa and IkBa antibodies and NF-kB driven luciferase activity was measured in cells transfected with NF-kB as described in Section 2. Activity was presented as fold increase. Representative blot shown is from one of the three independent experiments with similar results. Data are given as mean ±SEM of three independent experiments.
 표
Isoproterenol improves survival rate and reduces serum HMGB1 in CLP-induced septic mice in an HO-1 sensitive manner. Health male Balb/c mice were injected with isoproterenol (ISO, 10 mg/kg, i.p. n = 14) 1 h before CLP (n = 14). Survival was monitored daily for 10 days (a). ISO significantly increased survival rate (p < 0.038). In separate experiments, mice were treated with saline (n = 2), CLP (n = 6), CLP + ISO (n = 6), CLP + ISO + ZnPPIX (n = 6) and 24 h later tissue (heart, lung, iver, and kidney) HO-1 protein levels and serum HMGB1 levels were measured by Western blot methods (b).
표
Isoproterenol improves survival rate and reduces serum HMGB1 in CLP-induced septic mice in an HO-1 sensitive manner. Health male Balb/c mice were injected with isoproterenol (ISO, 10 mg/kg, i.p. n = 14) 1 h before CLP (n = 14). Survival was monitored daily for 10 days (a). ISO significantly increased survival rate (p < 0.038). In separate experiments, mice were treated with saline (n = 2), CLP (n = 6), CLP + ISO (n = 6), CLP + ISO + ZnPPIX (n = 6) and 24 h later tissue (heart, lung, iver, and kidney) HO-1 protein levels and serum HMGB1 levels were measured by Western blot methods (b).
![Model for the anti-inflammatory action of isoproterenol through HO-1 induction in RAW 264.7 cells. Activation of the b1-AR by isoproterenol leads to an increase in cAMP, which then activates protein kinase A (PKA) (Sun et al. [17]), and also stimulates PI3K and p38MAPK activity. Activated PI3K and p38MAPK make it possible for Nrf2 to move to nucleus, where binding of Nrf2 to the ARE promoter site, leads to the upregulation of HO-1 gene expression. Therefore, the non-selective b-AR blocker, propranolol, or the β1-selective AR blocker, metoprolol inhibits but the β1-selective AR agonist dobutamine, activates HO-1 induction. Likewise, the PI3K inhibitor, LY294002, or p38MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, inhibits HO-1 induction. It is not yet known whether cAMP activates PI3K, p38 MAPK, or Nrf2 translocation to induce HO-1 in RAW 264.7 cells. However, H89, a PKA inhibitor blocked ISO-induced HO-1 upregulation. The increased HO-1 expression induced by ISO inhibits NF-kB activity, which can be activated by LPS through TLR4; thus production of pro-inflammatory cytokines dependent on NF-kB, such as TNF-α, IL- 1β, NO and HMGB1 can be reduced. It should be noted, however, that LPS also induces HO-1 by production of ROS via TLR4, but it also activates NF-kB which could tilt the balance toward to pro-inflammation. Model for the anti-inflammatory action of isoproterenol through HO-1 induction in RAW 264.7 cells. Activation of the b1-AR by isoproterenol leads to an increase in cAMP, which then activates protein kinase A (PKA) (Sun et al. [17]), and also stimulates PI3K and p38MAPK activity. Activated PI3K and p38MAPK make it possible for Nrf2 to move to nucleus, where binding of Nrf2 to the ARE promoter site, leads to the upregulation of HO-1 gene expression. Therefore, the non-selective b-AR blocker, propranolol, or the β1-selective AR blocker, metoprolol inhibits but the β1-selective AR agonist dobutamine, activates HO-1 induction. Likewise, the PI3K inhibitor, LY294002, or p38MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, inhibits HO-1 induction. It is not yet known whether cAMP activates PI3K, p38 MAPK, or Nrf2 translocation to induce HO-1 in RAW 264.7 cells. However, H89, a PKA inhibitor blocked ISO-induced HO-1 upregulation. The increased HO-1 expression induced by ISO inhibits NF-kB activity, which can be activated by LPS through TLR4; thus production of pro-inflammatory cytokines dependent on NF-kB, such as TNF-α, IL- 1β, NO and HMGB1 can be reduced. It should be noted, however, that LPS also induces HO-1 by production of ROS via TLR4, but it also activates NF-kB which could tilt the balance toward to pro-inflammation.](https://nrms.kisti.re.kr/bitextimages/TRKO201300034890/TRKO201300034890_39_image_24.jpg) 표
Model for the anti-inflammatory action of isoproterenol through HO-1 induction in RAW 264.7 cells. Activation of the b1-AR by isoproterenol leads to an increase in cAMP, which then activates protein kinase A (PKA) (Sun et al. [17]), and also stimulates PI3K and p38MAPK activity. Activated PI3K and p38MAPK make it possible for Nrf2 to move to nucleus, where binding of Nrf2 to the ARE promoter site, leads to the upregulation of HO-1 gene expression. Therefore, the non-selective b-AR blocker, propranolol, or the β1-selective AR blocker, metoprolol inhibits but the β1-selective AR agonist dobutamine, activates HO-1 induction. Likewise, the PI3K inhibitor, LY294002, or p38MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, inhibits HO-1 induction. It is not yet known whether cAMP activates PI3K, p38 MAPK, or Nrf2 translocation to induce HO-1 in RAW 264.7 cells. However, H89, a PKA inhibitor blocked ISO-induced HO-1 upregulation. The increased HO-1 expression induced by ISO inhibits NF-kB activity, which can be activated by LPS through TLR4; thus production of pro-inflammatory cytokines dependent on NF-kB, such as TNF-α, IL- 1β, NO and HMGB1 can be reduced. It should be noted, however, that LPS also induces HO-1 by production of ROS via TLR4, but it also activates NF-kB which could tilt the balance toward to pro-inflammation.
표
Model for the anti-inflammatory action of isoproterenol through HO-1 induction in RAW 264.7 cells. Activation of the b1-AR by isoproterenol leads to an increase in cAMP, which then activates protein kinase A (PKA) (Sun et al. [17]), and also stimulates PI3K and p38MAPK activity. Activated PI3K and p38MAPK make it possible for Nrf2 to move to nucleus, where binding of Nrf2 to the ARE promoter site, leads to the upregulation of HO-1 gene expression. Therefore, the non-selective b-AR blocker, propranolol, or the β1-selective AR blocker, metoprolol inhibits but the β1-selective AR agonist dobutamine, activates HO-1 induction. Likewise, the PI3K inhibitor, LY294002, or p38MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, inhibits HO-1 induction. It is not yet known whether cAMP activates PI3K, p38 MAPK, or Nrf2 translocation to induce HO-1 in RAW 264.7 cells. However, H89, a PKA inhibitor blocked ISO-induced HO-1 upregulation. The increased HO-1 expression induced by ISO inhibits NF-kB activity, which can be activated by LPS through TLR4; thus production of pro-inflammatory cytokines dependent on NF-kB, such as TNF-α, IL- 1β, NO and HMGB1 can be reduced. It should be noted, however, that LPS also induces HO-1 by production of ROS via TLR4, but it also activates NF-kB which could tilt the balance toward to pro-inflammation.
 표
Cell viability of higenamine in C6 cells. Cell proliferation was tested using MTT. a Under normoxia, C6 cells were treated with different concentrations of higenamine (lM), and incubated for 24 h in CO2 incubator. b Cells were moved to hypoxic chamber and cell proliferation was measured after incubation of indicated time. c The indicated dose of higenamine (lM) was treated and incubated for12 h under hypoxic chamber as described in ‘‘Materials and methods’’
표
Cell viability of higenamine in C6 cells. Cell proliferation was tested using MTT. a Under normoxia, C6 cells were treated with different concentrations of higenamine (lM), and incubated for 24 h in CO2 incubator. b Cells were moved to hypoxic chamber and cell proliferation was measured after incubation of indicated time. c The indicated dose of higenamine (lM) was treated and incubated for12 h under hypoxic chamber as described in ‘‘Materials and methods’’
 표
Higenamine increases HO-1 and it protects hypoxic injury in C6 cells. Higenamine was treated as indicated dose and incubated for 8 h under a normoxic or b hypoxic condition and after that protein was extracted for western analysis with anti-HO-1 antibody. c A fixed concentration of higenamine (50 μM) was treated in the presence or absence of ZnPPIX (1, 10, and 30 μM). After incubation for 12 h under hypoxic condition, cell proliferation was tested with MTT. d Cells were treated with a fixed concentration of higenamine (50 μM) in the presence or absence of increasing concentration of ZnPPIX (1,10,30 μM), which was incubated for 12 h under hypoxia and proteins were extracted for western analysis using anti-HO-1 antibody. Results are means ± SE of three to four independent experiments. *P<0.05 compared to control. §P <0.05 compared to higenamine.
표
Higenamine increases HO-1 and it protects hypoxic injury in C6 cells. Higenamine was treated as indicated dose and incubated for 8 h under a normoxic or b hypoxic condition and after that protein was extracted for western analysis with anti-HO-1 antibody. c A fixed concentration of higenamine (50 μM) was treated in the presence or absence of ZnPPIX (1, 10, and 30 μM). After incubation for 12 h under hypoxic condition, cell proliferation was tested with MTT. d Cells were treated with a fixed concentration of higenamine (50 μM) in the presence or absence of increasing concentration of ZnPPIX (1,10,30 μM), which was incubated for 12 h under hypoxia and proteins were extracted for western analysis using anti-HO-1 antibody. Results are means ± SE of three to four independent experiments. *P<0.05 compared to control. §P <0.05 compared to higenamine.
 표
Phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase/Akt pathway-dependent HO-1 induction by higenamine. Cells were treated with indicated concentration of higneamine and incubated for 15 min and phosphorylation of Akt (a) was examined by western analysis using anti-Akt or p-Akt antibodies. Loading control was shown as t-Akt level in each lane. A fixed concentration of higenamine (50 lM) was treated in the presence or absence of LY 294002 and the levels of p-Akt (b) and HO-1 (c) were analyzed using corresponding antibodies, respectively. Results are means ± SE of three independent experiments.
표
Phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase/Akt pathway-dependent HO-1 induction by higenamine. Cells were treated with indicated concentration of higneamine and incubated for 15 min and phosphorylation of Akt (a) was examined by western analysis using anti-Akt or p-Akt antibodies. Loading control was shown as t-Akt level in each lane. A fixed concentration of higenamine (50 lM) was treated in the presence or absence of LY 294002 and the levels of p-Akt (b) and HO-1 (c) were analyzed using corresponding antibodies, respectively. Results are means ± SE of three independent experiments.
 표
Higenamine translocates Nrf-2 and activates ARE element. Cells were treated with higenamine as indicated concentration and incubated for 1 h and proteins were extracted from cytosol fraction and nuclear fraction as described in the ‘‘Materials and methods’’ section. a Then western blot analysis was performed using anti-Nrf2 antibody. The internal loading control for cytosol and nuclear were used b-actin and PCNA, respectively. b Transfection efficiency of siNrf-2 RNA was checked by western analysis and the expression of HO-1 by higenamine was examined in scrambled siRNA- and Nrf2- siRNA-transfected cells by western analysis. c ARE activity was measured in cells transfected with luciferase reporter plasmid construct harboring the ARE promoter after 2 h treatment with higenamine (50 μM). Results are means ± SE of three independent experiments.
표
Higenamine translocates Nrf-2 and activates ARE element. Cells were treated with higenamine as indicated concentration and incubated for 1 h and proteins were extracted from cytosol fraction and nuclear fraction as described in the ‘‘Materials and methods’’ section. a Then western blot analysis was performed using anti-Nrf2 antibody. The internal loading control for cytosol and nuclear were used b-actin and PCNA, respectively. b Transfection efficiency of siNrf-2 RNA was checked by western analysis and the expression of HO-1 by higenamine was examined in scrambled siRNA- and Nrf2- siRNA-transfected cells by western analysis. c ARE activity was measured in cells transfected with luciferase reporter plasmid construct harboring the ARE promoter after 2 h treatment with higenamine (50 μM). Results are means ± SE of three independent experiments.
 표
Higenamine inhibits ROS-induced apoptosis with PI3K-sensitive manner. Cells were pretreated with higenamine (10 and 50 lM) for 8 h before exposure to GOX (20 mU/ml) and, 8 h later, a TUNEL assay was performed as described in ‘‘Materials and methods’’ section. In a, 1, control; 2, GOX 20 mU/ml; 3, GOX 20 mU/ml with higenamine 10 lM; 4, GOX 20 mU/ml with higenamine 50 μM; 5, GOX 20 mU/ml with higenamine 50 μM + LY 294002 (10 μM). b Apoptotic cell reactions were analyzed. Results are means ± SE of three independent experiments.
표
Higenamine inhibits ROS-induced apoptosis with PI3K-sensitive manner. Cells were pretreated with higenamine (10 and 50 lM) for 8 h before exposure to GOX (20 mU/ml) and, 8 h later, a TUNEL assay was performed as described in ‘‘Materials and methods’’ section. In a, 1, control; 2, GOX 20 mU/ml; 3, GOX 20 mU/ml with higenamine 10 lM; 4, GOX 20 mU/ml with higenamine 50 μM; 5, GOX 20 mU/ml with higenamine 50 μM + LY 294002 (10 μM). b Apoptotic cell reactions were analyzed. Results are means ± SE of three independent experiments.
 표
Higenamine reduces inflammation and infarct volume in MCAO rats due to HO-1 induction. Higenamine (10 mg/kg, i.p, n = 12) was administered in rats 24 h prior to MCA occlusion. In ZnPPIXtreated animal study, ZnPPIX (10 mg/kg, i.p, n = 10) was administered 1 h before higenamine treatment. After the treatment, TTC staining was performed as described in ‘'‘'Materials and methods’'’' section. A typical slide was shown in a, in which (1) sham (n = 6), (2) MCAO (n = 16), (3) MCAO + higenamine (n = 12, 10 mg/kg), and (4) MCAO + higenamine (10 mg/ kg) + ZnPPIX (10 mg/kg) (n = 10). b Percent change of infarct volume by each treatment in MCAO rats was shown. c MPO activity and d, e HMGB1 expression were measured from brain tissues taken out 24 h after the MCA occluded rats, respectively. Results are means ± SE of four independent experiments.
표
Higenamine reduces inflammation and infarct volume in MCAO rats due to HO-1 induction. Higenamine (10 mg/kg, i.p, n = 12) was administered in rats 24 h prior to MCA occlusion. In ZnPPIXtreated animal study, ZnPPIX (10 mg/kg, i.p, n = 10) was administered 1 h before higenamine treatment. After the treatment, TTC staining was performed as described in ‘'‘'Materials and methods’'’' section. A typical slide was shown in a, in which (1) sham (n = 6), (2) MCAO (n = 16), (3) MCAO + higenamine (n = 12, 10 mg/kg), and (4) MCAO + higenamine (10 mg/ kg) + ZnPPIX (10 mg/kg) (n = 10). b Percent change of infarct volume by each treatment in MCAO rats was shown. c MPO activity and d, e HMGB1 expression were measured from brain tissues taken out 24 h after the MCA occluded rats, respectively. Results are means ± SE of four independent experiments.
 표
Higenamine reduces rHMGB1-induced apoptosis in C6 cells. Cells were treated with rHMGB1 (1, 2, and 4 lg/ml) and incubated for 4 h (for Bax, Bcl-2) and 6 h (for cleaved caspase-3), respectively. The extracted proteins were subjected to western blot analysis with corresponding antibodies (a). Different concentrations of higenmine were treated 1 h prior to application of rHMGB1 (2 lg/ml) in C6 cells. After indicated time of incubation, cells were harvested and western blot analysis was performed as described above (b). Results are means ± SE of three independent experiments.
표
Higenamine reduces rHMGB1-induced apoptosis in C6 cells. Cells were treated with rHMGB1 (1, 2, and 4 lg/ml) and incubated for 4 h (for Bax, Bcl-2) and 6 h (for cleaved caspase-3), respectively. The extracted proteins were subjected to western blot analysis with corresponding antibodies (a). Different concentrations of higenmine were treated 1 h prior to application of rHMGB1 (2 lg/ml) in C6 cells. After indicated time of incubation, cells were harvested and western blot analysis was performed as described above (b). Results are means ± SE of three independent experiments.
 표
Signals involved in preferential inhibition of VCAM-1 over ICAM-1 expression in response to TNF-in cultured endothelial cells and inhibition of phosphorylation of Akt and p38 MAP kinases by compound C. Cells were pretreated signal inhibitors 30 min prior to TNF-and incubated for 6 h to see which signals are involved in inhibition of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 (A). Cells were treated with indicated concentrations of compound C 30min prior to TNF-and then incubated for 30 min (B). Proteins were extracted and subjected to western blot analysis using corresponding antibodies. Data represent one of typical blots with similar results of triplicates. The intensity ratio was depicted as Arabic numbers on the top of each band when histogram was not presented.
표
Signals involved in preferential inhibition of VCAM-1 over ICAM-1 expression in response to TNF-in cultured endothelial cells and inhibition of phosphorylation of Akt and p38 MAP kinases by compound C. Cells were pretreated signal inhibitors 30 min prior to TNF-and incubated for 6 h to see which signals are involved in inhibition of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 (A). Cells were treated with indicated concentrations of compound C 30min prior to TNF-and then incubated for 30 min (B). Proteins were extracted and subjected to western blot analysis using corresponding antibodies. Data represent one of typical blots with similar results of triplicates. The intensity ratio was depicted as Arabic numbers on the top of each band when histogram was not presented.
 표
Effect of compound C treatment on VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression in the aorta of LPS-treated rats. Compound C (0.2 mg/kg) was administrated (i.v.) 30 min before LPS (10 mg/kg) injection. Six hours later rats were anesthetized and thoracic aortas were collected for western blotting and immunohistochemistry, respectively. Relative protein levels (ICAM-1 or VCAM-1/-actin) in sham (n = 3), LPS (n = 3), and LPS with compound C (LPS + C.C., n = 3) were shown in A. Representative images of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 immunoreactivity (B) for aortic sections of control (CTL), LPS, and LPS with compound C (LPS + C.C.). Of note, the increased VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 immunoreactivity in the aortic endothelium of LPS-treated rats were decreased by compound C.
표
Effect of compound C treatment on VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression in the aorta of LPS-treated rats. Compound C (0.2 mg/kg) was administrated (i.v.) 30 min before LPS (10 mg/kg) injection. Six hours later rats were anesthetized and thoracic aortas were collected for western blotting and immunohistochemistry, respectively. Relative protein levels (ICAM-1 or VCAM-1/-actin) in sham (n = 3), LPS (n = 3), and LPS with compound C (LPS + C.C., n = 3) were shown in A. Representative images of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 immunoreactivity (B) for aortic sections of control (CTL), LPS, and LPS with compound C (LPS + C.C.). Of note, the increased VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 immunoreactivity in the aortic endothelium of LPS-treated rats were decreased by compound C.
 표
Pharmacological inhibition of AMPK reversed metformin-mediated anti-inflammatory effect in LPS-activated macrophages. Cells were treated with metformin (10 mM) in the presence or absence of compound C (comp C; 12 μM) for 1 h. Then cells were stimulated with LPS (1 μg·mL−1) for the next 24 h. After incubation, cells were lysed and subjected to Western blot (A); culture medium samples were extracted for HMGB1 detection by HMGB1 analysis (B) as described in Methods. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
표
Pharmacological inhibition of AMPK reversed metformin-mediated anti-inflammatory effect in LPS-activated macrophages. Cells were treated with metformin (10 mM) in the presence or absence of compound C (comp C; 12 μM) for 1 h. Then cells were stimulated with LPS (1 μg·mL−1) for the next 24 h. After incubation, cells were lysed and subjected to Western blot (A); culture medium samples were extracted for HMGB1 detection by HMGB1 analysis (B) as described in Methods. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
 표
Involvement of VEGF in CKD712-mediated cell migration and its effect on the migration of HDFs. Confluent cells were treated with mitomycin C (8 mg·mL-1) for 2 h. After washing with PBS, the cells were wounded by scraping, and fresh medium was added. (A,B) Cells were treated with CKD712 at the indicated concentrations for 12 or 24 h and then cell migration was assessed. (C, D) Cell migration was also assessed in HDF cells stimulated with recombinant VEGF (10 ng·mL-1) or with CKD712 (10 mM) in presence or absence of anti-VEGF antibody (100 ng·mL-1). Representative photographs from three independent experiments are shown with similar results.
표
Involvement of VEGF in CKD712-mediated cell migration and its effect on the migration of HDFs. Confluent cells were treated with mitomycin C (8 mg·mL-1) for 2 h. After washing with PBS, the cells were wounded by scraping, and fresh medium was added. (A,B) Cells were treated with CKD712 at the indicated concentrations for 12 or 24 h and then cell migration was assessed. (C, D) Cell migration was also assessed in HDF cells stimulated with recombinant VEGF (10 ng·mL-1) or with CKD712 (10 mM) in presence or absence of anti-VEGF antibody (100 ng·mL-1). Representative photographs from three independent experiments are shown with similar results.
 표
Dependence on HO-1/AMPK signalling of the production of VEGF by CKD712 and the effect of SnPPIX and compound C on the cell migration induced by CKD712. The cells were pretreated with various inhibitors and then treated with CKD712. After incubation, samples of the culture media were collected and subjected to ELISA for VEGF (A– C). Confluent cells were treated with mitomycin C (8 mg·mL-1) for 2 h. After washing with PBS, the cells were wounded by scraping, and fresh medium was added. The cells were incubated with CKD712 (10 mM) in the presence or absence of SnPPIX (25 mM) (D) or compound C (10 mM) (E) for 12 h. The data are presented as the mean SD of three independent experiments.
표
Dependence on HO-1/AMPK signalling of the production of VEGF by CKD712 and the effect of SnPPIX and compound C on the cell migration induced by CKD712. The cells were pretreated with various inhibitors and then treated with CKD712. After incubation, samples of the culture media were collected and subjected to ELISA for VEGF (A– C). Confluent cells were treated with mitomycin C (8 mg·mL-1) for 2 h. After washing with PBS, the cells were wounded by scraping, and fresh medium was added. The cells were incubated with CKD712 (10 mM) in the presence or absence of SnPPIX (25 mM) (D) or compound C (10 mM) (E) for 12 h. The data are presented as the mean SD of three independent experiments.
 표
Effect of CKD712 on the HO-1/AMPK protein levels in HDFs. The cells were treated with CKD712 (1, 3, 5 and 10 mM) for 12 h (A) or incubated with CKD712 (10 mM) for different time periods (1, 4, 8, 12 and 24 h) (B). After incubation, the cells were harvested for Western blotting to detect HO-1, p-AMPK and p-ACC. The cells were treated with CKD712 (10 mM), with or without SnPPIX (25 mM) or compound C (10 mM) and incubated for 12 h (C) or 24 h (D). After incubation, the cells were lysed and analysed by Western blotting. The bands of the blots are representative of three independent experiments, with similar results. The data are presented as the mean SD of three independent experiments.
표
Effect of CKD712 on the HO-1/AMPK protein levels in HDFs. The cells were treated with CKD712 (1, 3, 5 and 10 mM) for 12 h (A) or incubated with CKD712 (10 mM) for different time periods (1, 4, 8, 12 and 24 h) (B). After incubation, the cells were harvested for Western blotting to detect HO-1, p-AMPK and p-ACC. The cells were treated with CKD712 (10 mM), with or without SnPPIX (25 mM) or compound C (10 mM) and incubated for 12 h (C) or 24 h (D). After incubation, the cells were lysed and analysed by Western blotting. The bands of the blots are representative of three independent experiments, with similar results. The data are presented as the mean SD of three independent experiments.
 표
Effect of siRNA transfection on the CKD712-mediated expression of HO-1 and AMPK and VEGF production in HDFs. After transfection with HO-1- or AMPK-siRNA, the cells were treated with CKD712 (10 mM) for 24 h (A) or 12 h (B). Then cells were harvested and analysed by Western blotting for HO-1 (A, E) or AMPK (B, D). The cells were treated with CKD712 (10 mM) for 12 h, and culture medium samples were collected and subjected to ELISA for VEGF (C, F). The data are presented as the mean SD of three independent experiments.
표
Effect of siRNA transfection on the CKD712-mediated expression of HO-1 and AMPK and VEGF production in HDFs. After transfection with HO-1- or AMPK-siRNA, the cells were treated with CKD712 (10 mM) for 24 h (A) or 12 h (B). Then cells were harvested and analysed by Western blotting for HO-1 (A, E) or AMPK (B, D). The cells were treated with CKD712 (10 mM) for 12 h, and culture medium samples were collected and subjected to ELISA for VEGF (C, F). The data are presented as the mean SD of three independent experiments.
 표
Effect of siRNA transfection on the expression of HO-1, AMPK and VEGF production induced by haemin in HDFs. After transfection with the corresponding siRNA, the cells were treated with haemin (15 mM) for 24 h (A) or 12 h (B). The cells were harvested and analysed by Western blotting for HO-1 (A, E) or for AMPK (B, D). The cells were treated with haemin (15 mM) for 12 h, and culture medium samples were collected and subjected to ELISA for VEGF (C, F). The data are presented as the mean SD of three independent experiments.
표
Effect of siRNA transfection on the expression of HO-1, AMPK and VEGF production induced by haemin in HDFs. After transfection with the corresponding siRNA, the cells were treated with haemin (15 mM) for 24 h (A) or 12 h (B). The cells were harvested and analysed by Western blotting for HO-1 (A, E) or for AMPK (B, D). The cells were treated with haemin (15 mM) for 12 h, and culture medium samples were collected and subjected to ELISA for VEGF (C, F). The data are presented as the mean SD of three independent experiments.
 표
The wound closure induced by CKD712 is antagonized by SnPPIX in an animal wound model. Two full-thickness 5-mm punch wounds were inflicted on the dorsal surface of each mouse, and the mice were injected (i.p) with saline, CKD712 (5 mg·kg-1), CKD712 (10 mg·kg-1) or CKD712 (10 mg·kg-1 plus SnPPIX (10 mg·kg-1). The time course of the changes in the wound size with different treatments in mice (A). Images of a representative mouse from each group taken on post-injury days 0, 3, 5, 8 and 12 are shown (B). The wound sizes at the indicated time points in topically treated mice.
표
The wound closure induced by CKD712 is antagonized by SnPPIX in an animal wound model. Two full-thickness 5-mm punch wounds were inflicted on the dorsal surface of each mouse, and the mice were injected (i.p) with saline, CKD712 (5 mg·kg-1), CKD712 (10 mg·kg-1) or CKD712 (10 mg·kg-1 plus SnPPIX (10 mg·kg-1). The time course of the changes in the wound size with different treatments in mice (A). Images of a representative mouse from each group taken on post-injury days 0, 3, 5, 8 and 12 are shown (B). The wound sizes at the indicated time points in topically treated mice.
해당 보고서가 속한 카테고리에서 활용도가 높은 상위 5개 콘텐츠를 보여줍니다.
더보기 버튼을 클릭하시면 더 많은 관련자료를 살펴볼 수 있습니다.
| 과제명(ProjectTitle) : | - |
|---|---|
| 연구책임자(Manager) : | - |
| 과제기간(DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 총연구비 (DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 키워드(keyword) : | - |
| 과제수행기간(LeadAgency) : | - |
| 연구목표(Goal) : | - |
| 연구내용(Abstract) : | - |
| 기대효과(Effect) : | - |
Copyright KISTI. All Rights Reserved.

※ AI-Helper는 부적절한 답변을 할 수 있습니다.