최소 단어 이상 선택하여야 합니다.
최대 10 단어까지만 선택 가능합니다.
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
NTIS 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
DataON 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Edison 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Kafe 바로가기
| 주관연구기관 | 국립농업과학원 National Institute of Agricultural Sciences |
|---|---|
| 보고서유형 | 최종보고서 |
| 발행국가 | 대한민국 |
| 언어 | 한국어 |
| 발행년월 | 2015-02 |
| 주관부처 | 농촌진흥청 Rural Development Administration(RDA) |
| 등록번호 | TRKO201500010657 |
| DB 구축일자 | 2015-07-11 |
Ⅳ. 연구개발결과
○ 1 세부과제명 : 지방 생산관련 전사조절인자 발굴 및 이용
- 종자의 지방함량을 조절하는 신규한 MYB96 전사조절인자를 발견하였다. MYB96은 지방합성에 결정적 역할을 하는 효소 유전자로 알려진 DGAT1과 PDAT1를 직접 조절 하였다.
- 종자 지방산 조성에 관여하는 DPBF2을 발견하였다. DPBF2가 돌연변이되면 종자 지방에 존재하는 지방산중 18:2가 증가하고 18:3이 감소 하였다. 또한 DPBF2를 과발현 시켰을 때 이와 반대로 18:3이 증가하고 18:2가 감소하였다. 이결과는
Ⅳ. 연구개발결과
○ 1 세부과제명 : 지방 생산관련 전사조절인자 발굴 및 이용
- 종자의 지방함량을 조절하는 신규한 MYB96 전사조절인자를 발견하였다. MYB96은 지방합성에 결정적 역할을 하는 효소 유전자로 알려진 DGAT1과 PDAT1를 직접 조절 하였다.
- 종자 지방산 조성에 관여하는 DPBF2을 발견하였다. DPBF2가 돌연변이되면 종자 지방에 존재하는 지방산중 18:2가 증가하고 18:3이 감소 하였다. 또한 DPBF2를 과발현 시켰을 때 이와 반대로 18:3이 증가하고 18:2가 감소하였다. 이결과는 DPBF2의 과발현에 의한 오메가3 불포화 지방산 생산 증진에 활용가능하다.
○ 1 협동과제명 : 지방 수송체 발굴을 통한 식물 지방 생산 증진 연구
- 피루브산 수송체인 BASS2를 종자 특이적으로 과발현시 종자 크기가 유의하게 증가한 것을 확인하였다. BASS2 과발현 종자의 총 지방산과 중성 지방 TAG와 C20:1 지방산의 양이 적게는 10%에서 많게는 32%까지 증가하였다.
- 대량 수송체 돌연변이 분석에 의한 지방 생산 증진에 과여하는 ABCG5를 발견하였다.
○ 2 협동과제명 : 식물 생산성 향상을 위한 탄수화물 대사 재설계 연구
- 엽록체 내 광호흡 bypass 구축을 위하여 mGDH 유전자와 남세균 HDH-ODC 유전자가 도입된 형질전환 식물체를 제작하였다. 남세균 이산화탄소 농축 시스템 유전자인 SbtA와 BicA를 도입하여 형질전환 식물체 제작하였다. 탄수화물 대사효율 향상을 위하여 FTR, APS 유전자가 도입된 형질전환 식물체를 제작 후을 단백질 수준에서 발현을 확인하였다.
- 다양한 성장 조건에서 형질전환 식물체의 표현형 및 대사 산물을 분석한 결과 mGDH, BicA 및 APS 형질전환체의 성장이 향상됨을 알 수 있었다.
○ 3 협동과제명 : 벼 자당 적재 재설계 및 조절 연구
- 벼 자당 적재 과정의 핵심 당수송체(SWEET) 유전자를 분리하고 벼의 기관 및 발달단계에서 유전자 발현을 비교하였다.
- 벼의 당 및 자당 수송체 유전자의 돌연변이 분리 및 특성을 분석하였다. 추가적으로 자당수송체(SUT)의 다중 돌연변이체를 제작 후 이중, 삼중, 사중 돌연변이체를 분리하여 표현형 및 당 대사체 분석을 통해 각 자당 수송체의 역할을 비교, 분석하였다.
- 벼 자당적재 경로의 최적화 시스템 모델링를 하였다. 체관부 특이적인 옥수수 SUT1(ZmSUT1) 발현 형질전환체인 HD3a-ZmSUT1 형질전환체와 OsSUT2의 과다발현 형질전환체의 순종 교배라인을 확보 후, 잎에서 작동하는 당 수송체인 OsSWEET 과다발현 형질전환체와 교배하여 해당 유전자의 삼중 교배라인을 확보하였다.
○ 4협동과제명 : NAM3 전사인자 과발현 벼와 2차 대사산물 생산과정의 네트워크 연구
- OsMDB1 계열 전사인자에 대해 마이크로어레이와 GST 항체를 이용한 CHiP-Seq 실험를 수행하여 OsMDB1이 직접 조절하는 목표유전자를 찾는 일을 수행하였다. 또한 단백질 결합칩을 이용하여 OsMBD1 전사인자의 binding motif인 ACCTACCT 를 찾았으며 2kb promoter 부위에서 이 motif 조사를 하였다.
- OsMDB1 과발현체가 야생현(WT) 보다 벼의 간장 길이가 55~70% 감소 한 것을 확인하였다.
○ 5협동과제명 : SnoRNA-target 유전체 발굴과 병저항성 네트워크 탐색
- snoR146 및 snoR108-target 유전자 및 snor146 mutant에서 10배 이상 down- 또는 up-regulation되는 유전자에 대한 돌연변이체를 대량 확보 하고 PstDC3000을 접종하고 병 저항성 유무를 확인하였다.
- BBX27은 snor146 mutant내에서 그 transcript가 intron 2내에 criptic 5’splice site가 존재하여 alternative splicing variant가 만들어지고 결과적으로 B-box domain만을 포함하는 단백질이 WT에 비하여 상대적으로 많이 형성됨되는데 bbx27 돌연변이체에서 PstDC3000에 대한 병 저항성이 30배 이상 감소하며, Yeast two-hybrid screening을 통해 BBX27ΔC과 결합하는 47개의 후보 단백질을 발굴함. 이들 중 ABA receptor의 하나인 RCAR6를 발견하였다.
-BBX27은 RCAR6의 파트너인 PP2CA와 결합하였고 실제로 bbx27 mutant는 ABA-sensitive 및 drought-resistant phenotype을 나타냄. 따라서 BBX27은 RCAR6-PP2CA 결합체를 modulation 함으로써 ABA signaling에 관여하고, 이 signaling은 병 저항성과 관계되는 것으로 확인하였다.
Vegetable oil is a nutrient source of essential fatty acid for human and an the highest energy source with carbon polymer for industrial uses. Because structure of fatty acids from vegetable oils of plants is similar with carbon chain of petroleum raw materials, the more than 10% of fatty acids prod
Vegetable oil is a nutrient source of essential fatty acid for human and an the highest energy source with carbon polymer for industrial uses. Because structure of fatty acids from vegetable oils of plants is similar with carbon chain of petroleum raw materials, the more than 10% of fatty acids produced from plants are used as industrial raw materials included with biofuels. Vegetable oils are mainly triglycerides (TAG: triacylglycerol), which is synthesized and accumulated in the seeds of plants. In 2011, the world consumption of vegetable oil was 1.5 hundred million tons that is $180 billion worth (World Vegetable Oil Consumption, 2011). Increasing demand of vegetable oil for consumption is expected to require more than double production of vegetable oil in 2040 (World Agriculture: Towards 2015/2030). As an important value of the two aspects of food and industrial raw materials for vegetable oils are lead to research in plant lipid metabolism in seed. In order to satisfy the growing demand for vegetable oils, increase of arable land for crop production is required. However, limitation of the arable land suggests that the development of alternative biotechnology for increasing vegetable oil production. In this study, we have identified and characterized the transcription factors to regulate vegetable oil production and fatty acid modification during seed development. MYB96 is a positive regulator for control of amount of vegetable oil. DPBF2 is a regulator synthesis of unsaturated fatty acids in seed development. PEI1 is a negative regulator for seed development.
Plant lipids such as seed storage lipid, surface lipid and lipid-derived intermediates are important for plant growth and development. Moreover, plant seed oil is very important nutrients and source materials for biodiesel, and thus its demand has been rapidly increased last few decades. To increase lipid production in plants, we studied several transporters that are related to lipid and its precursor. Here, (1) we report that BASS2 can increase the seed oil content by about 10~30%. BASS2 gene encodes a pyruvate transporter, and pyruvate is a precursor of fatty acid synthesis. We generated plants overexpressing BASS2 seed-specifically and found that contents of total lipids and C20:1 fatty acids (TAG indicator) from those seeds were increased upto 30%. (2) In the screen of knockout mutants of ABCA and ABCG subfamily members of ABC transporters, we identified ABCG5, of which function is critical for early seedling establishment. In the absence of sucrose, abcg5 mutant was defective in early seedling growth similar to mutants of storage lipids. Photosynthetic activity and contents of sucrose and starch was decreased in abcg5 cotyledon compared to those of WT. Moreover, development of shoot apical meristem and chloroplast was defective. ABCG5 protein was localized at the plasma membrane and expressed in cotyledon of seedling. (3) In penetration assay with tetrazolium salt, we isolated several abcg mutants that exhibited increased permeablity of seed coat materials. In summary, we proved that seed-specific overexpression of BASS2 increases seed oil production and identified several transporter that are likely involved lipid transport.
To support a rapidly increasing world population that is expected to reach eight billion by 2025, increased food production and improved crop plant productivity are crucial. In higher plants, green leaves function as phototropic source tissues to synthesize sugars that are distributed to non-phototropic sink tissues. Thus, the photosynthetic carbon metabolism in source leaves is thought to be a determinant of plant source capacity and productivity. In this project, we performed the engineering of carbohydrate metabolism in plant leaves to increase plant productivity. Target genes selected for remodeling of carbohydrate metabolism were mitochondrial glycolate dehydrogenase (mGDH), ferredoxinthoredoxin reductase (FTR), ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase small subunit (APS), cyanobacterial hydroxyacid dehydrogenase-oxalate decarboxylase (HDH-ODC), SbtA and BicA. For generating transgenic plants, we constructed overexpression vectors containing target genes and introduced into Arabidopsis via Agrobacterium mediated transformation. The expression of target genes in transgenic plants was confirmed by Western blot analysis. Growth phenotypes of transgenic plants overexpressing HDH-ODC, mGDH, FTR, SbtA, BicA and APS were analyzed under different growth conditions. mGDH transgenic plants showed increased growth compared to the wild type plants under various growth conditions. BicA plants showed slightly increased growth under high light conditions compared to the wild type. Several APS transgenic lines showd the enhanced growth and starch contents under the normal growth conditions.
Carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, that are synthesized in source organs are transported to sink organs to support growth and development. Phloem loading of sucrose is a crucial step that drives long-distance transport by elevating hydrostatic pressure in the phloem. Three phloem loading strategies have been identified, two active mechanisms, apoplastic loading via sucrose transporters and symplastic polymer trapping, and one passive mechanism. The first two active loading mechanisms require metabolic energy, carbohydrate is loaded into the phloem against a concentration gradient. The passive process, diffusion, involves equilibration of sucrose and other metabolites between cells through plasmodesmata. Many higher plant species including Arabidopsis utilize the active loading mechanisms to increase carbohydrate in the phloem to higher concentrations than that in mesophyll cells. In contrast, recent data revealed that a large number of plants, especially woody species, load sucrose passively by maintaining a high concentration in mesophyll cells. However, it still remains to determine how the worldwide important cereal crop, rice, loads sucrose into the phloem in source organs. Based on the literature and our results, we propose a potential strategy of phloem loading in rice. Elucidation of the phloem loading mechanism should improve our understanding of rice development and apply its manipulation towards the increase of crop productivity.
R2R3 MYB transcription factor, OsMDB1, was chosed as a representative result of the project. OsMDB1 was identified from microarray data by monitoring the expression profile of rice seed development. OsMDB1 was significantly expressed in early stage of panicles compared with those in other tissues. R2R3 MYB transcription factors, the largest group of plant MYB factors, are involved in the control of plant specific processes such as secondary metabolism, cellular morphogenesis, and responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. OsMDB1 belongs to subgroup 13 and 16. To examine the role of OsMDB1 in rice, we constructed the plasmids for rice transformation. In the constructs, OsMDB1 was expressed under the control of the promoter of rice PGD for a constitutive expression. The height of transgenic rice was reduced on average to 30% of the wild type height. To identify genes with altered expression levels in OsMDB1, a microarray analysis was performed to compare the expression profiles between the transgenic (#7 and #23) and WT plants from flag leaf, panicle, and sheath at the just before heading stage (Figure 4). The profiling was conducted on a 135 K Rice Genome Microarray (GreenGene Biotech, www.ggbio.com), covering 31439 rice genes. In the sheath, a total of 1,853 and 877 genes were up- and down-regulated regulated more than 2-fold, respectively, in the transgenic compared to WT plants. But only 33 and 57 genes were up-regulated more than 2-fold in the flag leaf and panicle, respectively, and 31 and 185 genes were down-regulated more than 2-fold. These results suggest that OsMDB1 may also be associated with the regulation of plant height. The physiological role of the products of those genes that were significantly induced or repressed in the transgenic plants compared to WT was visualized with the software MapMan. We found a highly significant up-regulation of genes involved in the DNA synthesis/chromatin structure (bin 28.1, P value <0.05) and the cell wall/degradation/pectate lyases and polygalacturonases (bin 10.6.3, P value <0.05). Gene repression was found for secondary metabolism (bin 16, P value <0.01) and misc.cytochrome P450 (bin 26.1, P value <0.05). Short rice might be benefit from lodging due to strong winds.
The snor146 mutant shows decreased disease resistance with reduced gene expression of immune receptors including pattern recognition receptors and R genes. This research was aiming to search for function of snoR146-target mRNA disease resistance network. Out of 29 snoR146-target genes at the pre-mRNA splicing level, we selected BBX27 for further analysis that contains cryptic 5´ splice site in intron 2 resulting in production of the truncated protein including only B-box domain. Th bbx27 insertional mutant shows 30 fold reduced resistance to PstDC3000 with decreased production of salicylic acid. The nuclear protein BBX27 specifically interacts with RCAR6 and PP2CA, an ABA receptor and an A-type protein phosphatase whose interaction initiates downstream ABA signaling pathways. bbx27 mutant shows enhanced ABA sensitivity and drought resistance phenotype, suggesting that BBX27 may inhibit ABA signaling by modulating RCAR6-PP2CA complex, which results in increase in disease resistance.
 표
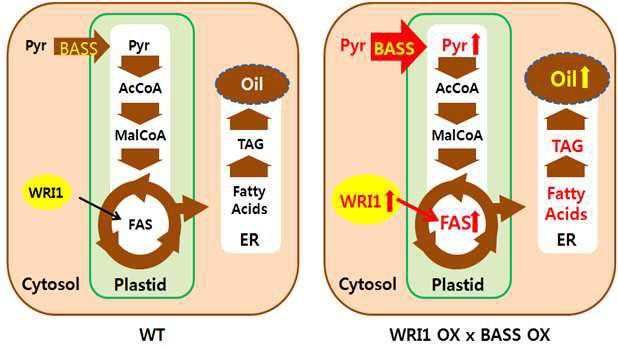
애기장대에 존재하는 피루브산 수송체 BASS를 종자에 특이적으로 과발현시키면, 지질 생산의 원료인 피루브산 공급이 증가하여 종자지방의 함량이 높아질 가능성이 있음. 특히 생합성 효소 발현을 조절하는 WRI1과 중복 과발현시키면 (WRI1 OX x BASS OX) 시너지 효과를 보일 가능성 있음. BASS는 지방산의 전구체인 피루브산을 색소체로 수송하여 acetyl coA (AcCoA) 생성을 가능하게 함. AcCoA는 지방산이 되고, 지방산은 다시 oil로 합성 될 수 있음. FAS: 지방산 합성 효소군, Pyr: 피루브산, WT: 야생종.
표
애기장대에 존재하는 피루브산 수송체 BASS를 종자에 특이적으로 과발현시키면, 지질 생산의 원료인 피루브산 공급이 증가하여 종자지방의 함량이 높아질 가능성이 있음. 특히 생합성 효소 발현을 조절하는 WRI1과 중복 과발현시키면 (WRI1 OX x BASS OX) 시너지 효과를 보일 가능성 있음. BASS는 지방산의 전구체인 피루브산을 색소체로 수송하여 acetyl coA (AcCoA) 생성을 가능하게 함. AcCoA는 지방산이 되고, 지방산은 다시 oil로 합성 될 수 있음. FAS: 지방산 합성 효소군, Pyr: 피루브산, WT: 야생종.
 표
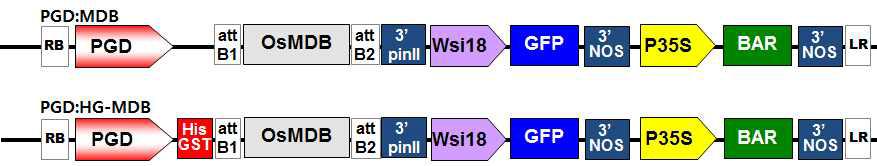
벼 형질전환체 발현벡터 모식도. OsMDB, Rice MYB DNA-binding domain protein; PGD pro, rice 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase promoter; 3'PinII, potato proteinase inhibitor II terminator; Wsi, LEA_4, Late embryogenesis abundant promoter; GFP, green fluorescent protein; 35S pro, cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter; Bar, phosphinothricin acetyltransferase; Noster, nopaline synthesis terminator.
표
벼 형질전환체 발현벡터 모식도. OsMDB, Rice MYB DNA-binding domain protein; PGD pro, rice 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase promoter; 3'PinII, potato proteinase inhibitor II terminator; Wsi, LEA_4, Late embryogenesis abundant promoter; GFP, green fluorescent protein; 35S pro, cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter; Bar, phosphinothricin acetyltransferase; Noster, nopaline synthesis terminator.
 표
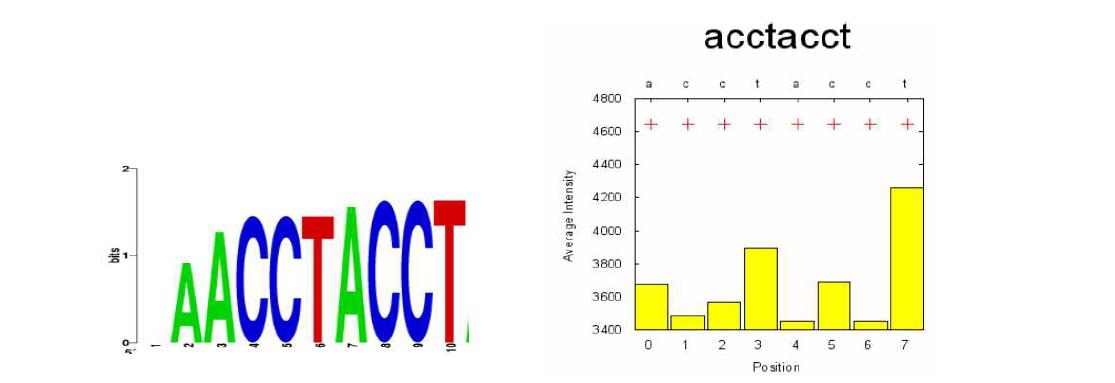
Identification of binding motifs of recombinant OsMDB1 from E.coli according to the Q9-PBM. The consensus binding sequences according to the binding intensities that were observed on the Q9 protein-binding 마이크로어레이. The overall consensus binding motif was obtained by multiple alignments of the significant binding sequences with ClustalW and visualized with the SeqLogo program. The effects of mutations on the binding intensities of the consensus binding motif. The average binding intensities (+) of probes containing ACCTACCT was plotted. The yellow boxes represent the average binding intensities of probes substituted at each position with other bases.
표
Identification of binding motifs of recombinant OsMDB1 from E.coli according to the Q9-PBM. The consensus binding sequences according to the binding intensities that were observed on the Q9 protein-binding 마이크로어레이. The overall consensus binding motif was obtained by multiple alignments of the significant binding sequences with ClustalW and visualized with the SeqLogo program. The effects of mutations on the binding intensities of the consensus binding motif. The average binding intensities (+) of probes containing ACCTACCT was plotted. The yellow boxes represent the average binding intensities of probes substituted at each position with other bases.
 표
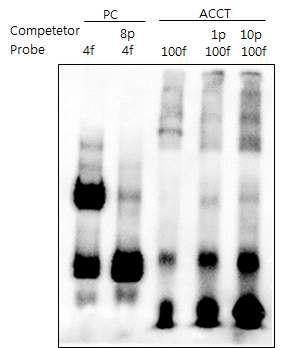
Identification of OsMDB1 binding motif in vitro. EMSA-based competition analysis of OsMDB1. Sequences of oligonucleotides used as probes and competitors are depicted. Wild type (probe), 21-bp sequence containing the ACCTACCT motif. Lane 1, positive control; Lane 2, positive control with competitor; lane 3, The OsMDB1-DsRed fusion protein was used for the EMSA with 21-bp sequences; lane 4 and 5; EMSA with competitors in 10-or 100-fold molar excess.
표
Identification of OsMDB1 binding motif in vitro. EMSA-based competition analysis of OsMDB1. Sequences of oligonucleotides used as probes and competitors are depicted. Wild type (probe), 21-bp sequence containing the ACCTACCT motif. Lane 1, positive control; Lane 2, positive control with competitor; lane 3, The OsMDB1-DsRed fusion protein was used for the EMSA with 21-bp sequences; lane 4 and 5; EMSA with competitors in 10-or 100-fold molar excess.
 표
애기장대에 존재하는 피루브산 수송체 BASS를 종자에 특이적으로 과발현시키면, 지질 생산의 원료인 피루브산 공급이 증가하여 종자지방의 함량이 높아질 가능성이 있음. 특히 생합성 효소 발현을 조절하는 WRI1과 중복 과발현시키면 (WRI1 OX x BASS OX) 시너지 효과를 보일 가능성 있음. BASS는 지방산의 전구체인 피루브산을 색소체로 수송하여 acetyl coA (AcCoA) 생성을 가능하게 함. AcCoA는 지방산이 되고, 지방산은 다시 oil로 합성 될 수 있음. FAS: 지방산 합성 효소군, Pyr: 피루브산, WT: 야생종.
표
애기장대에 존재하는 피루브산 수송체 BASS를 종자에 특이적으로 과발현시키면, 지질 생산의 원료인 피루브산 공급이 증가하여 종자지방의 함량이 높아질 가능성이 있음. 특히 생합성 효소 발현을 조절하는 WRI1과 중복 과발현시키면 (WRI1 OX x BASS OX) 시너지 효과를 보일 가능성 있음. BASS는 지방산의 전구체인 피루브산을 색소체로 수송하여 acetyl coA (AcCoA) 생성을 가능하게 함. AcCoA는 지방산이 되고, 지방산은 다시 oil로 합성 될 수 있음. FAS: 지방산 합성 효소군, Pyr: 피루브산, WT: 야생종.
 표
벼 형질전환체 발현벡터 모식도. OsMDB, Rice MYB DNA-binding domain protein; PGD pro, rice 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase promoter; 3'PinII, potato proteinase inhibitor II terminator; Wsi, LEA_4, Late embryogenesis abundant promoter; GFP, green fluorescent protein; 35S pro, cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter; Bar, phosphinothricin acetyltransferase; Noster, nopaline synthesis terminator.
표
벼 형질전환체 발현벡터 모식도. OsMDB, Rice MYB DNA-binding domain protein; PGD pro, rice 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase promoter; 3'PinII, potato proteinase inhibitor II terminator; Wsi, LEA_4, Late embryogenesis abundant promoter; GFP, green fluorescent protein; 35S pro, cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter; Bar, phosphinothricin acetyltransferase; Noster, nopaline synthesis terminator.
 표
Identification of binding motifs of recombinant OsMDB1 from E.coli according to the Q9-PBM. The consensus binding sequences according to the binding intensities that were observed on the Q9 protein-binding 마이크로어레이. The overall consensus binding motif was obtained by multiple alignments of the significant binding sequences with ClustalW and visualized with the SeqLogo program. The effects of mutations on the binding intensities of the consensus binding motif. The average binding intensities (+) of probes containing ACCTACCT was plotted. The yellow boxes represent the average binding intensities of probes substituted at each position with other bases.
표
Identification of binding motifs of recombinant OsMDB1 from E.coli according to the Q9-PBM. The consensus binding sequences according to the binding intensities that were observed on the Q9 protein-binding 마이크로어레이. The overall consensus binding motif was obtained by multiple alignments of the significant binding sequences with ClustalW and visualized with the SeqLogo program. The effects of mutations on the binding intensities of the consensus binding motif. The average binding intensities (+) of probes containing ACCTACCT was plotted. The yellow boxes represent the average binding intensities of probes substituted at each position with other bases.
 표
Identification of OsMDB1 binding motif in vitro. EMSA-based competition analysis of OsMDB1. Sequences of oligonucleotides used as probes and competitors are depicted. Wild type (probe), 21-bp sequence containing the ACCTACCT motif. Lane 1, positive control; Lane 2, positive control with competitor; lane 3, The OsMDB1-DsRed fusion protein was used for the EMSA with 21-bp sequences; lane 4 and 5; EMSA with competitors in 10-or 100-fold molar excess.
표
Identification of OsMDB1 binding motif in vitro. EMSA-based competition analysis of OsMDB1. Sequences of oligonucleotides used as probes and competitors are depicted. Wild type (probe), 21-bp sequence containing the ACCTACCT motif. Lane 1, positive control; Lane 2, positive control with competitor; lane 3, The OsMDB1-DsRed fusion protein was used for the EMSA with 21-bp sequences; lane 4 and 5; EMSA with competitors in 10-or 100-fold molar excess.
| 과제명(ProjectTitle) : | - |
|---|---|
| 연구책임자(Manager) : | - |
| 과제기간(DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 총연구비 (DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 키워드(keyword) : | - |
| 과제수행기간(LeadAgency) : | - |
| 연구목표(Goal) : | - |
| 연구내용(Abstract) : | - |
| 기대효과(Effect) : | - |
Copyright KISTI. All Rights Reserved.

※ AI-Helper는 부적절한 답변을 할 수 있습니다.