최소 단어 이상 선택하여야 합니다.
최대 10 단어까지만 선택 가능합니다.
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
NTIS 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
DataON 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Edison 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Kafe 바로가기
| 주관연구기관 | (주)젠닥스 |
|---|---|
| 보고서유형 | 최종보고서 |
| 발행국가 | 대한민국 |
| 언어 | 한국어 |
| 발행년월 | 2013-09 |
| 과제시작연도 | 2011 |
| 주관부처 | 농림축산식품부 Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs(MAFRA) |
| 등록번호 | TRKO201400000150 |
| 과제고유번호 | 1545002666 |
| 사업명 | 생명산업기술개발 |
| DB 구축일자 | 2014-05-07 |
○ 연구결과
• 비식용 및 비사료용 섬유질계 형질전환 에너지 작물 개발
- 국내에서 자생하는 비식용 및 비사료용 섬유질계 에너지 작물 선별 후, 참억새 8종, 물억새 7종, Miscanthus giganteus, 갈대 4종의 유전자원 수집 및 유지‧관리
- 참억새와 갈대의 미성숙 화기 이용 캘러스 유도와 식물체 재생을 위한 최적 시스템 개발
- 참억새는 95.8%의 캘러스 유도율과 58.3%의 신초 재생 효율을, 갈대는 99.9%의 캘러스 유도율과 100%의 식물체 재생 효율 확보
- 참억새와 갈대의 Ag
○ 연구결과
• 비식용 및 비사료용 섬유질계 형질전환 에너지 작물 개발
- 국내에서 자생하는 비식용 및 비사료용 섬유질계 에너지 작물 선별 후, 참억새 8종, 물억새 7종, Miscanthus giganteus, 갈대 4종의 유전자원 수집 및 유지‧관리
- 참억새와 갈대의 미성숙 화기 이용 캘러스 유도와 식물체 재생을 위한 최적 시스템 개발
- 참억새는 95.8%의 캘러스 유도율과 58.3%의 신초 재생 효율을, 갈대는 99.9%의 캘러스 유도율과 100%의 식물체 재생 효율 확보
- 참억새와 갈대의 Agrobacterium 매개 형질전환을 통하여 참억새 9계통, 갈대 8계통의 gfp 도입형질전환체를 생산 및 PCR과 GFP 발현 검정을 통한 안정적인 형질전환 확인
- 건조스트레스 유도성 프로모터에 의해 발현이 조절되는 gfp 유전자 도입 형질전환 식물체 개발
- 갈대의 rab21-gfp construct 도입 형질전환 식물체 40계통 생산 및 PCR과 건조처리 후 GFP 발현 검정으로 36계통에서 유전자의 안정적인 도입과 발현을 확인
- Cellulose 자가분해 유전자 도입 형질전환 및 선발 과정을 통하여 참억새와 갈대에서 형질전환 캘러스 확보 후, 형질전환 식물체 재생을 진행 중. 형질전환 식물체 확보 후, 특성 검정을 실시할 예정
• 셀룰로즈 분해능이 도입된 바이오에너지 모델작물 개발
- 벼로부터 건조유도성 프로모터 7종, 조직특이성 프로모터 6종, 항시발현 프로모터 3종 및 건조 유도성 유전자 3종을 분리
- 효모와 박테리아 유래의 셀룰라제 유전자 cel2 (exo-glucanase), cel4 (endo-glucanase), β-glu (β-glucosidase)를 단일 혹은 복합으로 벼 게놈에 도입한 형질전환체 및 프로모터::gfp 형질전환체 36종을 생산
- 벼에서 셀룰라제 유전자를 발현하기 위한 프로모터로는 항시발현용 프로모터 옥수수 유래 maize Ubiqutine와 벼로부터 분리한 972, 996 건조스트레스 유도성 프로모터를 사용하였으며 발현된 셀룰라제를 Apoplast로 집적
- 셀룰라제 유전자가 항시 발현되는 벼 중 일부는 성장 속도가 대조구에 비해 느렸으나, 유도성 프로모터로 발현시킨 경우는 정상적임. 형질전환 벼의 세포벽의 구조가 치밀하지 못하였으며, 당화율이 대조구 대비 두 배 이상 증가됨.
- 형질전환 벼를 곰팡이와 함께 고상발효를 한 경우 셀룰라제 생산율이 대조구에 비해 2배 이상 효율을 보임을 확인. 따라서 셀룰라제 유전자를 벼에서 발현하므로써 당화에 사용되는 효소 사용량을 감소하고 동시에 전처리 공정이 용이한 바이오매스로서의 활용 가능성을 확인함
• 바이오매스 당화효소 저가생산기술 개발
- 신규 셀룰레이즈 유전자 뿐 아니라 논문 분석과 data base 검색을 통하여 재조합 발현을 위한 후보 유전자를 선별
- 각각의 균주에서 만든 cDNA library로 부터 직접 셀룰레이즈 유전자를 증폭하거나 합성하는 방법으로 exo type 분해 효소 유전자 12 종, endo type 분해 효소 유전자 11종, 헤미셀루로즈 분해 효소 유전자 5종, β-glucosidase 유전자 5종, 기타효소 2종을 확보하여 directed - 효모를 이용한 효소의 재조합 대량생산을 위해 효모 TFP 기술을 이용하여 각 셀룰라제에 대한 고분비 생산균주(1~5 g/L 수준)를 선별함
- 선별된 생산균주를 5L 발효조를 이용하여 유가식 발효 배양을 셀룰레이즈를 최적 생산할 수 있는 기술을 개발하고 효모에서 생산된 4가지 핵심효소인 exoglucanase (CBH1,2), endoglucanase (EGL) 및 β-glucosidase (BGL)를 이용하여 다수의 KRIBB Cellulase Cocktail(KCC)을 제작하여 다양한 기질(Filter paper, Avicel, EFB, 볏짚)을 활용하여 효소 활성을 비교하고 바이오매스별 최적의 효소칵테일을 확인
- 전처리된 볏짚, 억새를 사용하여 재조합 균주를 사용한 생물통합에탄올 발효(consolidated bioprocessing)에서 외부 효소의 사용량을 50% 이상 절감하여 바이오에탄올의 생산 가능성이 확인
IV. Results of the research and development
1. Transformation system development for non-food and non-feed bioenegy crops Genetic resources of bioenergy crops, including Miscanthu sinensis, M. sacchariflorus,M. × giganteu and Phragmites communis were collected from native habitats except M. gigan
IV. Results of the research and development
1. Transformation system development for non-food and non-feed bioenegy crops Genetic resources of bioenergy crops, including Miscanthu sinensis, M. sacchariflorus,M. × giganteu and Phragmites communis were collected from native habitats except M. giganteus provided by Dongbu Farm Hannong Co. Ltd. and totally 20 genotypes of bioenergy crops were maintained in Sangmyung Univ.
Plant regeneration system were developed through the optimization of medium composition and plant growth regulator concentration using mature seeds of M. sinensis and P. communis. Also highly efficient plant regeneration system using immature inflorescences of M. sinensis and P. communis were established; 95.8% callus induction rate and 58.3 shoot induction rate in M. sinensis and 99.9% callus induction rate and 100% plant regeneration rate in P. communis were obtained.
Through Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, 9 transgenic lines in M. sinensis and 8 transgenic lines in P. communis were produced and the stable incorporation of trans gene were identified with PCR and GFP expression analysis.
Then, 40 lines of transgenic plants containing gfp gene under the control of drought stress inducible rab21 promoter were developed and the stable gene insertion and expression were confirmed using PCR and GFP fluorescence analysis.
Transgenic plant tissues containing four cellulose autolysis gene constructs with cellulase or beta-glucanase gene were obtained through Agrobacterium-mediated transformation in M. sinensis and P. communis. The transgenic tissues were used for the production of transgenic plants. After transgenic plant production, the molecular and physiochemical analysis will be conducted.
2. Development and commercialization of model plants expressing cellulases Seven drought inducible promoters, 6 tissue-specific promoters and 3 drought inducible genes were isolated from rice. A total of 36 transgenic rice plants that expressed cel2 (exo-glucanase), cel4 (endo-glucanase), β-glu (β-glucosidase) originated from yeast and bacteria in a single or multiple and promoter::gfp were constructed. The expression of cellulases in rice was driven by either the maize Ubiquitine contitutive promoter or drought inducible promoters, 972 and 996, with the signal peptide for targeting the cellulase to the apoplastic compartment for storage.
Some transgenic nce retardation, however its storage. plants contitutively expressmg cellulase exhibited growth phenotype was eliminated by use of inducible promoters. Transgenic plants showed an altered cell wall structure. A saccharification rate of transgenic rice straw was two fold higher than that of control plant. Solid state fermentation of transgenic nce straw with fungus resulted in two fold higher in cellulase production compared with that of control plant. These results indicated that transgenic plants expressing cellulase could be useful for bioethanol production by reducing the costs of cellulase as well as pretretment process.
3. Cost-effective production technology of biomass saccharification enzymes For the production of recombinant cellulase using yeast Saccharomyces cereVlsrae, numerous fungal cellulase genes were cloned from several novel and known fungal species. Cellulase genes were tried to improve for their activity and stability by using directed evolution and for different glycosylation patterns by using site directed mutagenesis, respectively. Improved cellulase genes were tried to overexpressed m yeast using translation fusion partner (TFP) technology for the hypersecretion of each cellulase. Finally, several yeast strains secreting different cellulases about 1-5 grams per liter were obtained. Fed batch fermentation of mixed yeasts producing different cellulases could provide recombinant cellulase cocktail showing hydrolyzing activity for various cellulosic substrate including alkali-pretreated rice straw. Demonstration of consolidated bioprocessing of cellulosic biomass to bioethanol using recombinant yeast mix developed in this research paves the way for low cost process for the production of cellulosic bioethanol.
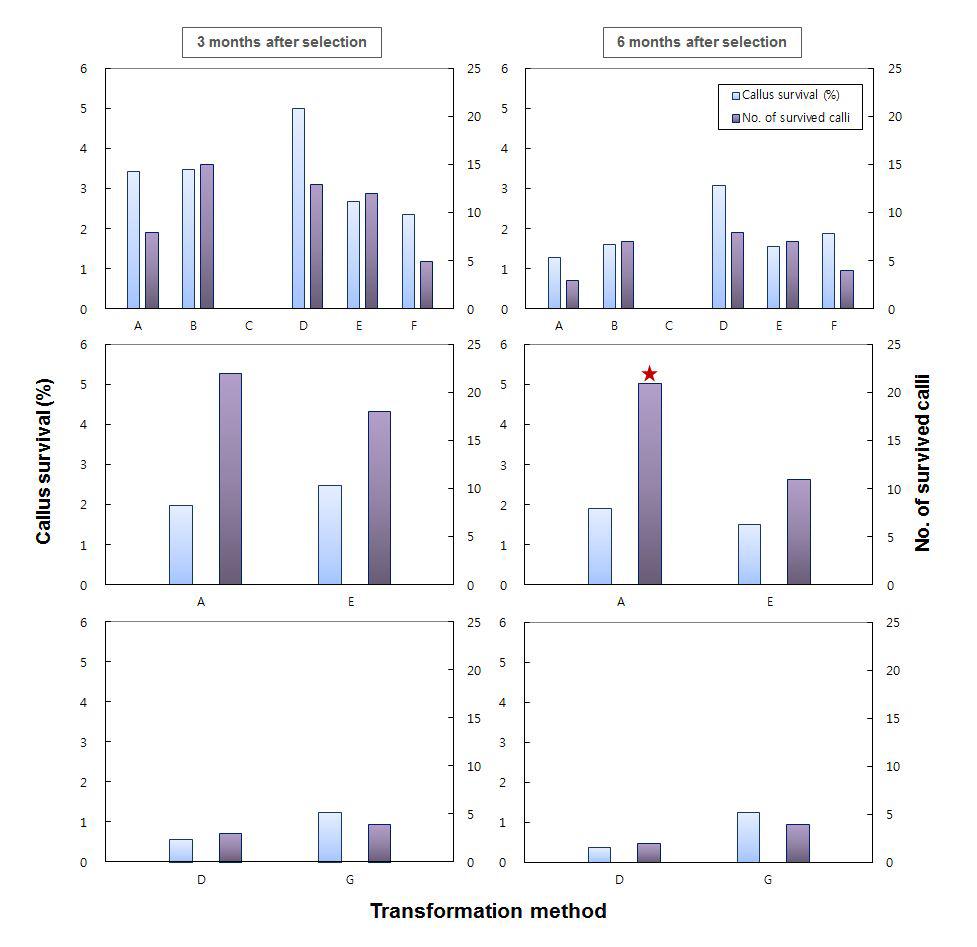 표
참억새 (Miscanthussinensis)의 미성숙 화기를 이용한 Agrobacterium 매개 형질전환 효율에 미치는 유전형과 Agrobacterium strain& vector,공조배양 기간 및 공조배양시 AgNO3 첨가의 효과 (상:Joy World,중 :정석항공관,하:제주다원, A:EHA105/pCAMBIA1301,공조배양 4일,B:EHA105/pCAMBIA1301,공조배양 4 일+AgNO3 5 mg/L, C: EHA105/pCAMBIA1301, 공조배양 7일, D: EHA105/pCAMBIA1301, 공조배양 7일+AgNO3 5 mg/L, E: EHA105/pCAMBIA1302,공조배양 4일,F:EHA105/pCAMBIA1302,공조배양 7,G: EHA105/pCAMBIA1302,공조배양 7일+AgNO3 5 mg/L,★:형질전환 신초 재생 처리구)
표
참억새 (Miscanthussinensis)의 미성숙 화기를 이용한 Agrobacterium 매개 형질전환 효율에 미치는 유전형과 Agrobacterium strain& vector,공조배양 기간 및 공조배양시 AgNO3 첨가의 효과 (상:Joy World,중 :정석항공관,하:제주다원, A:EHA105/pCAMBIA1301,공조배양 4일,B:EHA105/pCAMBIA1301,공조배양 4 일+AgNO3 5 mg/L, C: EHA105/pCAMBIA1301, 공조배양 7일, D: EHA105/pCAMBIA1301, 공조배양 7일+AgNO3 5 mg/L, E: EHA105/pCAMBIA1302,공조배양 4일,F:EHA105/pCAMBIA1302,공조배양 7,G: EHA105/pCAMBIA1302,공조배양 7일+AgNO3 5 mg/L,★:형질전환 신초 재생 처리구)
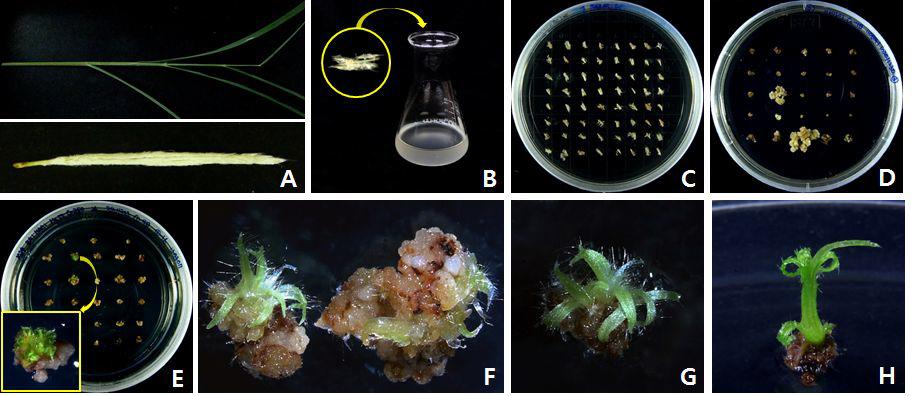 표
참억새 (Miscanthussinensis)의 미성숙 화기 이용 Agrobacterium 매개 형질전환을 통한 신초 재생 (A:식물재료,B:식물재료 절단 후 Agrobacterium 접종,C: acetosyringone100μM 첨가 배지에서 공조배양 후 cefotaxime500mg/L가 첨가 된 캘러스 유도배지에서 resting,D:hygromycin50mg/L가 첨가된 선발배지에서 형질전환 캘러스 유도,E:hygromycin 50mg/L가 첨가된 재생배지에서 형질전환 신초 유도,F~H:선발배지에서 재생된 형질전환 신초 계통.
표
참억새 (Miscanthussinensis)의 미성숙 화기 이용 Agrobacterium 매개 형질전환을 통한 신초 재생 (A:식물재료,B:식물재료 절단 후 Agrobacterium 접종,C: acetosyringone100μM 첨가 배지에서 공조배양 후 cefotaxime500mg/L가 첨가 된 캘러스 유도배지에서 resting,D:hygromycin50mg/L가 첨가된 선발배지에서 형질전환 캘러스 유도,E:hygromycin 50mg/L가 첨가된 재생배지에서 형질전환 신초 유도,F~H:선발배지에서 재생된 형질전환 신초 계통.
 표
참억새 (Miscanthussinensis)의 미성숙 화기를 이용한 Agrobacterium 매개 형질전환 효율에 미치는 유전형과 Agrobacterium strain& vector,공조배양 기간 및 공조배양시 AgNO3 첨가의 효과 (상:Joy World,중 :정석항공관,하:제주다원, A:EHA105/pCAMBIA1301,공조배양 4일,B:EHA105/pCAMBIA1301,공조배양 4 일+AgNO3 5 mg/L, C: EHA105/pCAMBIA1301, 공조배양 7일, D: EHA105/pCAMBIA1301, 공조배양 7일+AgNO3 5 mg/L, E: EHA105/pCAMBIA1302,공조배양 4일,F:EHA105/pCAMBIA1302,공조배양 7,G: EHA105/pCAMBIA1302,공조배양 7일+AgNO3 5 mg/L,★:형질전환 신초 재생 처리구)
표
참억새 (Miscanthussinensis)의 미성숙 화기를 이용한 Agrobacterium 매개 형질전환 효율에 미치는 유전형과 Agrobacterium strain& vector,공조배양 기간 및 공조배양시 AgNO3 첨가의 효과 (상:Joy World,중 :정석항공관,하:제주다원, A:EHA105/pCAMBIA1301,공조배양 4일,B:EHA105/pCAMBIA1301,공조배양 4 일+AgNO3 5 mg/L, C: EHA105/pCAMBIA1301, 공조배양 7일, D: EHA105/pCAMBIA1301, 공조배양 7일+AgNO3 5 mg/L, E: EHA105/pCAMBIA1302,공조배양 4일,F:EHA105/pCAMBIA1302,공조배양 7,G: EHA105/pCAMBIA1302,공조배양 7일+AgNO3 5 mg/L,★:형질전환 신초 재생 처리구)
 표
참억새 (Miscanthussinensis)의 미성숙 화기 이용 Agrobacterium 매개 형질전환을 통한 신초 재생 (A:식물재료,B:식물재료 절단 후 Agrobacterium 접종,C: acetosyringone100μM 첨가 배지에서 공조배양 후 cefotaxime500mg/L가 첨가 된 캘러스 유도배지에서 resting,D:hygromycin50mg/L가 첨가된 선발배지에서 형질전환 캘러스 유도,E:hygromycin 50mg/L가 첨가된 재생배지에서 형질전환 신초 유도,F~H:선발배지에서 재생된 형질전환 신초 계통.
표
참억새 (Miscanthussinensis)의 미성숙 화기 이용 Agrobacterium 매개 형질전환을 통한 신초 재생 (A:식물재료,B:식물재료 절단 후 Agrobacterium 접종,C: acetosyringone100μM 첨가 배지에서 공조배양 후 cefotaxime500mg/L가 첨가 된 캘러스 유도배지에서 resting,D:hygromycin50mg/L가 첨가된 선발배지에서 형질전환 캘러스 유도,E:hygromycin 50mg/L가 첨가된 재생배지에서 형질전환 신초 유도,F~H:선발배지에서 재생된 형질전환 신초 계통.
| 과제명(ProjectTitle) : | - |
|---|---|
| 연구책임자(Manager) : | - |
| 과제기간(DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 총연구비 (DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 키워드(keyword) : | - |
| 과제수행기간(LeadAgency) : | - |
| 연구목표(Goal) : | - |
| 연구내용(Abstract) : | - |
| 기대효과(Effect) : | - |
Copyright KISTI. All Rights Reserved.

※ AI-Helper는 부적절한 답변을 할 수 있습니다.