최소 단어 이상 선택하여야 합니다.
최대 10 단어까지만 선택 가능합니다.
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
NTIS 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
DataON 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Edison 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Kafe 바로가기
| 주관연구기관 | 국립기상연구소 |
|---|---|
| 연구책임자 | 한상옥 |
| 참여연구자 | 이용희 , 김연희 , 김동훈 , 임은순 , 하종철 , 이희춘 , 김기훈 , 신승숙 , 이승재 , 임나영 , 인소라 , 정선희 , 성지혜 , 김현욱 , 정승필 |
| 보고서유형 | 최종보고서 |
| 발행국가 | 대한민국 |
| 언어 | 한국어 |
| 발행년월 | 2011-12 |
| 과제시작연도 | 2011 |
| 주관부처 | 기상청 |
| 사업 관리 기관 | 국립기상연구소 |
| 등록번호 | TRKO201400002024 |
| 과제고유번호 | 1365001280 |
| 사업명 | 재해기상연구센터설립운영 |
| DB 구축일자 | 2014-04-19 |
Ⅳ. 연구 내용 및 결과
우리나라는 최근 30년간 연평균 약 14건의 기상재해가 발생하는데, 사상자가 연평균 약 158명, 피해액은 연평균 약 8,000억 원이다. 이러한 기상재해의 피해를 최소화하기 위해서 기상재해 현상 및 피해현황에 대한 인식과 정확한 조사를 통한 철저한 방재 대책이 필요한 실정이다. 따라서, 최근 발생한 재해 현황과 그에 따른 피해 정도를 조사·분석하여 재해 우심지역을 알아봄으로써 방재 대책 마련을 위한 기초 자료를 마련하고자 한다.
매년 발생되는 소방방재청의 재해연보 자료를 이용하여 1993년부터
Ⅳ. 연구 내용 및 결과
우리나라는 최근 30년간 연평균 약 14건의 기상재해가 발생하는데, 사상자가 연평균 약 158명, 피해액은 연평균 약 8,000억 원이다. 이러한 기상재해의 피해를 최소화하기 위해서 기상재해 현상 및 피해현황에 대한 인식과 정확한 조사를 통한 철저한 방재 대책이 필요한 실정이다. 따라서, 최근 발생한 재해 현황과 그에 따른 피해 정도를 조사·분석하여 재해 우심지역을 알아봄으로써 방재 대책 마련을 위한 기초 자료를 마련하고자 한다.
매년 발생되는 소방방재청의 재해연보 자료를 이용하여 1993년부터 2010년까지의 기상재해의 피해현황을 정리한 결과 원인별로는 태풍과 호우가 다른 원인에 비해 가장 피해액이 컸고, 지역별로는 강원도와 경상남도가 가장 크고, 사망자수는 경기도와 강원도가 가장 크게 나타났다. 특히 강원도는 면적당 피해액이 크고 인구당 피해액이 가장 높게 나타나 재해 취약지구로 분류할 수 있다.
또, 최근 2010년부터 2011년까지 발생한 기상재해 중에서 그 피해액을 100억원 이상을 기준으로 14사례에 대해 그에 따른 피해현황과 기상개황, 관련 보도 자료를 정리한 결과 2011년 7월 26일에서 29일 발생했던 우면산 산사태로 인한 피해액이 약 8,062억 원으로 가장 크고, 이것은 호우로 인한 피해액으로는 1993년 이래 19년 동안 가장 큰 피해액으로 기록되었다.
재해기상정보와 지리정보의 융합시스템 개발을 위한 기반연구로서 재해기상정보를 지리정보시스템(GIS)을 활용하여 가시화하는 기술을 개발하였다. 그 시작으로, ArcGIS를 활용하여 2005년부터 2010년까지의 대설로 인한 피해액과 대설량, 특보발표빈도의 지역적 분포를 가시화할 수 있는 대설재해지도를 제작하였다. 이렇게 제작된 대설재해지도는 Google Maps API(Application Programming Interface)를 활용하여 Google Maps에 중첩되게 표출함으로써, 일반인들이 재해정보를 습득하기가용이할 뿐만 아니라 지역별 재해정보를 통하여 재해에 대한 주민들의 예방효과 또한 기대할 수 있다. 대설재해지도에 의하면, 대설로 인한 피해액이 많은 지역은 전라북도 지역이지만 적설량이 많고 대설 주의보와 경보의 빈도가 높은 곳은 강원도 지역으로 나타났다. 이것은 ‘눈이 많이 내리는 지역이 반드시 대설에 취약한 지역이라고 정의할 수 없다는 것을 의미한다.
재해지도에서 보이는 공간적인 지역분포의 특성을 통계적으로 군집·분류하기 위해 자기조직화지도(Self-Organizing Map, SOM)와 K-Means 기법이 보편적으로 적용되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 관측 강수 자료를 이용하여 서로 다른 두 통계적 기법에서 유도되는 동일강우지역에 대한 최적군집개수를 비교·분석하였다. 본 연구를 위해 사용된 자료는 1980년부터 2010년까지의 61개 지상관측지점과 1997년부터 2010년까지의 343개 AWS 관측지점에서의 일강수 자료이다. 61개 관측지점자료를 사용하였을 경우, SOM과 K-Means 기법 모두 9개의 군집이 설정되어 최적군집개수는 동일하게 제시되었으나 그 분포에서는 차이를 나타내고 있다. AWS 자료를 포함한 404개의 관측지점자료를 이용하였을 경우는 SOM은 17개, K-Means는 19개의 서로 다른 최적군집개수가 제시되고 있으며, 공간적인 분포에 있어서도 매우 복잡한 양상을 보이고 있어 일관성있는 결론을 도출하기 어렵다. 본 연구는 우리나라 강수의 공간분포 특성을 반영하는 군집의 개수를 객관적인 통계기법을 적용하여 설정하였다는 것에 의의가 있다.
지구온난화에 의한 전지구 기온상승은 북극진동이나 엘니뇨, 라니냐와 같은 자연 변동성의 변화폭을 증가시켜 극단적인 이상기후가 많이 발생할 수 있는 조건을 형성하기 때문에 재해기상의 발생 가능성을 높게 만든다. 특히, 수문학적 순환을 강화 시켜 대표적인 재해기상인 홍수와 가뭄의 발생 가능성을 동시에 증가시킬 수 있다는 연구결과들이 발표된 바 있다. 한반도도 지속적인 기온상승과 더불어 강수의 형태 및 강도가 변화하고 있다고 보고되고 있으며, 이는 미래에 더욱 가속화될 것이라는 전망 결과들이 제시되고 있다.
이에 본 연구에서는 IPCC(Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 정부간 기후변화협의회) 4차 보고서에 참여한 ECHAM5 전지구기후모델로부터 생산된 A1B 시나리오 자료를 RegCM3 지역기후모델을 이용하여 역학적으로 상세화 하고, 홍수와 가뭄에 초점을 맞추어 수문기후학적인 측면에서 온실기체 증가가 미래 어떠한 변화를 초래할 가능성이 있는지 살펴보고자 하였다.
RegCM3 이중둥지격자시스템으로부터 한반도 지역에 20km로 상세화된 3시간 강수자료를 이용하여 극한강수의 강도 및 빈도를 동시에 살펴보기 위한 수문분석에 많이 적용되고 있는 IDF(Intensity-Duration-Frequency) 분석을 수행하였다. 아래의 3시간 강수량과 24시간 강수량에 대한 IDF 곡선에서는 x축이 return period, y축이 단위시간에 대한 precipitation intensity를 나타낸다. 여기서, return period가 100년이라는 것은 통계적으로 100년에 한번 나타날 수 있는 강수를 의미하는 것이다. 기준시나리오를 관측과 비교하면, 모델은 관측에 비하여 강수강도를 과다모사되는 경향을 보인다. 기준시나리오 대비 미래의 변화 경향을 보면, 지구온난화가 진행될수록 (21세기 후반으로 갈수록) return period의 감소가 뚜렷이 나타나고 있다.
2071-2100년도는 연평균 강수량의 감소가 전망되었음에도 불구하고, 극한 강수의 return period는 감소하여, 기준시나리오에서는 100년에 한번 나타날 수 있는 극한 강수가 21세기 후반에는 50년도 안되어서 나타날 가능성을 제시하고 있다. 특히 3시간 강수량에서 100년 return period에 대한 급격한 강수강도의 증가를 보이는데, 이는 홍수의 위험성이 훨씬 커짐을 의미한다. 또한 총강수량의 감소에도 불구하고 극한강수가 증가한다는 것은 약한 강수 빈도의 감소를 의미하므로 가뭄의 발생가능성이 증가를 동시에 내포하는 결과라고 해석할 수 있다.
홍수의 미래 발생가능성이 증가할 것으로 전망됨에 따라 과거 관측자료를 이용한 집중호우의 시·공간적인 특성을 살펴보는 것은 의미있는 일이다. 본 연구에서는 1973년부터 2010년까지의 ASOS(61지점)와 1998년부터 2010년까지의 AWS(352지점)의 강수 자료를 분석하여 일․시간 강수량의 장기간 경향성과 지역적 분포의 특성을 분석하였다. 또한, 일․시간 강수량의 지역별 상관도를 분석하여 국지적인 호우의 계절별·지역별 특성을 파악하였으며, IDF 곡선으로부터 극한강수의 발생빈도의 특성을 정리하였다.
1998년부터 2010년까지 13년 동안의 자료를 이용하여 각 지점 사이의 거리에 따른 강수량의 상관도를 분석한 결과 시간 강수의 e-folding 그래프를 보면, 5월이 거리에 따른 상관도의 감소가 가장 작으며, 7월과 8월이 거리에 따른 상관도의 감소가 가장 크게 나타났다. 월별 e-folding distance(표 1)는 5월이 약 162 km로 가장 크게 나타났으며, 7월이 약 55 km 이었으며, 8월이 약 45km로 가장 작게 나타났다.
이것은 5월의 강수는 거리에 따른 상관도가 높은 편으로 종관적인 시스템에서 내리는 강수인 것을 의미하며, 7월과 8월에 발생하는 강수는 지역적으로 변화가 많은 국지적인 강수인 것을 의미한다. 7월과 8월의 e-folding distance의 공간분포를 보면, 우리나라의 서쪽에서 특히 작은 값이 나타났다. 이는 7월과 8월에 발생하는 호우는 우리나라 동쪽보다 서쪽지역에서 지역적인 편차가 더 큰 것을 의미한다.
1973년부터 2010년까지의 강수 자료를 이용하여 일 강수의 IDF 곡선의 분석 결과 약 360 mm/day 강수는 100년에 한번 내릴 수 있는 강수로 분석되었으며, 시간
강수의 IDF 곡선 분석 결과에서는 약 80 mm/h의 강수는 100년에 한번 나타날 수 있는 강수로 분석되었다. 각 지점별로 100년에 한번 내릴 수 있는 일 강수의 공간 분포에서는 강원영동과 남해안 일부 지역에서 강도가 강하게 나타났으며, 경상북도 지역과 전라북도 지역에서 강도가 약하게 나타났다. 그리고 시간 강수의 경우, 충청남도 지역과 전라남도 지역에서 강도가 강하게 나타난 반면, 강원산간 지역과 경상남도 지역, 전라북도 일부 지역에서는 강도가 약하게 나타났다.
영동지역은 산 경사가 급한 태백산맥이 위치하고 동해가 인접하기 때문에 지형과 해양의 결합 효과로 인해 대설과 풍하측 강풍과 같은 악기상이 빈번하게 발생한다. 최근 2011년 2월 11일에서 14일까지 영동지역의 해안을 따라 극값을 경신하는 대설이 발생하여 교통, 농·어업에 막대한 손해를 입은 바 있다. 이에 본 연구에서는, 고해상도 WRF(Weather Research and Forecasting)를 이용하여 2011년 2월 11일부터 14일까지의 대설사례를 모의하고, 여러 가지 민감도실험을 통해 그 발생 메커니즘을 규명하고자 하였다.
모델의 정량적인 성능 검증을 위해 많은 강설량이 나타났던 동해와 대관령 지점에 대해 3시간 누적 강수량을 관측값과 비교한 것을 보면, 모델은 관측에서 보이는 강수의 시간적 분포를 관측과 유사하게 모사하고 있으며, 두 시계열에 대한 상관계수는 동해 0.72, 대관령 0.70로 높게 나타났다. 강수밴드가 11일 야간과 12일 새벽 동해안 해안에서 극값을 보이고 12일 아침 대관령 내륙으로 이동하는 경향성도 비교적 현실적으로 모의하고 있다. 규준실험의 현실적인 모사결과 기반 하에, 동해안 대설을 유발하는 주요인자로 제시되는 지형과 해수면 온도의 영향을 파악하기 위해 지형을 완화시키고 해수면온도를 높게 설정하는 민감도 실험을 수행하였다. 지형의 굴곡이나 경사를 감소시킨 민감도 실험의 경우, 해안 지역에서 산맥의 경사면을 따르는 연직적인 상승운동이나 하강운동이 현저히 줄어들었으며, 총강수량은 큰 차이를 보이지 않았으나 그 공간적 분포가 규준실험과 다르게 나타났다. 해수면 온도를 증가시킨 민감도 실험의 경우는 규준실험보다 해양에서 연직 운동이 활발해지면서 더 많은 열과 수분을 공급하여 강설을 강화시키는 것으로 나타났다.
기존의 집중호우나 대설의 예측이 초단기(2-6시간) 규모로 다루어져 그 대비와 방재정책 수립에 어려움이 있었다. 이에, 하루(24시간) 정도 후 특정지역(약 80kmx 80km)에 대한 집중호우 확률예보시스템을 개발하기 위한 선행연구를 수행하였다.
이 연구를 위한 가설은 특정 공간과 시간규모에서 대기의 상태를 앙상블멤버 형태로 알고 있을 때 구름모델을 활용하여 각각의 대기상태로부터 강수가 어느 정도 산출되는지 계산함으로써 강수량 앙상블을 구하고, 그로부터 1시간 누적강수의 확률밀도 함수를 계산할 수 있다는 것이다. 본 연구에서 사용한 구름모델은 일본 나고야대학에서 개발한 CReSS(Cloud Resolving Storm Simulator)이고, 현업 UM 지역모델(12km)의 예측장으로부터 앙상블 대기상태인 39개의 모델사운딩을 얻었다. 아래의 그림은 ‘11년 7월 수도권 집중호우 사례에 대해 적용하여 구한 구름모델 앙상블의 1시간 누적강수량 확률밀도함수를 AWS 관측치와 UM의 3시간 누적강수의 확률밀도함수와 비교한 것이다.
Ⅳ. Research Contents and Results
Over the last 30 years, in our country, about 14 meteorological disasters occur on an average, causing the average about 158 casualties and the averaged annual damage is about 800 billion won. In order to minimize the damages caused by meteorological disasters as
Ⅳ. Research Contents and Results
Over the last 30 years, in our country, about 14 meteorological disasters occur on an average, causing the average about 158 casualties and the averaged annual damage is about 800 billion won. In order to minimize the damages caused by meteorological disasters as such, it is needed to establish thorough disaster prevention measures through recognition on meteorological disaster phenomenon and actual state of damages and accurate survey. Thus, we are to prepare the basic data to establish the disaster prevention measures by investigating the area where disasters are much apprehended to occur through survey and analysis on the level of damages caused by disasters as well as the actual state of disasters recently occurred.
According to summarized results on the status of damages caused by meteorological disasters from 1993 to 2010 using the data in disaster yearbook published by National Emergency Management Agency every year, based on the classification by cause, the damages due to typhoons and heavy rains were the greatest compared to other causes, and based on the classification by region, the damages due to disasters were the greatest in Gangwon Province and South Gyeongsang Province and the number of dead people were the largest in Gyeonggi Province and Gangwon Province. In particular, Gangwon Province can be classified as a district vulnerable to disasters, recording a great number of damages per area and the amount of damages per population as the highest(Fig1).
In addition, according to summarized results on status of damages, general meteorological state, related news data for 14 cases based on more than 10 billion damages among meteorological disasters occurred from recent 2010 to 2011, the damages caused by Mt. Woomyeon landslide occurred on July 26 to July 29 were recorded as the greatest amount of about 806.2 billion won which was the greatest damages for 19 years since 1993 among damages due to heavy rain.
We developed the technology to visualize the information on high-impact weather utilizing the geographic information system (GIS) as a basic research for development of system integrating the information on high-impact weather and geographic information. As the start, we manufactured a map of heavy snow disasters to visualize the regional distribution on the amount of damages due to heavy snow, quantity of heavy snow, and frequency of news flash announcement, using ArcGIS from 2005 to 2010(Fig 2). The map of heavy snow disasters manufactured like this not only enables the general public to easily acquire the disaster information by expressing the information in Google maps in an overlapping manner using Google Maps API(Application Programming Interface) but also enables us to expect the preventive effects of inhabitants with respect to disasters through regional information on disasters.
According to the map of heavy snow disasters, North Jeolla Province suffers the greatest damages due to heavy snow, but Gangwon Province was represented as the region where there were much snowfall and the heavy-snowfall watch &warning were frequently issued. This means that the
region where there are much snowfall cannot always be defined as the region vulnerable to heavy snow.
In order to collect and classify the characteristics of spatial regional distribution shown in disaster map statistically, the self-organizing map (Self-Organizing Map, SOM) and method of K-Means are applied generally. In this research, we compared and analyzed the optimum number of clusters with regard to the same rainfall region derived from two different statistical methods using observation data for precipitation(Fig 3). The data used for this search is daily precipitation data at 61 ground observation points from 1980 to 2010 and at 343 AWS observation points from 1997 to 2010. In case that data at 61 ground observation points was used, the optimum number of clusters was presented as the same by representing 9 clusters set in both SOM and K-Mean methods, but shows some differences in distribution. In case that data at 404 observation points was used, the optimum number of clusters was presented as different by representing 17 clusters for SOM, and 19 clusters for K-Means, and the patterns are shown as very complicated even in spatial distribution, so it is difficult to draw any consistent conclusion. In this research, we can find the meaning in having set the number of clusters reflecting characteristics of the spatial distribution of precipitation in our country with applying the objective statistical method.
Because the global temperature rise caused by global warming creates the conditions to cause extreme abnormal climate a lot by increasing the variation range of natural variability, such as Arctic oscillation or El Niñ, la Niñ, it increases the possibility of occurrences of disastrous meteorology. In particular, the results of researches have been published that it may increase the possibility of occurrences of flood and drought which are typical disastrous meteorology at the same in future by strengthening the hydrological circulation. It is reported that even in Korean peninsula, the shape and intensity of precipitation are changing together with a continuous rise in temperature, and the results of prospect are presented that this will be accelerated more in future.
At this, in this research, we arranged in detail, A1B scenario data produced by ECHAM5 global climate model participated in the 4th report of IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) dynamically, using the RegCM3
regional climate model, and intended to investigate what changes can be caused by increase of greenhouse gases in future in terms of hydrological climatology, with a focus on flood and drought.
We carried out the IDF(Intensity-Duration-Frequency)analysis which is applied a lot to hydrological analysis to investigate the intensity and frequency of extreme precipitation simultaneously using the detailed data of three-hour precipitation in Korean peninsula with the grid spacing of 20km from RegCM3 double-nested system. Fig 5 is an IDF curve for 3 hour precipitation and 24 hour precipitation and in the curve, x-axis represents the return period while y-axis represents the precipitation intensity per unit hour. Here, the return period of 100 years means the precipitation that may occur once for 100 years statistically. When the reference scenario is compared to observations, in this model, intensity of precipitation shows the tendency of being simulated excessively compared to observations. Looking into the tendency of change in future compared to reference scenario, as the global warming goes on(in future, as passes toward the second half of the 21st century), the shortening of return period is represented clearly. Although the average annual precipitation was predicted to reduce in 2071-2100 (Fig 4), due to shortening of return period, in reference scenario, it is presented the possibility that the extreme precipitation which may occur once for 100 years, may appear in less than 50 years in the second half of the 21st century. Especially in three hour precipitation, the rapid increase of precipitation intensity in 100 year return period is shown, which means that the risk of flooding increases much more. In addition, the fact that extreme precipitation increases despite decrease of total precipitation means the decrease in the frequency of light precipitation, so it can be interpreted that the possibility of occurrence of drought contains that of increase of extreme precipitation at the same time.
As the possibility of flood in future is predicted to increase, it is meaningful
to investigate the spatial and temporal characteristics of localized torrential rainfall, using the observation data in the past. In this research, we analyzed the long-term trends and the characteristics for regional distribution of daily and temporal precipitation by analyzing precipitation data of the ASOS (61 points) from 1973 to 2010 and the AWS (352 points) from 1998 to 2010. In addition, we investigated the seasonal and regional characteristics of localized heavy rain by analyzing the regional correlation of daily and temporal precipitation and summarized the characteristics of frequency of occurrence of extreme precipitation from IDF curve.
According to the results of correlation analysis on precipitation based on distance between each point using the data covering 13 years from 1998 to 2010, looking into e-folding graph for temporal precipitation (Fig 6), the decrease of correlation based on distance is the least in May while the decrease of correlation based on distance is the greatest in July and August. As for monthly e-folding distance (Table 1), it was represented as about 162 km, the longest in May, about 55 km in July and about 45km, the shortest in August. respectively.
This means that the precipitation in May is one falling from synoptic systems with a higher degree of correlation depending on the distance, and that the precipitation in July and August is localized one with a lot of changes in region.
Looking into the spatial distribution of e-folding distance in July and August,
we can see that there occurred very small values in the west of our country.
This means that in case of heavy rain that occurs in July and August, the regional deviations are larger in the west region than in the east region in our country.
According to results of analysis on IDF curve for daily precipitation using the precipitation data from 1973 to 2010, it was analyzed that the precipitation of about 360 mm/day was one that may fall once for 100 years, and according to results of analysis on IDF curve for temporal precipitation, it was analyzed that the precipitation of about 80 mm/h was one that may fall once for 100 years, respectively. In spatial distribution of daily precipitation that may fall once for 100 years for each point, In Gangwon Yeong Dong area and some areas of south coast, its intensity was represented as high while in North Gyeongsang Province area and North Jeolla Province area, its intensity was represented as low. And in case of temporal precipitation, in South Chungcheong Province area and South Jeolla Province area, its intensity was represented as high while in mountainous areas of Gangwon Province, South Gyeongsang Province area and some areas of North Jeolla Province, its intensity was represented as low.
Yeong Dong region is located near Taebaek mountain range with steep slope and is adjacent to East Sea, so due to combined effects of topography and ocean, there occurs bad meteorology like heavy snow and down-slope windstorm frequently. Recently from Feb. 11 to Feb.14 in 2011, there occurred the heavy snow exceeding the extremity along the coast of Yeong Dong area, causing massive damage to transportation, agriculture and fishery. At this, in this research, we simulated the heavy snow that occurred from Feb. 11 to Feb.14 in 2011, using the high resolution WRF(Weather Research and Forecasting) and intended to elucidate the mechanism of occurrence through various kinds of sensitivity experiments.
In Fig 6, for the verification on quantitative performance of model, there is represented the comparison between observation values and accumulated precipitation for 3 hours in East Sea and Daegwanryeong point where a large quantity of snowfall occurred. The model simulates the temporal distribution of precipitation shown in the observation in a similar manner with observations, and the correlation coefficient for two time series was represented as 0.72 in East Sea, 0.70 in Daegwanryeong relatively high, respectively. The band of precipitation shows the extreme values on the 11th night and the 12th dawn in the coast of East Sea and also simulates the tendency of moving to inland of Daegwanryeong on the 12th morning relatively realistically. Based on results of realistic simulation of standard experiment, in order to investigate the impact of topography and temperature of sea surface suggested as main factors that cause heavy snow in East Sea, we carried out the sensitivity experiment with relieving the topography and setting the temperature of sea surface as high. In case of sensitivity experiment which reduced the topographic flection or slope, the vertical upward movement or downward movement along the mountain
slopes from coastal areas was reduced significantly, and although the differences in total precipitation were represented not much, its spatial distribution was represented as different from standard experiment. In case of sensitivity experiment which increased the temperature of sea surface, it was represented that as the vertical movement in the ocean became more active than the standard experiment, it supplied more heat and humidity to accelerate the snowfall.
Because the existing prediction of localized torrential rainfall or heavy snow was made on a scale of very short period (2-6 hours), there were difficulties in making the provisions against them and establishing the disaster prevention policy. Accordingly, we carried out the precedent research to develop the probability forecast system for localized torrential rainfall in a specific area(about 80km x 80km) after one day (24 hours) or so passed. For this search, we made the hypothesis that when the state of atmosphere is known in a particular spatial and temporal scale as the type of ensemble members, we can obtain the ensemble of precipitation by calculating how much the precipitation is yield from each atmospheric state utilizing the cloud model, and we can calculate the probability density function of accumulated precipitation for 1 hour. The cloud model used in this research is CReSS(Cloud Resolving Storm Simulator) developed at the University of Nagoya, Japan, and we obtained 39 model soundings at ensemble standby state from prediction field of UM regional model at work-site operation(12km).
The Fig 7 represents a comparison among the probability density function for 1 hour accumulated precipitation of cloud model ensemble obtained by applying to the case of localized torrential rainfall in metropolitan area in July, 2011 and the probability density function for 1 hour accumulated precipitation of the AWS observations and 3 hour accumulated precipitation of UM.
 표
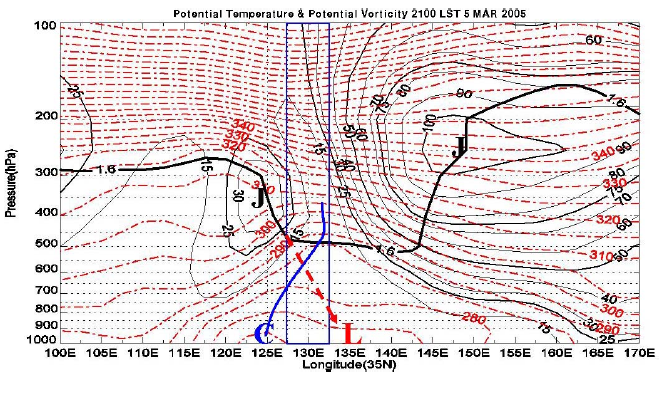
Vertical cross section of potential temperature(dashed dotted line, unit : K), and wind speed(solid line, unit : ms-1) at 35°N for 2100 LST 2 March 2005 in the Busan case. Heavy solid line with letter C and heavy dotted arrow with letter L represent axis of cold dome and upper-level trough from tropopause undulation, respectively. The dynamic tropopause and jet core is denoted by heavy solid line and letter J.
표
Vertical cross section of potential temperature(dashed dotted line, unit : K), and wind speed(solid line, unit : ms-1) at 35°N for 2100 LST 2 March 2005 in the Busan case. Heavy solid line with letter C and heavy dotted arrow with letter L represent axis of cold dome and upper-level trough from tropopause undulation, respectively. The dynamic tropopause and jet core is denoted by heavy solid line and letter J.
 표
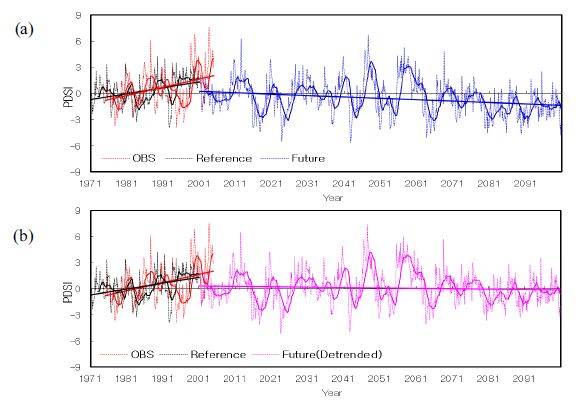
Time-series of the PDSI (dotted line), 25 months moving average (thick line), and its trend (thick linear line) derived from the observation (red color), reference simulation (black color), and future simulation with original temperature (blue color, a) and detrended temperature (pink color, b). Here, time-series of the PDSI derive from the observation and reference simulation are the same in (a) and (b).
표
Time-series of the PDSI (dotted line), 25 months moving average (thick line), and its trend (thick linear line) derived from the observation (red color), reference simulation (black color), and future simulation with original temperature (blue color, a) and detrended temperature (pink color, b). Here, time-series of the PDSI derive from the observation and reference simulation are the same in (a) and (b).
 표
Vertical cross section of potential temperature(dashed dotted line, unit : K), and wind speed(solid line, unit : ms-1) at 35°N for 2100 LST 2 March 2005 in the Busan case. Heavy solid line with letter C and heavy dotted arrow with letter L represent axis of cold dome and upper-level trough from tropopause undulation, respectively. The dynamic tropopause and jet core is denoted by heavy solid line and letter J.
표
Vertical cross section of potential temperature(dashed dotted line, unit : K), and wind speed(solid line, unit : ms-1) at 35°N for 2100 LST 2 March 2005 in the Busan case. Heavy solid line with letter C and heavy dotted arrow with letter L represent axis of cold dome and upper-level trough from tropopause undulation, respectively. The dynamic tropopause and jet core is denoted by heavy solid line and letter J.
 표
Time-series of the PDSI (dotted line), 25 months moving average (thick line), and its trend (thick linear line) derived from the observation (red color), reference simulation (black color), and future simulation with original temperature (blue color, a) and detrended temperature (pink color, b). Here, time-series of the PDSI derive from the observation and reference simulation are the same in (a) and (b).
표
Time-series of the PDSI (dotted line), 25 months moving average (thick line), and its trend (thick linear line) derived from the observation (red color), reference simulation (black color), and future simulation with original temperature (blue color, a) and detrended temperature (pink color, b). Here, time-series of the PDSI derive from the observation and reference simulation are the same in (a) and (b).
| 과제명(ProjectTitle) : | - |
|---|---|
| 연구책임자(Manager) : | - |
| 과제기간(DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 총연구비 (DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 키워드(keyword) : | - |
| 과제수행기간(LeadAgency) : | - |
| 연구목표(Goal) : | - |
| 연구내용(Abstract) : | - |
| 기대효과(Effect) : | - |
Copyright KISTI. All Rights Reserved.

※ AI-Helper는 부적절한 답변을 할 수 있습니다.