최소 단어 이상 선택하여야 합니다.
최대 10 단어까지만 선택 가능합니다.
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
NTIS 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
DataON 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Edison 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Kafe 바로가기
| 주관연구기관 | 건국대학교 KonKuk University |
|---|---|
| 보고서유형 | 최종보고서 |
| 발행국가 | 대한민국 |
| 언어 | 한국어 |
| 발행년월 | 2012-04 |
| 과제시작연도 | 2011 |
| 주관부처 | 농림축산식품부 Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs(MAFRA) |
| 연구관리전문기관 | 농림수산식품기술기획평가원 Korea Institute of Planning and Evalution for Technology of Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisherie |
| 등록번호 | TRKO201400026543 |
| 과제고유번호 | 1545002680 |
| 사업명 | 생명산업기술개발 |
| DB 구축일자 | 2014-11-14 |
○ 연구결과
(1)반섬유소로부터 L-ribose의 생물학적 분해공정 개발
1.L-Arabinose생산:Endo-arabinanase와 alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase를 사용하여 반응조건을 최적화하여 최적 조건에서 20g/larabinan으로부터 2시간 동안 16g/lL-arabinose를 생산
2.반섬유소로부터 L-arabinose생산:볏짚 2g과 sugarbeet2g에서 각각 L-arabinose가 1.5mg과 12mg이 생산되어 sugarbeet가 8배 높은 효율을 보임.
3.L-Ribul
○ 연구결과
(1)반섬유소로부터 L-ribose의 생물학적 분해공정 개발
1.L-Arabinose생산:Endo-arabinanase와 alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase를 사용하여 반응조건을 최적화하여 최적 조건에서 20g/larabinan으로부터 2시간 동안 16g/lL-arabinose를 생산
2.반섬유소로부터 L-arabinose생산:볏짚 2g과 sugarbeet2g에서 각각 L-arabinose가 1.5mg과 12mg이 생산되어 sugarbeet가 8배 높은 효율을 보임.
3.L-Ribulose생산:L-Arabinoseisomerase를 사용하여 500g/lL-arabinose로부터 2시간 반응하여 95g/lL-ribulose생산
4. L-Ribose 생산: 효소의 유전자 진화와 분자모델링을 사용하여 효소를 개량하여 300 g/l L-ribulose로부터 1시간 동안 213g/lL-ribose를 생산
5. L-Arabinose로부터 L-ribose 생산 최적화: L-arabinose isomerase와 mannose-6-phosphate isomerase를 사용하여 500g/lL-arabinose으로부터 3시간 동안 118g/lL-ribose를 생산
(3)반섬유소로부터 L-arabinose및 L-ribose의 대량 생산 조건 확립
1.고정화 효소 함유 생물반응기에서 20 g/l sugar beet arabinan로부터 14일간 12 g/l이상 L-arabinose생산
2.고정화 효소 함유 생물반응기에서 300g/lL-arabinose로부터 10일간 50g/l이상 L-ribose생산
3.L-Arabinose및 L-ribose의 정제 조건 확립하고 시제품 L-ribulose19gram 및 L-ribose5.5 gram 제조
Ⅳ. Results
(1) Enzymatic hydrolysis of hemicellulose for L-arabinose production
1. Screening, selection, cloning, and expression of endo-arabinanases from Bacillus licheniformis and Caldicellulorsiruptor saccharolyticus; and alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase from C. saccharolyticus.
2. Enzyme pur
Ⅳ. Results
(1) Enzymatic hydrolysis of hemicellulose for L-arabinose production
1. Screening, selection, cloning, and expression of endo-arabinanases from Bacillus licheniformis and Caldicellulorsiruptor saccharolyticus; and alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase from C. saccharolyticus.
2. Enzyme purification, molecular mass determination, optimization of temperature and pH, thermostability measurement, and substrate specificity determination of endo-arabinanases from B. licheniformis and C. saccharolyticus; and alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase from C. saccharolyticus.
3. The ratio of two enzymes, temperature, pH, and the concentrations of enzymes and substrate were optimized. Under the optimal conditions, endo-arabinanase and alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase from C. saccharolyticus produced 16 g/l L-arabinose from 20 g/l arabinan.
4. L-Arabinose production from hemicellulose: 1.5 mg and 12 mg L-arabinose was produced 2 g rice straw and 2 g sugar beet, respectively.
(2) Bioconversion of L-arabinose into L-ribose
1. Screening, selection, cloning, and expression of L-arabinose isomerases from Geobacillus stearothermophilus, G. thermodenitrificans, and Thermotoga neopolitana; mannose-6-phosphate isomerases from Bacillus subtilus, G. thermodenitrificans, Thermus thermophilus, T. thermophilus R142N, and G. thermodenitrificans W17Q N90A L129F.
2. Enzyme purification, molecular mass determination, optimization of temperature and pH, thermostability measurement, and substrate specificity determination of L-arabinose isomerases from Geobacillus stearothermophilus, G. thermodenitrificans, and Thermotoga neopolitana; mannose-6-phosphate isomerases from Bacillus subtilus, G. thermodenitrificans, Thermus thermophilus, T. thermophilus R142N, and G. thermodenitrificans W17Q N90A L129F.
3. Optimization of L-ribulose production: The temperature, pH, and the concentrations of enzyme and substrate by L-arabinose isomerase from G. thermodenitrificans were optimized. Under the optimal conditions, the enzyme produced 95 g/l L-ribulose from 500 g/l L-arabinose for 2 h.
4. Optimization of L-ribose production: The temperature, pH, and the concentrations of enzyme and substrate by mannose-6-phosphate isomerases from B. subtilus, G. thermodenitrificans, and T. thermophilus were optimized. Under the optimal conditions, T. thermophilus mannose-6-phosphate isomerase produced 213 g/l L-ribose from 300 g/l L-ribulose for 3 h, with a conversion yield of 71% and productivity of 71 g L−1 h-1.
5. mprovement for activities of L-ribose-producing enzymes by DNA evolution and molecular modeling
- A W17Q-N90A-L129F variant of G. thermodenitrificans mannose-6-phosphate isomerase was obtained using error-prone PCR and site-directed mutagenesis.
The specific activity, catalytic efficiency, and productivity of the variant were 3.1-, 7.1- ,and 4.5-fold higher than the wild-type enzyme, respectively. The variant produced 213 g/l L-ribose from 300 g/l L-ribulose for 1 h, with a conversion yield of 71% and productivity of 213 g L−1 h-1.
- As L-ribulose was docked to T. thermophilus mannose-6-phosphate isomerase based on molecular modeling, its phosphate-binding site was found to be a molecular determinant. The R142N variant was developed through substrate-tailred optimization. The specific activity, catalytic efficiency, and productivity of the variant were 1.4-, 1.6-, and 1.5-fold higher than the wild-type enzyme, respectively. The variant produced 213 g/l L-ribose from 300g/l L-ribulose for 2 h, with a conversion yield of 71% and productivity of 107 g L−1 h-1.
6. The ratio of two enzymes, temperature, pH, and the concentrations of enzymes and substrate were optimized. Under the optimal conditions, L-arabinose isomerase와 mannose-6-phosphate isomerase from G. thermodenitrificans produced 118 g/l L-ribose from 500 g/l L-arabinosefor 2 h, with a conversion yield of 24% and productivity of 39 g L−1 h-1.
(3) Optimization for the production of L-arabinose and L-ribose from hemicellulose
1. Immobilized L-arabinose-producing enzymes in a bioreactor produced more than 12 g/l L-arabinose for 14 days from 20 g/l sugar beet arabinan at endo:exo ratio of 1:10 absorbed on Duolite A568, pH of 6.0, temperature of 80℃, and dilution rate of 0.6 h-1.
2. Immobilized cells containing L-arabinose isomerase and mannose-6-phosphate isomerase in a bioreactor produced more than 50 g/l L-ribose for 10 days from 300 g/l L-arabinose absorbed on alginate at pH of 7.5, temperature of 60℃, and dilution rate of 0.1 h-1.
3. Purification of L-arabinose and L-ribose from the reaction products: After crystallization by adding 3 times volume of ethanol to the concentrated reaction solution, filtrate was applied to Dowex monosphere 99CA resin. The active fraction of the elute was collected, concentrated and dried. The dried product was the purified L-arabinose or L-ribose.
(4) Preparation of the purified L-arabinose and L-ribose as 19 gram of 97.5% L-ribulose and 5.5 gram of 80.9% L-ribose.
 표
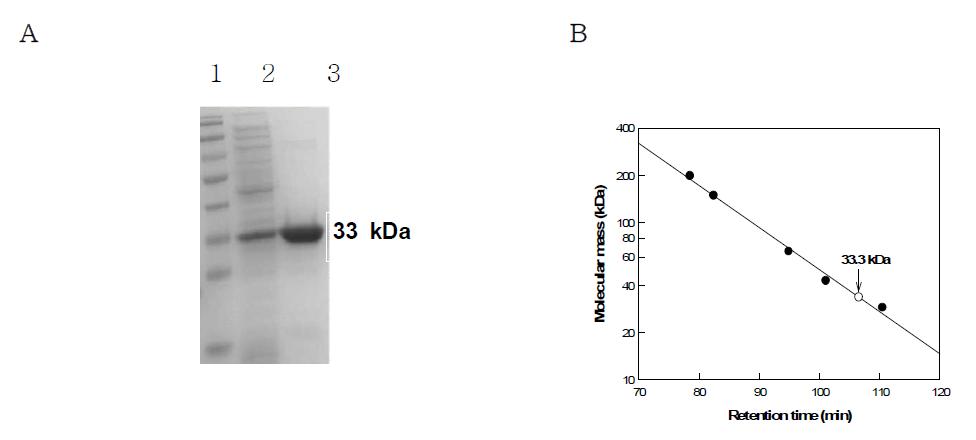
(a) SDS-PAGE analysis of purified enzyme from each purification step. Lane1, molecular mass markers; lane2, crude enzyme; lane3, His-Trap column product (purified enzyme). (b). Determination of molecular mass of endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase from B. licheniformis by gel-filteration chromatography using a Sephacryl S-300 HR 16/60 column. The reference proteins (●) were b-amylase from sweet potato (200 kDa), aldolase (158 kDa), albumin (66 kDa), ovalbumin (43 kDa) and carbonic anhydrase from bovine (29 kDa). The molecular mass ofendo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase was 33.3 kDa (○).
표
(a) SDS-PAGE analysis of purified enzyme from each purification step. Lane1, molecular mass markers; lane2, crude enzyme; lane3, His-Trap column product (purified enzyme). (b). Determination of molecular mass of endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase from B. licheniformis by gel-filteration chromatography using a Sephacryl S-300 HR 16/60 column. The reference proteins (●) were b-amylase from sweet potato (200 kDa), aldolase (158 kDa), albumin (66 kDa), ovalbumin (43 kDa) and carbonic anhydrase from bovine (29 kDa). The molecular mass ofendo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase was 33.3 kDa (○).
 표
Alignment of the amino acid sequences of C. saccharolyticus α -L-arabinofuranosidase with GH family 51 α-L-arabinofuranosidases. CSAraf, C. saccharolyticus; GSAraf, Geobacillus caldoxylosilyticus; BSAraf, Bacillus stearothermophilus; AKAraf, Anoxybacillus kestanbolensis; and BLAraf, Bifidobacteriumlongum. The catalytic residues (E173 and E292) and consensus sequences of GH family 51 are highlighted with black and gray backgrounds, respectively.
표
Alignment of the amino acid sequences of C. saccharolyticus α -L-arabinofuranosidase with GH family 51 α-L-arabinofuranosidases. CSAraf, C. saccharolyticus; GSAraf, Geobacillus caldoxylosilyticus; BSAraf, Bacillus stearothermophilus; AKAraf, Anoxybacillus kestanbolensis; and BLAraf, Bifidobacteriumlongum. The catalytic residues (E173 and E292) and consensus sequences of GH family 51 are highlighted with black and gray backgrounds, respectively.
 표
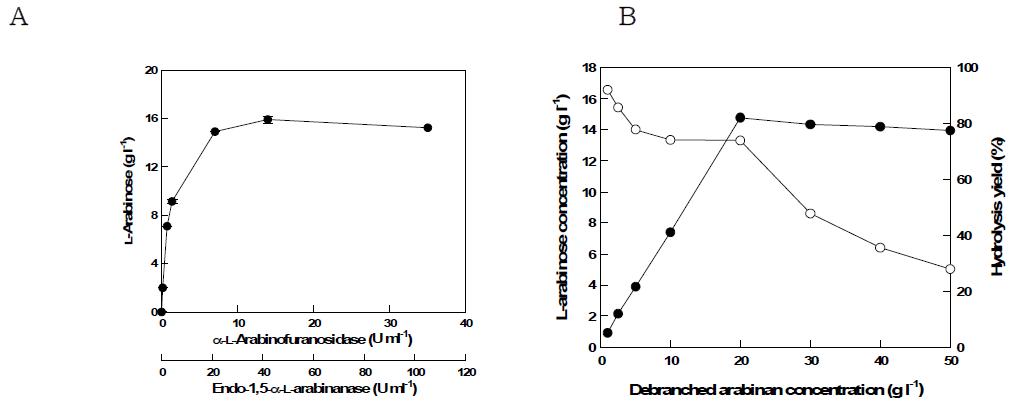
(a) Effect of enzymes concentration on L-arabinose production from debranched arabinan at the optimal unit ratio (endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase:α -L-arabinofuranosidase=3:1) (b) Effect of substrate concentration on L-arabinose production from debranched arabinan with 42 U/ml endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase and 14 U/ml α-L-arabinofuranosidase.
표
(a) Effect of enzymes concentration on L-arabinose production from debranched arabinan at the optimal unit ratio (endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase:α -L-arabinofuranosidase=3:1) (b) Effect of substrate concentration on L-arabinose production from debranched arabinan with 42 U/ml endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase and 14 U/ml α-L-arabinofuranosidase.
 표
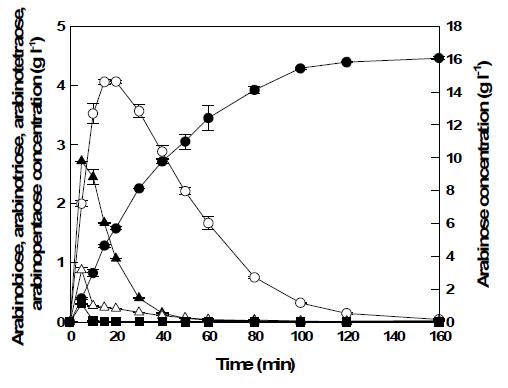
Time courses of L-arabinose production from debranched arabinan under the optimal conditions. The optimal conditions for debranched arabinan were pH 6.5, 75 °C, 20 g/l debranched arabinan, 42 U/ml endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase, and 14 U/ml α -l-arabinofuranosidase. L-Arabinose (●), arabinobiose (△), arabinotriose (■), arabinotetraose (□), and arabinopentaose (▲).
표
Time courses of L-arabinose production from debranched arabinan under the optimal conditions. The optimal conditions for debranched arabinan were pH 6.5, 75 °C, 20 g/l debranched arabinan, 42 U/ml endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase, and 14 U/ml α -l-arabinofuranosidase. L-Arabinose (●), arabinobiose (△), arabinotriose (■), arabinotetraose (□), and arabinopentaose (▲).
 표
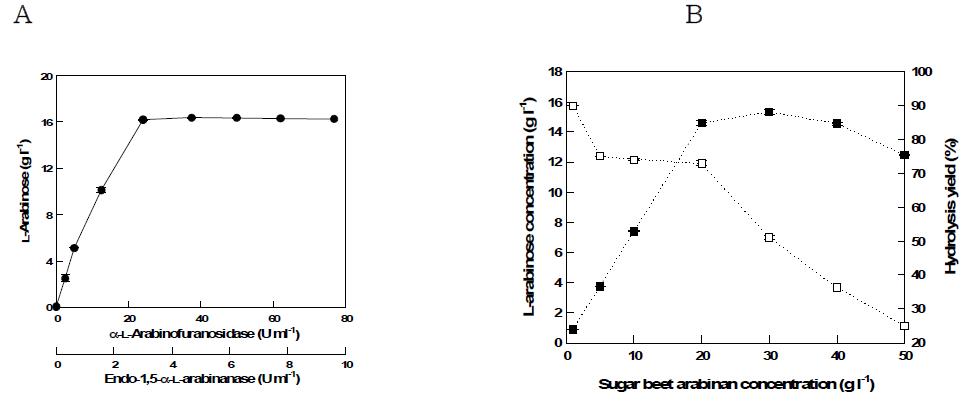
(a) Effect of enzymes concentration on L-arabinose production from Sugar beet arabinan at the optimal unit ratio (endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase:α -L-arabinofuranosidase=1:8) (b) Effect of substrate concentration on L-arabinose production from Sugar beet arabinan with 3 U ml-1 endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase and 24 U ml-1 α-L-arabinofuranosidase.
표
(a) Effect of enzymes concentration on L-arabinose production from Sugar beet arabinan at the optimal unit ratio (endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase:α -L-arabinofuranosidase=1:8) (b) Effect of substrate concentration on L-arabinose production from Sugar beet arabinan with 3 U ml-1 endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase and 24 U ml-1 α-L-arabinofuranosidase.
 표
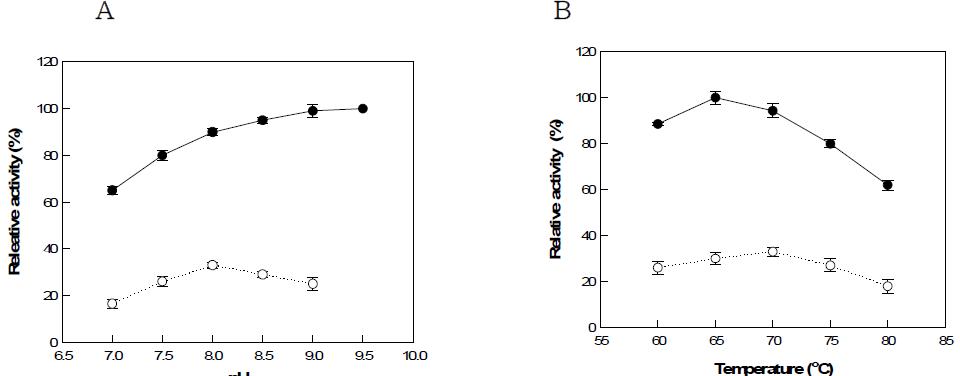
Effects of (a) pH and (b) temperature on L-ribulose production using GTAI double-site mutant enzyme in the absence (○) and presence (●) of borate. The reactions for pH experiments were allowed to proceed at 70°C in 50 mM Tris-HCl or 50 mM borate buffer at 65°C. The reactions for temperatue experiments were allowed to proceed at pH 8.5 in 50 mM Tris-HCl or 50 mM borate buffer at pH 9.0.
표
Effects of (a) pH and (b) temperature on L-ribulose production using GTAI double-site mutant enzyme in the absence (○) and presence (●) of borate. The reactions for pH experiments were allowed to proceed at 70°C in 50 mM Tris-HCl or 50 mM borate buffer at 65°C. The reactions for temperatue experiments were allowed to proceed at pH 8.5 in 50 mM Tris-HCl or 50 mM borate buffer at pH 9.0.
 표
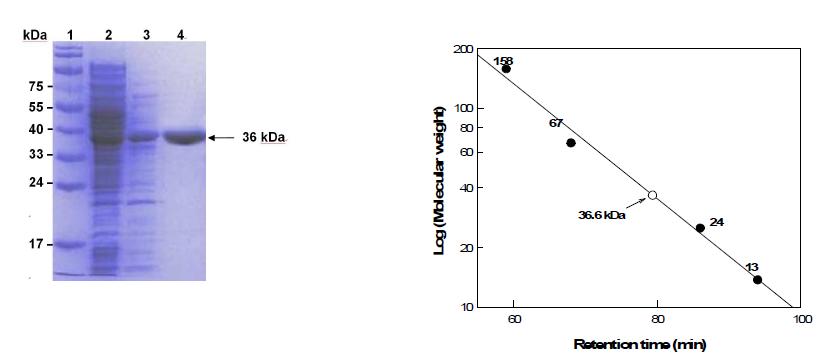
PAGE analysis of mannose-6-phosphate isomerase from G. thermodenitrificans. (A) SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie blue. Lane 1, molecular mass markers; lane 2, crude extract, lane 3, supernatant after heat treatment at 70℃ for 5 min, lane 4, Hi-trap column product (purified enzyme). (B) Determination of molecular mass of mannose-6-phosphate isomerase by gel-filtration chromatography.
표
PAGE analysis of mannose-6-phosphate isomerase from G. thermodenitrificans. (A) SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie blue. Lane 1, molecular mass markers; lane 2, crude extract, lane 3, supernatant after heat treatment at 70℃ for 5 min, lane 4, Hi-trap column product (purified enzyme). (B) Determination of molecular mass of mannose-6-phosphate isomerase by gel-filtration chromatography.
 표
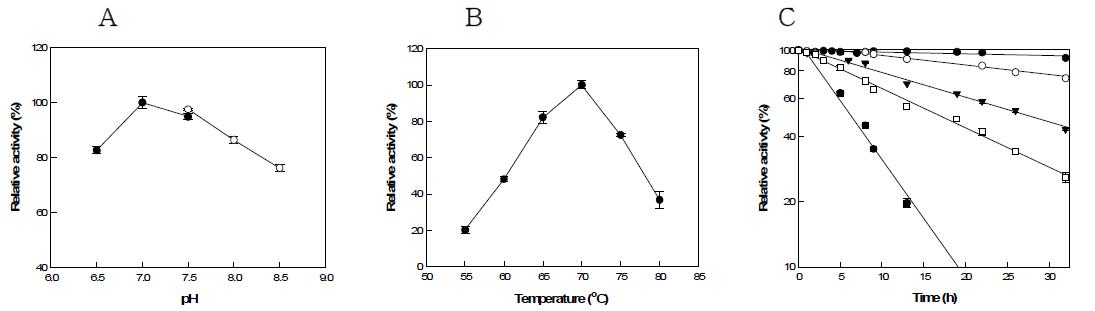
(a) Effect of pH on the activity of G. thermodenitrificans mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. PIPES(●), EPPS(○). (b) Effect of temperature on activity of G. thermodenitrificans mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. (c) Thermal inactivation of G. thermodenitrificans mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. 60(●), 65(○), 70(▼), 75(□), 80℃(■).
표
(a) Effect of pH on the activity of G. thermodenitrificans mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. PIPES(●), EPPS(○). (b) Effect of temperature on activity of G. thermodenitrificans mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. (c) Thermal inactivation of G. thermodenitrificans mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. 60(●), 65(○), 70(▼), 75(□), 80℃(■).
 표
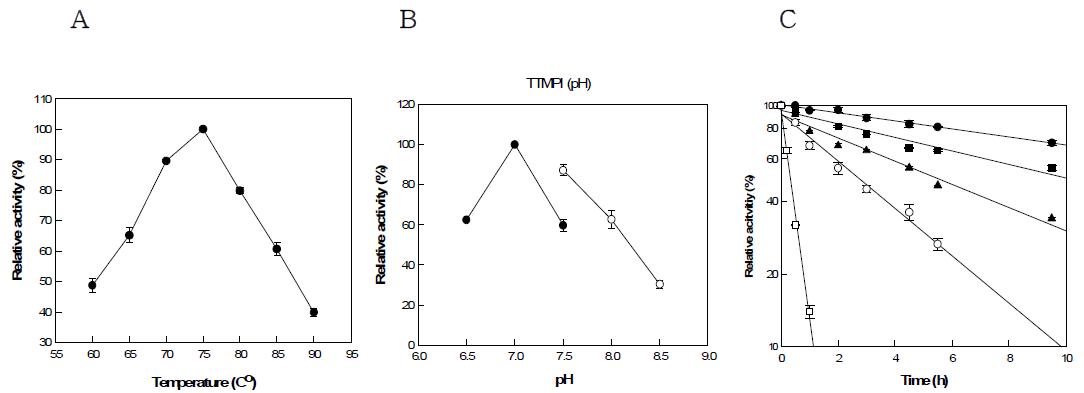
(a) Effect of pH on the activity of Thermus thermophilus mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. PIPES(●), EPPS(○). (b) Effect of temperature on activity of Thermus thermophilus mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. (c) Thermal inactivation of Thermus thermophilus mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. 65(●), 70(■), 75(▲), 80(○), 85℃(□).
표
(a) Effect of pH on the activity of Thermus thermophilus mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. PIPES(●), EPPS(○). (b) Effect of temperature on activity of Thermus thermophilus mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. (c) Thermal inactivation of Thermus thermophilus mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. 65(●), 70(■), 75(▲), 80(○), 85℃(□).
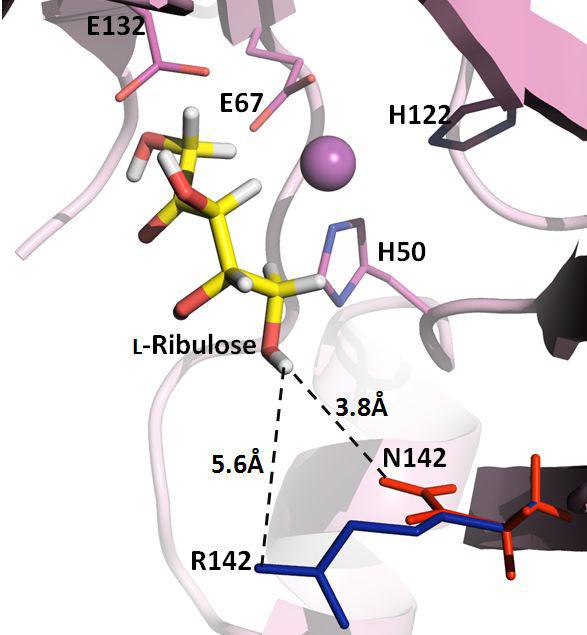 표
Docking of L-ribulose into the active-site of the wild-type and mutant enzymes. The yellow, blue, red sticks represent L-ribulose as substrate and arginine and asparagine residues at position 142, respectively. The dashed line was distance between residue and substrate. The figure was produced using PYMOL.
표
Docking of L-ribulose into the active-site of the wild-type and mutant enzymes. The yellow, blue, red sticks represent L-ribulose as substrate and arginine and asparagine residues at position 142, respectively. The dashed line was distance between residue and substrate. The figure was produced using PYMOL.
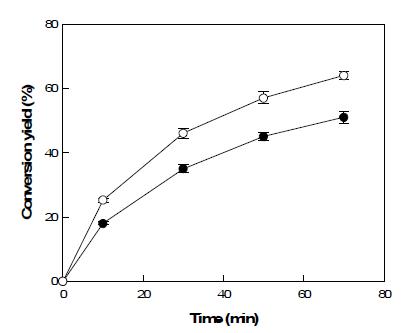 표
Time courses of L-ribose production from L-ribulose to by the wild-type (●) and R142A mutant (○) mannose-6-phosphate isomerases from T. thermophilus. The reactions were performed in 50 mM PIPES buffer (pH 7.0) containing 10 mM L-ribulose, 70U/ml of enzyme, and 0.5 mM of each metal ion at 70°C for 70 min. Data represent the means of three experiments and error bars represent standard deviation.
표
Time courses of L-ribose production from L-ribulose to by the wild-type (●) and R142A mutant (○) mannose-6-phosphate isomerases from T. thermophilus. The reactions were performed in 50 mM PIPES buffer (pH 7.0) containing 10 mM L-ribulose, 70U/ml of enzyme, and 0.5 mM of each metal ion at 70°C for 70 min. Data represent the means of three experiments and error bars represent standard deviation.
 표
(a) SDS-PAGE analysis of purified enzyme from each purification step. Lane1, molecular mass markers; lane2, crude enzyme; lane3, His-Trap column product (purified enzyme). (b). Determination of molecular mass of endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase from B. licheniformis by gel-filteration chromatography using a Sephacryl S-300 HR 16/60 column. The reference proteins (●) were b-amylase from sweet potato (200 kDa), aldolase (158 kDa), albumin (66 kDa), ovalbumin (43 kDa) and carbonic anhydrase from bovine (29 kDa). The molecular mass ofendo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase was 33.3 kDa (○).
표
(a) SDS-PAGE analysis of purified enzyme from each purification step. Lane1, molecular mass markers; lane2, crude enzyme; lane3, His-Trap column product (purified enzyme). (b). Determination of molecular mass of endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase from B. licheniformis by gel-filteration chromatography using a Sephacryl S-300 HR 16/60 column. The reference proteins (●) were b-amylase from sweet potato (200 kDa), aldolase (158 kDa), albumin (66 kDa), ovalbumin (43 kDa) and carbonic anhydrase from bovine (29 kDa). The molecular mass ofendo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase was 33.3 kDa (○).
 표
Alignment of the amino acid sequences of C. saccharolyticus α -L-arabinofuranosidase with GH family 51 α-L-arabinofuranosidases. CSAraf, C. saccharolyticus; GSAraf, Geobacillus caldoxylosilyticus; BSAraf, Bacillus stearothermophilus; AKAraf, Anoxybacillus kestanbolensis; and BLAraf, Bifidobacteriumlongum. The catalytic residues (E173 and E292) and consensus sequences of GH family 51 are highlighted with black and gray backgrounds, respectively.
표
Alignment of the amino acid sequences of C. saccharolyticus α -L-arabinofuranosidase with GH family 51 α-L-arabinofuranosidases. CSAraf, C. saccharolyticus; GSAraf, Geobacillus caldoxylosilyticus; BSAraf, Bacillus stearothermophilus; AKAraf, Anoxybacillus kestanbolensis; and BLAraf, Bifidobacteriumlongum. The catalytic residues (E173 and E292) and consensus sequences of GH family 51 are highlighted with black and gray backgrounds, respectively.
 표
(a) Effect of enzymes concentration on L-arabinose production from debranched arabinan at the optimal unit ratio (endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase:α -L-arabinofuranosidase=3:1) (b) Effect of substrate concentration on L-arabinose production from debranched arabinan with 42 U/ml endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase and 14 U/ml α-L-arabinofuranosidase.
표
(a) Effect of enzymes concentration on L-arabinose production from debranched arabinan at the optimal unit ratio (endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase:α -L-arabinofuranosidase=3:1) (b) Effect of substrate concentration on L-arabinose production from debranched arabinan with 42 U/ml endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase and 14 U/ml α-L-arabinofuranosidase.
 표
Time courses of L-arabinose production from debranched arabinan under the optimal conditions. The optimal conditions for debranched arabinan were pH 6.5, 75 °C, 20 g/l debranched arabinan, 42 U/ml endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase, and 14 U/ml α -l-arabinofuranosidase. L-Arabinose (●), arabinobiose (△), arabinotriose (■), arabinotetraose (□), and arabinopentaose (▲).
표
Time courses of L-arabinose production from debranched arabinan under the optimal conditions. The optimal conditions for debranched arabinan were pH 6.5, 75 °C, 20 g/l debranched arabinan, 42 U/ml endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase, and 14 U/ml α -l-arabinofuranosidase. L-Arabinose (●), arabinobiose (△), arabinotriose (■), arabinotetraose (□), and arabinopentaose (▲).
 표
(a) Effect of enzymes concentration on L-arabinose production from Sugar beet arabinan at the optimal unit ratio (endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase:α -L-arabinofuranosidase=1:8) (b) Effect of substrate concentration on L-arabinose production from Sugar beet arabinan with 3 U ml-1 endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase and 24 U ml-1 α-L-arabinofuranosidase.
표
(a) Effect of enzymes concentration on L-arabinose production from Sugar beet arabinan at the optimal unit ratio (endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase:α -L-arabinofuranosidase=1:8) (b) Effect of substrate concentration on L-arabinose production from Sugar beet arabinan with 3 U ml-1 endo-1,5-α-L-arabinanase and 24 U ml-1 α-L-arabinofuranosidase.
 표
Effects of (a) pH and (b) temperature on L-ribulose production using GTAI double-site mutant enzyme in the absence (○) and presence (●) of borate. The reactions for pH experiments were allowed to proceed at 70°C in 50 mM Tris-HCl or 50 mM borate buffer at 65°C. The reactions for temperatue experiments were allowed to proceed at pH 8.5 in 50 mM Tris-HCl or 50 mM borate buffer at pH 9.0.
표
Effects of (a) pH and (b) temperature on L-ribulose production using GTAI double-site mutant enzyme in the absence (○) and presence (●) of borate. The reactions for pH experiments were allowed to proceed at 70°C in 50 mM Tris-HCl or 50 mM borate buffer at 65°C. The reactions for temperatue experiments were allowed to proceed at pH 8.5 in 50 mM Tris-HCl or 50 mM borate buffer at pH 9.0.
 표
PAGE analysis of mannose-6-phosphate isomerase from G. thermodenitrificans. (A) SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie blue. Lane 1, molecular mass markers; lane 2, crude extract, lane 3, supernatant after heat treatment at 70℃ for 5 min, lane 4, Hi-trap column product (purified enzyme). (B) Determination of molecular mass of mannose-6-phosphate isomerase by gel-filtration chromatography.
표
PAGE analysis of mannose-6-phosphate isomerase from G. thermodenitrificans. (A) SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie blue. Lane 1, molecular mass markers; lane 2, crude extract, lane 3, supernatant after heat treatment at 70℃ for 5 min, lane 4, Hi-trap column product (purified enzyme). (B) Determination of molecular mass of mannose-6-phosphate isomerase by gel-filtration chromatography.
 표
(a) Effect of pH on the activity of G. thermodenitrificans mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. PIPES(●), EPPS(○). (b) Effect of temperature on activity of G. thermodenitrificans mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. (c) Thermal inactivation of G. thermodenitrificans mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. 60(●), 65(○), 70(▼), 75(□), 80℃(■).
표
(a) Effect of pH on the activity of G. thermodenitrificans mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. PIPES(●), EPPS(○). (b) Effect of temperature on activity of G. thermodenitrificans mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. (c) Thermal inactivation of G. thermodenitrificans mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. 60(●), 65(○), 70(▼), 75(□), 80℃(■).
 표
(a) Effect of pH on the activity of Thermus thermophilus mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. PIPES(●), EPPS(○). (b) Effect of temperature on activity of Thermus thermophilus mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. (c) Thermal inactivation of Thermus thermophilus mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. 65(●), 70(■), 75(▲), 80(○), 85℃(□).
표
(a) Effect of pH on the activity of Thermus thermophilus mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. PIPES(●), EPPS(○). (b) Effect of temperature on activity of Thermus thermophilus mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. (c) Thermal inactivation of Thermus thermophilus mannose-6-phosphate isomerase. 65(●), 70(■), 75(▲), 80(○), 85℃(□).
 표
Docking of L-ribulose into the active-site of the wild-type and mutant enzymes. The yellow, blue, red sticks represent L-ribulose as substrate and arginine and asparagine residues at position 142, respectively. The dashed line was distance between residue and substrate. The figure was produced using PYMOL.
표
Docking of L-ribulose into the active-site of the wild-type and mutant enzymes. The yellow, blue, red sticks represent L-ribulose as substrate and arginine and asparagine residues at position 142, respectively. The dashed line was distance between residue and substrate. The figure was produced using PYMOL.
 표
Time courses of L-ribose production from L-ribulose to by the wild-type (●) and R142A mutant (○) mannose-6-phosphate isomerases from T. thermophilus. The reactions were performed in 50 mM PIPES buffer (pH 7.0) containing 10 mM L-ribulose, 70U/ml of enzyme, and 0.5 mM of each metal ion at 70°C for 70 min. Data represent the means of three experiments and error bars represent standard deviation.
표
Time courses of L-ribose production from L-ribulose to by the wild-type (●) and R142A mutant (○) mannose-6-phosphate isomerases from T. thermophilus. The reactions were performed in 50 mM PIPES buffer (pH 7.0) containing 10 mM L-ribulose, 70U/ml of enzyme, and 0.5 mM of each metal ion at 70°C for 70 min. Data represent the means of three experiments and error bars represent standard deviation.
| 과제명(ProjectTitle) : | - |
|---|---|
| 연구책임자(Manager) : | - |
| 과제기간(DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 총연구비 (DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 키워드(keyword) : | - |
| 과제수행기간(LeadAgency) : | - |
| 연구목표(Goal) : | - |
| 연구내용(Abstract) : | - |
| 기대효과(Effect) : | - |
Copyright KISTI. All Rights Reserved.

※ AI-Helper는 부적절한 답변을 할 수 있습니다.