최소 단어 이상 선택하여야 합니다.
최대 10 단어까지만 선택 가능합니다.
SAI
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
NTIS 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
DataON 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Edison 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Kafe 바로가기
| 주관연구기관 | 강원대학교 Kangwon National University |
|---|---|
| 보고서유형 | 최종보고서 |
| 발행국가 | 대한민국 |
| 언어 | 한국어 |
| 발행년월 | 2015-12 |
| 과제시작연도 | 2014 |
| 주관부처 | 농림축산식품부 Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs(MAFRA) |
| 연구관리전문기관 | 농림수산식품기술기획평가원 Korea Institute of Planning and Evalution for Technology of Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisherie |
| 등록번호 | TRKO201600003487 |
| 과제고유번호 | 1545009394 |
| 사업명 | 농생명산업기술개발 |
| DB 구축일자 | 2016-07-02 |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.23000/TRKO201600003487 |
Ⅴ. 연구개발 결과
1. 구토 및 설사형 바실러스 세레우스 동시 검출을 위한 Multiplex Conventional PCR키트 및 Multiplex Real-Time PCR 키트의 개발
● 바실러스 세레우스에서 구토형 및 설사형 독소 유전자들, non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS, CER primers), cereulide (ces), haemolysin BL (hblDCA), enterotoxin FM (entFM), non-haemolytic enterotoxin (nheABC),
Ⅴ. 연구개발 결과
1. 구토 및 설사형 바실러스 세레우스 동시 검출을 위한 Multiplex Conventional PCR키트 및 Multiplex Real-Time PCR 키트의 개발
● 바실러스 세레우스에서 구토형 및 설사형 독소 유전자들, non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS, CER primers), cereulide (ces), haemolysin BL (hblDCA), enterotoxin FM (entFM), non-haemolytic enterotoxin (nheABC), 및 cytotoxin K (cytK), 그리고 B.cereus group 마커인 groEL을 목표 대상으로 하는 제1, 제2 및 제3 프라이머 세트를 개발하고 multiplex PCR kit를 제작하고 이들의 민감도, 특이도 및 검출한계 등을 시험함.
●구토형 및 설사형 독소 유전자들의 프로파일/유병률(gene profile/prevalence rate)을 다양한 식품, 환경 및 임상 시료에서 분리한 바실러스 세레우스 야생균주 총 496개에서 조사한 결과, groEL은 모든 균주들에서 양성 이였으며(100%). CER 및 ces는 구토형 균주들에서만 발견되었으나, 설사형 장독소 유전자들인 hblD, nheA, entFM 및 cytK의 유병률은 각각 59.4%, 92.3%, 77.2% 및 47.5%로써 매우 다양한 유전자 프로파일을 나타냈음.
● 제1, 제2 및 제3 프라이머 세트의 PCR 검출한계는 순수배양액에서 추출한 genomic DNA에서는 각각 약 2, 2 및 0.2 pg/reaction tube 이었으며, 인위접종한 식품 시료에서는 각각 약 103, 102 및 102 cfu/g으로 제2 및 제3 프라이머 세트가 우수하였음. 제2 프라이머 세트의 entFM, nheA, hblD, cytK 및 ces 프라이머에 대한 PCR 산물 크기는 각각 488, 376,163, 106, 및 70 bp 이며, 제3 프라이머 세트의 entFM, nheA, hblD, cytK 및 ces 프라이머에 대한 PCR 산물의 크기는 각각 255, 163, 127, 97 및 81 bp임.
● 최종적으로 multiplex conventional PCR kit에 제2 프라이머 세트를, multiplex real-time PCR kit에 제3 프라이머 세트를 사용하고, 사용자 편의를 고려한 동결건조형 키트들을 시제품으로 제작하였음. 두 PCR kits와 표준배지배양법을 AOAC protocol에 따라 인위접종시료, 그리고 실제 식품 및 환경 시료 등을 대상으로 비교 검증한 결과, 세 가지 방법 중 multiplex real-time PCR kit가 가장 우수하였음. 도한 AOAC 검증방법에 따라 3개의 독립된 실험실에서 각각 두 PCR kits의 검증을 수행하여 개발된 PCR kits의 우수한 성능을 검증하였음.
2. 병원성 대장균 5종류 동시검출을 위한 Multiplex Conventional PCR, Internal amplification control, Real-time PCR 키트의 개발
● 5종 병원성 대장균들-장병원성(EPEC), 장출혈성(EHEC), 장침투성(EIEC), 장독소형(ETEC), 및 장부착성(EAEC) 대장균-을 검출하기 위해서 각 병원성 특이 마커 유전자(eaeA, ipaH, aggR, LT, STh, STp, stx1, stx2, bfp, lacY, 16srRNA)에 대한 Primer set 및 Primer/Probe set을 개발하였음.
● Real-time PCR의 위양성 및 위음성 단점을 보완하기 위하여 IAC(내재증폭대조유전자)를 개발하였음.
● 병원성 대장균 5종류를 신속하게 동시 검출할 수 있는 Multiplex Conventional PCR 및 IAC 포함 multiplex real-time PCR 검출법을 개발하였음.
● 개발된 PCR 키트에 대한 AOAC 검증방법을 차용한 현장 적용 테스트 및 검증으로 병원성 대장균 및 기타 식중독균의 검출 시험 및 인위접종 시료를 통해 일선 현장에서 사용시 그 유효성을 입증하였음.
● 따라서 본 연구를 통하여 시료 내 존재하는 병원성 대장균의 신속검출을 위한 PCR 키트 개발을 성공적으로 달성하였음.
1. multiplex PCR and real-time PCR detection kits for emetic and enterotoxigenic B. cereus
● Bacillus cereus comprises the largest group of endospore-forming bacteria and can cause emetic and diarrheal food poisoning. It is widespread in nature and therefore, considered a major foodborne pathogen
1. multiplex PCR and real-time PCR detection kits for emetic and enterotoxigenic B. cereus
● Bacillus cereus comprises the largest group of endospore-forming bacteria and can cause emetic and diarrheal food poisoning. It is widespread in nature and therefore, considered a major foodborne pathogen. There is a growing demand for fast, accurate, reliable and economic detection of potentially toxigenic B. cereus. A multiplex PCR assay for the rapid detection of enterotoxic and emetic strains in Bacillus cereus was developed and evaluated among B. cereus emetic and enterotoxic reference strains, B. cereus group members and non-target strains.
● A total of 496 B. cereus strains isolated from various sources (food, environmental, clinical) were assessed by a multiplex PCR for the presence of enterotoxin genes. The prevalence rate of nheA, entFM, hblC, and cytK enterotoxin genes among all B. cereus strains was 92.33%, 77.21%, 59.47%, and 47.58%, respectively. Enterotoxigenic profiles were determined in emetic toxin- (8 patterns) and enterotoxin-producing strains (12 patterns). The results provide important information on toxin prevalence and toxigenic profiles of B. cereus from various sources. Our findings revealed that B. cereus must be considered a serious health hazard and Bacillus thuringiensis should be considered of a greater potential concern to food safety among all B. cereus group members. Also, there is need for intensive and continuous monitoring of products embracing both emetic-toxin and enterotoxin genes.
● Design and verification of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd primer sets for PCR kits. All primer sets were designed specifically to target genes for B. cereus group (groEL), diarrheal (cytK, nheA, hblC, entFM) and emetic strains (CER or ces) and the specificity, sensitivity and detection limits of the primer sets-based PCR approaches were confirmed on pure culture and inoculated foods. The minimum detection limits of PCR approaches using the 1st, 2nd and 3rd primer sets were respectively 20, 2, and 0.2 pg of DNA per reaction tube in pure culture and also respectively 103, 103 and 103 cfu/g in food samples in artificial contamination of seven different food matrices with distinct bacterial counts and improved approximately 101 cfu/g after 7 h enrichment. The sizes of PCR product using the 2nd or 3rd primer sets were 488, 376, 163, 106, and 70 bp, or 255, 163, 127, 97 and 81 bp for entFM, nheA, hblD, cytK and ces respectively.
● Development and validation of multiplex PCR and real-time PCR kits. A highly sensitive pentaplex real-time PCR high resolution melt curve assay using the 3rd primer set was developed for simultaneous detection of 4 major enterotoxin and 1 emetic genes. The average melting temperatures (Tm) of PCR products were 72.20℃, 74.23℃, 76.55℃, 78.42℃ and 81.90℃ for ces, cytK, nheA, entFM and hblD, respectively. The inclusivity and exclusivity of the multiplex assay were evaluated using 71 bacterial strains including 17 emetic B. cereus reference strains, 9 enterotoxic B. cereus reference strains, 4 B. cereus group members, 23 wild B. cereus strains, 18 non-target strains, and was further tested on artificially inoculated foods. The DNA intercalating dye SYTO9 used in this study generated higher resolution melt curve peaks than SYBR Green dye for the target strains and genes in which the peaks were sharp and easily distinguishable from each other. The developed kits were validated by the same modified method based on the AOAC validation protocol in three independent laboratories from different cities. The validation results presented that the multiplex real-time kit was better than the multiplex PCR kit and the conventional culture method in sensitivity and specificity in pure cultures of B. cereus, artificially inoculated foods and naturally contaminated foods. Taken together, the developed multiplex PCR and multiplex real-time PCR kits can be the rapid and reliable tools for the simultaneous monitoring of both emetic and enterotoxic strains of B. cereus present in food and food-related samples.
● To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that an assay for simultaneous detection of B. cereus group, emetic and enterotoxic strains with such a wide range of detection target genes in food and environmental samples has been described.
2. multiplex PCR detection kits for 5 pathotypes of pathogenic E. coli
● Escherichia coli is the predominant facultative organism in the human gastrointestinal tract. Strains of pathogenic E. coli (PEC), which have acquired virulence factors, have the ability to cause foodborne and waterborne disease in human. Of the strains that cause diarrheal diseases, five pathotypes are recognized. But PEC strains display a heterogeneous range of phenotypic properties making it difficult to find a common agar to selectively and differentially recover these pathogens. Different molecular methods are used for identification of PEC, and these methods are based on genes related to the pathogenicity of each category. The prevent study was undertaken to establish a rapid PCR system for identification of the main five prevalent categories of PEC and a real-time PCR assay incorporating an internal amplification control (IAC).
● To develop a PCR for PEC detection, we analyzed genetic information of virulence genes and established system of Conventional PCR and Real-time PCR which based genetic marker. And we developed and evaluated an IAC which could effectively eliminate false-negative results. Multiplex PCR kits, Real-time PCR kits and IAC kits for PEC were developed and validation testing was conducted using food samples spiked with PEC.
● Therefore in this study, we developed Multiplex Conventional PCR and Real-time PCR for PEC detection. We established primer set and primer/probe set for the identification of PEC virulence genes (eaeA, ipaH, aggR, LT, STd, STp, stx1, stx2, bfp, lacY and 16s rRNA) and developed IAC kit by using the Sequence of Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus enabling the distinction of true negative results from false negative results caused by PCR malfunction. The effectiveness of developed PCR kits were verified with detection of pathogenic E. coli, other foodborne pathogens and food samples artificial inoculation. Throughout this study it was successfully achieved the development of PCR kits for the rapid detection of pathogenic E. coli present in the sample.
● The PCR kits for pathogenic E. coli can be used for rapid and an efficient detecting of PEC containing food samples. These kits are a useful tool to clarify the source and routes of Pathogenic E. coli.
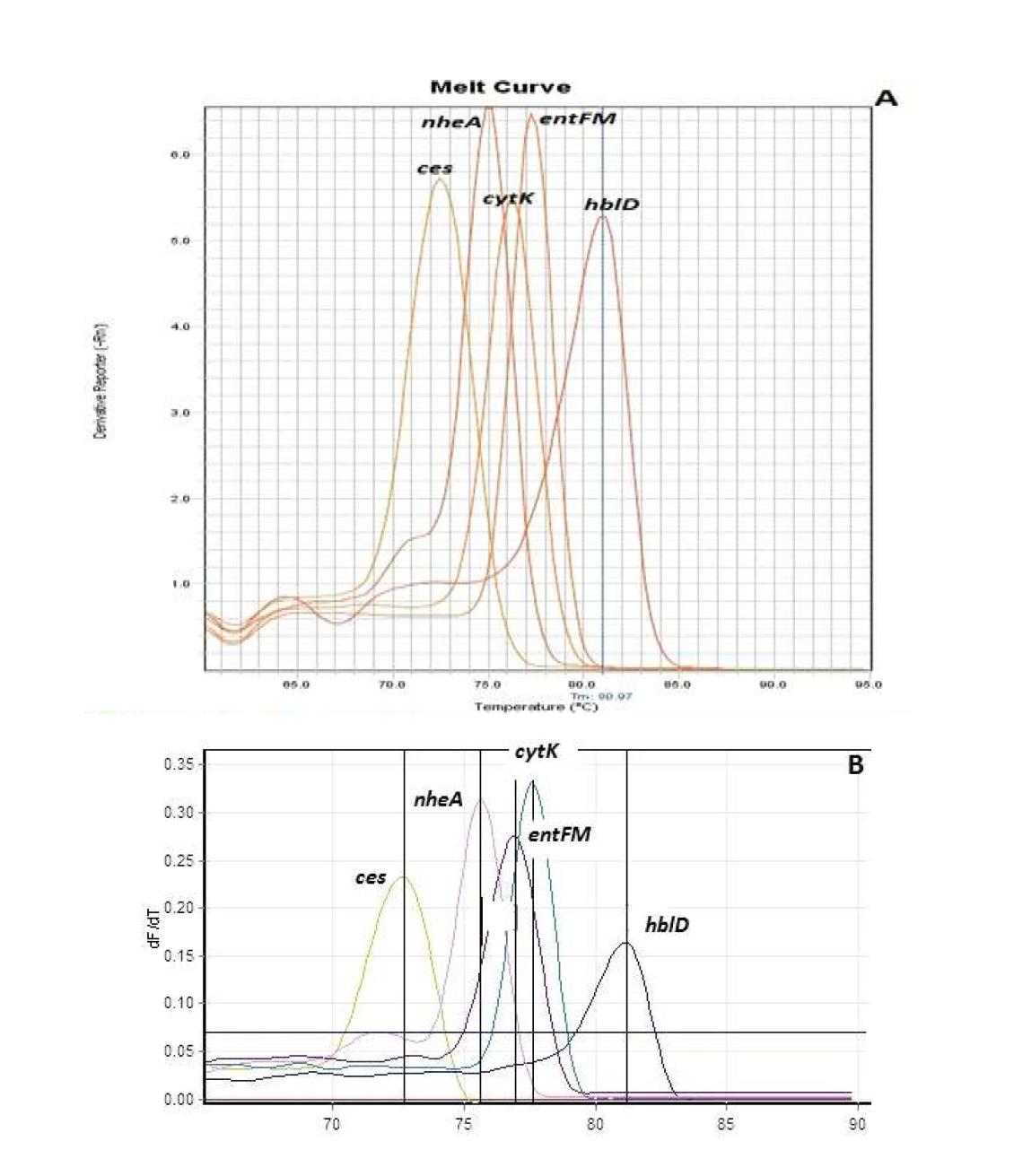 표
Melting curves of different genes in singleplex real time PCR (2nd set of primers) using (A) StepOne PCR machine: cytK: Tm 76.21°C, nheA: Tm 75.47°C, entFM: Tm 77.91°C, ces: Tm 72.57, hblD: Tm 81.05°C; (B) Rotor Gene 6000 real time PCR machine: cytK: Tm 76.31°C, nheA: Tm 75.55°C, entFM: Tm 77.51°C, ces: Tm 72.57, hblD: Tm 81.01°C
표
Melting curves of different genes in singleplex real time PCR (2nd set of primers) using (A) StepOne PCR machine: cytK: Tm 76.21°C, nheA: Tm 75.47°C, entFM: Tm 77.91°C, ces: Tm 72.57, hblD: Tm 81.05°C; (B) Rotor Gene 6000 real time PCR machine: cytK: Tm 76.31°C, nheA: Tm 75.55°C, entFM: Tm 77.51°C, ces: Tm 72.57, hblD: Tm 81.01°C
 표
Melting curves of different genes in singleplex real time PCR (2nd set of primers) using (A) StepOne PCR machine: cytK: Tm 76.21°C, nheA: Tm 75.47°C, entFM: Tm 77.91°C, ces: Tm 72.57, hblD: Tm 81.05°C; (B) Rotor Gene 6000 real time PCR machine: cytK: Tm 76.31°C, nheA: Tm 75.55°C, entFM: Tm 77.51°C, ces: Tm 72.57, hblD: Tm 81.01°C
표
Melting curves of different genes in singleplex real time PCR (2nd set of primers) using (A) StepOne PCR machine: cytK: Tm 76.21°C, nheA: Tm 75.47°C, entFM: Tm 77.91°C, ces: Tm 72.57, hblD: Tm 81.05°C; (B) Rotor Gene 6000 real time PCR machine: cytK: Tm 76.31°C, nheA: Tm 75.55°C, entFM: Tm 77.51°C, ces: Tm 72.57, hblD: Tm 81.01°C
해당 보고서가 속한 카테고리에서 활용도가 높은 상위 5개 콘텐츠를 보여줍니다.
더보기 버튼을 클릭하시면 더 많은 관련자료를 살펴볼 수 있습니다.
| 과제명(ProjectTitle) : | - |
|---|---|
| 연구책임자(Manager) : | - |
| 과제기간(DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 총연구비 (DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 키워드(keyword) : | - |
| 과제수행기간(LeadAgency) : | - |
| 연구목표(Goal) : | - |
| 연구내용(Abstract) : | - |
| 기대효과(Effect) : | - |
| 내보내기 구분 |
|
|---|---|
| 구성항목 |
관리번호, 제목(한글), 저자명(한글), 발행일자, 전자원문, 초록(한글), 초록(영문) 관리번호, 제목(한글), 제목(영문), 저자명(한글), 저자명(영문), 주관연구기관(한글), 주관연구기관(영문), 발행일자, 총페이지수, 주관부처명, 과제시작일, 보고서번호, 과제종료일, 주제분류, 키워드(한글), 전자원문, 키워드(영문), 입수제어번호, 초록(한글), 초록(영문), 목차 |
| 저장형식 |
|
| 메일정보 |
|
| 안내 |
총 건의 자료가 검색되었습니다. 다운받으실 자료의 인덱스를 입력하세요. (1-10,000) 검색결과의 순서대로 최대 10,000건 까지 다운로드가 가능합니다. 데이타가 많을 경우 속도가 느려질 수 있습니다.(최대 2~3분 소요) 다운로드 파일은 UTF-8 형태로 저장됩니다. ~ |
Copyright KISTI. All Rights Reserved.
AI-Helper는 오픈소스 모델을 사용합니다. 사용하고 있는 오픈소스 모델과 라이센스는 아래에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
AI-Helper uses Open Source Models. You can find the source code of these open source models, along with applicable license information below. (helpdesk@kisti.re.kr)
OpenAI의 API Key를 브라우저에 등록하여야 ChatGPT 모델을 사용할 수 있습니다.
등록키는 삭제 버튼을 누르거나, PDF 창을 닫으면 삭제됩니다.

※ AI-Helper는 부적절한 답변을 할 수 있습니다.