최소 단어 이상 선택하여야 합니다.
최대 10 단어까지만 선택 가능합니다.
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
NTIS 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
DataON 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Edison 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Kafe 바로가기
| 주관연구기관 | 국립기상과학원 National Institute of Meteorological Research |
|---|---|
| 연구책임자 | 최병철 |
| 참여연구자 | 주상원 , 전계학 , 심재관 , 김희원 , 김현봉 , 박창근 , 김건태 , 김선정 , 김유준 , 김해민 , 김현욱 , 남형구 , 안보영 , 이진화 , 인소라 , 정승필 , 정종혁 |
| 보고서유형 | 최종보고서 |
| 발행국가 | 대한민국 |
| 언어 | 한국어 |
| 발행년월 | 2017-12 |
| 과제시작연도 | 2017 |
| 주관부처 | 기상청 Korea Meteorological Administration(KMA) |
| 등록번호 | TRKO201800035587 |
| 과제고유번호 | 1365002480 |
| 사업명 | 기상업무지원기술개발연구 |
| DB 구축일자 | 2018-07-21 |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.23000/TRKO201800035587 |
Ⅳ. 연구 내용 및 결과
○ 2017년 모바일 기상관측차량을 활용한 동계 집중관측(ICE-POP, TEST EVENT)과 하계 집중관측(산악기상연구), AWS 비교관측, 관측지원 등이 이루어 졌다. 특히 2018년 평창올림픽과 연계하여 겨울철 강설에 대한 관측을 지속적으로 수행하였다. 모바일 관측차량에 대한 부수적인 성과로 헬륨가스 압력용기 적재 장치의 개선에 대한 발명품 특허를 출원하였으며, 기상라이다시스템의 경우는 운영과 점검에 대한 노하우를 기술하여 향후 활용에 대비하였다.
관측자료를 활용한 다양한 연구를 수
Ⅳ. 연구 내용 및 결과
○ 2017년 모바일 기상관측차량을 활용한 동계 집중관측(ICE-POP, TEST EVENT)과 하계 집중관측(산악기상연구), AWS 비교관측, 관측지원 등이 이루어 졌다. 특히 2018년 평창올림픽과 연계하여 겨울철 강설에 대한 관측을 지속적으로 수행하였다. 모바일 관측차량에 대한 부수적인 성과로 헬륨가스 압력용기 적재 장치의 개선에 대한 발명품 특허를 출원하였으며, 기상라이다시스템의 경우는 운영과 점검에 대한 노하우를 기술하여 향후 활용에 대비하였다.
관측자료를 활용한 다양한 연구를 수행하였다. PARSIVEL을 이용하여 눈 밀도를 예상하고, 이를 기상재해 방재 등 다양한 분야에 활용하고자 하였으며, 강우운동에너지의 지역적 특성을 분석하였다. 차량의 GNSS 관측장비를 활용한 관측을 통해 수증기 임계값을 비교하였으며, 영동지역의 강수 발생을 위한 수증기 임계값은 6mm이고, 8mm 이상일 때 강한 강수의 빈도가 높게 나타났다. 강수 전 구름에 대하여 스캔라이다와 레윈존데자료를 분석한 결과 운저에서 과냉각수적 층을 관측하였으며, 운저아래에서 대기수상체들 간의 결착(riming)현상이 일어나는 것을 관측하였다.
2017년 여름철 집중관측은 남부지역의 집중관측은 거창관측소에서 5일간 수행하였으며, 레윈 존데 분석결과 대기하층(< 3 km)에서 높은 상대습도(>80%)와 상당온위(>240 K)가 관측되었다. 또한, 풍상측(거창)의 강수량(31.3mm)과 강수 빈도는 남부 산악지역(가야산, 북상) 보다 높았으며, 주풍향의 영향을 받은 가야산(26mm)이 북상(8mm)에 비해 3배 이상의 많은 강수량을 나타냈다.
수증기와 강수의 연관성 분석을 통해 강수 발생을 위한 수증기 임계값은 40mm 정도였으며, 60mm 근처에서 강한 강수가 발생하였다. COMS 위성자료 분석을 통해 지상에서 강수가 관측되었던 시각에 구름이 급격하게 발달하는 것을 확인 하였다.
○ 수치모델의 시·공간적 한계를 극복하고자 UM모델과 더불어, 중규모 모델(WRF)과 구름 분해 모델(CReSS)을 통한 고해상도 재해기상 예보·분석 시스템을 구축하였다. 이를 활용하여 2017년에 발생한 집중호우, 대설, 우박, 낙뢰 등 총 38개 사례를 분석하였으며, 사례에 대한 분류와 상세분석을 추가 수행이 필요하다.
재해기상에 대한 이해를 높이기 위해 고해상도 수치모델을 활용한 연구를 수행하였다. 2016년 8월 29일 울릉도에서 발생한 집중호우사례의 경우 울릉도 북쪽의 한기와 남쪽의 난기가 수렴하면서 집중호우가 발생하였고, 지형효과에 의해 남쪽에 강수가 집중되었다. 강설 메커니즘을 보기 위하여 2016년 2월 23~24일과 12월 13~14일에 발생한 강설 에피소드에 대한 집중관측 및 수치 모의 실험을 수행하였다. 구름분해모델(CReSS)의 모의 결과, 상당온위의 연직 구조와 상·하층간 윈드 시어, 구름층의 위치와 강수 유형의 변화 경향 등 관측된 특성을 잘 재현하였다. 관측과 모델링 결과로부터 눈결정 특성은 주로 850hPa 온도에 의해 결정되는 것으로 판단된다. 이례적으로 2017년 1월 20일에는 뇌전을 동반한 대설 사례가 발생하여 이에 대한 대류운 발생 메커니즘을 분석하였다. 이때 해수온도가 높고, 상층의 –42 ℃한기가 남하하였다. 모의된 해기차가 25.56 ℃ 으로 대기 상·하층간의 기온차이가 커 대기불안정이 나타났으며, 그 결과 강설을 유발하는 운정고도–40℃이하의 대류성 구름이 크게 발달하였다. 또한 LDAPS 분석장과 강릉과 대관령에서 레윈존데 관측자료를 이용하여 겨울철 강수 사례에 LDAPS 분석장 검증을 수행하였다. 강릉의 기온편차는 –1~1℃도의 분포를 보였으며, 대관령은 3~5℃의 분포를 보였다. 습도 편차는 강릉의 경우 –10~5%, 대관령은 –5 ~15%로 나타났다.
○ 본 연구에서는 영향예보의 기반마련을 위해 자기조직화지도를 활용하여 적설동질지역을 구분하여 지역별 적설 특징을 분석했다. 적설동질지역은 7개 군집으로 나타났으며, 강설량 및 관측일수, 최대강설량을 이용하여 각 그룹의 특징을 구분했다. 호우 재해를 이해하고 대비하기 위한 연구로 수정 가능한 공간 단위 문제(MAUP; Modifiable Areal Unit Problem)를 적용하여 호우 재해의 취약성의 변화를 비교 분석하였다. 재해 발생 빈도와 같이 공간 구획의 변화에 따라 피해의 규모가 누적 되거나 나뉘는 경우 연구의 결과는 공간 구분에 따라 많은 차이가 발생한다. 강수의 차등화 방안에 대해서는 재해 유발 강우량을 고려한 지역별 위험기준강우량의 차등화를 포함하여, 시·공간 단계의 해상도를 높이고자 하였다. 3시간, 6시간으로 구분된 이동누적강우량 자료의 누적분포 분석을 통하여 관심, 주의, 경계, 심각의 4단계의 위험 기준 강우량을 지역별로 분석하였다. 위험기준 강우량은 피해 발생 후 지역별로 복구 및 개선된 사항을 고려한다면, 향후 위험 기준을 주기적으로 조정해야 할 것으로 판단된다. 또한, 태풍에 의한 피해 연구는 과거에 영향을 미친 태풍에 대해서 강우 분포의 패턴을 중점으로 유사한 특징을 가진 최적군집의 개수를 산출했다. 그 결과, 우리나라 태풍 영향기간 중 유사한 특징을 나타내는 강우 분포의 최적군집 개수는 12개로 산출되었으며, 이동경로가 다르더라도 강우의 패턴이 유사하게 나타날 수 있음이 확인되었다.
(출처 : 요약문 19p)
Ⅳ Contents and Results
○ In 2017, mobile observation vehicle with upper air observation was operated during the period of winter intensive observation(ICE-POP, TEST-EVENT), summer intensive observation, AWS comparative observation, etc. For the lidar mobile vehicles, we described the know-how of
Ⅳ Contents and Results
○ In 2017, mobile observation vehicle with upper air observation was operated during the period of winter intensive observation(ICE-POP, TEST-EVENT), summer intensive observation, AWS comparative observation, etc. For the lidar mobile vehicles, we described the know-how of operation and maintenance of “Lidar observation vehicle”. Also, the pressure vessel loading device inside the mobile observation vehicle was improved and was patented.
We used PARSIVEL to predict snow density and applied it to various fields such as weather disaster prevention and to analyze the regional characteristics of rainfall kinetic energy. We conducted target observation using the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) datasets of mobile observation vehicles during the intensive observation period in winter 2016. As a result, the threshold of water vapor that could cause precipitation in the Yeongdong region is 6 mm, and heavy precipitation frequently occurred especially when it was greater than 8 mm. There is precipitation phenomenon at observation site due to rain front followed expansion and decline of the North Pacific high pressure and typhoon “Nanmadol”. It was possible to confirm that warm moist air flow over the south sea flowed on the observation site whereby high relative humidity (>80%) and equivalent potential temperature ( > 240 K) from rawinsonde were observed. The threshold of water vapor that could cause precipitation for the three sites is 40 mm, and heavy precipitation frequently occurred especially when it was around 60 mm.
○ The HIWRC has constructed a high-resolution disaster weather forecasting and analysis system through a medium-scale model (WRF) and cloud resolving storm model (CReSS). Utilizing these system we analyzed 38 cases including heavy rainfall, heavy snow, hail and lightning during 2017. In the future, the HIWRC will carry out additional analysis on various cases and provide the results of various models at the same time. We analyzed the heavy rainfall case in Ulleungdo on 29 August 2016 using high-resolution numerical simulation. This case was caused by convergence of the cold wind and warm wind from the north and south, respectively. And precipitation was concentrated in the south region of Ulleungdo by the topography effect. Using high resolution disaster weather forecasting analysis system, we analyzed the mechanism of the convective cloud occurrence in the January 20, 2017 case which caused heavy snowfall in the Youngdong area of Gangwon. At this time, the temperature of the sea surface was high, and the –42 °C in the upper layer to descended to the lower layer. The simulated temperature difference between the sea surface and the upper air was 25.56 °C. We investigated the intensive observation and numerical simulation of cold clouds and snow crystal characteristics for two snowfall episodes that occurred on 23-24 February and 13-14 December, 2016. The CReSS successfully represented the variations of snow crystal habits (riming to dendrite) as well as cloud locations along with the clear wind shear and vertical structures of equivalent potential temperature. The observation and model simulations clearly suggested that snow crystal habits predominantly depend on the 850-hPa temperature. An observation system experiment was conducted to investigate the effects of radiosonde observations carried out at Geochang meteorological observatory in 2017 on the prediction performance of UM LDAPS. The temperature bias distribution of Gangneung was –1~1℃, and Daegwallyeong was 3~5℃. Relative humidity bias was –10~5% in Gangneung and –5~15% in Daegwallyeong.
○ We need to analyze the climatic characteristics of each region. In this study, homogeneous regions for snowfall analysis were classified using Self-Organizing Map for impact-based forecast and warning services. As a result, homogeneous regions of snowfall were analyzed into 7 clusters and the characteristics of each group were analyzed. MAUP (modifiable areal unit problem) was applied to analyze the changes in the vulnerability of heavy rain disasters. If the scale of the damage is accumulated according to the change of the space compartment, such as the frequency of the disaster, the result will vary greatly. Risk-based rainfall has been attempted to improve the resolution of city, space, and stage, including the differentiation of risk-based rainfall by region considering disaster-induced rainfall. Three hours, and six hours accumulative rainfall data were analyzed for categorising the four levels of rainfall amount of interest, attention, boundary, and serious. A number of optimal clusters with similar characteristics was calculated based on the distribution pattern of rainfall for typhoons that affected the past. As a result, the optimum number of clusters of rainfall distribution, which showed similar characteristics during typhoon effect period in Korea, was calculated as 12. According to the cluster analysis result, even if the path of the typhoon is similar, the pattern of rainfall may be different.
Also, the pattern of rainfall may be similar even if the path is different.
(출처 : Summary 24p)
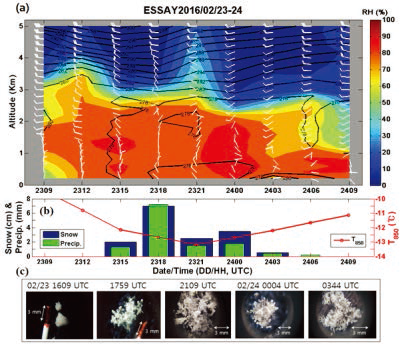 표
Time series of (a) thermodynamic profiles, (b) snow and precipitation amounts along with 850hPa temperature, and (c) main snow crystal habits for Episode 1. The white flag, shading, and black line in Fig. 3.1.4.2 denote wind (unit; ms-1), relative humidity, and equivalent potential temperature, respectively
표
Time series of (a) thermodynamic profiles, (b) snow and precipitation amounts along with 850hPa temperature, and (c) main snow crystal habits for Episode 1. The white flag, shading, and black line in Fig. 3.1.4.2 denote wind (unit; ms-1), relative humidity, and equivalent potential temperature, respectively
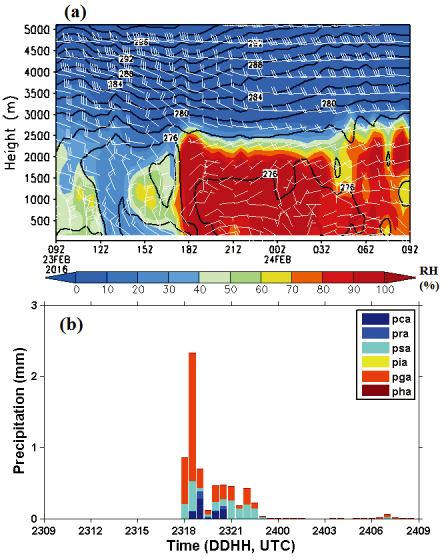 표
Time series of (a) vertical profiles of relative humidity (RH; shading), equivalent potential temperature (black line), and wind (white flag, unit; ms-1) and (b) accumulated precipitation of cloud water (pca), rain (pra), snow (psa), cloud ice (pia), graupel (pga), and hail (pha) derived from the CReSS simulations for Episode 1. All outputs were extracted at 30-min interval
표
Time series of (a) vertical profiles of relative humidity (RH; shading), equivalent potential temperature (black line), and wind (white flag, unit; ms-1) and (b) accumulated precipitation of cloud water (pca), rain (pra), snow (psa), cloud ice (pia), graupel (pga), and hail (pha) derived from the CReSS simulations for Episode 1. All outputs were extracted at 30-min interval
 표
Time series of (a) thermodynamic profiles, (b) snow and precipitation amounts along with 850hPa temperature, and (c) main snow crystal habits for Episode 1. The white flag, shading, and black line in Fig. 3.1.4.2 denote wind (unit; ms-1), relative humidity, and equivalent potential temperature, respectively
표
Time series of (a) thermodynamic profiles, (b) snow and precipitation amounts along with 850hPa temperature, and (c) main snow crystal habits for Episode 1. The white flag, shading, and black line in Fig. 3.1.4.2 denote wind (unit; ms-1), relative humidity, and equivalent potential temperature, respectively
 표
Time series of (a) vertical profiles of relative humidity (RH; shading), equivalent potential temperature (black line), and wind (white flag, unit; ms-1) and (b) accumulated precipitation of cloud water (pca), rain (pra), snow (psa), cloud ice (pia), graupel (pga), and hail (pha) derived from the CReSS simulations for Episode 1. All outputs were extracted at 30-min interval
표
Time series of (a) vertical profiles of relative humidity (RH; shading), equivalent potential temperature (black line), and wind (white flag, unit; ms-1) and (b) accumulated precipitation of cloud water (pca), rain (pra), snow (psa), cloud ice (pia), graupel (pga), and hail (pha) derived from the CReSS simulations for Episode 1. All outputs were extracted at 30-min interval
| 과제명(ProjectTitle) : | - |
|---|---|
| 연구책임자(Manager) : | - |
| 과제기간(DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 총연구비 (DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 키워드(keyword) : | - |
| 과제수행기간(LeadAgency) : | - |
| 연구목표(Goal) : | - |
| 연구내용(Abstract) : | - |
| 기대효과(Effect) : | - |
Copyright KISTI. All Rights Reserved.

※ AI-Helper는 부적절한 답변을 할 수 있습니다.