최소 단어 이상 선택하여야 합니다.
최대 10 단어까지만 선택 가능합니다.
SAI
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
NTIS 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
DataON 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Edison 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Kafe 바로가기
| 주관연구기관 | 서울대학교 Seoul National University |
|---|---|
| 연구책임자 | Takuji Oda |
| 보고서유형 | 최종보고서 |
| 발행국가 | 대한민국 |
| 언어 | 한국어 |
| 발행년월 | 2019-08 |
| 과제시작연도 | 2018 |
| 주관부처 | 과학기술정보통신부 Ministry of Science and ICT |
| 연구관리전문기관 | 한국연구재단 National Research Foundation of Korea |
| 등록번호 | TRKO201900021946 |
| 과제고유번호 | 1711076236 |
| 사업명 | 원자력연구기반확충사업(R&D) |
| DB 구축일자 | 2020-05-23 |
| 키워드 | 액체금속.불순물.용해도.확산도.양자역학 계산.Liquid metal.Impurity.Solubility.Diffusivity.QM calculation. |
본 연구과제는 양자 역학 계산에 기반을 둔 전산 기법을 개발하여 액체 금속 내 불순물 원자의 용해도 및 확산도를 정확하게 계산하고, 이를 바탕으로 몇몇 중요한 불순물의 거동에 대한 이해를 심화하는 것을 목표로 하였다. 구체적으로, 밀도함수이론(DFT)을 기반으로 적합한 양자 역학 계산 방법을 선택하여 액체 금속(소듐, 납)에 대한 제일 원리 분자동역학 시뮬레이션을 수행하였고, 진동 분석 및 준조화 근사계산을 통하여 고온에서 기체 분자 및 고체 결정의 에너지를 계산하였다. 또한, EAM 퍼텐셜 모델을 액체 금속에 대하여 구축하여 DF
본 연구과제는 양자 역학 계산에 기반을 둔 전산 기법을 개발하여 액체 금속 내 불순물 원자의 용해도 및 확산도를 정확하게 계산하고, 이를 바탕으로 몇몇 중요한 불순물의 거동에 대한 이해를 심화하는 것을 목표로 하였다. 구체적으로, 밀도함수이론(DFT)을 기반으로 적합한 양자 역학 계산 방법을 선택하여 액체 금속(소듐, 납)에 대한 제일 원리 분자동역학 시뮬레이션을 수행하였고, 진동 분석 및 준조화 근사계산을 통하여 고온에서 기체 분자 및 고체 결정의 에너지를 계산하였다. 또한, EAM 퍼텐셜 모델을 액체 금속에 대하여 구축하여 DFT 계산 결과 및 실험 결과를 합리적인 수준으로 재현하였다. 이를 통하여 액체 금속 내 불순물의 용해도 및 확산도를 계산하는 방법론을 성공적으로 개발하였고, 계산 결과를 바탕으로 액체 금속 내 불순물의 물리·화학적 상태에 대한 세밀한 분석을 진행하였다. 용해도 및 확산도의 경우 실험 데이터와 비교하였을 때 합리적인 수준에서 정확하게 계산됨을 확인하였다. 결론적으로, 액체 금속의 불순물 거동을 체계적으로 설명하기 위한 이론적 개념을 정립하였다.
(출처 : 보고서 요약서 3p)
□ 연구의 목적 및 내용
Liquid Na and liquid Pb are promising coolant materials which will be used in some generation IV reactors. In comparison with water, however, the experience and knowledge accumulated for the utilization of liquid metals are limited.
The solubility and diffusivity of impurities i
□ 연구의 목적 및 내용
Liquid Na and liquid Pb are promising coolant materials which will be used in some generation IV reactors. In comparison with water, however, the experience and knowledge accumulated for the utilization of liquid metals are limited.
The solubility and diffusivity of impurities in liquid metals are important properties to understand the material corrosion and the radionuclides transport phenomena. For evaluation of these by experiments, several difficulties in handling of liquid metals, such as high reactivity, difficult purity control, high temperature, etc, make it take long time and large cost to accurately determine the solubility and diffusivity.
In this project, therefore, we have developed a computational method based on quantum mechanical calculation to accurately determine solubility and diffusivity of impurity atoms in liquid metals at much shorter time and lower cost than experiments. In addition, we applied the developed methods to some important impurities to deepen the understanding of impurity behaviors in liquid metal.
To achieve ghis goal, we worked on the following three subjects in this project.
1. Selection of select a quantum mechanical (QM) calculation suitable for liquid metals: Because QM calculation includes several approximations in it, we first need to choose appropriate approximations that can give good results for the purpose of this project.
2. Development of method to determine solubility and diffusivity of impurity in liquid metals: For evaluation of solubility and diffusivity, we need to develop a method to simulate energies of materials at high temperatures. These methods should be coupled with the QM calculation selected in Subject-1 to achieve high accuracy.
3. Benchmark test of the developed method and its application to important impurities: To ensure the validity of the developed method, we need to do benchmark tests. After the confirmation of validity, we can apply the method to various important impurities, such as H, Cs, Sr, Fe, I, Xe and U, in order to acquire a comprehensive understanding of impurity behaviors in the liquid metals.
□ 연구개발성과
○ To solve the three subjects, we set and worked on 9 tasks over 3 years in this project.
○ For Task-1 in 2016, we tested and then selected first-principles calculation based on density functional theory (DFT) with PBE functional as the best method to calculate solubility and diffusivity of impurity in liquid metals.
○ For Taks-2 in 2016, we tested and confirmed with O2 that vibration analysis coupled with the DFT calculation enables us to determine thermodynamic quantities of gaseous impurity at high temperatures accurately.
○ For Taks-3 in 2016, we tested and confirmed with bcc-Fe that vibrational analysis under quasi-harmonic approximation (QHA) combined with DFT-PBE calculation enables us to the energy of impurities whose standard state is solid.
○ For TASK-4 in 2017, we developed a method to construct an embedded-atom method (EAM) potential in a straightforward manner for liquid metals. The energies/forces/stresses of liquids calculated by DFT-PBE were used as the fitting target. Using this method, we successfully generated for liquid Na and liquid Pb including O impurity.
○ For TASK-5 in 2017, we established methods to evaluate solubility and diffusivity of impurity in liquid metals. Then, for TASK-6 in 2017, we have tested the performance of the developed methods. For solubility, O solubility in liquid Na was tested, which suggests that an expected calculation error in the solution enthalpy is around 10-30 kJ/mol. The validity of this suggestion is further confirmed with solution enthalpy calculation of other impurities in TASK 7. For diffusivity, we have calculated self-diffusion coefficients and O diffusion coefficients in liquid Na and liquid Pb. The test results showed that the error from QM calculation is around up to 10%, while the error from experiment is up to 50%.
○ For TASK-7 in 2018, especially for solubility in liquid Na, we applied the developed method to several impurities relevant with safety and corrosion in SFR, including H, Cs, Sr, Fe, I, Xe and U. For many impurities, the calculation errors in the solution enthalpy were less than a few tens of kJ/mol.
○ For TASK-8 in 2018, we investigated (1) chemical states of second-row impurities in liquid LBE and Na, (2) chemical states of 3d-transition metals in liquid LBE and Na, which is important to understand steel corrosion behavior, (3) qualitative and quantitative analysis on chemical states of 3d/4d/5d TM in liquid Na, and (4) effective solution enthalpy of Fe in liquid Na under oxygen-saturated condition. For example, the result of (2) uncovered the reason why steel corrosion severely occurs in liquid Pb and liquid LBE but not in liquid Na were successfully explained.
○ For TASK-9 in 2018, we wrote this report and discussed possible future researches. So far, 3 SCI papers were published, and we have been preparing 2 additional SCI papers.
□ 연구개발성과의 활용계획 (기대효과)
○ The developed method can be applied to all elements in the periodic table. Thus, in future, we can achieve an all-element database of impurity in liquid metal on the physiochemical states, solubility and diffusivity. For example, such database can be used to establish safety regulation, to develop new structural materials, and possibly to develop new liquid metals composed of multiple elements. Clearly, such all-element database for liquid metal have not been established yet, and will be first-of-kind comprehensive database for liquid metal.
○ The findings of this research as well as expected findings that can be achieved from systematic application of the developed methods in near future provide scientific knowledge-base on the chemistry of liquid metals. Such scientific knowledge-base will help not only engineering R&D but also public understanding and acceptance for the use of advanced nuclear systems.
○ In combination with available experimental data, the determined solubility and diffusivity can be used for the safety evaluation of several advanced nuclear systems including SFR, LFR, ADS and fusion reactors.
○ The knowledge on physiochemical states of impurities in liquid Na and liquid Pb-Bi eutectic obtained in this project can be used to interpret experimental results. In addition, it can be used to list up promising structural materials to solve corrosion issues in the use of liquid metals.
(출처 : 영문 요약문 5p)
 표
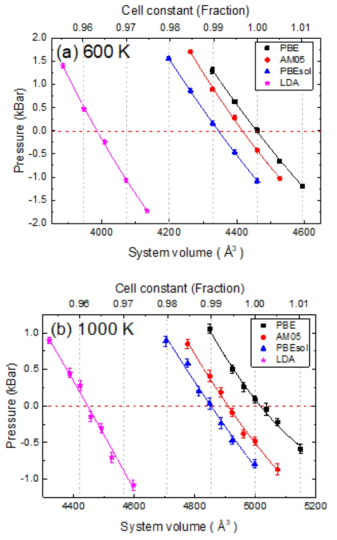
The pressure-volume relation of liquid Na at (a) 600 K and (b) 1000 K. The PBE (black squares), AM05 (red circles), PBEsol (blue triangles) and LDA (pink stars) are presented with the 2nd polynomial fit weighted by the size of error bar of each data point. Error bar sizes are presented to be horizontal lines in each data point
표
The pressure-volume relation of liquid Na at (a) 600 K and (b) 1000 K. The PBE (black squares), AM05 (red circles), PBEsol (blue triangles) and LDA (pink stars) are presented with the 2nd polynomial fit weighted by the size of error bar of each data point. Error bar sizes are presented to be horizontal lines in each data point
 표
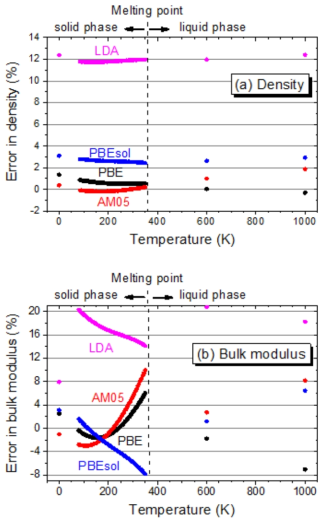
The relative errors of (a) the density and (b) the bulk moduli calculated by four functionals (PBE, AM05, PBEsol and LDA) are presented as a function of temperature. As a reference experiment which is utilized in the present evaluation, the density of Touloukian et al. and bulk moduli of Swanson et al. in the solid state Na, and both properties of Fink et al. in a liquid state Na were used
표
The relative errors of (a) the density and (b) the bulk moduli calculated by four functionals (PBE, AM05, PBEsol and LDA) are presented as a function of temperature. As a reference experiment which is utilized in the present evaluation, the density of Touloukian et al. and bulk moduli of Swanson et al. in the solid state Na, and both properties of Fink et al. in a liquid state Na were used
![Enthalpy (left) and entropy (right) of an O2 molecule as a function of temperature, by vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot) [33]. For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -8.77 kJ/mol and 17.5 J/mol/K, respectively Enthalpy (left) and entropy (right) of an O2 molecule as a function of temperature, by vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot) [33]. For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -8.77 kJ/mol and 17.5 J/mol/K, respectively](https://nrms.kisti.re.kr/bitextimages/TRKO201900021946/TRKO201900021946_37_image_1.png) 표
Enthalpy (left) and entropy (right) of an O2 molecule as a function of temperature, by vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot) [33]. For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -8.77 kJ/mol and 17.5 J/mol/K, respectively
표
Enthalpy (left) and entropy (right) of an O2 molecule as a function of temperature, by vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot) [33]. For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -8.77 kJ/mol and 17.5 J/mol/K, respectively
 표
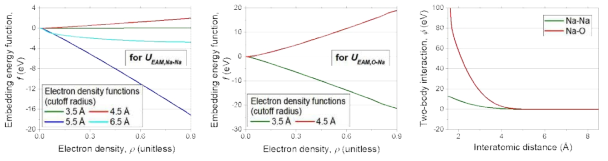
EAM potential model for Na system with O impurity: (left) the embedding energy functions for UEAM,Na-Na, (middle) the embedding energy functions for UEAM,O-Na, and (right) two-body interaction functions for Na-Na and Na-O pairs. For the electron density function, g(r), the form given in Eq. 4.2.3 is utilized. The cutoff values for g(r) functions are given in the figure legends
표
EAM potential model for Na system with O impurity: (left) the embedding energy functions for UEAM,Na-Na, (middle) the embedding energy functions for UEAM,O-Na, and (right) two-body interaction functions for Na-Na and Na-O pairs. For the electron density function, g(r), the form given in Eq. 4.2.3 is utilized. The cutoff values for g(r) functions are given in the figure legends
 표
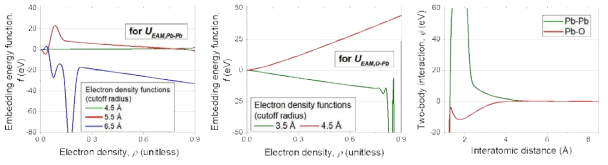
EAM potential model for Pb system with O impurity: (left) the embedding energy functions for UEAM,Pb-Pb, (middle) the embedding energy functions for UEAM,O-Pb, and (right) two-body interaction functions for Na-Na and Na-O pairs. For the electron density function, g(r), the form given in Eq. 4.2.3 is utilized. The cutoff values for g(r) functions are given in the figure legends
표
EAM potential model for Pb system with O impurity: (left) the embedding energy functions for UEAM,Pb-Pb, (middle) the embedding energy functions for UEAM,O-Pb, and (right) two-body interaction functions for Na-Na and Na-O pairs. For the electron density function, g(r), the form given in Eq. 4.2.3 is utilized. The cutoff values for g(r) functions are given in the figure legends
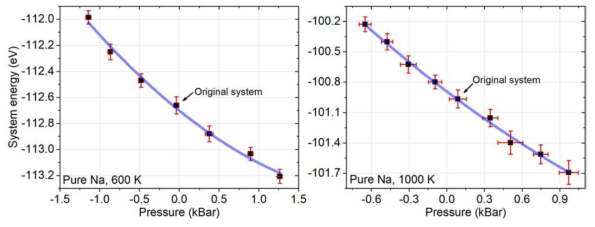 표
Pressure-energy relationships for pure liquid Na at 600 K (left) and at 1000 K (right). Data points of the "Original system" correspond to the energy and pressure in Table 5.1-2. Each error bar includes the SEMs from thermal fluctuations during each simulation and the deviation among three simulations of the same volume
표
Pressure-energy relationships for pure liquid Na at 600 K (left) and at 1000 K (right). Data points of the "Original system" correspond to the energy and pressure in Table 5.1-2. Each error bar includes the SEMs from thermal fluctuations during each simulation and the deviation among three simulations of the same volume
 표
Estimated converged energy and pressure with current system volume at each temperature for O-including liquid Na systems. Using the standard errors of energy and pressure for each simulation in Table 5.1-4, the system energies and pressures in Table 5.1-4 were averaged over three simulations at each temperature
표
Estimated converged energy and pressure with current system volume at each temperature for O-including liquid Na systems. Using the standard errors of energy and pressure for each simulation in Table 5.1-4, the system energies and pressures in Table 5.1-4 were averaged over three simulations at each temperature
![Enthalpy diagram showing calculation results and experimental data. Enthalpy unit: kJ/mol. - Calculation data are colored in red while experimental data are colored in blue and are in parentheses. - The calculation results in Section 5.1.3.3, the O2 solution enthalpy, correspond to process (1). - The available experimental data [41], the Na2O solution enthalpy, correspond to process (2). * Estimated using other experimental data (46.9 kJ/mol) in diagram Enthalpy diagram showing calculation results and experimental data. Enthalpy unit: kJ/mol. - Calculation data are colored in red while experimental data are colored in blue and are in parentheses. - The calculation results in Section 5.1.3.3, the O2 solution enthalpy, correspond to process (1). - The available experimental data [41], the Na2O solution enthalpy, correspond to process (2). * Estimated using other experimental data (46.9 kJ/mol) in diagram](https://nrms.kisti.re.kr/bitextimages/TRKO201900021946/TRKO201900021946_62_image_1.png) 표
Enthalpy diagram showing calculation results and experimental data. Enthalpy unit: kJ/mol. - Calculation data are colored in red while experimental data are colored in blue and are in parentheses. - The calculation results in Section 5.1.3.3, the O2 solution enthalpy, correspond to process (1). - The available experimental data [41], the Na2O solution enthalpy, correspond to process (2). * Estimated using other experimental data (46.9 kJ/mol) in diagram
표
Enthalpy diagram showing calculation results and experimental data. Enthalpy unit: kJ/mol. - Calculation data are colored in red while experimental data are colored in blue and are in parentheses. - The calculation results in Section 5.1.3.3, the O2 solution enthalpy, correspond to process (1). - The available experimental data [41], the Na2O solution enthalpy, correspond to process (2). * Estimated using other experimental data (46.9 kJ/mol) in diagram
![Self-diffusion coefficients (left) and O impurity diffusion coefficients in liquid Pb. In the left figure, Experiment-1 is taken from [G. Mathiak, A. Griesche, K.H. Kraatz, G. Frohberg, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 205–207 (1996) 412]. In the right figure, Experiment-1 is from [B.F. Gromov, B.A. Shmatko, 1997; cited in an IAEA handbook, https://inis.iaea.org/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/46/133/46133907.pdf], Experiment-2 from [S. Otsuka, Z. Kosuka, Metallurgical Transactions B 6 (1975) 389], and Experiment-3 from [H. Charle, J. Osterwald, Z. Phys. Chem. 99 (1976) 199] Self-diffusion coefficients (left) and O impurity diffusion coefficients in liquid Pb. In the left figure, Experiment-1 is taken from [G. Mathiak, A. Griesche, K.H. Kraatz, G. Frohberg, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 205–207 (1996) 412]. In the right figure, Experiment-1 is from [B.F. Gromov, B.A. Shmatko, 1997; cited in an IAEA handbook, https://inis.iaea.org/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/46/133/46133907.pdf], Experiment-2 from [S. Otsuka, Z. Kosuka, Metallurgical Transactions B 6 (1975) 389], and Experiment-3 from [H. Charle, J. Osterwald, Z. Phys. Chem. 99 (1976) 199]](https://nrms.kisti.re.kr/bitextimages/TRKO201900021946/TRKO201900021946_85_image_2.png) 표
Self-diffusion coefficients (left) and O impurity diffusion coefficients in liquid Pb. In the left figure, Experiment-1 is taken from [G. Mathiak, A. Griesche, K.H. Kraatz, G. Frohberg, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 205–207 (1996) 412]. In the right figure, Experiment-1 is from [B.F. Gromov, B.A. Shmatko, 1997; cited in an IAEA handbook, https://inis.iaea.org/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/46/133/46133907.pdf], Experiment-2 from [S. Otsuka, Z. Kosuka, Metallurgical Transactions B 6 (1975) 389], and Experiment-3 from [H. Charle, J. Osterwald, Z. Phys. Chem. 99 (1976) 199]
표
Self-diffusion coefficients (left) and O impurity diffusion coefficients in liquid Pb. In the left figure, Experiment-1 is taken from [G. Mathiak, A. Griesche, K.H. Kraatz, G. Frohberg, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 205–207 (1996) 412]. In the right figure, Experiment-1 is from [B.F. Gromov, B.A. Shmatko, 1997; cited in an IAEA handbook, https://inis.iaea.org/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/46/133/46133907.pdf], Experiment-2 from [S. Otsuka, Z. Kosuka, Metallurgical Transactions B 6 (1975) 389], and Experiment-3 from [H. Charle, J. Osterwald, Z. Phys. Chem. 99 (1976) 199]
![Enthalpy and entropy of an H2 molecule as a function of temperature, calculated from vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot) [33]. For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -8.676 kJ/mol and 8.9 J/mol/K, respectively Enthalpy and entropy of an H2 molecule as a function of temperature, calculated from vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot) [33]. For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -8.676 kJ/mol and 8.9 J/mol/K, respectively](https://nrms.kisti.re.kr/bitextimages/TRKO201900021946/TRKO201900021946_93_image_1.png) 표
Enthalpy and entropy of an H2 molecule as a function of temperature, calculated from vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot) [33]. For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -8.676 kJ/mol and 8.9 J/mol/K, respectively
표
Enthalpy and entropy of an H2 molecule as a function of temperature, calculated from vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot) [33]. For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -8.676 kJ/mol and 8.9 J/mol/K, respectively
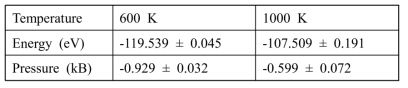
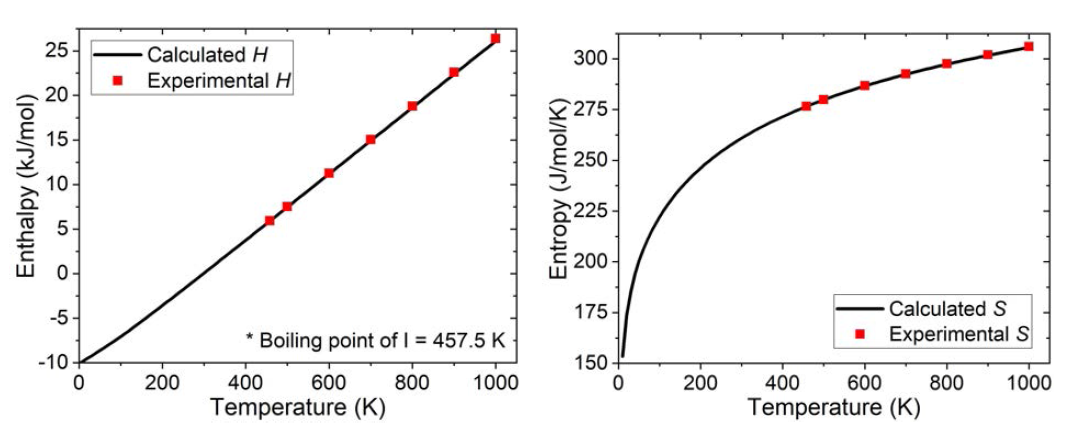 표
Enthalpy and entropy of an I2 molecule as a function of temperature, calculated from vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot). For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -10.091 kJ/mol and 8.7 J/mol/K, respectively
표
Enthalpy and entropy of an I2 molecule as a function of temperature, calculated from vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot). For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -10.091 kJ/mol and 8.7 J/mol/K, respectively
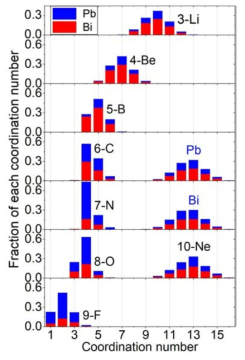 표
Distributions of CNs in FPMD simulations at 1000 K. For each CN bar, partial CN fractions for Pb and Bi are expressed in blue and red colors, respectively. Note that Pb, Bi, and Ne indicate similar distributions with partial CN fractions reflecting the LBE composition (Pb: 44.5 at.% and Bi: 55.5 at.%)
표
Distributions of CNs in FPMD simulations at 1000 K. For each CN bar, partial CN fractions for Pb and Bi are expressed in blue and red colors, respectively. Note that Pb, Bi, and Ne indicate similar distributions with partial CN fractions reflecting the LBE composition (Pb: 44.5 at.% and Bi: 55.5 at.%)
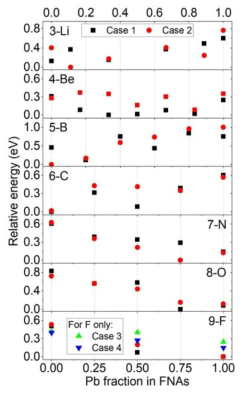 표
Potential energy differences among systems having different FNA compositions. A different “case” means that the initial configuration brought from the FPMD is different. Four cases are examined for F, of which the CN is approximately two. An x value of 0.0 means that the FNAs are all Bi, whereas 1.0 means that the FNAs are all Pb. An increasing tendency suggests the preference for Bi with a decrease in tendency for Pb
표
Potential energy differences among systems having different FNA compositions. A different “case” means that the initial configuration brought from the FPMD is different. Four cases are examined for F, of which the CN is approximately two. An x value of 0.0 means that the FNAs are all Bi, whereas 1.0 means that the FNAs are all Pb. An increasing tendency suggests the preference for Bi with a decrease in tendency for Pb
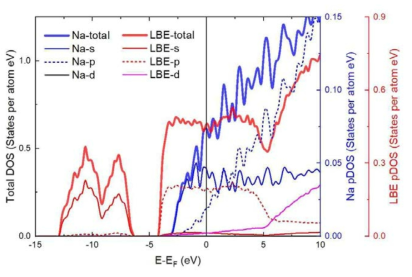 표
Total and partial DOS of pure liquid Na and LBE at 1000 K. The x-axis is the shifted energy level (E-EF) so that the Fermi energy level (EF) lies at 0 eV. The left axis is used for the scale of the total DOS, and the blue and read right axes are used for the scales of the pDOSs of Na and LBE, respectively
표
Total and partial DOS of pure liquid Na and LBE at 1000 K. The x-axis is the shifted energy level (E-EF) so that the Fermi energy level (EF) lies at 0 eV. The left axis is used for the scale of the total DOS, and the blue and read right axes are used for the scales of the pDOSs of Na and LBE, respectively
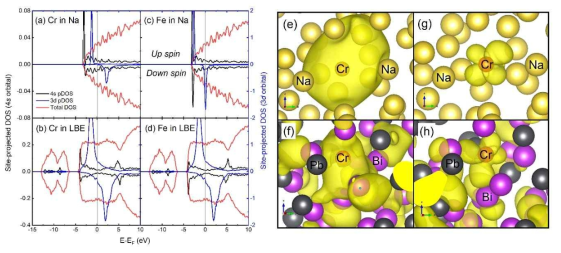 표
(a)-(d) Site-projected DOSs of Cr and Fe in liquid Na and liquid LBE at 1000 K. For each figure, the left and right axes are used for the scales of the 4s and 3d orbitals, respectively. (e)-(h) The isosurfaces of electron charge densities with energies at the first peak position of the Cr-4s band in (e) liquid Na and (f) LBE and at the first peak position of the Cr-3d band in (g) liquid Na and (h) LBE. The small red, large yellow, large black and large purple spheres represent Cr, Na, Pb, Bi atoms, respectively. As an isosurface value, 0.0020 electrons/Å3 is used
표
(a)-(d) Site-projected DOSs of Cr and Fe in liquid Na and liquid LBE at 1000 K. For each figure, the left and right axes are used for the scales of the 4s and 3d orbitals, respectively. (e)-(h) The isosurfaces of electron charge densities with energies at the first peak position of the Cr-4s band in (e) liquid Na and (f) LBE and at the first peak position of the Cr-3d band in (g) liquid Na and (h) LBE. The small red, large yellow, large black and large purple spheres represent Cr, Na, Pb, Bi atoms, respectively. As an isosurface value, 0.0020 electrons/Å3 is used
 표
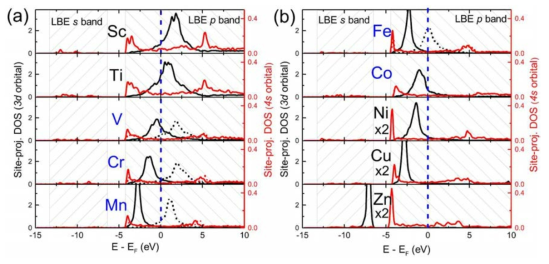
Site-projected DOSs of 3d-TM impurity atoms in liquid Na at 1000 K. The 4s, 4p, and 3d orbitals are presented as the black, red, and blue solid lines, respectively. For each figure, the left axis is used as the scale for s and p orbitals, and the right axis is used as the scale for d orbitals. For the spin-polarized systems, the DOSs of spin-up and spin-down are presented as positive and negative values, respectively
표
Site-projected DOSs of 3d-TM impurity atoms in liquid Na at 1000 K. The 4s, 4p, and 3d orbitals are presented as the black, red, and blue solid lines, respectively. For each figure, the left axis is used as the scale for s and p orbitals, and the right axis is used as the scale for d orbitals. For the spin-polarized systems, the DOSs of spin-up and spin-down are presented as positive and negative values, respectively
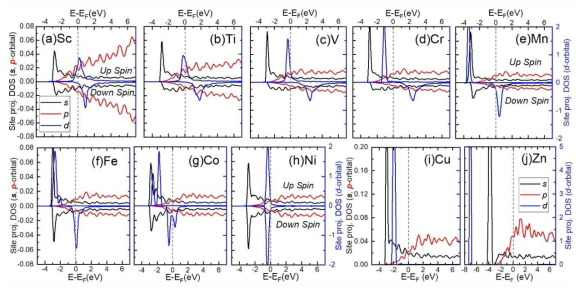
 표
Site-projected partial DOSs of 3d metal impurity atoms (a) Sc-Mn, (b) Fe-Zn dissolved in liquid LBE at 1000 K. The d and s orbitals are portrayed as black and red solid lines, respectively. If the system is spin polarized (from V to Co), spin-up and spin-down states are presented as solid and dash lines, respectively. The regions with slashed lines indicate the LBE 6s and 6p bands. The Fermi energy level lies at 0 eV
표
Site-projected partial DOSs of 3d metal impurity atoms (a) Sc-Mn, (b) Fe-Zn dissolved in liquid LBE at 1000 K. The d and s orbitals are portrayed as black and red solid lines, respectively. If the system is spin polarized (from V to Co), spin-up and spin-down states are presented as solid and dash lines, respectively. The regions with slashed lines indicate the LBE 6s and 6p bands. The Fermi energy level lies at 0 eV
 표
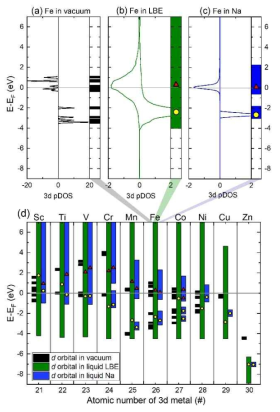
(a)-(c) Partial DOSs of Fe-3d orbitals and the positions and widths of the Fe-3d orbitals with a DOS value larger than 0.02 states per atom eV in a vacuum, liquid LBE, and liquid Na. (d) The positions and widths of 3d orbitals in a vacuum, liquid LBE, and liquid Na as a function of the atomic number for all 3d-TMs. In the liquid systems, the peak positions of the 3d orbitals are presented as yellow circles. When a system is spin-polarized, the peak positions of spin-up and spin-down orbitals are separately shown as yellow circles and red triangles, respectively
표
(a)-(c) Partial DOSs of Fe-3d orbitals and the positions and widths of the Fe-3d orbitals with a DOS value larger than 0.02 states per atom eV in a vacuum, liquid LBE, and liquid Na. (d) The positions and widths of 3d orbitals in a vacuum, liquid LBE, and liquid Na as a function of the atomic number for all 3d-TMs. In the liquid systems, the peak positions of the 3d orbitals are presented as yellow circles. When a system is spin-polarized, the peak positions of spin-up and spin-down orbitals are separately shown as yellow circles and red triangles, respectively
 표
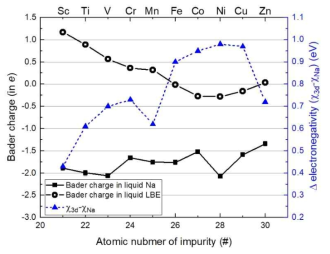
Bader charges of 3d-TM impurity atoms in liquid Na and LBE at 1000 K and the differences in electronegativity between 3d-TMs and Na. The left and right axes are used for the scales of the Bader charge and the electronegativity difference, respectively. The standard errors are displayed as vertical lines for the Bader charge. For the electronegativity, empirical values are used
표
Bader charges of 3d-TM impurity atoms in liquid Na and LBE at 1000 K and the differences in electronegativity between 3d-TMs and Na. The left and right axes are used for the scales of the Bader charge and the electronegativity difference, respectively. The standard errors are displayed as vertical lines for the Bader charge. For the electronegativity, empirical values are used
 표
The pressure-volume relation of liquid Na at (a) 600 K and (b) 1000 K. The PBE (black squares), AM05 (red circles), PBEsol (blue triangles) and LDA (pink stars) are presented with the 2nd polynomial fit weighted by the size of error bar of each data point. Error bar sizes are presented to be horizontal lines in each data point
표
The pressure-volume relation of liquid Na at (a) 600 K and (b) 1000 K. The PBE (black squares), AM05 (red circles), PBEsol (blue triangles) and LDA (pink stars) are presented with the 2nd polynomial fit weighted by the size of error bar of each data point. Error bar sizes are presented to be horizontal lines in each data point
 표
The relative errors of (a) the density and (b) the bulk moduli calculated by four functionals (PBE, AM05, PBEsol and LDA) are presented as a function of temperature. As a reference experiment which is utilized in the present evaluation, the density of Touloukian et al. and bulk moduli of Swanson et al. in the solid state Na, and both properties of Fink et al. in a liquid state Na were used
표
The relative errors of (a) the density and (b) the bulk moduli calculated by four functionals (PBE, AM05, PBEsol and LDA) are presented as a function of temperature. As a reference experiment which is utilized in the present evaluation, the density of Touloukian et al. and bulk moduli of Swanson et al. in the solid state Na, and both properties of Fink et al. in a liquid state Na were used
![Enthalpy (left) and entropy (right) of an O2 molecule as a function of temperature, by vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot) [33]. For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -8.77 kJ/mol and 17.5 J/mol/K, respectively Enthalpy (left) and entropy (right) of an O2 molecule as a function of temperature, by vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot) [33]. For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -8.77 kJ/mol and 17.5 J/mol/K, respectively](https://nrms.kisti.re.kr/bitextimages/TRKO201900021946/TRKO201900021946_37_image_1.png) 표
Enthalpy (left) and entropy (right) of an O2 molecule as a function of temperature, by vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot) [33]. For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -8.77 kJ/mol and 17.5 J/mol/K, respectively
표
Enthalpy (left) and entropy (right) of an O2 molecule as a function of temperature, by vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot) [33]. For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -8.77 kJ/mol and 17.5 J/mol/K, respectively
 표
EAM potential model for Na system with O impurity: (left) the embedding energy functions for UEAM,Na-Na, (middle) the embedding energy functions for UEAM,O-Na, and (right) two-body interaction functions for Na-Na and Na-O pairs. For the electron density function, g(r), the form given in Eq. 4.2.3 is utilized. The cutoff values for g(r) functions are given in the figure legends
표
EAM potential model for Na system with O impurity: (left) the embedding energy functions for UEAM,Na-Na, (middle) the embedding energy functions for UEAM,O-Na, and (right) two-body interaction functions for Na-Na and Na-O pairs. For the electron density function, g(r), the form given in Eq. 4.2.3 is utilized. The cutoff values for g(r) functions are given in the figure legends
 표
EAM potential model for Pb system with O impurity: (left) the embedding energy functions for UEAM,Pb-Pb, (middle) the embedding energy functions for UEAM,O-Pb, and (right) two-body interaction functions for Na-Na and Na-O pairs. For the electron density function, g(r), the form given in Eq. 4.2.3 is utilized. The cutoff values for g(r) functions are given in the figure legends
표
EAM potential model for Pb system with O impurity: (left) the embedding energy functions for UEAM,Pb-Pb, (middle) the embedding energy functions for UEAM,O-Pb, and (right) two-body interaction functions for Na-Na and Na-O pairs. For the electron density function, g(r), the form given in Eq. 4.2.3 is utilized. The cutoff values for g(r) functions are given in the figure legends
 표
Pressure-energy relationships for pure liquid Na at 600 K (left) and at 1000 K (right). Data points of the "Original system" correspond to the energy and pressure in Table 5.1-2. Each error bar includes the SEMs from thermal fluctuations during each simulation and the deviation among three simulations of the same volume
표
Pressure-energy relationships for pure liquid Na at 600 K (left) and at 1000 K (right). Data points of the "Original system" correspond to the energy and pressure in Table 5.1-2. Each error bar includes the SEMs from thermal fluctuations during each simulation and the deviation among three simulations of the same volume
 표
Estimated converged energy and pressure with current system volume at each temperature for O-including liquid Na systems. Using the standard errors of energy and pressure for each simulation in Table 5.1-4, the system energies and pressures in Table 5.1-4 were averaged over three simulations at each temperature
표
Estimated converged energy and pressure with current system volume at each temperature for O-including liquid Na systems. Using the standard errors of energy and pressure for each simulation in Table 5.1-4, the system energies and pressures in Table 5.1-4 were averaged over three simulations at each temperature
![Enthalpy diagram showing calculation results and experimental data. Enthalpy unit: kJ/mol. - Calculation data are colored in red while experimental data are colored in blue and are in parentheses. - The calculation results in Section 5.1.3.3, the O2 solution enthalpy, correspond to process (1). - The available experimental data [41], the Na2O solution enthalpy, correspond to process (2). * Estimated using other experimental data (46.9 kJ/mol) in diagram Enthalpy diagram showing calculation results and experimental data. Enthalpy unit: kJ/mol. - Calculation data are colored in red while experimental data are colored in blue and are in parentheses. - The calculation results in Section 5.1.3.3, the O2 solution enthalpy, correspond to process (1). - The available experimental data [41], the Na2O solution enthalpy, correspond to process (2). * Estimated using other experimental data (46.9 kJ/mol) in diagram](https://nrms.kisti.re.kr/bitextimages/TRKO201900021946/TRKO201900021946_62_image_1.png) 표
Enthalpy diagram showing calculation results and experimental data. Enthalpy unit: kJ/mol. - Calculation data are colored in red while experimental data are colored in blue and are in parentheses. - The calculation results in Section 5.1.3.3, the O2 solution enthalpy, correspond to process (1). - The available experimental data [41], the Na2O solution enthalpy, correspond to process (2). * Estimated using other experimental data (46.9 kJ/mol) in diagram
표
Enthalpy diagram showing calculation results and experimental data. Enthalpy unit: kJ/mol. - Calculation data are colored in red while experimental data are colored in blue and are in parentheses. - The calculation results in Section 5.1.3.3, the O2 solution enthalpy, correspond to process (1). - The available experimental data [41], the Na2O solution enthalpy, correspond to process (2). * Estimated using other experimental data (46.9 kJ/mol) in diagram
![Self-diffusion coefficients (left) and O impurity diffusion coefficients in liquid Pb. In the left figure, Experiment-1 is taken from [G. Mathiak, A. Griesche, K.H. Kraatz, G. Frohberg, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 205–207 (1996) 412]. In the right figure, Experiment-1 is from [B.F. Gromov, B.A. Shmatko, 1997; cited in an IAEA handbook, https://inis.iaea.org/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/46/133/46133907.pdf], Experiment-2 from [S. Otsuka, Z. Kosuka, Metallurgical Transactions B 6 (1975) 389], and Experiment-3 from [H. Charle, J. Osterwald, Z. Phys. Chem. 99 (1976) 199] Self-diffusion coefficients (left) and O impurity diffusion coefficients in liquid Pb. In the left figure, Experiment-1 is taken from [G. Mathiak, A. Griesche, K.H. Kraatz, G. Frohberg, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 205–207 (1996) 412]. In the right figure, Experiment-1 is from [B.F. Gromov, B.A. Shmatko, 1997; cited in an IAEA handbook, https://inis.iaea.org/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/46/133/46133907.pdf], Experiment-2 from [S. Otsuka, Z. Kosuka, Metallurgical Transactions B 6 (1975) 389], and Experiment-3 from [H. Charle, J. Osterwald, Z. Phys. Chem. 99 (1976) 199]](https://nrms.kisti.re.kr/bitextimages/TRKO201900021946/TRKO201900021946_85_image_2.png) 표
Self-diffusion coefficients (left) and O impurity diffusion coefficients in liquid Pb. In the left figure, Experiment-1 is taken from [G. Mathiak, A. Griesche, K.H. Kraatz, G. Frohberg, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 205–207 (1996) 412]. In the right figure, Experiment-1 is from [B.F. Gromov, B.A. Shmatko, 1997; cited in an IAEA handbook, https://inis.iaea.org/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/46/133/46133907.pdf], Experiment-2 from [S. Otsuka, Z. Kosuka, Metallurgical Transactions B 6 (1975) 389], and Experiment-3 from [H. Charle, J. Osterwald, Z. Phys. Chem. 99 (1976) 199]
표
Self-diffusion coefficients (left) and O impurity diffusion coefficients in liquid Pb. In the left figure, Experiment-1 is taken from [G. Mathiak, A. Griesche, K.H. Kraatz, G. Frohberg, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 205–207 (1996) 412]. In the right figure, Experiment-1 is from [B.F. Gromov, B.A. Shmatko, 1997; cited in an IAEA handbook, https://inis.iaea.org/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/46/133/46133907.pdf], Experiment-2 from [S. Otsuka, Z. Kosuka, Metallurgical Transactions B 6 (1975) 389], and Experiment-3 from [H. Charle, J. Osterwald, Z. Phys. Chem. 99 (1976) 199]
![Enthalpy and entropy of an H2 molecule as a function of temperature, calculated from vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot) [33]. For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -8.676 kJ/mol and 8.9 J/mol/K, respectively Enthalpy and entropy of an H2 molecule as a function of temperature, calculated from vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot) [33]. For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -8.676 kJ/mol and 8.9 J/mol/K, respectively](https://nrms.kisti.re.kr/bitextimages/TRKO201900021946/TRKO201900021946_93_image_1.png) 표
Enthalpy and entropy of an H2 molecule as a function of temperature, calculated from vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot) [33]. For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -8.676 kJ/mol and 8.9 J/mol/K, respectively
표
Enthalpy and entropy of an H2 molecule as a function of temperature, calculated from vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot) [33]. For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -8.676 kJ/mol and 8.9 J/mol/K, respectively
 표
Enthalpy and entropy of an I2 molecule as a function of temperature, calculated from vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot). For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -10.091 kJ/mol and 8.7 J/mol/K, respectively
표
Enthalpy and entropy of an I2 molecule as a function of temperature, calculated from vibration analysis (line) and from experimental data (dot). For comparison, the enthalpy and entropy calculated at RT were equalized to the experimental values by adding -10.091 kJ/mol and 8.7 J/mol/K, respectively
 표
Distributions of CNs in FPMD simulations at 1000 K. For each CN bar, partial CN fractions for Pb and Bi are expressed in blue and red colors, respectively. Note that Pb, Bi, and Ne indicate similar distributions with partial CN fractions reflecting the LBE composition (Pb: 44.5 at.% and Bi: 55.5 at.%)
표
Distributions of CNs in FPMD simulations at 1000 K. For each CN bar, partial CN fractions for Pb and Bi are expressed in blue and red colors, respectively. Note that Pb, Bi, and Ne indicate similar distributions with partial CN fractions reflecting the LBE composition (Pb: 44.5 at.% and Bi: 55.5 at.%)
 표
Potential energy differences among systems having different FNA compositions. A different “case” means that the initial configuration brought from the FPMD is different. Four cases are examined for F, of which the CN is approximately two. An x value of 0.0 means that the FNAs are all Bi, whereas 1.0 means that the FNAs are all Pb. An increasing tendency suggests the preference for Bi with a decrease in tendency for Pb
표
Potential energy differences among systems having different FNA compositions. A different “case” means that the initial configuration brought from the FPMD is different. Four cases are examined for F, of which the CN is approximately two. An x value of 0.0 means that the FNAs are all Bi, whereas 1.0 means that the FNAs are all Pb. An increasing tendency suggests the preference for Bi with a decrease in tendency for Pb
 표
Total and partial DOS of pure liquid Na and LBE at 1000 K. The x-axis is the shifted energy level (E-EF) so that the Fermi energy level (EF) lies at 0 eV. The left axis is used for the scale of the total DOS, and the blue and read right axes are used for the scales of the pDOSs of Na and LBE, respectively
표
Total and partial DOS of pure liquid Na and LBE at 1000 K. The x-axis is the shifted energy level (E-EF) so that the Fermi energy level (EF) lies at 0 eV. The left axis is used for the scale of the total DOS, and the blue and read right axes are used for the scales of the pDOSs of Na and LBE, respectively
 표
(a)-(d) Site-projected DOSs of Cr and Fe in liquid Na and liquid LBE at 1000 K. For each figure, the left and right axes are used for the scales of the 4s and 3d orbitals, respectively. (e)-(h) The isosurfaces of electron charge densities with energies at the first peak position of the Cr-4s band in (e) liquid Na and (f) LBE and at the first peak position of the Cr-3d band in (g) liquid Na and (h) LBE. The small red, large yellow, large black and large purple spheres represent Cr, Na, Pb, Bi atoms, respectively. As an isosurface value, 0.0020 electrons/Å3 is used
표
(a)-(d) Site-projected DOSs of Cr and Fe in liquid Na and liquid LBE at 1000 K. For each figure, the left and right axes are used for the scales of the 4s and 3d orbitals, respectively. (e)-(h) The isosurfaces of electron charge densities with energies at the first peak position of the Cr-4s band in (e) liquid Na and (f) LBE and at the first peak position of the Cr-3d band in (g) liquid Na and (h) LBE. The small red, large yellow, large black and large purple spheres represent Cr, Na, Pb, Bi atoms, respectively. As an isosurface value, 0.0020 electrons/Å3 is used
 표
Site-projected DOSs of 3d-TM impurity atoms in liquid Na at 1000 K. The 4s, 4p, and 3d orbitals are presented as the black, red, and blue solid lines, respectively. For each figure, the left axis is used as the scale for s and p orbitals, and the right axis is used as the scale for d orbitals. For the spin-polarized systems, the DOSs of spin-up and spin-down are presented as positive and negative values, respectively
표
Site-projected DOSs of 3d-TM impurity atoms in liquid Na at 1000 K. The 4s, 4p, and 3d orbitals are presented as the black, red, and blue solid lines, respectively. For each figure, the left axis is used as the scale for s and p orbitals, and the right axis is used as the scale for d orbitals. For the spin-polarized systems, the DOSs of spin-up and spin-down are presented as positive and negative values, respectively
 표
Site-projected partial DOSs of 3d metal impurity atoms (a) Sc-Mn, (b) Fe-Zn dissolved in liquid LBE at 1000 K. The d and s orbitals are portrayed as black and red solid lines, respectively. If the system is spin polarized (from V to Co), spin-up and spin-down states are presented as solid and dash lines, respectively. The regions with slashed lines indicate the LBE 6s and 6p bands. The Fermi energy level lies at 0 eV
표
Site-projected partial DOSs of 3d metal impurity atoms (a) Sc-Mn, (b) Fe-Zn dissolved in liquid LBE at 1000 K. The d and s orbitals are portrayed as black and red solid lines, respectively. If the system is spin polarized (from V to Co), spin-up and spin-down states are presented as solid and dash lines, respectively. The regions with slashed lines indicate the LBE 6s and 6p bands. The Fermi energy level lies at 0 eV
 표
(a)-(c) Partial DOSs of Fe-3d orbitals and the positions and widths of the Fe-3d orbitals with a DOS value larger than 0.02 states per atom eV in a vacuum, liquid LBE, and liquid Na. (d) The positions and widths of 3d orbitals in a vacuum, liquid LBE, and liquid Na as a function of the atomic number for all 3d-TMs. In the liquid systems, the peak positions of the 3d orbitals are presented as yellow circles. When a system is spin-polarized, the peak positions of spin-up and spin-down orbitals are separately shown as yellow circles and red triangles, respectively
표
(a)-(c) Partial DOSs of Fe-3d orbitals and the positions and widths of the Fe-3d orbitals with a DOS value larger than 0.02 states per atom eV in a vacuum, liquid LBE, and liquid Na. (d) The positions and widths of 3d orbitals in a vacuum, liquid LBE, and liquid Na as a function of the atomic number for all 3d-TMs. In the liquid systems, the peak positions of the 3d orbitals are presented as yellow circles. When a system is spin-polarized, the peak positions of spin-up and spin-down orbitals are separately shown as yellow circles and red triangles, respectively
 표
Bader charges of 3d-TM impurity atoms in liquid Na and LBE at 1000 K and the differences in electronegativity between 3d-TMs and Na. The left and right axes are used for the scales of the Bader charge and the electronegativity difference, respectively. The standard errors are displayed as vertical lines for the Bader charge. For the electronegativity, empirical values are used
표
Bader charges of 3d-TM impurity atoms in liquid Na and LBE at 1000 K and the differences in electronegativity between 3d-TMs and Na. The left and right axes are used for the scales of the Bader charge and the electronegativity difference, respectively. The standard errors are displayed as vertical lines for the Bader charge. For the electronegativity, empirical values are used
해당 보고서가 속한 카테고리에서 활용도가 높은 상위 5개 콘텐츠를 보여줍니다.
더보기 버튼을 클릭하시면 더 많은 관련자료를 살펴볼 수 있습니다.
| 과제명(ProjectTitle) : | - |
|---|---|
| 연구책임자(Manager) : | - |
| 과제기간(DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 총연구비 (DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 키워드(keyword) : | - |
| 과제수행기간(LeadAgency) : | - |
| 연구목표(Goal) : | - |
| 연구내용(Abstract) : | - |
| 기대효과(Effect) : | - |
| 내보내기 구분 |
|
|---|---|
| 구성항목 |
관리번호, 제목(한글), 저자명(한글), 발행일자, 전자원문, 초록(한글), 초록(영문) 관리번호, 제목(한글), 제목(영문), 저자명(한글), 저자명(영문), 주관연구기관(한글), 주관연구기관(영문), 발행일자, 총페이지수, 주관부처명, 과제시작일, 보고서번호, 과제종료일, 주제분류, 키워드(한글), 전자원문, 키워드(영문), 입수제어번호, 초록(한글), 초록(영문), 목차 |
| 저장형식 |
|
| 메일정보 |
|
| 안내 |
총 건의 자료가 검색되었습니다. 다운받으실 자료의 인덱스를 입력하세요. (1-10,000) 검색결과의 순서대로 최대 10,000건 까지 다운로드가 가능합니다. 데이타가 많을 경우 속도가 느려질 수 있습니다.(최대 2~3분 소요) 다운로드 파일은 UTF-8 형태로 저장됩니다. ~ |
Copyright KISTI. All Rights Reserved.
AI-Helper는 오픈소스 모델을 사용합니다. 사용하고 있는 오픈소스 모델과 라이센스는 아래에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
AI-Helper uses Open Source Models. You can find the source code of these open source models, along with applicable license information below. (helpdesk@kisti.re.kr)
OpenAI의 API Key를 브라우저에 등록하여야 ChatGPT 모델을 사용할 수 있습니다.
등록키는 삭제 버튼을 누르거나, PDF 창을 닫으면 삭제됩니다.

※ AI-Helper는 부적절한 답변을 할 수 있습니다.