최소 단어 이상 선택하여야 합니다.
최대 10 단어까지만 선택 가능합니다.
SAI
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
NTIS 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
DataON 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Edison 바로가기
다음과 같은 기능을 한번의 로그인으로 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Kafe 바로가기
| 주관연구기관 | 한국과학기술원 Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology |
|---|---|
| 연구책임자 | 김진우 |
| 보고서유형 | 최종보고서 |
| 발행국가 | 대한민국 |
| 언어 | 한국어 |
| 발행년월 | 2018-10 |
| 과제시작연도 | 2017 |
| 주관부처 | 과학기술정보통신부 Ministry of Science and ICT |
| 연구관리전문기관 | 한국연구재단 National Research Foundation of Korea |
| 등록번호 | TRKO201900025868 |
| 과제고유번호 | 1711057860 |
| 사업명 | 집단연구지원 |
| DB 구축일자 | 2020-09-05 |
| 키워드 | 호메오도메인.전사인자.세포 간 단백질 이동.세포 간 신호전달.운명 동조화.비유전자 침투성 신경세포 프로그래밍.신경발달.신경퇴행.단백질 전달.Homeodomain.Transcription factors.Intercellular protein transfer.Intercellular communication.Fate synchronization.Non-genome invasive neuronal programming.Neurodevelopment.Neuroregeneration.Protein drug delivery. |
본 연구개발과제는 새로운 세포 간 신호전달 및 운명 결정 방법인 호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포 간 이동 현상의 원리를 규명하는 한편, 이 현상을 응용한 치료법의 개발을 목표로 한국과 프랑스 간 공동연구로 진행하였다. 본 연구를 통해
● 현재 알려진 약 200종의 호메오도메인 전사인자 전체를 대상으로 한 이동성 전사인자의 분류를 통해, 기존 10여종을 포함 80종 이상의 신규 분비형 호메오도메인 전사인자를 발굴하였다.
● 또한, 호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포 간 이동을 조절하는 유전자를 검색하여 TorsinA, HSP70, S
본 연구개발과제는 새로운 세포 간 신호전달 및 운명 결정 방법인 호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포 간 이동 현상의 원리를 규명하는 한편, 이 현상을 응용한 치료법의 개발을 목표로 한국과 프랑스 간 공동연구로 진행하였다. 본 연구를 통해
● 현재 알려진 약 200종의 호메오도메인 전사인자 전체를 대상으로 한 이동성 전사인자의 분류를 통해, 기존 10여종을 포함 80종 이상의 신규 분비형 호메오도메인 전사인자를 발굴하였다.
● 또한, 호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포 간 이동을 조절하는 유전자를 검색하여 TorsinA, HSP70, Sdc2 등을 발굴하였다.
● 또한, 동물 모델을 이용한 호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포 간 이동의 유효성 검증을 통해 Otx2, Vax2, En2, Prox1 등의 신경 재생 촉진 기능을 규명하였다.
● 이 과정에서 Otx2(AA), Vax1(AA), Otx2-scFv 등 호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포 간 이동의 이상이 있는 동물 모델을 확립하여 해당 분야 연구 활성화 기반을 마련하였다.
● 더 나아가 세포 간 이동 가능한 호메오도메인 전사인자를 손상된 신경 조직에 주입하여 손상된 신경의 퇴화 억제는 물론 신경 재생을 촉진하는데 성공하였다.
● 이러한 세포 이동성 전사인자의 세포 간 이동을 응용하여 망막신경 퇴행증과 파킨슨 치료제를 개발하고 있다.
(출처 : 요약서 3p)
Purpose
The goal of this exploratory application is to elucidate, in the vertebrate nervous system, uncovered aspects of fate determination and early/late development. In particular, we will focus on the role of homeodomain transcription factors (homeoproteins) intercellular transfer in the fate
Purpose
The goal of this exploratory application is to elucidate, in the vertebrate nervous system, uncovered aspects of fate determination and early/late development. In particular, we will focus on the role of homeodomain transcription factors (homeoproteins) intercellular transfer in the fate determination of neural progenitor/stem cells (NPCs/NSCs) and in boundary formation within the neuroepithelium. We will investigate the mechanisms of secretion, the extracellular expression, and the trans-cellular targets of several homeoproteins. By studying and exploiting this novel signaling pathway that takes place throughout adulthood, we wish to better understand the origin of neurological and psychiatric diseases and to tackle the development of non-genome invasive tools for regenerative medicine.
contents
1. Establishing the systems studying intercellular transfer of homeodomain transcription factors
2. Validation using in vivo animal models
3. Systemic approaches for the discovery of key neurogenic transcription factors
4. Application for neuroregeneration
Developement results
1. Establishing the systems studying intercellular transfer of homeodomain transcription factors
● Expression and analyses of the secretion and intercellular transfer of ~200 homeoproteins
● Identification of molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the secretion and penetration of homeoproteins
2. Validation using in vivo animal models
● Intercellular transfer of transcription factors in vivo
● Generation of animal models that lack or facilitate intercellular transfer of transcription factors
3. Systemic approaches for the discovery of key neurogenic transcription factors
● Identification of key transcription factors that can induce differentiation to a specific lineage from NPC/NSC
● Guided differentiation of neural precursors from ESC or iPSC on culture plate
4. Application for neuroregeneration
● Local introduction of movable transcription factors in animal models of neurodegenerative diseases
● Implantation of transcription factor-induced monopotent neural precursor cells into neurodegenerative disease model animals
● Development of tissue-specific delivery methods of transcription factors
Expected Contribution
This study will allow us to shed new light on poorly understood aspects of the early and late development and of the physiology of the vertebrate nervous system. It will also permit the development of original animal models of several neurological and psychiatric pathologies. Closer to translational research, the penetrative peptide sequence present in homeodomains, i.e. Penetratin, has been broadly applied to deliver hydrophilic drugs and macromolecules (i.e. proteins and nucleic acids) into animal cells. This non-genome invasive delivery system has recently attracted the attention of the drug market because, unlike conventional gene therapy, it does not modify the genome. Nevertheless, one still needs to better understand the molecular basis of target cell competence for uptake and (re)programming. Furthermore, this research will provide priceless information regarding ways to optimize the use of homeodomain proteins in therapeutic protocols. The studies on movable homeodomain proteins will be immediately applicable to the following neuroscience fields.
● Non-genome invasiveprogramming of neural stem cells
● Non-genome invasive regulation of neurogenesis in vivo
● Non-genome invasive generation of neurons from stem cells
(출처 : SUMMARY 6p)
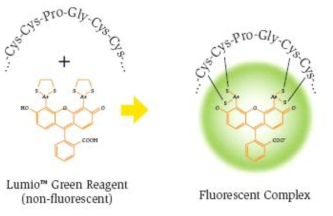 표
Tetra-Cystein (Lumio) tag을 이용한 형광 단백질 검출법 원리. 기존 단백질 이동을 관찰하기 위해 주로 사용된 GFP tag 등은 그 자체가 이미 30 kDa에 가까운 크기를 가지는 단백질로, 자칫 호메오도메인 전사인자 자체가 가지고 있는 단백질의 3차 구조에 영향을 줄 가능성이 높아, 200여개의 각기 다른 특징을 가지는 호메오도메인 전사인자를 표지하는 과정에서 예상치 못한 실험 오류가 나올 수 있을 것으로 판단됨. 따라서 상대적으로 간단한 6개의 아미노산만으로 형광을 표지할 수 있는 Lumio tag을 이용해 호메오도메인 전사인자가 가지는 단백질 구조를 방해하지 않으면서도 효과적인 형광 검출을 통해 이동성 및 비이동성 전사인자의 발굴에 사용할 예정임. 그림에서 보는 것과 같이 Lumio tag이 포함하는 4개의 Cysteine 잔기들에 불활성 Lumio 화학물질이 반응하면 활성화되어 녹색이나 적색의 형광을 띄는 특징을 이용해 세포 외부로 분비된 단백질의 양을 형광의 intensity를 측정함으로 간접적으로 확인할 수 있다. 또한, 세포 내부에 존재하는 단백질의 양은 transfection한 세포를 형광현미경으로 측정하거나 FACS를 이용한 형광 검측법으로 확인하여 세포 내부와 세포 외부에 분포하는 호메오도메인 전사인자의 양을 조사하고자 하였다
표
Tetra-Cystein (Lumio) tag을 이용한 형광 단백질 검출법 원리. 기존 단백질 이동을 관찰하기 위해 주로 사용된 GFP tag 등은 그 자체가 이미 30 kDa에 가까운 크기를 가지는 단백질로, 자칫 호메오도메인 전사인자 자체가 가지고 있는 단백질의 3차 구조에 영향을 줄 가능성이 높아, 200여개의 각기 다른 특징을 가지는 호메오도메인 전사인자를 표지하는 과정에서 예상치 못한 실험 오류가 나올 수 있을 것으로 판단됨. 따라서 상대적으로 간단한 6개의 아미노산만으로 형광을 표지할 수 있는 Lumio tag을 이용해 호메오도메인 전사인자가 가지는 단백질 구조를 방해하지 않으면서도 효과적인 형광 검출을 통해 이동성 및 비이동성 전사인자의 발굴에 사용할 예정임. 그림에서 보는 것과 같이 Lumio tag이 포함하는 4개의 Cysteine 잔기들에 불활성 Lumio 화학물질이 반응하면 활성화되어 녹색이나 적색의 형광을 띄는 특징을 이용해 세포 외부로 분비된 단백질의 양을 형광의 intensity를 측정함으로 간접적으로 확인할 수 있다. 또한, 세포 내부에 존재하는 단백질의 양은 transfection한 세포를 형광현미경으로 측정하거나 FACS를 이용한 형광 검측법으로 확인하여 세포 내부와 세포 외부에 분포하는 호메오도메인 전사인자의 양을 조사하고자 하였다
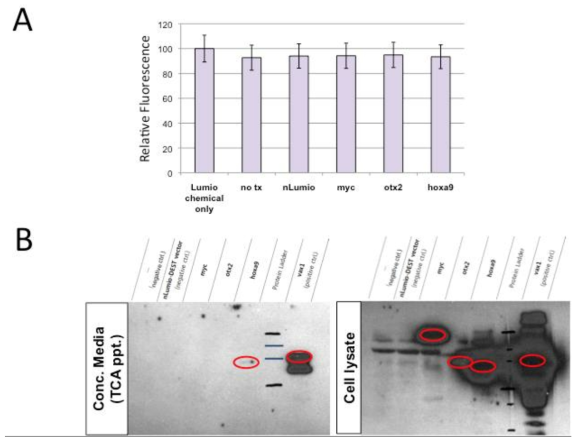 표
세포 내 단백질에 대한 Lumio chemical의 비특이적 반응. (A) 293T 세포에 각 호메오도메인 전사인자들을 발현한 후 세포 배양액을 10% (final) trichloroacetic acid (TCA)로 처리하여 세포 배양액 내 macromolecule의 침전을 얻고, 이 배양액 단백질 (Conc. Media) 중 호메오도메인 전사인자의 존재 여부를 V5 antibody를 이용한 Western blot으로 조사함 (A, 왼쪽). 세포에 해당 단백질이 정상적으로 발현되었는지를 조사하기 위해 cell lysate를 얻고 세포 내에 존재하는 전사인자의 양을 역시 V5 antibody를 이용한 Western blot으로 조사함. (B) 동일 세포 배양액 네 존재하는 Lumio-tag 단백질의 양을 정량하기 위해 Lumio-Green chemical을 처리한 후 Ex.508nm/Em523nm 의 조건에서 형광 강도를 측정함. 그 결과 세포에 정상적으로 발현이 되었고, 세포 외부로 일부 단백질들이 분비되었음에도 불구하고 전혀 그들 사이의 차이를 검증할 수가 없었다
표
세포 내 단백질에 대한 Lumio chemical의 비특이적 반응. (A) 293T 세포에 각 호메오도메인 전사인자들을 발현한 후 세포 배양액을 10% (final) trichloroacetic acid (TCA)로 처리하여 세포 배양액 내 macromolecule의 침전을 얻고, 이 배양액 단백질 (Conc. Media) 중 호메오도메인 전사인자의 존재 여부를 V5 antibody를 이용한 Western blot으로 조사함 (A, 왼쪽). 세포에 해당 단백질이 정상적으로 발현되었는지를 조사하기 위해 cell lysate를 얻고 세포 내에 존재하는 전사인자의 양을 역시 V5 antibody를 이용한 Western blot으로 조사함. (B) 동일 세포 배양액 네 존재하는 Lumio-tag 단백질의 양을 정량하기 위해 Lumio-Green chemical을 처리한 후 Ex.508nm/Em523nm 의 조건에서 형광 강도를 측정함. 그 결과 세포에 정상적으로 발현이 되었고, 세포 외부로 일부 단백질들이 분비되었음에도 불구하고 전혀 그들 사이의 차이를 검증할 수가 없었다
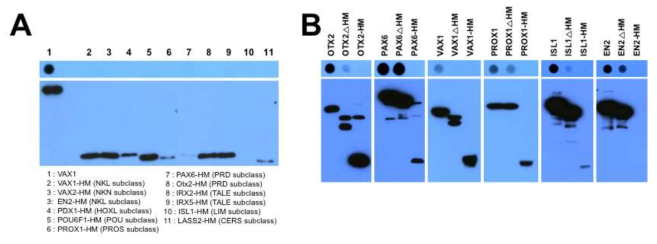
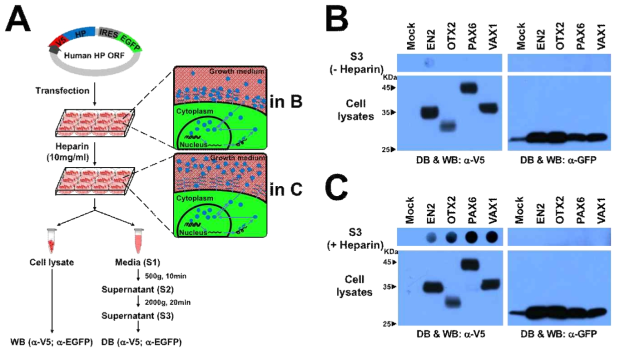 표
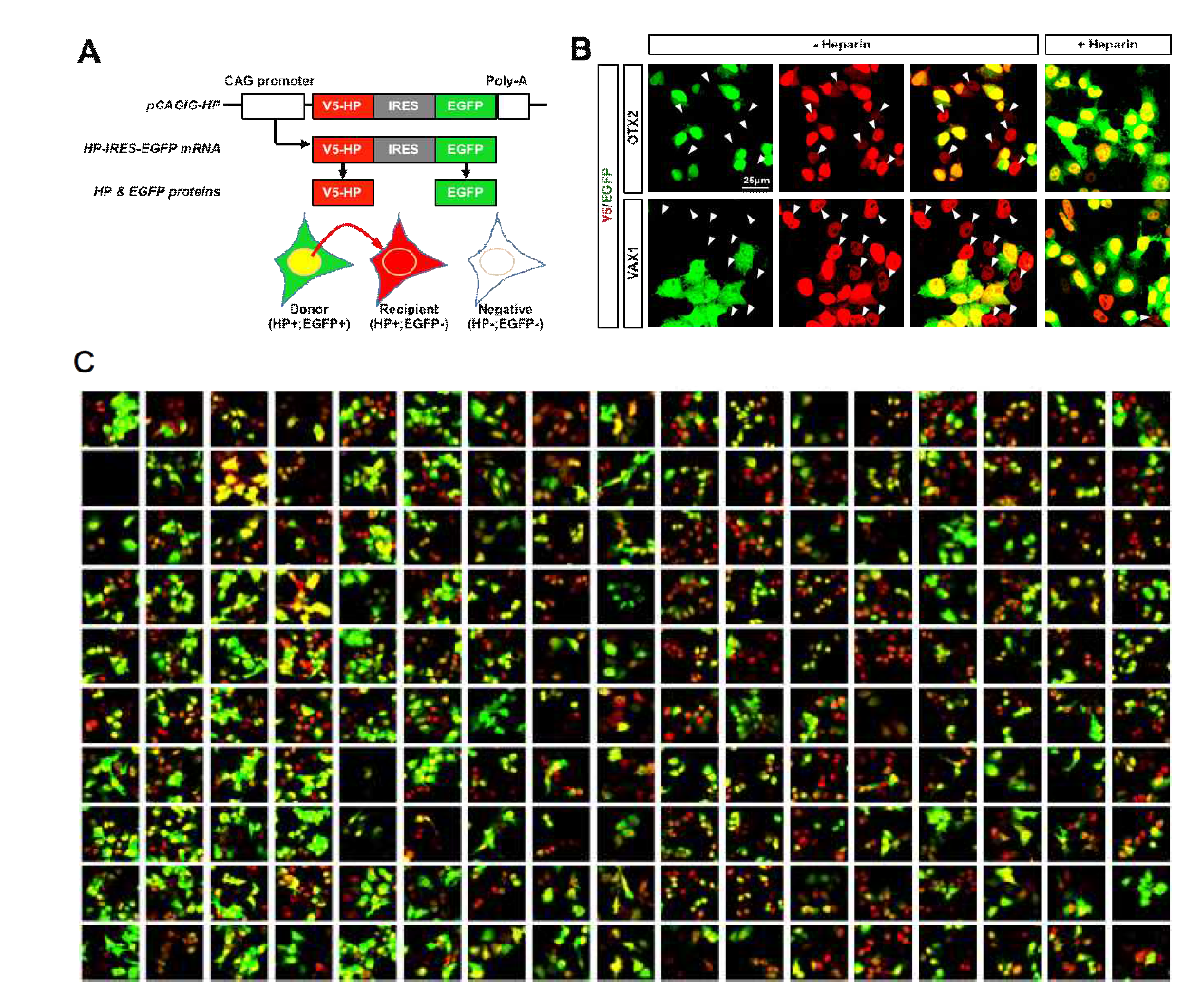
분비형 전사인자에 대한 high-throughput screening을 위한 assay system 확립. (A) 단백질의 N-말단이 V5-tag으로 표지된 EN2, OTX2, PAX6, VAX1을 각각 12well culture dish에 있는 293T 세포에 발현 후 (DNA 500ng/401mm2) 해당 세포를 heparin이 10mg/ml농도로 첨가된 Freestyle 293 Expression Medium (Invitrogen, medium 양, 1ml/12well)에서 3시간동안 배양하여 세포 외부로 분비된 HP들을 포집함. 3시간 이후에 세포배양액 0.5ml을 분리하여 dot-blot kit를 이용, PVDF membrane에 결합시킨 후 각 dot에 존재하는 V5가 표지된 HP의 상대적 양을 V5 antibody를 이용한 Dot blot (DB)으로 조사함. 이와 동시에, 이들 HP의 정상적인 세포 내 발현을 V5 antibody를 이용한 Western blot (WB)으로 조사함. (B) 세포배양액에 heparin을 첨가하지 않은 경우에는, 각각의 HP들이 세포내에서 정상적으로 발현되고 있음에도 불구하고 EN2를 제외한 기존 분비 HP들을 DB을 통하여 검출할 수 없었음. (C) 세포배양액에 heparin을 첨가한 경우에는 기존 분비 HP들을 DB을 이용하여 유의한 수준으로 검출 할 수 있었음. 이를 통하여 대부분의 HP들은 세포 외부의 heparin sulfate proteoglycan에 결합되어 존재한다는 사실을 간접적으로 확인함. HP cDNA 뒤에 존재하는 internal ribosome entry site (IRES)를 통해 연결된 비분비성 enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)의 세포 배양액으로의 분비 여부를 통해 세포 사멸과 이에 의한 비특이적 HP의 배양액 노출 가능성을 확인하였을 때, EGFP가 검출된 샘플이 하나도 존재하지 않은 것을 통해 유전자 과발현에 의한 세포 독성 및 세포 사멸에 의한 비특이적 HP의 배양액 노출은 없는 것으로 확인함
표
분비형 전사인자에 대한 high-throughput screening을 위한 assay system 확립. (A) 단백질의 N-말단이 V5-tag으로 표지된 EN2, OTX2, PAX6, VAX1을 각각 12well culture dish에 있는 293T 세포에 발현 후 (DNA 500ng/401mm2) 해당 세포를 heparin이 10mg/ml농도로 첨가된 Freestyle 293 Expression Medium (Invitrogen, medium 양, 1ml/12well)에서 3시간동안 배양하여 세포 외부로 분비된 HP들을 포집함. 3시간 이후에 세포배양액 0.5ml을 분리하여 dot-blot kit를 이용, PVDF membrane에 결합시킨 후 각 dot에 존재하는 V5가 표지된 HP의 상대적 양을 V5 antibody를 이용한 Dot blot (DB)으로 조사함. 이와 동시에, 이들 HP의 정상적인 세포 내 발현을 V5 antibody를 이용한 Western blot (WB)으로 조사함. (B) 세포배양액에 heparin을 첨가하지 않은 경우에는, 각각의 HP들이 세포내에서 정상적으로 발현되고 있음에도 불구하고 EN2를 제외한 기존 분비 HP들을 DB을 통하여 검출할 수 없었음. (C) 세포배양액에 heparin을 첨가한 경우에는 기존 분비 HP들을 DB을 이용하여 유의한 수준으로 검출 할 수 있었음. 이를 통하여 대부분의 HP들은 세포 외부의 heparin sulfate proteoglycan에 결합되어 존재한다는 사실을 간접적으로 확인함. HP cDNA 뒤에 존재하는 internal ribosome entry site (IRES)를 통해 연결된 비분비성 enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)의 세포 배양액으로의 분비 여부를 통해 세포 사멸과 이에 의한 비특이적 HP의 배양액 노출 가능성을 확인하였을 때, EGFP가 검출된 샘플이 하나도 존재하지 않은 것을 통해 유전자 과발현에 의한 세포 독성 및 세포 사멸에 의한 비특이적 HP의 배양액 노출은 없는 것으로 확인함
 표
각 호메오도메인 전사인자의 상대적 분비능. ‘그림4’와 같은 결과 내 DB의 dot intensity와 WB의 밴드 intensity를 Multi Gauge V3.0 software (Fuji, Tokyo, Japan)로 측정한 후, 각 HP들의 상대적 분비 값을 측정하였음. 실험에 사용한 3개의 세포주 모두에서 유사한 정도로 분비되는 것으로 확인된 Pitx1의 ‘세포 배양액 DB의 dot intensity/세포 내 단백질 WB의 밴드 intensity’를 100으로 정하고 이에 대한 상대 값으로 해당 HP들의 분비능 (상대적 분비능, relative secretion index, RSI)을 지정하였음
표
각 호메오도메인 전사인자의 상대적 분비능. ‘그림4’와 같은 결과 내 DB의 dot intensity와 WB의 밴드 intensity를 Multi Gauge V3.0 software (Fuji, Tokyo, Japan)로 측정한 후, 각 HP들의 상대적 분비 값을 측정하였음. 실험에 사용한 3개의 세포주 모두에서 유사한 정도로 분비되는 것으로 확인된 Pitx1의 ‘세포 배양액 DB의 dot intensity/세포 내 단백질 WB의 밴드 intensity’를 100으로 정하고 이에 대한 상대 값으로 해당 HP들의 분비능 (상대적 분비능, relative secretion index, RSI)을 지정하였음
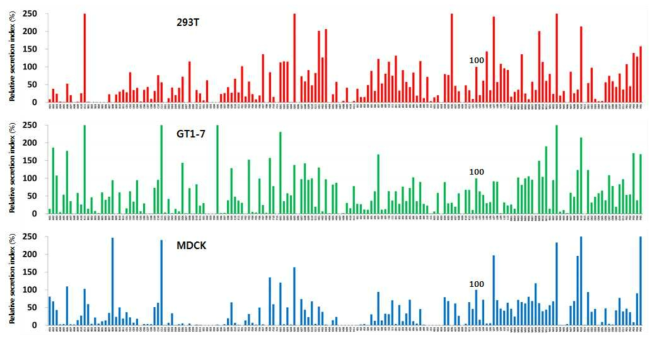
 표
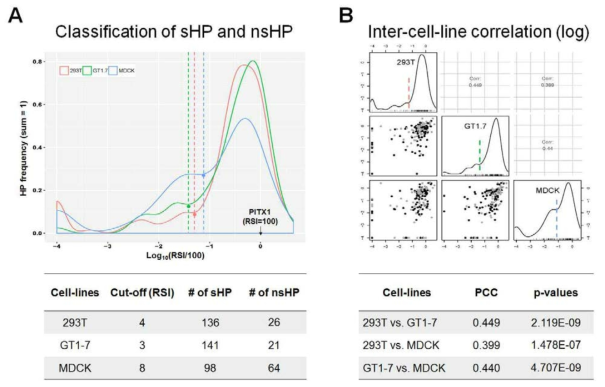
호메오도메인 전사인자의 분비 여부 판별. (A) 총 170개의 HP들 중 3개의 세포주 모두에서 정상적인 발현이 관찰되지 않은 7개 HP들과 HP이 아닌 1개의 단백질을 제외한 162개 HP을 대 상으로하여 이들의 각 세포주에서의 RSI를 로그값으로 변환(Log10(RSI/100))한 후, 그 분포를 확인한 결과 양봉분포(bimodal distribution)를 나타냄. 이때, 가장 큰 분포를 나타내는 그래프의 시작점을 경계값(Cut-off, 그래프에서 점선으로 표시함)으로 설정하고 이보다 작은 RSI값을 가지는 HP들을 비분비성-HP(non secretory-HP, nsHP)으로, 이보다 큰 RSI값을 가지는 HP들을 분비성 -HP(secretory-HP, sHP)으로 분류하기로 결정함. 293T 세포주에서는 약84% (136개), GT1-7 세포주에서는 약87% (141개), MDCK 세포주에서는 약60% (98개)의 HP이 sHP으로 분류됨. (B) 피어슨상관계수(Pearson’s correlation coefficient, PCC)를 측정함으로써 서로 다른 세포주에서 나타나는 분비능의 상관관계를 조사함. 모든 경우에 약하기는 하지만 상관관계가 있음을 확인하였음
표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 분비 여부 판별. (A) 총 170개의 HP들 중 3개의 세포주 모두에서 정상적인 발현이 관찰되지 않은 7개 HP들과 HP이 아닌 1개의 단백질을 제외한 162개 HP을 대 상으로하여 이들의 각 세포주에서의 RSI를 로그값으로 변환(Log10(RSI/100))한 후, 그 분포를 확인한 결과 양봉분포(bimodal distribution)를 나타냄. 이때, 가장 큰 분포를 나타내는 그래프의 시작점을 경계값(Cut-off, 그래프에서 점선으로 표시함)으로 설정하고 이보다 작은 RSI값을 가지는 HP들을 비분비성-HP(non secretory-HP, nsHP)으로, 이보다 큰 RSI값을 가지는 HP들을 분비성 -HP(secretory-HP, sHP)으로 분류하기로 결정함. 293T 세포주에서는 약84% (136개), GT1-7 세포주에서는 약87% (141개), MDCK 세포주에서는 약60% (98개)의 HP이 sHP으로 분류됨. (B) 피어슨상관계수(Pearson’s correlation coefficient, PCC)를 측정함으로써 서로 다른 세포주에서 나타나는 분비능의 상관관계를 조사함. 모든 경우에 약하기는 하지만 상관관계가 있음을 확인하였음
 표
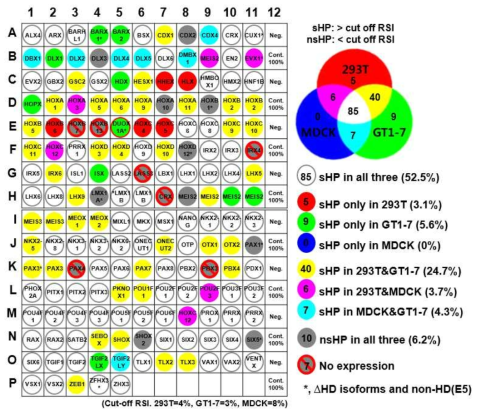
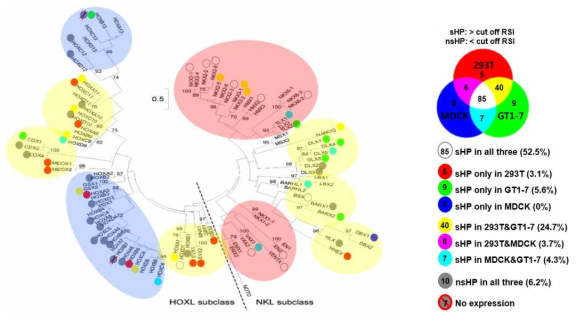
호메오도메인 전사인자의 서로다른 세포주에서의 분비능 비교. ‘그림 6A’의 결과를 도식화하여 나타냄. 그림에서 나타낸 서로다른 색깔은 각각의 HP이 해당하는 세포주에서 sHP 으로 분류되었음을 의미함. 전체 HP들 중94%에 해당하는 152개의 HP이 실험에 사용한 3개의 세포주들 중 적어도 한 개의 세포주에서 분비능을 가짐을 확인함. 이는 세포밖으로의 분비능은 대부분의 HP들이 가지는 일반적인 특징임을 시사함. 그러나 전체 HP들 중 52.5%에 해당하는 85개의 HP들만이 실험에 사용한 3개의 세포주 모두에서 분비능을 나타냈으며, 6.2%에 해당하는 10개의 HP은 3개의 세포주 모두에서 분비능이 없는 nsHP으로 분류되었음. 이러한 결과를 통하여 HP의 분비능은 이들의 가지는 일반적인 특징이기는 하지만 세포의 종류와 그 환경에 따라 다르게 나타날 수 있음을 확인하였음
표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 서로다른 세포주에서의 분비능 비교. ‘그림 6A’의 결과를 도식화하여 나타냄. 그림에서 나타낸 서로다른 색깔은 각각의 HP이 해당하는 세포주에서 sHP 으로 분류되었음을 의미함. 전체 HP들 중94%에 해당하는 152개의 HP이 실험에 사용한 3개의 세포주들 중 적어도 한 개의 세포주에서 분비능을 가짐을 확인함. 이는 세포밖으로의 분비능은 대부분의 HP들이 가지는 일반적인 특징임을 시사함. 그러나 전체 HP들 중 52.5%에 해당하는 85개의 HP들만이 실험에 사용한 3개의 세포주 모두에서 분비능을 나타냈으며, 6.2%에 해당하는 10개의 HP은 3개의 세포주 모두에서 분비능이 없는 nsHP으로 분류되었음. 이러한 결과를 통하여 HP의 분비능은 이들의 가지는 일반적인 특징이기는 하지만 세포의 종류와 그 환경에 따라 다르게 나타날 수 있음을 확인하였음
 표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 주변 세포 침투능력 검증. 293T, GT1-7 및 MDCK 세포들을 이용한 분비능 측정에 이용한 호메오도메인 전사인자들을 대상으로 하여 이들의 주변 세포로의 침투 능력을 조사하였음. 이를 위하여 HeLa 세포에 ‘호메오도메인 전사인자-IRES(Internal Ribosome Entry Site, 내부 리보솜 유입점)-GFP(Green Fluorescent Protein, 초록 형광 단백질)’ 시스템으로 제작된 각각의 호메오도메인 전사인자들을 과발현시킨 후 면역형광염색하여 관찰하였음. ‘호메오도 메인 전사인자-IRES-GFP’ 시스템은 ‘호메오도메인 전사인자-IRES-GFP’를 하나의 전사체로 만든 후, ‘호메오도메인 전사인자’와 ‘GFP’를 각각의 독립된 단백질로 발현시킬 수 있는 시스템으로, 형광 현미경 관찰시에 호메오도메인 전사인자의 신호와 GFP의 신호가 동시에 나타나는 세포를 조사함으로써 각각의 호메오도메인 전사인자가 과발현된 세포를 확인할 수 있으며, 호메오도메인 전사인자의 신호만 나타나는 세포를 조사함으로써 호메오도메인 전사인자의 주변 세포로의 침투능력을 확인할 수 있음
표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 주변 세포 침투능력 검증. 293T, GT1-7 및 MDCK 세포들을 이용한 분비능 측정에 이용한 호메오도메인 전사인자들을 대상으로 하여 이들의 주변 세포로의 침투 능력을 조사하였음. 이를 위하여 HeLa 세포에 ‘호메오도메인 전사인자-IRES(Internal Ribosome Entry Site, 내부 리보솜 유입점)-GFP(Green Fluorescent Protein, 초록 형광 단백질)’ 시스템으로 제작된 각각의 호메오도메인 전사인자들을 과발현시킨 후 면역형광염색하여 관찰하였음. ‘호메오도 메인 전사인자-IRES-GFP’ 시스템은 ‘호메오도메인 전사인자-IRES-GFP’를 하나의 전사체로 만든 후, ‘호메오도메인 전사인자’와 ‘GFP’를 각각의 독립된 단백질로 발현시킬 수 있는 시스템으로, 형광 현미경 관찰시에 호메오도메인 전사인자의 신호와 GFP의 신호가 동시에 나타나는 세포를 조사함으로써 각각의 호메오도메인 전사인자가 과발현된 세포를 확인할 수 있으며, 호메오도메인 전사인자의 신호만 나타나는 세포를 조사함으로써 호메오도메인 전사인자의 주변 세포로의 침투능력을 확인할 수 있음
 표
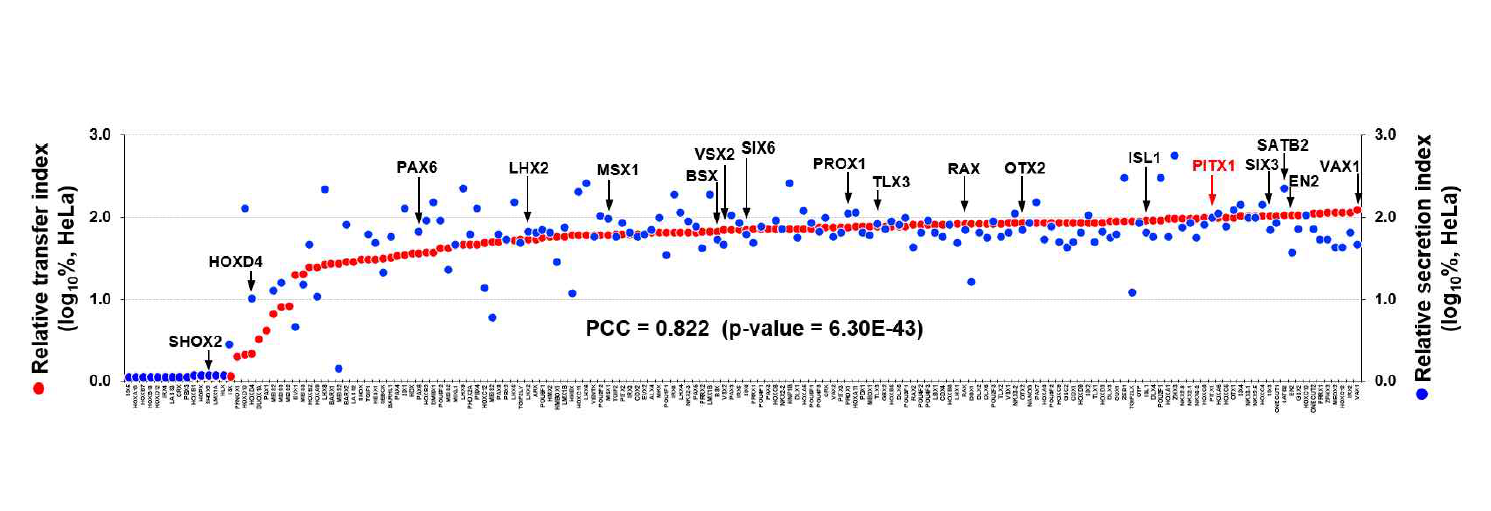
호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포 간 이동 정도 비교 그래프. HP의 상대적 분비능을 측정한 선행연구에서 기준으로 삼았던 Pitx1의 면역형광염색결과에서 ‘HP의 신호(red)만 나타나는 세포의 수 / HP의 신호(red)와 GFP의 신호(green)가 동시에 나타나는 세포(yellow)의 수’를 100으로 정하고 이에 대한 상대값으로 각각의 HP들의 주변세포로의 침투능 (상대적 침투능, relative transfer index, RTI)을 지정하였음. HP의 주변세포로의 침투능력(좌측 Y축)을 세포밖으로의 분비능력(우측 Y축)과 비교해보았을 때, 이들의 상관관계가 매우 높은 것으로 나타남. 이러한 결과는, HP은 일단 세포 밖으로 분비가 되면 주변 세포로의 이동은 쉽게 일어날수 있음을 시사함
표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포 간 이동 정도 비교 그래프. HP의 상대적 분비능을 측정한 선행연구에서 기준으로 삼았던 Pitx1의 면역형광염색결과에서 ‘HP의 신호(red)만 나타나는 세포의 수 / HP의 신호(red)와 GFP의 신호(green)가 동시에 나타나는 세포(yellow)의 수’를 100으로 정하고 이에 대한 상대값으로 각각의 HP들의 주변세포로의 침투능 (상대적 침투능, relative transfer index, RTI)을 지정하였음. HP의 주변세포로의 침투능력(좌측 Y축)을 세포밖으로의 분비능력(우측 Y축)과 비교해보았을 때, 이들의 상관관계가 매우 높은 것으로 나타남. 이러한 결과는, HP은 일단 세포 밖으로 분비가 되면 주변 세포로의 이동은 쉽게 일어날수 있음을 시사함
 표
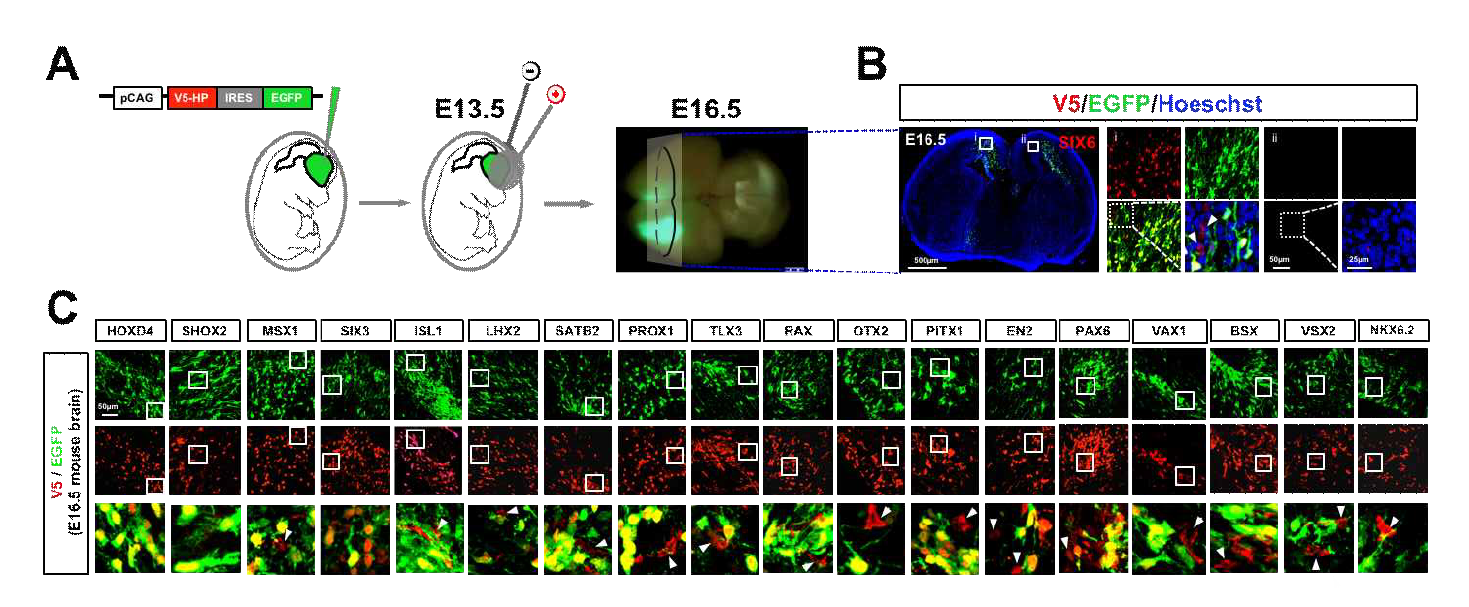
호메오도메인 전사인자의 생체내에서의 세포 간 이동 현상. (A) sHP 또는 nsHP들의 세포 간 이동 현상이 생체 내에서도 동일하게 일어나는 것인지를 확인하기 위하여, HeLa 세포주를 이용한 HP의 주변 침투능 검증에 사용한것과 동일한 HP 유전자 카세트를 수정 후 13.5일된 생쥐 배아 뇌실에 elecroporation을 통해 도입함. (B) 유전자 카세트 도입 3일 후인 수정 후 16.5일에 배아 뇌를 적출하여 배아 뇌신경세포에서 HP의 신호(red)만을 나타내는 세포의 존재 여부를 V5와 EGFP에 대한 면역형광 염색을 통하여 확인함으로써 HP의 생체내에서의 세포간 이동을 조사함. (C) 그 결과, 앞선 3개의 세포주를 사용한 HP의 분비능 조사와 HeLa 세포주를 사용한 HP의 주변세포로의 침투능 조사에서 분비능 및 침투능을 모두 가진다고 검증된 OTX2, EN2, PAX6, VAX1 등의 HP 들의 결과에서는 모두 세포간 이동을 나타내는 HP의 신호(red)만을 나타내는 세포를 다수 확인 할 수 있었으나, 세포밖으로의 분비능 및 주변세포로의 침투능이 모두 없다고 검증된 SHOX2의 경우에는 세포간 이동을 나타내는 HP의 신호(red)만을 나타내는 세포 없이 EGFP를 동시에 발현하는 세포들에만 머무르고 있음을 확인함
표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 생체내에서의 세포 간 이동 현상. (A) sHP 또는 nsHP들의 세포 간 이동 현상이 생체 내에서도 동일하게 일어나는 것인지를 확인하기 위하여, HeLa 세포주를 이용한 HP의 주변 침투능 검증에 사용한것과 동일한 HP 유전자 카세트를 수정 후 13.5일된 생쥐 배아 뇌실에 elecroporation을 통해 도입함. (B) 유전자 카세트 도입 3일 후인 수정 후 16.5일에 배아 뇌를 적출하여 배아 뇌신경세포에서 HP의 신호(red)만을 나타내는 세포의 존재 여부를 V5와 EGFP에 대한 면역형광 염색을 통하여 확인함으로써 HP의 생체내에서의 세포간 이동을 조사함. (C) 그 결과, 앞선 3개의 세포주를 사용한 HP의 분비능 조사와 HeLa 세포주를 사용한 HP의 주변세포로의 침투능 조사에서 분비능 및 침투능을 모두 가진다고 검증된 OTX2, EN2, PAX6, VAX1 등의 HP 들의 결과에서는 모두 세포간 이동을 나타내는 HP의 신호(red)만을 나타내는 세포를 다수 확인 할 수 있었으나, 세포밖으로의 분비능 및 주변세포로의 침투능이 모두 없다고 검증된 SHOX2의 경우에는 세포간 이동을 나타내는 HP의 신호(red)만을 나타내는 세포 없이 EGFP를 동시에 발현하는 세포들에만 머무르고 있음을 확인함
 표
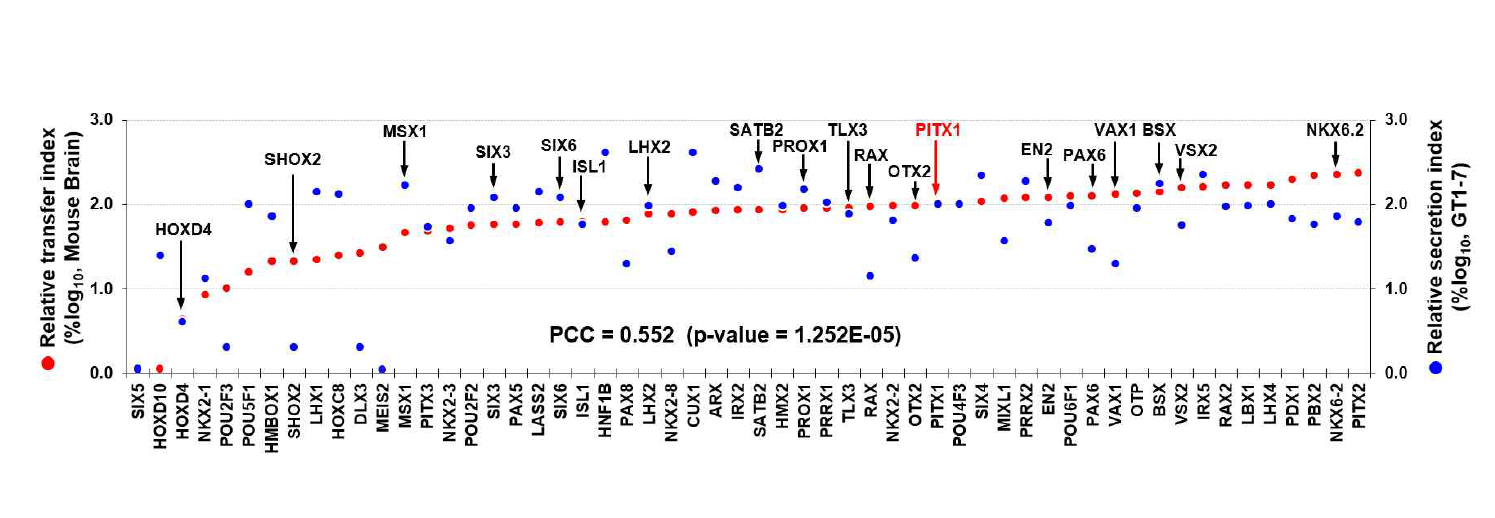
호메오도메인 전사인자의 생체 내 세포 간 이동 정도 비교. Pitx1의 면역형광염색결과에서 ‘HP의 신호(red)만 나타나는 세포의 수 / HP의 신호(red)와 GFP의 신호(green)가 동시에 나타나는 세포(yellow)의 수’를 100으로 정하고 이에 대한 상대값으로 각각의 HP들의 생체내에서의 세포간 이동 정도(RTI)를 측정하였음. HP의 생체내에서의 주변세포로의 이동정도(좌측 Y축)를 mouse 시상하부 유래 신경세포인 GT1-7 세포에서의 HP의 분비정도(우측 Y축)와 비교해보았을 때, 약한수준이기는 하지만 상관관계가 있음 확인함. 이를 통하여 HP의 세포간 이동 및 침투현상은 세포종류 및 환경조건에 따라 다르게 나타나기는 하지만 생체 조건에서도 여전히 동일하게 나타나는 현상임을 검증하였음
표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 생체 내 세포 간 이동 정도 비교. Pitx1의 면역형광염색결과에서 ‘HP의 신호(red)만 나타나는 세포의 수 / HP의 신호(red)와 GFP의 신호(green)가 동시에 나타나는 세포(yellow)의 수’를 100으로 정하고 이에 대한 상대값으로 각각의 HP들의 생체내에서의 세포간 이동 정도(RTI)를 측정하였음. HP의 생체내에서의 주변세포로의 이동정도(좌측 Y축)를 mouse 시상하부 유래 신경세포인 GT1-7 세포에서의 HP의 분비정도(우측 Y축)와 비교해보았을 때, 약한수준이기는 하지만 상관관계가 있음 확인함. 이를 통하여 HP의 세포간 이동 및 침투현상은 세포종류 및 환경조건에 따라 다르게 나타나기는 하지만 생체 조건에서도 여전히 동일하게 나타나는 현상임을 검증하였음
 표
ANTP 호메오도메인 전사인자 subclass별 분비능 비교. 호메오도메인 전사인자 중 가장 많은 수를 차지하는 ANTP family의 분비능을 각 subclass로 나누어 비교한 결과, Hox subclass보다 NKL subclass가 더 분비능이 높음을 알 수 있음. 특히, Nkx subclass member와 enrailed와 Vax1을 포함하는 Emx subclass의 분비능이 높음을 알 수 있음. 따라서, 이들 subclass가 공통적으로 가지는 호메오도메인 내의 아미노산 서열 또는 호메오도메인 외부의 특징적 아미노산 서열 및 구조를 좀 더 비교 분석해 볼 필요성이 있음
표
ANTP 호메오도메인 전사인자 subclass별 분비능 비교. 호메오도메인 전사인자 중 가장 많은 수를 차지하는 ANTP family의 분비능을 각 subclass로 나누어 비교한 결과, Hox subclass보다 NKL subclass가 더 분비능이 높음을 알 수 있음. 특히, Nkx subclass member와 enrailed와 Vax1을 포함하는 Emx subclass의 분비능이 높음을 알 수 있음. 따라서, 이들 subclass가 공통적으로 가지는 호메오도메인 내의 아미노산 서열 또는 호메오도메인 외부의 특징적 아미노산 서열 및 구조를 좀 더 비교 분석해 볼 필요성이 있음
 표
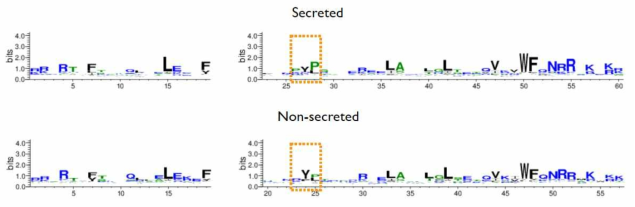
분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자와 비분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자의 호메오도메인 서열 비교. (top) 분비성 호메오도메인 (40종) 서열을 multiple alignment하고 sequence 패턴을 분석함.(bottom) 마찬가지로, 비분비성 호메오도메인 (16종) 서열을 multiple alignment하고 sequence 패턴을 분석함. 이 과정에 호메오도메인 subclass에 따른 sequence bias를 고려하기 위해서 Henikoff’s weighting scheme를 적용함. 그 결과, 분비성 호메오도메인은 비분비성 호메오도메인에 비해 N-말단 20-30번 부위에 proline (P) 선호도가 있는 반면, 비분비성 호메오도메인에는 없는 것으로 확인됨
표
분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자와 비분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자의 호메오도메인 서열 비교. (top) 분비성 호메오도메인 (40종) 서열을 multiple alignment하고 sequence 패턴을 분석함.(bottom) 마찬가지로, 비분비성 호메오도메인 (16종) 서열을 multiple alignment하고 sequence 패턴을 분석함. 이 과정에 호메오도메인 subclass에 따른 sequence bias를 고려하기 위해서 Henikoff’s weighting scheme를 적용함. 그 결과, 분비성 호메오도메인은 비분비성 호메오도메인에 비해 N-말단 20-30번 부위에 proline (P) 선호도가 있는 반면, 비분비성 호메오도메인에는 없는 것으로 확인됨
![분비성 호메오도메인과 비분비성 호메오도메인의 구조 비교. (left) 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자인 ej139의 알려진 구조. (right) 비분비성 호메오도메인인 ej042의 알려진 구조. ‘그림16’의 orange box에 해당하는 residue(red stick)와 주변 5A 이내에 인접한 ATOM을 stick으로 표시함. 해당 sequence는 ej139에서는 PLP[23-25]의 패턴을 나타내고, ej042에서는 KYL[22-24]의 패턴을 나타냄. 현재 가설(호메오도메인이 DNA에 binding되지 않은 conformation[open form]을 가질 수 있고, 이 점이 secretion에 관련이 있다)을 바탕으로 추측해 볼 때, ej139 PLP의 양쪽 proline은 open form에서 helix-turn-helix 구조 안정화와 관련있을 수 있음. ej042의 L24는 hydrophobic core를 형성하면서 현재 conformation(closed form)에서의 helix packing에 관련된다고 추측됨 분비성 호메오도메인과 비분비성 호메오도메인의 구조 비교. (left) 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자인 ej139의 알려진 구조. (right) 비분비성 호메오도메인인 ej042의 알려진 구조. ‘그림16’의 orange box에 해당하는 residue(red stick)와 주변 5A 이내에 인접한 ATOM을 stick으로 표시함. 해당 sequence는 ej139에서는 PLP[23-25]의 패턴을 나타내고, ej042에서는 KYL[22-24]의 패턴을 나타냄. 현재 가설(호메오도메인이 DNA에 binding되지 않은 conformation[open form]을 가질 수 있고, 이 점이 secretion에 관련이 있다)을 바탕으로 추측해 볼 때, ej139 PLP의 양쪽 proline은 open form에서 helix-turn-helix 구조 안정화와 관련있을 수 있음. ej042의 L24는 hydrophobic core를 형성하면서 현재 conformation(closed form)에서의 helix packing에 관련된다고 추측됨](https://nrms.kisti.re.kr/bitextimages/TRKO201900025868/TRKO201900025868_41_image_1.png) 표
분비성 호메오도메인과 비분비성 호메오도메인의 구조 비교. (left) 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자인 ej139의 알려진 구조. (right) 비분비성 호메오도메인인 ej042의 알려진 구조. ‘그림16’의 orange box에 해당하는 residue(red stick)와 주변 5A 이내에 인접한 ATOM을 stick으로 표시함. 해당 sequence는 ej139에서는 PLP[23-25]의 패턴을 나타내고, ej042에서는 KYL[22-24]의 패턴을 나타냄. 현재 가설(호메오도메인이 DNA에 binding되지 않은 conformation[open form]을 가질 수 있고, 이 점이 secretion에 관련이 있다)을 바탕으로 추측해 볼 때, ej139 PLP의 양쪽 proline은 open form에서 helix-turn-helix 구조 안정화와 관련있을 수 있음. ej042의 L24는 hydrophobic core를 형성하면서 현재 conformation(closed form)에서의 helix packing에 관련된다고 추측됨
표
분비성 호메오도메인과 비분비성 호메오도메인의 구조 비교. (left) 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자인 ej139의 알려진 구조. (right) 비분비성 호메오도메인인 ej042의 알려진 구조. ‘그림16’의 orange box에 해당하는 residue(red stick)와 주변 5A 이내에 인접한 ATOM을 stick으로 표시함. 해당 sequence는 ej139에서는 PLP[23-25]의 패턴을 나타내고, ej042에서는 KYL[22-24]의 패턴을 나타냄. 현재 가설(호메오도메인이 DNA에 binding되지 않은 conformation[open form]을 가질 수 있고, 이 점이 secretion에 관련이 있다)을 바탕으로 추측해 볼 때, ej139 PLP의 양쪽 proline은 open form에서 helix-turn-helix 구조 안정화와 관련있을 수 있음. ej042의 L24는 hydrophobic core를 형성하면서 현재 conformation(closed form)에서의 helix packing에 관련된다고 추측됨
 표
호메오도메인 비의존성 분비. (A) 각 호메오도메인 subclass에 해당하는 전사인자들로부터 호메오도메인 만을 선택적으로 분리한 후 293T 세포에 발현한 후 각 호메오도메인들의 분비능을 조사함. 모든 종류의 호메오도메인은 그 자체만으로는 분비가 일어나지 않음 . (B) 기존에 알려진 분비형 호메오도메인 전사인자들에서 호메오도메인이 선택적으로 제거되었거나 호메오도메인 만을 가지는 변이형을 293T 세포에 발현 후 정상 호메오도메인 전사인자와 분비성을 비교 조사함. 기존에 알려진 분비형 호메오도메인 전사인자들인 Otx2, Pax6와 En2 등은 호메오도메인이 제거된 상태에서도 분비가 일어남을 확인하였음. 이는 특정 호메오도메인이 세포 외부로 분비를 결정하는 중요한 motif를 가지고 있지는 않다는 것과, 호메오도메인 이외의 부분에 호메오도메인 전사인자의 분비성을 조절하는 motif가 존재할 가능성을 시사함. (위) Media에 존재하는 단백질을 검출하는 dot-blot. (아래) 세포 내부에 있는 단백질들을 조사하는 Western blot
표
호메오도메인 비의존성 분비. (A) 각 호메오도메인 subclass에 해당하는 전사인자들로부터 호메오도메인 만을 선택적으로 분리한 후 293T 세포에 발현한 후 각 호메오도메인들의 분비능을 조사함. 모든 종류의 호메오도메인은 그 자체만으로는 분비가 일어나지 않음 . (B) 기존에 알려진 분비형 호메오도메인 전사인자들에서 호메오도메인이 선택적으로 제거되었거나 호메오도메인 만을 가지는 변이형을 293T 세포에 발현 후 정상 호메오도메인 전사인자와 분비성을 비교 조사함. 기존에 알려진 분비형 호메오도메인 전사인자들인 Otx2, Pax6와 En2 등은 호메오도메인이 제거된 상태에서도 분비가 일어남을 확인하였음. 이는 특정 호메오도메인이 세포 외부로 분비를 결정하는 중요한 motif를 가지고 있지는 않다는 것과, 호메오도메인 이외의 부분에 호메오도메인 전사인자의 분비성을 조절하는 motif가 존재할 가능성을 시사함. (위) Media에 존재하는 단백질을 검출하는 dot-blot. (아래) 세포 내부에 있는 단백질들을 조사하는 Western blot
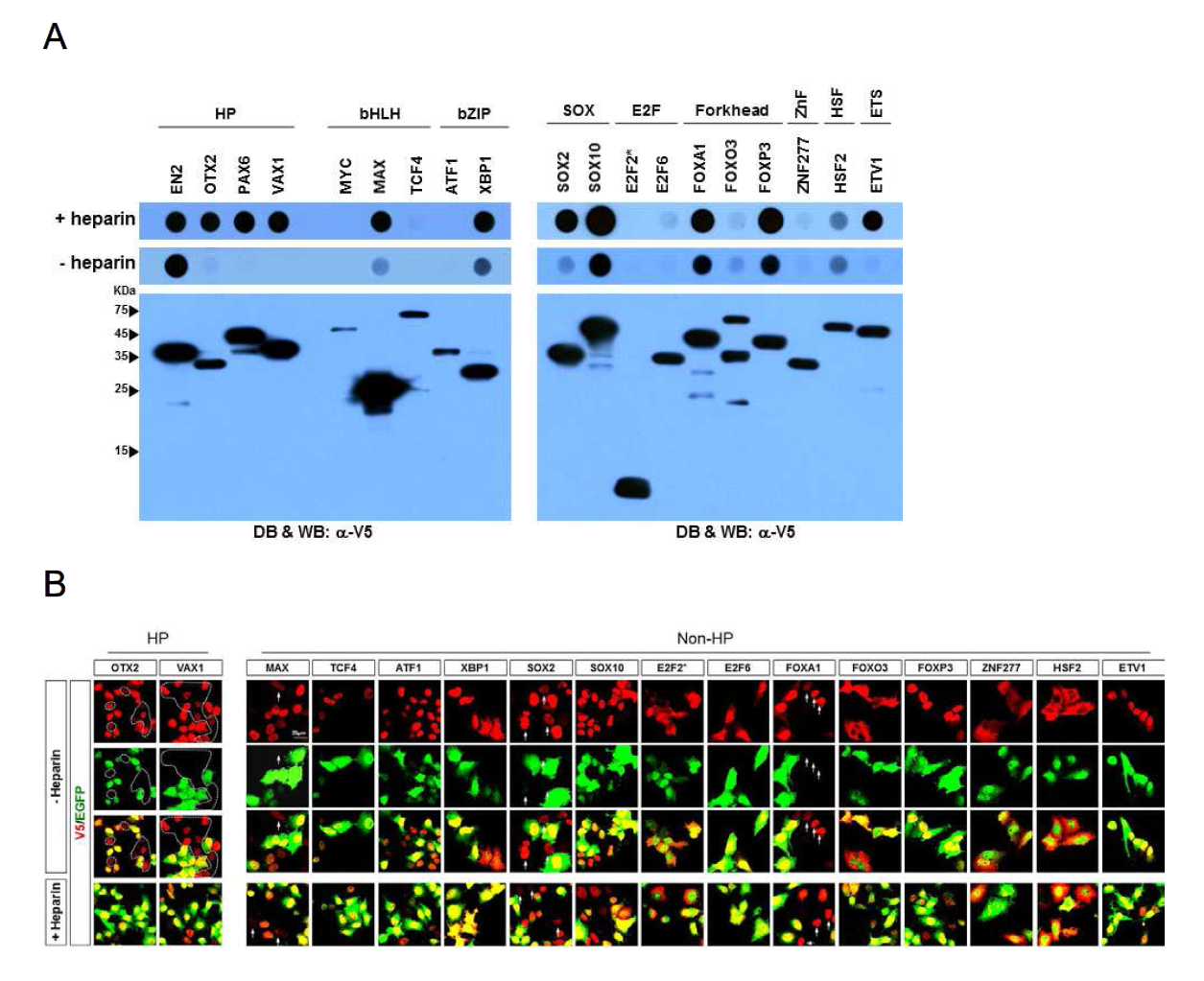 표
비호메오도메인 전사인자들의 분비능 및 세포 간 이동 조사. (A) HeLa 세포를 이용하여 호메오도메인 전사인자들과 다른 class 전사인자들(비호메오도메인 전사인자)의 분비능을 측정함. 그 결과 이들중 일부가 호메오도메인 전사인자들처럼 세포 외부로 분비가 됨을 확인함. 이를 통하여 전사인자들의 세포 간 이동이 호메오도메인 전사인자에만 국한된 현상이 아님을 확인함. 그러나 이들은 호메오도메인 전사인자들과는 다르게 heparin의 존재 여부에 관계없이 동일한 분비능을 보이는 것으로 보아, 호메오도메인 전사인자들의 분비경로와는 다른 경로를 통하여 세포 외부로 분비될 가능성을 생각해볼 수 있었음. (B) 전사인자의 신호(Red)만 나타나는 세포가 존재함을 확인함으로써, 분비능을 가지는 비호메오도메인 전사인자들중 일부(MAX, SOX2, 그리고 FOXA1)는 주변 세포로의 침투능력 또한 가지고 있음을 확인함. 이들의 주변세포로의 침투능 또한 호메오도메인 전사인자와는 다르게 heparin의 존재 여부와는 관계없이 동일하게 나타남을 확인함
표
비호메오도메인 전사인자들의 분비능 및 세포 간 이동 조사. (A) HeLa 세포를 이용하여 호메오도메인 전사인자들과 다른 class 전사인자들(비호메오도메인 전사인자)의 분비능을 측정함. 그 결과 이들중 일부가 호메오도메인 전사인자들처럼 세포 외부로 분비가 됨을 확인함. 이를 통하여 전사인자들의 세포 간 이동이 호메오도메인 전사인자에만 국한된 현상이 아님을 확인함. 그러나 이들은 호메오도메인 전사인자들과는 다르게 heparin의 존재 여부에 관계없이 동일한 분비능을 보이는 것으로 보아, 호메오도메인 전사인자들의 분비경로와는 다른 경로를 통하여 세포 외부로 분비될 가능성을 생각해볼 수 있었음. (B) 전사인자의 신호(Red)만 나타나는 세포가 존재함을 확인함으로써, 분비능을 가지는 비호메오도메인 전사인자들중 일부(MAX, SOX2, 그리고 FOXA1)는 주변 세포로의 침투능력 또한 가지고 있음을 확인함. 이들의 주변세포로의 침투능 또한 호메오도메인 전사인자와는 다르게 heparin의 존재 여부와는 관계없이 동일하게 나타남을 확인함
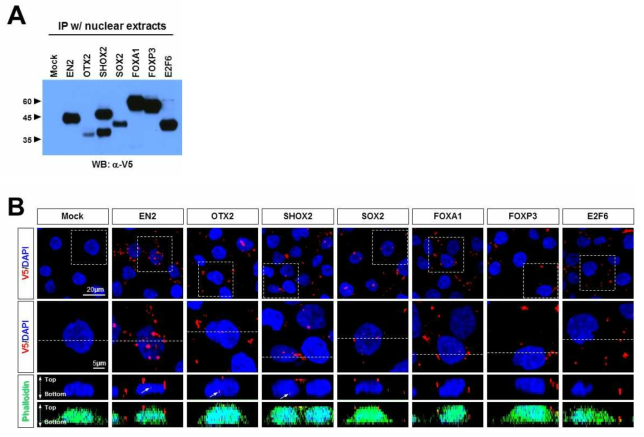 표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 선택적 특성인 세포 침투능력. (A) 선행연구를 통해 규명한 비호메오도메인 전사인자들의 분비 및 세포 간 이동 능력과 호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포 간 이동의 공통적 특징을 규명하고자 비호메오도메인 전사인자들 중 분비능을 가지는 동시에 세포간 이동성을 보인 SOX2, FOXA1과, 분비능은 있지만 세포간 이동성이 없는 FOXP3, 비분비성 E2F6 단백질을 293T 세포에 발현 후 핵 추출물을 분리하여 해당 단백질들의 상대적 농도를 확인함. (B) 이들 전사인자들을 포함한 핵추출물을 HeLa 세포 배양액에 처리한 결과 이들 비호메오도메인 전사인자들은 모두가 HeLa 세포에 침투하지 못하고 세포 외부에 있음을 확인함. 이와 대조적으로 비분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자인 SHOX2의 경우는 HeLa 세포에 처리 시 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자인 EN2, OTX2와 마찬가지로 세포 내부로 침투하였음을 확인함. 이러한 결과를 통하여 비호메오도메인 전사인자들의 세포 간 이동은 호메오도메인 전사인자들처럼 단백질 자체로 이루어지는 것이 아니라 exosome과 같은 막구조를 통한 간접적인 현상일 가능성을 확인할 수 있었음. 또한 세포 외부로의 분비는 다양한 전사인자들의 특징이지만, 주변 세포막을 직접 침투할 수 있는 능력은 호메오도메인 전사인자들만의 선택적 특성이라는 점을 확인하였음
표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 선택적 특성인 세포 침투능력. (A) 선행연구를 통해 규명한 비호메오도메인 전사인자들의 분비 및 세포 간 이동 능력과 호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포 간 이동의 공통적 특징을 규명하고자 비호메오도메인 전사인자들 중 분비능을 가지는 동시에 세포간 이동성을 보인 SOX2, FOXA1과, 분비능은 있지만 세포간 이동성이 없는 FOXP3, 비분비성 E2F6 단백질을 293T 세포에 발현 후 핵 추출물을 분리하여 해당 단백질들의 상대적 농도를 확인함. (B) 이들 전사인자들을 포함한 핵추출물을 HeLa 세포 배양액에 처리한 결과 이들 비호메오도메인 전사인자들은 모두가 HeLa 세포에 침투하지 못하고 세포 외부에 있음을 확인함. 이와 대조적으로 비분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자인 SHOX2의 경우는 HeLa 세포에 처리 시 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자인 EN2, OTX2와 마찬가지로 세포 내부로 침투하였음을 확인함. 이러한 결과를 통하여 비호메오도메인 전사인자들의 세포 간 이동은 호메오도메인 전사인자들처럼 단백질 자체로 이루어지는 것이 아니라 exosome과 같은 막구조를 통한 간접적인 현상일 가능성을 확인할 수 있었음. 또한 세포 외부로의 분비는 다양한 전사인자들의 특징이지만, 주변 세포막을 직접 침투할 수 있는 능력은 호메오도메인 전사인자들만의 선택적 특성이라는 점을 확인하였음
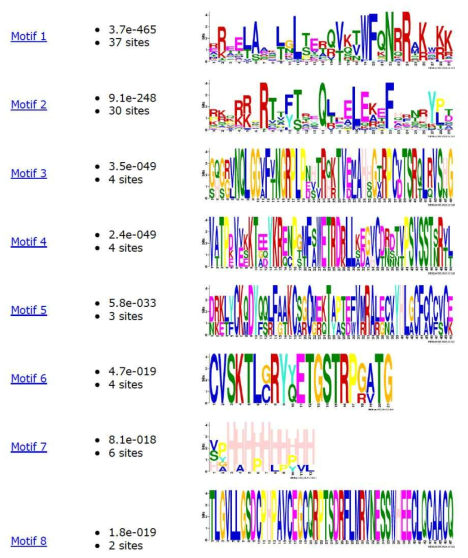 표
분비형 호메오도메인 전사인자의 구조적 특징. 91개 중 발현이 확인된 81개의 호메오도메인 전사인자들은 50% 이상 32개, 11-50%가 6개, 10% 이하가 43개임. 이들을 다시 50% 이상을 분비성, 50% 이하를 비분비성으로 분류하여 그들 사이의 아미노산 배열의 상호 연관성을 MEME 프로그램으로 분석한 후 3개 이상의 전사인자에서 공통적으로 나타난 6개 이상 20개 이하의 아미노산 서열로 이루어진 motif들 만을 다시 분석함. 분비성 전사인자들에서는 호메오도메인 내부의 여러 motif가 가장 연관성이 높게 나왔고, 그 다음으로 paired domain, LIM domain 등이 그다음 특징으로 나옴. 비분비성에서도 마찬가지로 호메오도메인 내부의 motif와 POU domain 등이 높은 연관성을 가지는 것으로 나타남. 이들 중 유일하게 분비성 전사인자의 Motif 7이 호메오도메인 외부 아미노산 서열들로 총 6개의 전사인자에서 관찰되었으며, 이는 반복된 Histidine을 가지고 있음
표
분비형 호메오도메인 전사인자의 구조적 특징. 91개 중 발현이 확인된 81개의 호메오도메인 전사인자들은 50% 이상 32개, 11-50%가 6개, 10% 이하가 43개임. 이들을 다시 50% 이상을 분비성, 50% 이하를 비분비성으로 분류하여 그들 사이의 아미노산 배열의 상호 연관성을 MEME 프로그램으로 분석한 후 3개 이상의 전사인자에서 공통적으로 나타난 6개 이상 20개 이하의 아미노산 서열로 이루어진 motif들 만을 다시 분석함. 분비성 전사인자들에서는 호메오도메인 내부의 여러 motif가 가장 연관성이 높게 나왔고, 그 다음으로 paired domain, LIM domain 등이 그다음 특징으로 나옴. 비분비성에서도 마찬가지로 호메오도메인 내부의 motif와 POU domain 등이 높은 연관성을 가지는 것으로 나타남. 이들 중 유일하게 분비성 전사인자의 Motif 7이 호메오도메인 외부 아미노산 서열들로 총 6개의 전사인자에서 관찰되었으며, 이는 반복된 Histidine을 가지고 있음
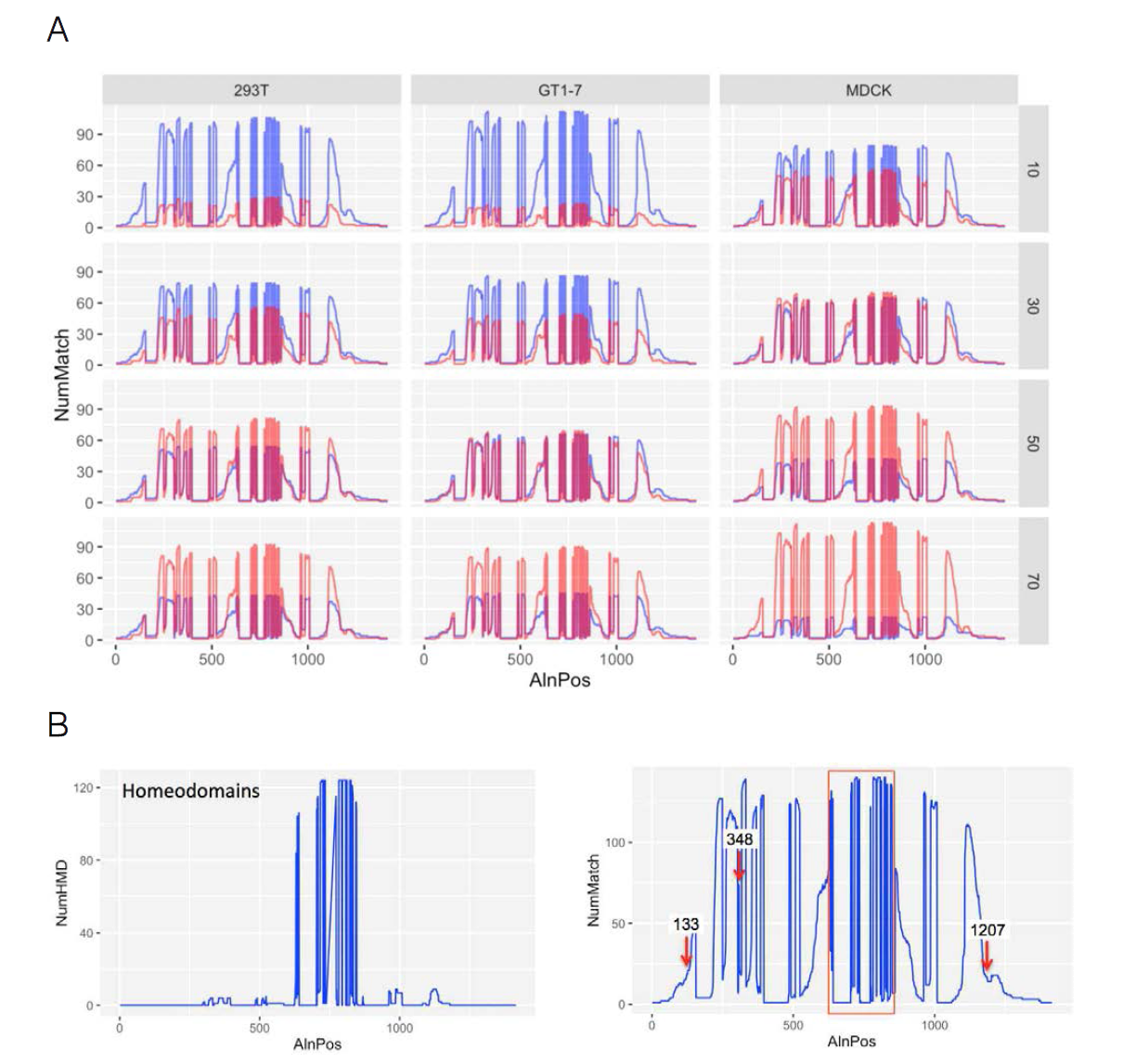 표
분비성 및 비분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자들의 아미노산 배열 비교. (A) 분비성 (sHP, 푸른색) 및 비분비성 (ns-HP, 붉은색) 호메오도메인 전사인자의 아미노산 서열을 MUSCLE multiple alignment software를 이용하여 align 한 후 특정 부위에서 반복되어 나타나는 유사한 특징의 아미노산의 숫자를 Y-축으로 나타냄. 분비성 판별 기준을 증감하면서 이 과정에서도 peak 크기가 변하지 않는 부분을 분비성 또는 비분비성 전사인자들에 공통적으로 보존되어 있는 부위로 잠정 판정함. (B) 그 결과 호메오도메인 (약 600-800번에 걸쳐서 분포) 앞쪽의 133번과 348번, 그리고 호메오도메인 뒤쪽으로 1207번 위치에 분포하는 아미노산 서열이 분비성과 비분비성에 다른 특징을 가짐을 확인함. 해당 부위를 화살표로 표시함. 왼쪽은 호메오도메인의 분포만을 별도로 나타낸 그림
표
분비성 및 비분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자들의 아미노산 배열 비교. (A) 분비성 (sHP, 푸른색) 및 비분비성 (ns-HP, 붉은색) 호메오도메인 전사인자의 아미노산 서열을 MUSCLE multiple alignment software를 이용하여 align 한 후 특정 부위에서 반복되어 나타나는 유사한 특징의 아미노산의 숫자를 Y-축으로 나타냄. 분비성 판별 기준을 증감하면서 이 과정에서도 peak 크기가 변하지 않는 부분을 분비성 또는 비분비성 전사인자들에 공통적으로 보존되어 있는 부위로 잠정 판정함. (B) 그 결과 호메오도메인 (약 600-800번에 걸쳐서 분포) 앞쪽의 133번과 348번, 그리고 호메오도메인 뒤쪽으로 1207번 위치에 분포하는 아미노산 서열이 분비성과 비분비성에 다른 특징을 가짐을 확인함. 해당 부위를 화살표로 표시함. 왼쪽은 호메오도메인의 분포만을 별도로 나타낸 그림
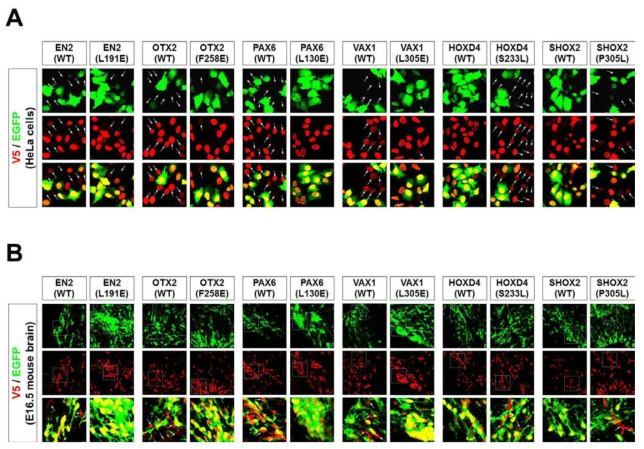 표
변이형 호메오도메인 전사인자의 주변 세포 침투능력 검증. ‘그림 24’에서 분비능 측정에 이용한 변이형 호메오도메인 전사인자들을 대상으로 하여 이들의 주변 세포로의 침투 능력을 조사하였음. 분비능을 가지는 소수성 아미노산 대신 극성 아미노산을 가지도록 만든 호메오도메인 전사인자-변이형인 EN2-L191E, OTX2-F258E, PAX6-L130E, 그리고 VAX1-L305E의 경우 의 경우, 호메오도메인 전사인자의 신호(Red)만 나타나는 세포의 수가 현저히 감소하였음. 반면 비분비성 특징을 나타내는 극성 아미노산 대신 소수성 아미노산을 가지도록 만든 호메오도메인 전사인자-변이형인 HOXD4-S233L과 SHOX2-P305L의 경우에는 호메오도메인 전사인자의 신호(Red)만 나타나는 세포의 수가 크게 증가하였음. (A) HeLa 세포를 이용한 변이형 호메오도메인 전사인자의 침투능력 검증. (B) 생쥐 배아 뇌실을 이용한 변이형 호메오도메인 전사인자의 생체내에서의 세포 간이동 검증
표
변이형 호메오도메인 전사인자의 주변 세포 침투능력 검증. ‘그림 24’에서 분비능 측정에 이용한 변이형 호메오도메인 전사인자들을 대상으로 하여 이들의 주변 세포로의 침투 능력을 조사하였음. 분비능을 가지는 소수성 아미노산 대신 극성 아미노산을 가지도록 만든 호메오도메인 전사인자-변이형인 EN2-L191E, OTX2-F258E, PAX6-L130E, 그리고 VAX1-L305E의 경우 의 경우, 호메오도메인 전사인자의 신호(Red)만 나타나는 세포의 수가 현저히 감소하였음. 반면 비분비성 특징을 나타내는 극성 아미노산 대신 소수성 아미노산을 가지도록 만든 호메오도메인 전사인자-변이형인 HOXD4-S233L과 SHOX2-P305L의 경우에는 호메오도메인 전사인자의 신호(Red)만 나타나는 세포의 수가 크게 증가하였음. (A) HeLa 세포를 이용한 변이형 호메오도메인 전사인자의 침투능력 검증. (B) 생쥐 배아 뇌실을 이용한 변이형 호메오도메인 전사인자의 생체내에서의 세포 간이동 검증
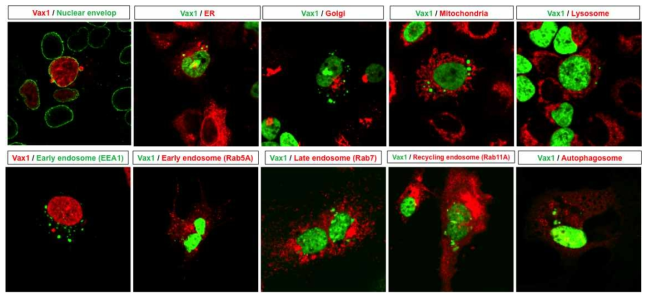 표
Vax1의 세포 내 소기관 내의 위치. Vax1의 subcellular organelle marker와의 co-staining을 통해 Vax1은 핵에 주로 분포하며 세포질에서는 응집된 형태로 나타남을 알 수 있음. 이러한 응집된 Vax1 분포는 핵막 및 ER과는 중복되어 있지만, Golgi와는 중복되어 있지 않음. 이는 일반적인 분비단백질이 거치는 ER-Golgi를 통한 분비를 따르지는 않음을 시사함. 그 외 mitochondria, lysosome 등의 세포 소기관과 endosome, autophagosome 등 단백질의 세포 내 이동에 관여하는 이동낭 (trafficking vesicle) 등과도 겹치지 않음. 이는 Vax1이 세포 핵 내에서 출발하여 세포 외부로 특수한 수송 과정을 통해 분비됨을 시사함
표
Vax1의 세포 내 소기관 내의 위치. Vax1의 subcellular organelle marker와의 co-staining을 통해 Vax1은 핵에 주로 분포하며 세포질에서는 응집된 형태로 나타남을 알 수 있음. 이러한 응집된 Vax1 분포는 핵막 및 ER과는 중복되어 있지만, Golgi와는 중복되어 있지 않음. 이는 일반적인 분비단백질이 거치는 ER-Golgi를 통한 분비를 따르지는 않음을 시사함. 그 외 mitochondria, lysosome 등의 세포 소기관과 endosome, autophagosome 등 단백질의 세포 내 이동에 관여하는 이동낭 (trafficking vesicle) 등과도 겹치지 않음. 이는 Vax1이 세포 핵 내에서 출발하여 세포 외부로 특수한 수송 과정을 통해 분비됨을 시사함
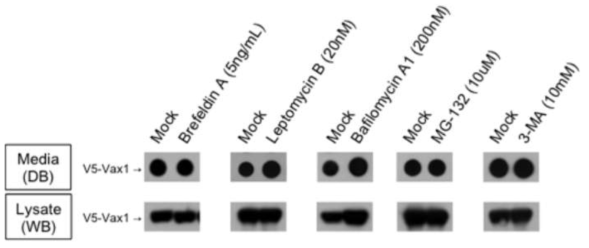 표
Vax1 분비에 미치는 세포 내 단백질 이동 억제 약물의 효과. Vax1의 분비가 기존 알려진 정형적인 ER-Golgi 경로에 대한 억제 약물인 brefeldinA(12시간); 핵공을 통한 핵->세포질로의 단백질 이동을 억제하는 leptomycinB(4시간); 리소좀에서의 단백질 분해를 억제하는 bafilomycinA1(24시간); proteasome을 통한 단백질 분해를 억제하는 MG132(4시간); PI3K의 활성 억제를 통해 autophagy를 저해하는 3-MA(12시간) 후 세포 배양액에 분비된 Vax1 단백질의 양을 비교함. 그 결과, Vax1의 분비는 ER-Golgi를 매개하지 않으며, 핵공을 통한 세포질로의 이동도 필요하지 않음을 확인함. 또한, Vax1은 proteasome을 통한 분해보다는 리소좀을 통해 분해될 가능성이 높고, 이 과정은 세포질에서 단백질을 리소좀으로 이동하는 autophagy를 매개하지는 않을 것이라는 가능성을 시사함
표
Vax1 분비에 미치는 세포 내 단백질 이동 억제 약물의 효과. Vax1의 분비가 기존 알려진 정형적인 ER-Golgi 경로에 대한 억제 약물인 brefeldinA(12시간); 핵공을 통한 핵->세포질로의 단백질 이동을 억제하는 leptomycinB(4시간); 리소좀에서의 단백질 분해를 억제하는 bafilomycinA1(24시간); proteasome을 통한 단백질 분해를 억제하는 MG132(4시간); PI3K의 활성 억제를 통해 autophagy를 저해하는 3-MA(12시간) 후 세포 배양액에 분비된 Vax1 단백질의 양을 비교함. 그 결과, Vax1의 분비는 ER-Golgi를 매개하지 않으며, 핵공을 통한 세포질로의 이동도 필요하지 않음을 확인함. 또한, Vax1은 proteasome을 통한 분해보다는 리소좀을 통해 분해될 가능성이 높고, 이 과정은 세포질에서 단백질을 리소좀으로 이동하는 autophagy를 매개하지는 않을 것이라는 가능성을 시사함
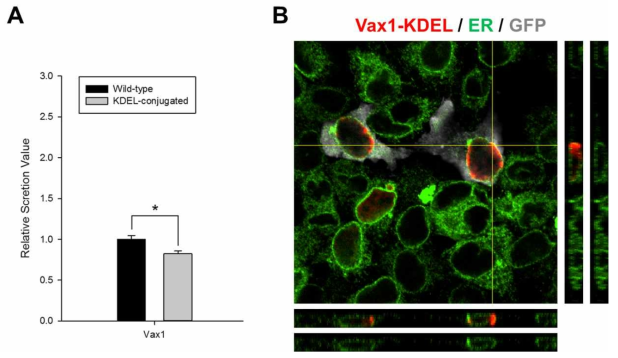 표
Vax1의 분비에 미치는 소포체 위치화의 조사. (A) HeLa 세포에 Vax1 일반형과 소포체 위치화 신호 (KDEL: Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu) 추가 돌연변이를 각각 과발현 후 배양액에 분비된 Vax1의 양과 세포 내 Vax1의 양을 Dot-Blot (DB)과 WB으로 조사하여 상대적 분비 계수를 측정함. (B) HeLa 세포에 Vax1-KDEL-V5-IRES-EGFP를 발현하고 세포 내 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. GFP (회색)는 Vax1 단백질 (붉은색)들과 동일한 DNA construct에 encoding 되어 있으며 독립적으로 번역이 되므로 Vax1을 발현하는 세포를 표지함. 소포체 (녹색)는 소포체 단백질 중의 하나인 Calnexin 단백질을 항원으로 인식하는 항체를 사용하여 표지함
표
Vax1의 분비에 미치는 소포체 위치화의 조사. (A) HeLa 세포에 Vax1 일반형과 소포체 위치화 신호 (KDEL: Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu) 추가 돌연변이를 각각 과발현 후 배양액에 분비된 Vax1의 양과 세포 내 Vax1의 양을 Dot-Blot (DB)과 WB으로 조사하여 상대적 분비 계수를 측정함. (B) HeLa 세포에 Vax1-KDEL-V5-IRES-EGFP를 발현하고 세포 내 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. GFP (회색)는 Vax1 단백질 (붉은색)들과 동일한 DNA construct에 encoding 되어 있으며 독립적으로 번역이 되므로 Vax1을 발현하는 세포를 표지함. 소포체 (녹색)는 소포체 단백질 중의 하나인 Calnexin 단백질을 항원으로 인식하는 항체를 사용하여 표지함
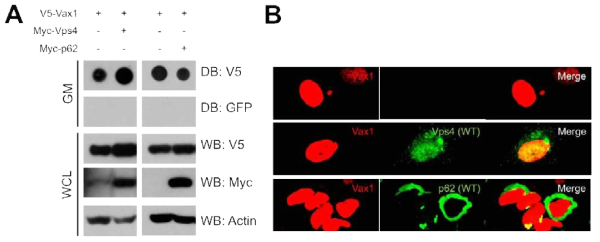 표
Vax1 단백질의 핵막 구조 매개 분비. Vax1 단백질의 비정형적 이동이 핵막에서 유래한 vesicle을 매개할 가능성을 확인하기 위해 endosome 막에서 small vesicle을 형성하는 정상 Vps4와 autophagy 과정에서 유비퀴틴화된 단백질을 막구조로 이동하는 역할을 하는 p62를 HeLa Vax1과 함께 발현한 후 Vax1의 분비(A)와 세포 내 분포(B)를 조사함. 그 결과 Vps4는 Vax1의 분비를 증진하는 것을 알 수 있음. 반대로 p62는 Vax1의 분비를 억제함. 이 결과들은 Vax1의 분비에 Vps4가 관여하는 MVB는 긍정적 연관성을 가지고 있으며, autophagy는 부정적 연관성을 가지고 있음을 시사함
표
Vax1 단백질의 핵막 구조 매개 분비. Vax1 단백질의 비정형적 이동이 핵막에서 유래한 vesicle을 매개할 가능성을 확인하기 위해 endosome 막에서 small vesicle을 형성하는 정상 Vps4와 autophagy 과정에서 유비퀴틴화된 단백질을 막구조로 이동하는 역할을 하는 p62를 HeLa Vax1과 함께 발현한 후 Vax1의 분비(A)와 세포 내 분포(B)를 조사함. 그 결과 Vps4는 Vax1의 분비를 증진하는 것을 알 수 있음. 반대로 p62는 Vax1의 분비를 억제함. 이 결과들은 Vax1의 분비에 Vps4가 관여하는 MVB는 긍정적 연관성을 가지고 있으며, autophagy는 부정적 연관성을 가지고 있음을 시사함
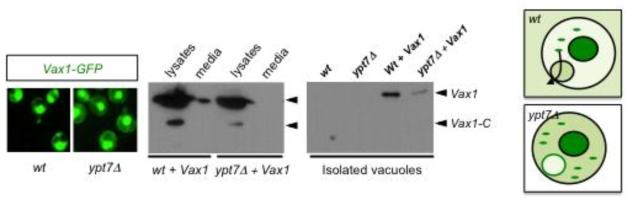 표
효모 vacuole을 매개로 한 Vax1의 수송. 그림 8에서 제시된 lysosome을 매개로한 Vax1의 분비 과정은 효모의 vacuole을 통한 세포내 단백질의 분비 과정과 유사점이 있다. 이를 증명하기 위해 Vax1을 효모에 발현 후 Vax1의 분비와 이동을 검증함. Vax1-GFP 단백질을 정상 (wt) 및 vacuole로의 소포 이동이 저해된 ypt7d 효모에 발현 한 후 세포 내 분포 (왼쪽 그림)와 세포 배양액으로의 분비를 각각 면역형광염색과 Western blotting으로 조사함. 그 결과 Vax1은 정상 효모 배양액에서는 관찰이 되지만 ypt7d 효모에서는 관찰이 되지 않음. 이는 Vax1이 세포 내 막구조 소포에 의해 vaculoe로 이동한 후 분비가 된다는 것을 의미한다. 이를 좀 더 명확히 증명하기 위해 wt과 ypt7d 효모에서 vaculoe을 분리한 후 vacuole에 포함된 Vax1을 관찰한 결과, wt에 비해 ypt7d 효모의 vacuole에 있는 Vax1 단백질의 양이 현저히 적음을 알 수 있었음
표
효모 vacuole을 매개로 한 Vax1의 수송. 그림 8에서 제시된 lysosome을 매개로한 Vax1의 분비 과정은 효모의 vacuole을 통한 세포내 단백질의 분비 과정과 유사점이 있다. 이를 증명하기 위해 Vax1을 효모에 발현 후 Vax1의 분비와 이동을 검증함. Vax1-GFP 단백질을 정상 (wt) 및 vacuole로의 소포 이동이 저해된 ypt7d 효모에 발현 한 후 세포 내 분포 (왼쪽 그림)와 세포 배양액으로의 분비를 각각 면역형광염색과 Western blotting으로 조사함. 그 결과 Vax1은 정상 효모 배양액에서는 관찰이 되지만 ypt7d 효모에서는 관찰이 되지 않음. 이는 Vax1이 세포 내 막구조 소포에 의해 vaculoe로 이동한 후 분비가 된다는 것을 의미한다. 이를 좀 더 명확히 증명하기 위해 wt과 ypt7d 효모에서 vaculoe을 분리한 후 vacuole에 포함된 Vax1을 관찰한 결과, wt에 비해 ypt7d 효모의 vacuole에 있는 Vax1 단백질의 양이 현저히 적음을 알 수 있었음
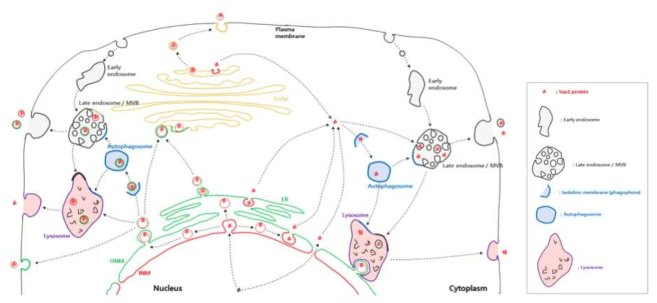 표
분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자의 가능한 세포 내 이동 경로. 호메오도메인 전사인자가 세포 외부로 방출되는 과정은 세포질에서 세포막을 직접 투과하는 과정이나 세포질에 분비과립 내에 위치하여 세포막과 융합 후 분비되는 방식이 가능함. 세포질 내 단백질 형태나 분비과립 형태로 존재하기 위해서 호메오도메인 전사인자들은 핵에서 핵공을 통해 외부로 나오거나 핵 탈출 중간체를 이용해 분비 과립 형태로 세포질로 이동함. 이러한 과정은 직접 핵막이 세포질로 바로 노출되거나 핵외막과 연결된 소포체를 매개하는 방식이 가능함. 이러한 다양한 가능성을 염두에 두고 향후 호메오도메인 전사인자 단백질들의 분비 과정을 규명하는 연구를 계획할 예정임
표
분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자의 가능한 세포 내 이동 경로. 호메오도메인 전사인자가 세포 외부로 방출되는 과정은 세포질에서 세포막을 직접 투과하는 과정이나 세포질에 분비과립 내에 위치하여 세포막과 융합 후 분비되는 방식이 가능함. 세포질 내 단백질 형태나 분비과립 형태로 존재하기 위해서 호메오도메인 전사인자들은 핵에서 핵공을 통해 외부로 나오거나 핵 탈출 중간체를 이용해 분비 과립 형태로 세포질로 이동함. 이러한 과정은 직접 핵막이 세포질로 바로 노출되거나 핵외막과 연결된 소포체를 매개하는 방식이 가능함. 이러한 다양한 가능성을 염두에 두고 향후 호메오도메인 전사인자 단백질들의 분비 과정을 규명하는 연구를 계획할 예정임
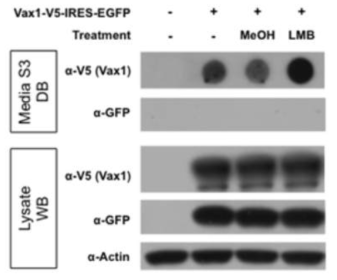 표
핵 탈출 비의존성 Vax1 분비. HeLa 세포에 Vax1-V5-IRES-EGFP를 발현하고 해당 세포를 12시간 동안 MeOH 또는 핵공 의존성 핵 탈출을 억제하는 leptomycin B (LMB)를 처리 후 세포 배양액에 존재하는 Vax1을 검출함. LMB 처리는 Vax1의 세포 배양액으로 분비된 Vax1의 양을 증가시킴. 해당 세포들에서 Vax1과 동시에 발현된 EGFP의 경우는 어떤 조건에서도 세포 배양액으로 분비가 되지 않는 것으로 보아, LMB 처리에 의한 Vax1의 분비 증가는 Vax1의 분비가 핵공에 의한 것이 아님을 시사함
표
핵 탈출 비의존성 Vax1 분비. HeLa 세포에 Vax1-V5-IRES-EGFP를 발현하고 해당 세포를 12시간 동안 MeOH 또는 핵공 의존성 핵 탈출을 억제하는 leptomycin B (LMB)를 처리 후 세포 배양액에 존재하는 Vax1을 검출함. LMB 처리는 Vax1의 세포 배양액으로 분비된 Vax1의 양을 증가시킴. 해당 세포들에서 Vax1과 동시에 발현된 EGFP의 경우는 어떤 조건에서도 세포 배양액으로 분비가 되지 않는 것으로 보아, LMB 처리에 의한 Vax1의 분비 증가는 Vax1의 분비가 핵공에 의한 것이 아님을 시사함
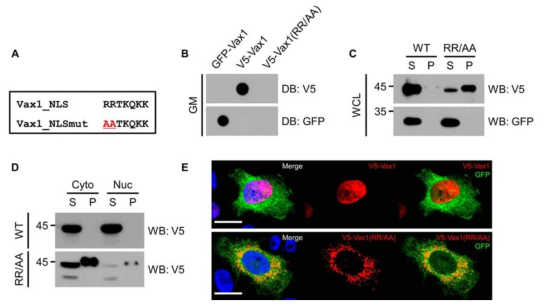 표
Vax1 핵 위치 돌연변이의 조사. (A) Vax1의 호메오도메인 상에 존재하는 핵 위치신호(nuclear localization signal, NLS)에 해당하는 151번과 152번 위치에 있는 arginine(R) 아미노산을 alanine(A)으로 변경함. 정상 Vax1과 Vax1의 NLS 변이형 Vax1(RR/AA)를 HeLa 세포에 과발현한 후 해당 단백질들의 분비를 DB로 조사하고 (B), 이들 단백질들의 세포 내 상대량을 RIPA buffer로 추출한 세포 내 단백질들을 WB로 조사함. Vax1(RR/AA)는 정상 Vax1에 비해 RIPA에 의해 추출되는 분획(soluble, S)에 양이 줄어들어 있었으며, RIPA에 의해 추출되지 않은 분획(precipitate, P)에 집중되어 있음. 이는 Vax1(RR/AA)가 세포 내에서 응집체를 만들 가능성을 시사함. (D) 정상 Vax1과 Vax1의 NLS 변이형 Vax1(RR/AA)의 세포 내 위치를 핵과 세포질 나눈 세포 분획의 WB를 통해 조사함. 또한, 각 분획에서 Vax1의 응집 여부를 RIPA 추출 여부를 통해 조사함. (E) 정상 Vax1과 Vax1의 NLS 변이형 Vax1(RR/AA)의 세포 내 위치를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. DAPI는 핵내 DNA를 표지하며, GFP는 Vax1 단백질들과 동일한 DNA construct에 encoding 되어 있으며 독립적으로 번역이 되므로 Vax1을 발현하는 세포를 표지함. GFP는 주로 세포질에 분포하며 일부는 핵에도 존재함
표
Vax1 핵 위치 돌연변이의 조사. (A) Vax1의 호메오도메인 상에 존재하는 핵 위치신호(nuclear localization signal, NLS)에 해당하는 151번과 152번 위치에 있는 arginine(R) 아미노산을 alanine(A)으로 변경함. 정상 Vax1과 Vax1의 NLS 변이형 Vax1(RR/AA)를 HeLa 세포에 과발현한 후 해당 단백질들의 분비를 DB로 조사하고 (B), 이들 단백질들의 세포 내 상대량을 RIPA buffer로 추출한 세포 내 단백질들을 WB로 조사함. Vax1(RR/AA)는 정상 Vax1에 비해 RIPA에 의해 추출되는 분획(soluble, S)에 양이 줄어들어 있었으며, RIPA에 의해 추출되지 않은 분획(precipitate, P)에 집중되어 있음. 이는 Vax1(RR/AA)가 세포 내에서 응집체를 만들 가능성을 시사함. (D) 정상 Vax1과 Vax1의 NLS 변이형 Vax1(RR/AA)의 세포 내 위치를 핵과 세포질 나눈 세포 분획의 WB를 통해 조사함. 또한, 각 분획에서 Vax1의 응집 여부를 RIPA 추출 여부를 통해 조사함. (E) 정상 Vax1과 Vax1의 NLS 변이형 Vax1(RR/AA)의 세포 내 위치를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. DAPI는 핵내 DNA를 표지하며, GFP는 Vax1 단백질들과 동일한 DNA construct에 encoding 되어 있으며 독립적으로 번역이 되므로 Vax1을 발현하는 세포를 표지함. GFP는 주로 세포질에 분포하며 일부는 핵에도 존재함
 표
분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자의 핵 탈출 중간체 발견. 분비능을 가지는 호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포내에서의 분포 형태를 면역형광염색법으로 관찰하는 과정에서 그들이 세포핵 내부에 존재하고 있음은 물론 세포핵에서 가까운 부위에서 작은 소낭(small vesicle)의 형태로도 존재하고 있음을 확인하였음. 또한 이들 중의 일부는 세포핵에서 곧바로 나오는듯한 모습을 하고 있음을 확인할 수 있었으며, 이들을 감싸고 있는 소낭이 모두 핵막에 존재하는 핵막 단백질인 LaminB로 구성되어 있음을 확인할 수 있었음. 이러한 사실은 세포핵 안에 존재하던 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자들이 세포핵 바깥으로 배출되는 과정에서 그것이 직접 핵막을 통과하여 분비될 가능성을 제시함
표
분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자의 핵 탈출 중간체 발견. 분비능을 가지는 호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포내에서의 분포 형태를 면역형광염색법으로 관찰하는 과정에서 그들이 세포핵 내부에 존재하고 있음은 물론 세포핵에서 가까운 부위에서 작은 소낭(small vesicle)의 형태로도 존재하고 있음을 확인하였음. 또한 이들 중의 일부는 세포핵에서 곧바로 나오는듯한 모습을 하고 있음을 확인할 수 있었으며, 이들을 감싸고 있는 소낭이 모두 핵막에 존재하는 핵막 단백질인 LaminB로 구성되어 있음을 확인할 수 있었음. 이러한 사실은 세포핵 안에 존재하던 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자들이 세포핵 바깥으로 배출되는 과정에서 그것이 직접 핵막을 통과하여 분비될 가능성을 제시함
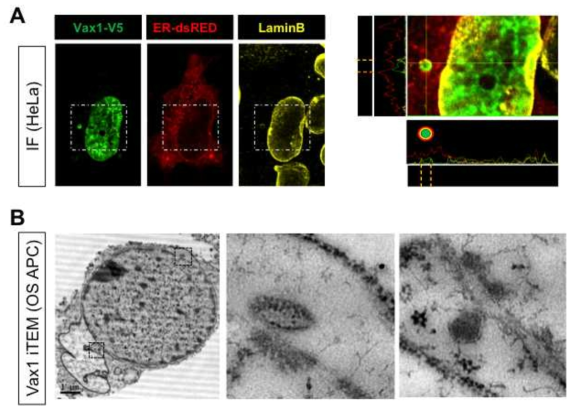 표
Vax1의 핵 탈출 중간체 위치. (A) Vax1 호메오도메인 전사인자를 HeLa 세포에 발현 시 핵 내 뿐만 아니 라 핵 주변 구조에도 위치함을 알 수 있음. 이러한 핵 주변 구조체는 핵 내막 단백질인 laminB와 소포체 막단백질인 ER-dsRed 단백질을 함께 포함함을 알 수 있음. (B) 이러한 Vax1의 핵막 유래 구조체 내 위치는 생쥐 시신경 신경조세포 전구세포 (optic stalk astrocyte precursor (OS-APC))에서도 관찰됨. 특히 Vax1을 포함하는 구조체는 단일막구조 뿐만 아니라 이중막구조까지 관찰되며 일부는 핵막에서 돌출된 형태를 보임
표
Vax1의 핵 탈출 중간체 위치. (A) Vax1 호메오도메인 전사인자를 HeLa 세포에 발현 시 핵 내 뿐만 아니 라 핵 주변 구조에도 위치함을 알 수 있음. 이러한 핵 주변 구조체는 핵 내막 단백질인 laminB와 소포체 막단백질인 ER-dsRed 단백질을 함께 포함함을 알 수 있음. (B) 이러한 Vax1의 핵막 유래 구조체 내 위치는 생쥐 시신경 신경조세포 전구세포 (optic stalk astrocyte precursor (OS-APC))에서도 관찰됨. 특히 Vax1을 포함하는 구조체는 단일막구조 뿐만 아니라 이중막구조까지 관찰되며 일부는 핵막에서 돌출된 형태를 보임
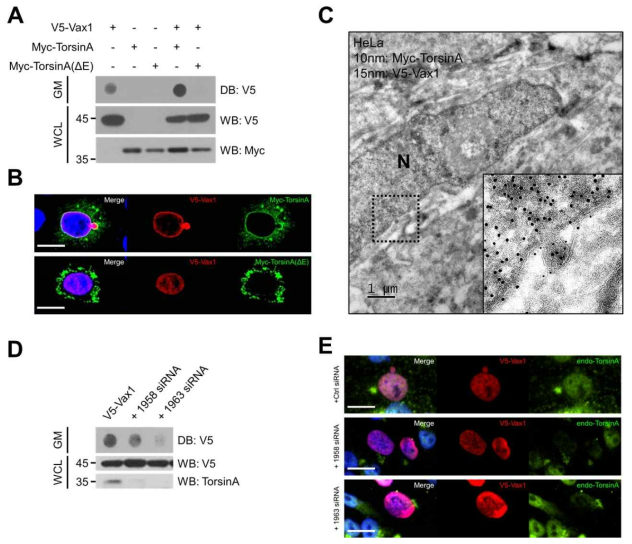 표
TorsinA에 의한 Vax1 분비 조절. (A) HeLa 세포에 TorsinA-WT과 ATPase inactive TorsinA-ΔE를 V5-Vax1과 함께 과발현 후 배양액에 분비된 Vax1의 양과 세포 내 Vax1의 양을 Dot-Blot (DB)과 WB으로 조사함. (B) TorsinA의 Vax1의 세포 내 분포에 미치는 영향을 면역형 광염색으로 조사함. (C) Vax1과 TorsinA를 각각 표지한 입자가 핵막으로부터 돌출된 부분에 함께 위치하는 것을 면역투과전자현미경 기법으로 확인함. (D) Human TorsinA에 대한 siRNA를 2종 합성하여 Vax1을 과발현하는 HeLa 세포에 처리 후 Vax1의 분비를 조사함. (E) TorsinA siRNA를 처리한 세포에서 Vax1의 세포 내 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사함
표
TorsinA에 의한 Vax1 분비 조절. (A) HeLa 세포에 TorsinA-WT과 ATPase inactive TorsinA-ΔE를 V5-Vax1과 함께 과발현 후 배양액에 분비된 Vax1의 양과 세포 내 Vax1의 양을 Dot-Blot (DB)과 WB으로 조사함. (B) TorsinA의 Vax1의 세포 내 분포에 미치는 영향을 면역형 광염색으로 조사함. (C) Vax1과 TorsinA를 각각 표지한 입자가 핵막으로부터 돌출된 부분에 함께 위치하는 것을 면역투과전자현미경 기법으로 확인함. (D) Human TorsinA에 대한 siRNA를 2종 합성하여 Vax1을 과발현하는 HeLa 세포에 처리 후 Vax1의 분비를 조사함. (E) TorsinA siRNA를 처리한 세포에서 Vax1의 세포 내 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사함
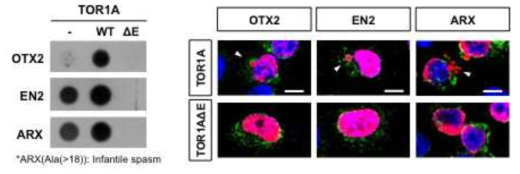 표
Torsin에 의한 호메오도메인 단백질 분비 조절. 선행연구를 통해 VAX1 단백질의 분비가 ER 내부/핵막 간 단백질인 Torsin에 의해 조절됨을 증명한 바 있다. 이러한 Torsin의 기능이 다른 호메오도메인 전사인자의 분비에도 관련되어 있는지를 증명하고자 정상 (WT)과 비활성화 (dE) Torsin을 각 분비성 호메오도메인 단백질과 함께 HeLa 세포에 발현 후 세포 외부로 분비된 호메오도메인 단백질을 dot blot으로 검증하였다. 그 결과 Torsin WT은 분비를 촉진하는 반면 dE 변이형은 이들 단백질의 분비를 공통적으로 억제하였다. 또한 dE가 함께 발현된 세포에서 호메오도메인 단백질은 정상 세포에서 발현시 관찰되는 핵 돌출구조가 관찰되지 않음을 알 수 있다. 이는 Torsin에 의해 유도되는 핵 내막 유래 소포에 의해 호메오도메인 전사인자 단백질들의 분비가 매개된다는 것을 간접적으로 제시한다
표
Torsin에 의한 호메오도메인 단백질 분비 조절. 선행연구를 통해 VAX1 단백질의 분비가 ER 내부/핵막 간 단백질인 Torsin에 의해 조절됨을 증명한 바 있다. 이러한 Torsin의 기능이 다른 호메오도메인 전사인자의 분비에도 관련되어 있는지를 증명하고자 정상 (WT)과 비활성화 (dE) Torsin을 각 분비성 호메오도메인 단백질과 함께 HeLa 세포에 발현 후 세포 외부로 분비된 호메오도메인 단백질을 dot blot으로 검증하였다. 그 결과 Torsin WT은 분비를 촉진하는 반면 dE 변이형은 이들 단백질의 분비를 공통적으로 억제하였다. 또한 dE가 함께 발현된 세포에서 호메오도메인 단백질은 정상 세포에서 발현시 관찰되는 핵 돌출구조가 관찰되지 않음을 알 수 있다. 이는 Torsin에 의해 유도되는 핵 내막 유래 소포에 의해 호메오도메인 전사인자 단백질들의 분비가 매개된다는 것을 간접적으로 제시한다
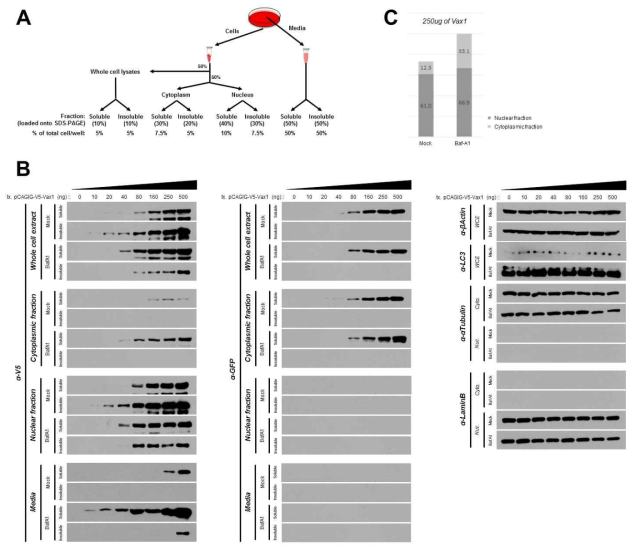 표
세포 내 Vax1 농도 구배를 통한 BafilomycinA1의 작용 역추론. Vax1의 분비를 극적으로 증가시키는 bafilomycinA1의 적용 범위를 추론하기 위해 Vax1의 세포 내 농도를 조절하여 세포 분획 별로 조사함. BafilomycinA1의 첨가로 인해 Vax1의 세포 외 분비 (Media)가 증가하며, 동시에 세포 내 (WCE; whole cell extract) Vax1의 양적인 증가를 확인함. 세포 분획법을 통해 세포질 (Cyto; cytoplasm)과 세포핵 (Nuc; nucleus)을 분리하여 각각의 분획에 존재하는 Vax1의 양을 비교하여 세포 내 Vax1의 양적인 증가가 세포질에서의 Vax1 증가에서 기인한 것임을 확인함
표
세포 내 Vax1 농도 구배를 통한 BafilomycinA1의 작용 역추론. Vax1의 분비를 극적으로 증가시키는 bafilomycinA1의 적용 범위를 추론하기 위해 Vax1의 세포 내 농도를 조절하여 세포 분획 별로 조사함. BafilomycinA1의 첨가로 인해 Vax1의 세포 외 분비 (Media)가 증가하며, 동시에 세포 내 (WCE; whole cell extract) Vax1의 양적인 증가를 확인함. 세포 분획법을 통해 세포질 (Cyto; cytoplasm)과 세포핵 (Nuc; nucleus)을 분리하여 각각의 분획에 존재하는 Vax1의 양을 비교하여 세포 내 Vax1의 양적인 증가가 세포질에서의 Vax1 증가에서 기인한 것임을 확인함
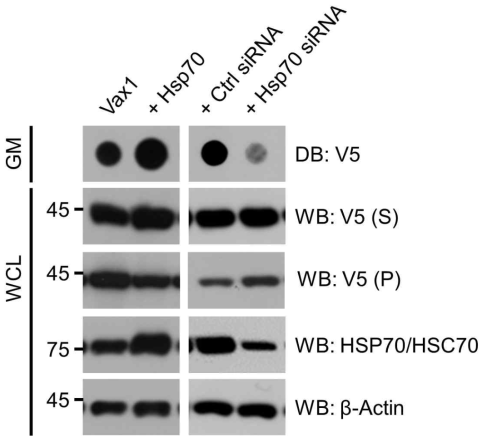 표
Hsp70에 의한 Vax1 분비 조절. Vax1과 상호작용하는 것으로 확인된 단백질들 중 세포 내 단백질들의 용해도와 관련이 있는 후보를 검색한 결과 heat-shock protein 70 (Hsp70)과 Hsp28이 확인됨 (Kim et al. (2014)). 이 중 Hsp70이 Vax1의 세포 내 용해도를 조절하여 Vax1 단백질의 분비를 조절할 가능성을 확인하기 위해 Vax1을 Hsp70이 과발현된 상태에서 함께 발현하거나, siRNA를 이용하여 Hsp70의 양을 줄인 세포에 Vax1을 발현하고 Vax1의 세포 외 분비를 DB로 조사함. 세포 내 Vax1 양은 WB로 조사함. Vax1은 Hsp70 양이 증가된 세포에서 분비가 촉진되고, Hsp70 양이 감소된 세포에서는 분비가 감소함을 확인함. 이는 Hsp70이 Vax1의 세포 내 용해도를 증가시켜 분비를 촉진할 것이라는 가설을 지지함
표
Hsp70에 의한 Vax1 분비 조절. Vax1과 상호작용하는 것으로 확인된 단백질들 중 세포 내 단백질들의 용해도와 관련이 있는 후보를 검색한 결과 heat-shock protein 70 (Hsp70)과 Hsp28이 확인됨 (Kim et al. (2014)). 이 중 Hsp70이 Vax1의 세포 내 용해도를 조절하여 Vax1 단백질의 분비를 조절할 가능성을 확인하기 위해 Vax1을 Hsp70이 과발현된 상태에서 함께 발현하거나, siRNA를 이용하여 Hsp70의 양을 줄인 세포에 Vax1을 발현하고 Vax1의 세포 외 분비를 DB로 조사함. 세포 내 Vax1 양은 WB로 조사함. Vax1은 Hsp70 양이 증가된 세포에서 분비가 촉진되고, Hsp70 양이 감소된 세포에서는 분비가 감소함을 확인함. 이는 Hsp70이 Vax1의 세포 내 용해도를 증가시켜 분비를 촉진할 것이라는 가설을 지지함
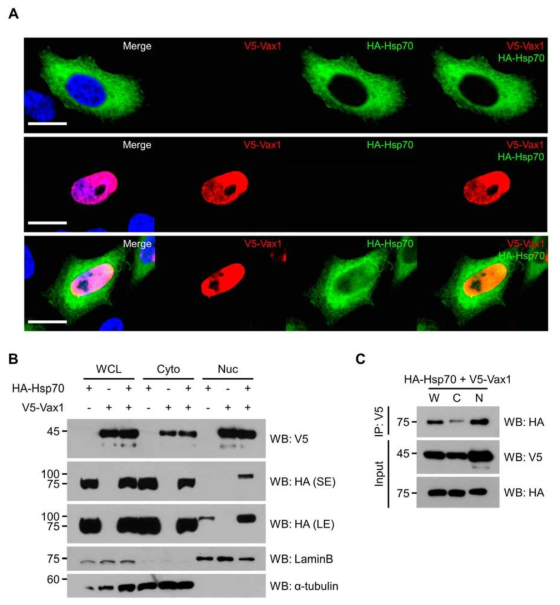 표
Vax1과 Hsp70 사이의 세포 내 관계 조사. (A) Vax1과 Hsp70의 독립적 세포 내 분포와 공동으로 발현된 세포에서의 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. Vax1의 경우는 Hsp70 존재 여부와 상관없이 지속적으로 세포핵 내에 존재함. Hsp70은 그 자체로는 주로 세포질에 존재하지만, Vax1과 함께 발현되면 세포핵 내에서도 일부가 관찰됨. (B) Vax1과 Hsp70 사이의 세포 내 분포를 세포 분획별 웨스턴 블롯 (WB)으로 조사함. (A)의 결과와 유사하게 Hsp70은 Vax1과 함께 발현된 상황에서는 세포핵에서도 관찰이 됨. 이 경과들은 Vax1이 Hsp70과 결합하여 세포핵 내부로 끌고 갈 가능성을 의미한다. (C) Vax1과 Hsp70 사이의 상호작용을 co-IP를 이용하여 직접 조사함. 그 결과 HA-Hsp70이 V5 항체를 이용하여 V5-Vax1을 IP하면 함께 분리됨을 알 수 있음
표
Vax1과 Hsp70 사이의 세포 내 관계 조사. (A) Vax1과 Hsp70의 독립적 세포 내 분포와 공동으로 발현된 세포에서의 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. Vax1의 경우는 Hsp70 존재 여부와 상관없이 지속적으로 세포핵 내에 존재함. Hsp70은 그 자체로는 주로 세포질에 존재하지만, Vax1과 함께 발현되면 세포핵 내에서도 일부가 관찰됨. (B) Vax1과 Hsp70 사이의 세포 내 분포를 세포 분획별 웨스턴 블롯 (WB)으로 조사함. (A)의 결과와 유사하게 Hsp70은 Vax1과 함께 발현된 상황에서는 세포핵에서도 관찰이 됨. 이 경과들은 Vax1이 Hsp70과 결합하여 세포핵 내부로 끌고 갈 가능성을 의미한다. (C) Vax1과 Hsp70 사이의 상호작용을 co-IP를 이용하여 직접 조사함. 그 결과 HA-Hsp70이 V5 항체를 이용하여 V5-Vax1을 IP하면 함께 분리됨을 알 수 있음
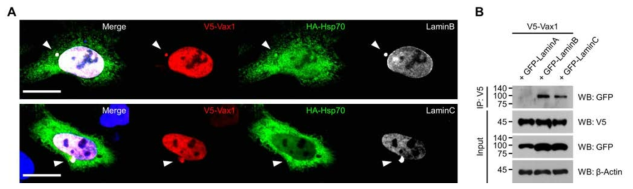 표
Vax1 막소포와 핵막 구조체, 그리고 Hsp70의 관계 조사. (A) Vax1의 막소포와 Hsp70의 세포 내 상호 분포를 핵막 구조체 표시자인 LaminB, LaminC 단백질과 함께 면역형광염색으로 조사함. (화살표 머리) Vax1, Hsp70, 핵막 구조체가 하나의 신호로 겹쳐지는 것으로 보아 Vax1의 막소포는 핵막에서 유래되었으며, Vax1에 의해 세포핵으로 내제화된 Hsp70이 Vax1의 막소포 형성에 참여하고 있음을 유추할 수 있음. (B) 핵막 구조체 단백질 lamin과 Vax1 사이의 상호작용을 면역침강반응으로 조사함
표
Vax1 막소포와 핵막 구조체, 그리고 Hsp70의 관계 조사. (A) Vax1의 막소포와 Hsp70의 세포 내 상호 분포를 핵막 구조체 표시자인 LaminB, LaminC 단백질과 함께 면역형광염색으로 조사함. (화살표 머리) Vax1, Hsp70, 핵막 구조체가 하나의 신호로 겹쳐지는 것으로 보아 Vax1의 막소포는 핵막에서 유래되었으며, Vax1에 의해 세포핵으로 내제화된 Hsp70이 Vax1의 막소포 형성에 참여하고 있음을 유추할 수 있음. (B) 핵막 구조체 단백질 lamin과 Vax1 사이의 상호작용을 면역침강반응으로 조사함
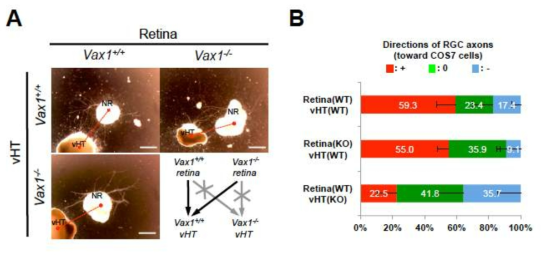 표
Vax1의 비자가성 망막 신경 축삭 성장 촉진 효과. 수정 후 13일째 정상 생쥐 망막과 ventral hypothalamus (vHT), 그리고, Vax1 결핍 생쥐 망막과 vHT를 각각 분리한 후 교차 상호 배양을 통해 Vax1의 존재 여부가 망막 신경의 성장에 미치는 영향을 조사함. Vax1이 결핍된 망막은 정상 vHT와 Vax1 결핍 vHT와 배양시 정상적인 축삭의 성장을 보인 반면, 정상 망막과 Vax1 결핍 망막 모두 Vax1 결핍 vHT와 공동 배양 시는 축삭 성장이 억제되는 양상을 나타냄. 이는 Vax1의 망막 내부 발현 보다는 vHT에서의 발현이 망막 신경 축삭의 성장에 필수적임을 시사함
표
Vax1의 비자가성 망막 신경 축삭 성장 촉진 효과. 수정 후 13일째 정상 생쥐 망막과 ventral hypothalamus (vHT), 그리고, Vax1 결핍 생쥐 망막과 vHT를 각각 분리한 후 교차 상호 배양을 통해 Vax1의 존재 여부가 망막 신경의 성장에 미치는 영향을 조사함. Vax1이 결핍된 망막은 정상 vHT와 Vax1 결핍 vHT와 배양시 정상적인 축삭의 성장을 보인 반면, 정상 망막과 Vax1 결핍 망막 모두 Vax1 결핍 vHT와 공동 배양 시는 축삭 성장이 억제되는 양상을 나타냄. 이는 Vax1의 망막 내부 발현 보다는 vHT에서의 발현이 망막 신경 축삭의 성장에 필수적임을 시사함
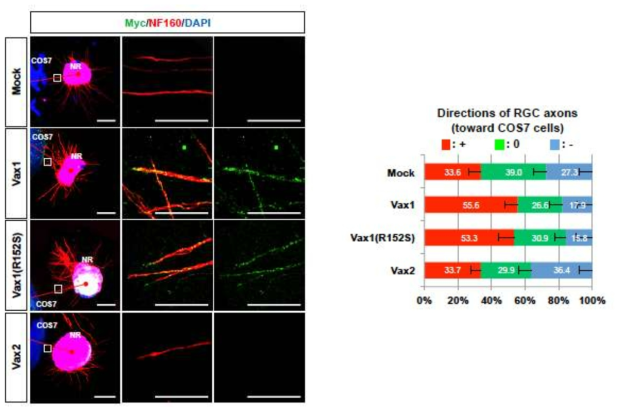 표
Vax1 전사인자활성 비의존적 망막 신경 축삭 촉진 효과. 정상 Vax1과 전사인자 활성이 결핍된 Vax1(R152S), 또는 Vax2를 COS7 세포에 발현 한 후 수정후 13일째 생쥐 망막과 공동 배양하여 이들 세포가 Vax1이 생체 내에서 기능을 하는 vHT를 대체할 수 있는지를 조사함. 생쥐 망막 신경 축삭은 Vax1을 발현하는 COS7 세포와 Vax1(R152S)를 발현하는 COS7 세포에는 선택적 성장을 하지만, 일반 COS7과 Vax2를 발현하는 COS7 세포로는 선택적 성장을 하지 않는 것으로 나타남. 이는 Vax1 전사인자 활성이 아니라 Vax1 단백질 자체가 망막 신경 축삭의 성장에 필요함을 시사함. 흥미롭게, 망막 신경 축삭 성장을 유도한 Vax1과 Vax1(R152S)의 경우는 망막 신경 유전자를 발현한 COS7 세포뿐만 아니라 유전자를 발현해 주지 않은 망막 신경 축삭에서도 면역형광염색시 검출이 되는 것으로 확인됨. 이와 달리 망막 신경 축삭 성장을 유도하지 않은 Vax2의 경우는 망막 신경 축삭에는 전혀 검출이되지 않음. 이는 Vax1 및 Vax1(R152S) 단백질이 망막 신경 축삭으로 이동을 하였음을 의미하는 결과로 판단됨
표
Vax1 전사인자활성 비의존적 망막 신경 축삭 촉진 효과. 정상 Vax1과 전사인자 활성이 결핍된 Vax1(R152S), 또는 Vax2를 COS7 세포에 발현 한 후 수정후 13일째 생쥐 망막과 공동 배양하여 이들 세포가 Vax1이 생체 내에서 기능을 하는 vHT를 대체할 수 있는지를 조사함. 생쥐 망막 신경 축삭은 Vax1을 발현하는 COS7 세포와 Vax1(R152S)를 발현하는 COS7 세포에는 선택적 성장을 하지만, 일반 COS7과 Vax2를 발현하는 COS7 세포로는 선택적 성장을 하지 않는 것으로 나타남. 이는 Vax1 전사인자 활성이 아니라 Vax1 단백질 자체가 망막 신경 축삭의 성장에 필요함을 시사함. 흥미롭게, 망막 신경 축삭 성장을 유도한 Vax1과 Vax1(R152S)의 경우는 망막 신경 유전자를 발현한 COS7 세포뿐만 아니라 유전자를 발현해 주지 않은 망막 신경 축삭에서도 면역형광염색시 검출이 되는 것으로 확인됨. 이와 달리 망막 신경 축삭 성장을 유도하지 않은 Vax2의 경우는 망막 신경 축삭에는 전혀 검출이되지 않음. 이는 Vax1 및 Vax1(R152S) 단백질이 망막 신경 축삭으로 이동을 하였음을 의미하는 결과로 판단됨
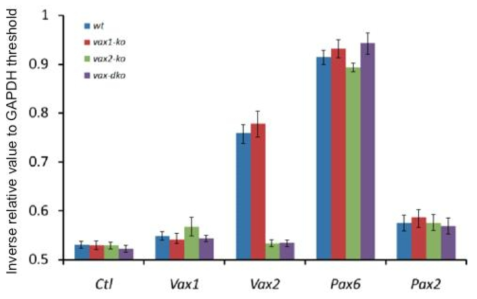 표
생쥐 망막에서 Vax1 mRNA 발현 검사. 수정 후 14.5일 정상 (wt), Vax1 결핍 (vax1-ko), Vax2 결핍 (vax2-ko), Vax1과 Vax2 공동 결핍 (vax-dko) 생쥐 망막에서 RNA를 분리 후 RT-qPCR을 통해 Vax1, Vax2, Pax6, Pax6, Pax2 mRNA의 양을 측정 후 이 값을 GAPDH PCR product에 대한 상대적 양으로 변환 후 상호 비교함. 그 결과 정상 망막에서의 Vax1 양이 Vax1이 결핍된 망막에서의 Vax1 양과 비교해 거의 차이가 없는 것으로 보아, 망막 내 미세한 양의 Vax1 mRNA에서 합성된 Vax1이 단백질이 그림 7에서 면역형광 염색에서 나타난 결과가 아님을 증명함
표
생쥐 망막에서 Vax1 mRNA 발현 검사. 수정 후 14.5일 정상 (wt), Vax1 결핍 (vax1-ko), Vax2 결핍 (vax2-ko), Vax1과 Vax2 공동 결핍 (vax-dko) 생쥐 망막에서 RNA를 분리 후 RT-qPCR을 통해 Vax1, Vax2, Pax6, Pax6, Pax2 mRNA의 양을 측정 후 이 값을 GAPDH PCR product에 대한 상대적 양으로 변환 후 상호 비교함. 그 결과 정상 망막에서의 Vax1 양이 Vax1이 결핍된 망막에서의 Vax1 양과 비교해 거의 차이가 없는 것으로 보아, 망막 내 미세한 양의 Vax1 mRNA에서 합성된 Vax1이 단백질이 그림 7에서 면역형광 염색에서 나타난 결과가 아님을 증명함
 표
생체 내 Vax1 단백질의 세포 간 이동 증거. Vax1의 mRNA의 발현을 in situ RNA hybridization을 통하여 조사한 결과 Vax1은 optic stalk에서만 발현이 되고 망막에는 전혀 발현이 되지 않지만 (A), 면역형광염색을 통해 Vax1 단백질의 분포를 조사한 결과 Vax1 단백질은 망막에서도 발현이 되는 것으로 검출이 됨 (B, 녹색). 하지만, 망막에서 Vax1이 검출된 망막 갱글리온세포는 optic stalk의 경우와 달리 Vax1 유전자 부위에서 발현되는 lacZ에 의해 생성된 b-galactosidase (b-Gal) 단백질이 전혀 검출이 되지 않음. 이는 망막 갱글리온세포내에 존재하는 Vax1 단백질은 세포 내부에서 생성된 것이 아니라 세포 외부에서 이동된 것임을 시사함
표
생체 내 Vax1 단백질의 세포 간 이동 증거. Vax1의 mRNA의 발현을 in situ RNA hybridization을 통하여 조사한 결과 Vax1은 optic stalk에서만 발현이 되고 망막에는 전혀 발현이 되지 않지만 (A), 면역형광염색을 통해 Vax1 단백질의 분포를 조사한 결과 Vax1 단백질은 망막에서도 발현이 되는 것으로 검출이 됨 (B, 녹색). 하지만, 망막에서 Vax1이 검출된 망막 갱글리온세포는 optic stalk의 경우와 달리 Vax1 유전자 부위에서 발현되는 lacZ에 의해 생성된 b-galactosidase (b-Gal) 단백질이 전혀 검출이 되지 않음. 이는 망막 갱글리온세포내에 존재하는 Vax1 단백질은 세포 내부에서 생성된 것이 아니라 세포 외부에서 이동된 것임을 시사함
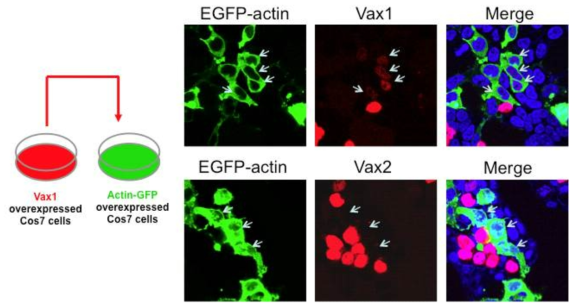 표
Vax1의 세포 간 이동. Myc-Vax1 또는 Myc-Vax2를 각각 COS7 세포에 발현하고 이 세포들을 Actin-EGFP를 발현하는 COS7 세포와 섞어서 24시간 동안 배양 후 Actin-EGFP를 발현하는 세포에 Vax1 또는 Vax2의 존재 여부를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. Vax1을 발현하는 세포와 공동 배양한 Actin-EGFP COS7 세포들 중 일부는 Vax1을 포함하고 있는 반면, Vax2를 발현하는 세포와 공동 배양한 Actin-EGFP COS7 세포들은 전혀 Vax2를 포함하고 있지 않았다. 이 결과는 Vax1이 특이적으로 주변 세포로 이동할 수 있는 특징을 가지고 있음을 시사한다
표
Vax1의 세포 간 이동. Myc-Vax1 또는 Myc-Vax2를 각각 COS7 세포에 발현하고 이 세포들을 Actin-EGFP를 발현하는 COS7 세포와 섞어서 24시간 동안 배양 후 Actin-EGFP를 발현하는 세포에 Vax1 또는 Vax2의 존재 여부를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. Vax1을 발현하는 세포와 공동 배양한 Actin-EGFP COS7 세포들 중 일부는 Vax1을 포함하고 있는 반면, Vax2를 발현하는 세포와 공동 배양한 Actin-EGFP COS7 세포들은 전혀 Vax2를 포함하고 있지 않았다. 이 결과는 Vax1이 특이적으로 주변 세포로 이동할 수 있는 특징을 가지고 있음을 시사한다
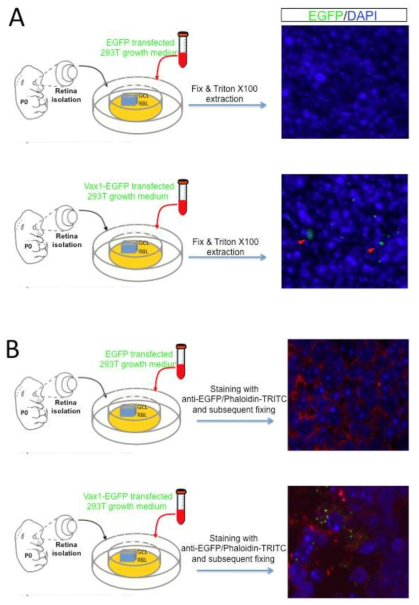 표
Vax1 단백질의 망막조직 내부로의 이동과 및 망막 신경세포 외부에의 집중적 분포. 그림 17의 배양 세포주를 이용한 실험과 마찬가지로 EGFP 또는 Vax1-EGFP를 발현하는 세포의 배양액을 P0 생쥐 망막조직에 3 시간 동안 처리한 후 망막세포 내부로 이동한 EGFP 단백질 (A)과 세포 외부에 남아 있는 EGFP 단백질 (B)을 differential fixing & staining method를 통해 조사함. 그 결과 Vax1 단백질은 망막조직 외부에 다량 결합하고 있으며 (B), 일부는 세포 내부에까지 이동할 수 있음 (A)을 알 수 있다
표
Vax1 단백질의 망막조직 내부로의 이동과 및 망막 신경세포 외부에의 집중적 분포. 그림 17의 배양 세포주를 이용한 실험과 마찬가지로 EGFP 또는 Vax1-EGFP를 발현하는 세포의 배양액을 P0 생쥐 망막조직에 3 시간 동안 처리한 후 망막세포 내부로 이동한 EGFP 단백질 (A)과 세포 외부에 남아 있는 EGFP 단백질 (B)을 differential fixing & staining method를 통해 조사함. 그 결과 Vax1 단백질은 망막조직 외부에 다량 결합하고 있으며 (B), 일부는 세포 내부에까지 이동할 수 있음 (A)을 알 수 있다
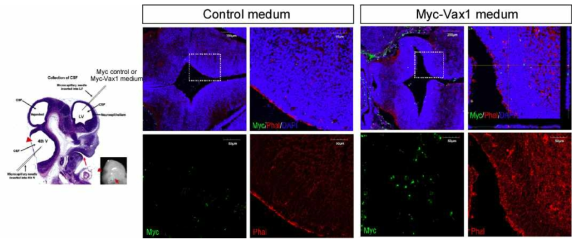 표
Vax1 단백질의 뇌 조직 침투. Myc-Vax1을 발현하는 293T 세포 배양액을 수정 후 14일 된 생쥐 배아 뇌실에 미세주입 후 12 시간 후 생쥐 전뇌 세포에 도입된 Vax1 단백질을 Myc을 이용한 면역형광염색으로 확인함. 그 결과 Myc 만을 발현하는 293T 세포 배양액을 주입한 뇌에서는 Myc 면역 형광 염색이 검출되지 않은 반면, Myc-Vax1 배양액을 주입한 전뇌 뇌실 근처의 세포들은 Myc-Vax1 면역형광 신호를 나타내었다. 이는 Myc-Vax1-293T 배양액 내 존재하던 Myc-Vax1 단백질이 뇌세포로 이동함을 시사하는 결과로 해석된다
표
Vax1 단백질의 뇌 조직 침투. Myc-Vax1을 발현하는 293T 세포 배양액을 수정 후 14일 된 생쥐 배아 뇌실에 미세주입 후 12 시간 후 생쥐 전뇌 세포에 도입된 Vax1 단백질을 Myc을 이용한 면역형광염색으로 확인함. 그 결과 Myc 만을 발현하는 293T 세포 배양액을 주입한 뇌에서는 Myc 면역 형광 염색이 검출되지 않은 반면, Myc-Vax1 배양액을 주입한 전뇌 뇌실 근처의 세포들은 Myc-Vax1 면역형광 신호를 나타내었다. 이는 Myc-Vax1-293T 배양액 내 존재하던 Myc-Vax1 단백질이 뇌세포로 이동함을 시사하는 결과로 해석된다
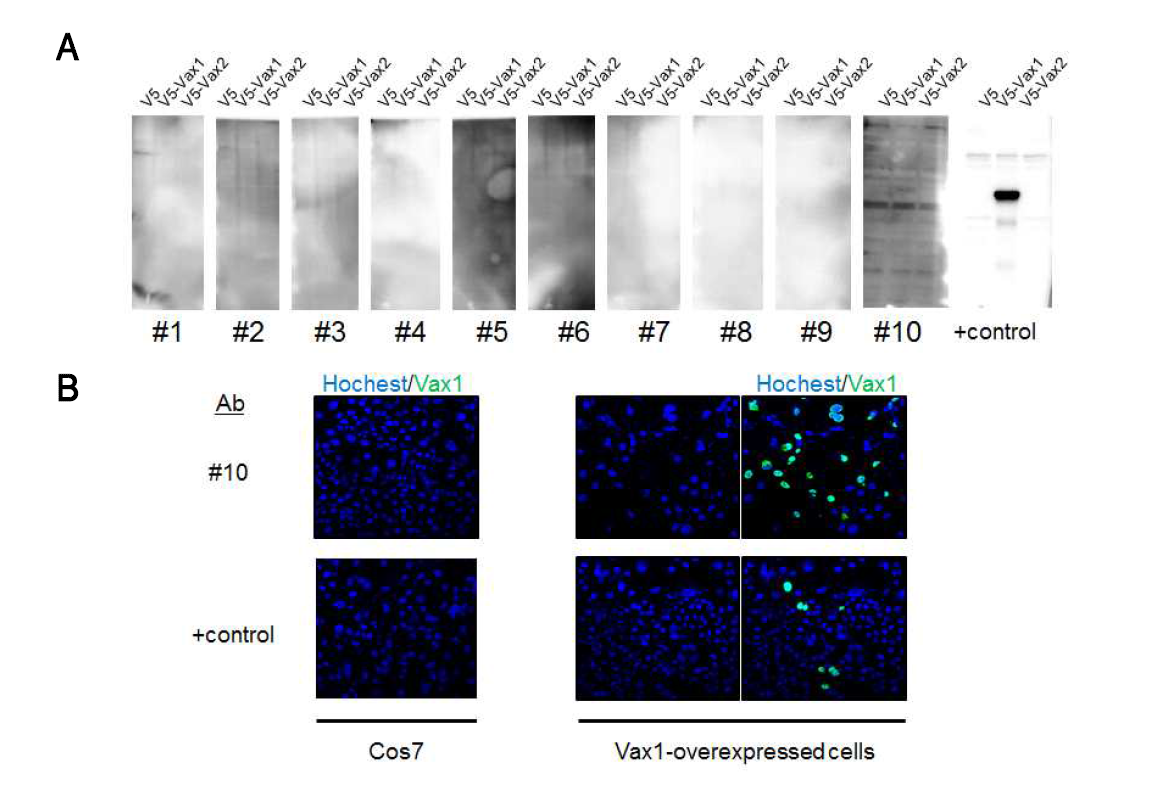 표
Vax1 단일항체 제작을 위한 생쥐 혈청 테스트 결과. (A) Vax1 N-말단을 항원을 주입한 생쥐에서 분리한 생쥐 백혈구에서 유도된 hybridoma 세포 배양액을 Western blot의 항체로 사용하여 Vax1과 Vax2를 발현하는 cell lysate 내에 존재하는 Vax1 단백질에 대한 특이성을 조사함. Positive control인 rabbit polyclonal antibody에 비해 상대적으로 낮은 titer 때문에 약하게 10번 클론에서 신호가 확인됨. (B) Western blot에서 신호가 확인된 10번 클론이 denature된 단백질 보다 정상적 구조의 Vax1 단백질에 대한 특이성이 높은지를 확인하기 위해 면역형광염색을 통해 조사한 결과 rabbit polyclonal antibody 보다도 더 높은 신호를 보였다. 이를 통해 10번 클론은 정상 구조의 Vax1 단백질을 인식하는 특징이 있으므로, 향후 생체 내에서 정상적 구조의 Vax1 단백질의 작용을 저해할 목적으로 사용이 가능하다는 결론을 얻었음. 현재 FRL에서 Vax1-mAb10 clone을 이용하여 single chain IgG (scIgG) 유전자를 cloning 하려고 함. Vax1-scIgG 유전자가 확보되면 이를 생쥐에 RGC에 발현하여 RGC 외부에 분포하는 Vax1 단백질의 기능을 저하하여 RGC 성장 이상 여부를 관찰할 예정임
표
Vax1 단일항체 제작을 위한 생쥐 혈청 테스트 결과. (A) Vax1 N-말단을 항원을 주입한 생쥐에서 분리한 생쥐 백혈구에서 유도된 hybridoma 세포 배양액을 Western blot의 항체로 사용하여 Vax1과 Vax2를 발현하는 cell lysate 내에 존재하는 Vax1 단백질에 대한 특이성을 조사함. Positive control인 rabbit polyclonal antibody에 비해 상대적으로 낮은 titer 때문에 약하게 10번 클론에서 신호가 확인됨. (B) Western blot에서 신호가 확인된 10번 클론이 denature된 단백질 보다 정상적 구조의 Vax1 단백질에 대한 특이성이 높은지를 확인하기 위해 면역형광염색을 통해 조사한 결과 rabbit polyclonal antibody 보다도 더 높은 신호를 보였다. 이를 통해 10번 클론은 정상 구조의 Vax1 단백질을 인식하는 특징이 있으므로, 향후 생체 내에서 정상적 구조의 Vax1 단백질의 작용을 저해할 목적으로 사용이 가능하다는 결론을 얻었음. 현재 FRL에서 Vax1-mAb10 clone을 이용하여 single chain IgG (scIgG) 유전자를 cloning 하려고 함. Vax1-scIgG 유전자가 확보되면 이를 생쥐에 RGC에 발현하여 RGC 외부에 분포하는 Vax1 단백질의 기능을 저하하여 RGC 성장 이상 여부를 관찰할 예정임
 표
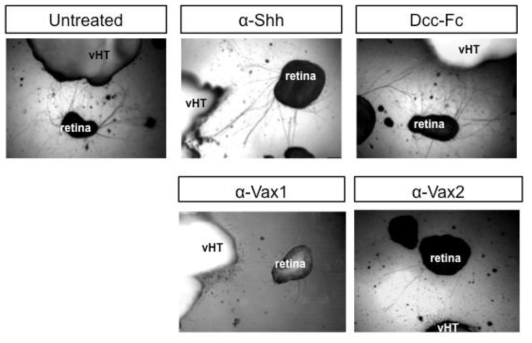
vHT에서 발현되며 각각 Vax1의 upstream과 downstream에 위치하며, 망막 RGC 성장 촉진 효과가 있는 것으로 알려진 Shh와 Netrin이 실재로 vHT로의 RGC axon 성장에 어떤 기여를 하는지를 조사하기 위하여, vHT와 망막 공동배양액에 Shh 항체 (a-Shh)와 Netrin 수용체인 Dcc의 extracellular domain에 human immunoglobulin 유전자의 Fc 부위를 연결하여 제작한 DCC-FC를 각각 처리하여 RGC axon에 존재하는 Shh 수용체와 Netrin 수용체가 Shh 및 Netrin과 결합을 하지 못하도록 유도함. 그 결과, Shh 항체나 DCC-FC 모두 vHT에 대한 RGC axon의 성장을 저해하지 못함. 따라서, Shh나 Netrin이 vHT에 대한 RGC axon 성장에 필수적인 역할을 하는 인자는 아님을 확인함
표
vHT에서 발현되며 각각 Vax1의 upstream과 downstream에 위치하며, 망막 RGC 성장 촉진 효과가 있는 것으로 알려진 Shh와 Netrin이 실재로 vHT로의 RGC axon 성장에 어떤 기여를 하는지를 조사하기 위하여, vHT와 망막 공동배양액에 Shh 항체 (a-Shh)와 Netrin 수용체인 Dcc의 extracellular domain에 human immunoglobulin 유전자의 Fc 부위를 연결하여 제작한 DCC-FC를 각각 처리하여 RGC axon에 존재하는 Shh 수용체와 Netrin 수용체가 Shh 및 Netrin과 결합을 하지 못하도록 유도함. 그 결과, Shh 항체나 DCC-FC 모두 vHT에 대한 RGC axon의 성장을 저해하지 못함. 따라서, Shh나 Netrin이 vHT에 대한 RGC axon 성장에 필수적인 역할을 하는 인자는 아님을 확인함
 표
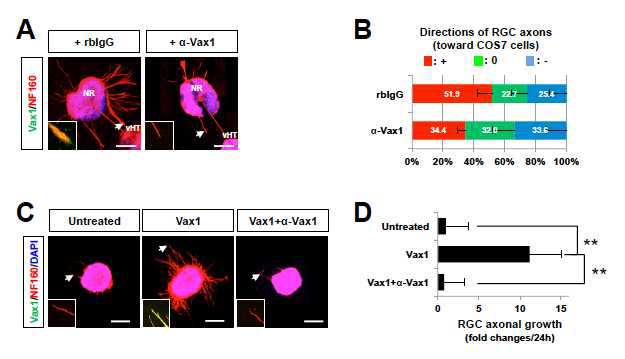
세포 외부 Vax1 단백질의 망막 신경 축삭 성장 유도 효과. (A,B) 기존 연구를 통해 확인한 세포 외부로 분비되는 Vax1 단백질이 망막 신경 성장 작용을 유도할 수 있는지를 직접 확인하기 위해 GST-표지가 된 Vax1 단백질을 생쥐 망막 배양액에 처리한 후 망막 축삭의 성장을 조사함. 그 결과 외부에서 추가한 Vax1 단백질은 망막 신경 축삭 내부로 침투할 수 있음을 면역형광염색으로 확인함. 이러한 Vax1의 망막 신경 축삭으로의 이동은 Vax1 항체를 이용해 Vax1을 항체와 복합체로 만든 경우는 억제가 되는 것으로 보아 Vax1의 망막 신경 침투는 Vax1 단백질 자체의 효과이며, 특정 Vax1 단백질의 3차원적 구조가 필요한 것으로 이에 필요한 것으로 확인됨. (C,D) 이러한 Vax1 단백질의 망막 신경 축삭으로의 이동과 축삭 성장 유도 효과는 재조합 단백질만이 가지는 기능이 아니라 vHT에서 발현되는 생체 내 Vax1 단백질 또한 동일한 활성이 있음을 증명하기 위해 vHT와 망막의 공동 배양액에 Vax1 항체를 추가한 결과 Vax1의 망막 신경 축삭으로의 이동과 축삭의 성장 모두 억제됨을 알 수 있음
표
세포 외부 Vax1 단백질의 망막 신경 축삭 성장 유도 효과. (A,B) 기존 연구를 통해 확인한 세포 외부로 분비되는 Vax1 단백질이 망막 신경 성장 작용을 유도할 수 있는지를 직접 확인하기 위해 GST-표지가 된 Vax1 단백질을 생쥐 망막 배양액에 처리한 후 망막 축삭의 성장을 조사함. 그 결과 외부에서 추가한 Vax1 단백질은 망막 신경 축삭 내부로 침투할 수 있음을 면역형광염색으로 확인함. 이러한 Vax1의 망막 신경 축삭으로의 이동은 Vax1 항체를 이용해 Vax1을 항체와 복합체로 만든 경우는 억제가 되는 것으로 보아 Vax1의 망막 신경 침투는 Vax1 단백질 자체의 효과이며, 특정 Vax1 단백질의 3차원적 구조가 필요한 것으로 이에 필요한 것으로 확인됨. (C,D) 이러한 Vax1 단백질의 망막 신경 축삭으로의 이동과 축삭 성장 유도 효과는 재조합 단백질만이 가지는 기능이 아니라 vHT에서 발현되는 생체 내 Vax1 단백질 또한 동일한 활성이 있음을 증명하기 위해 vHT와 망막의 공동 배양액에 Vax1 항체를 추가한 결과 Vax1의 망막 신경 축삭으로의 이동과 축삭의 성장 모두 억제됨을 알 수 있음
 표
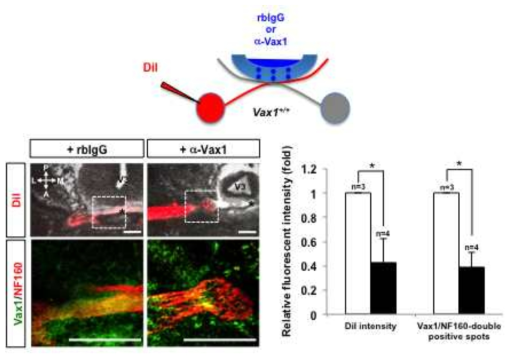
시신경 교차점 형성을 위한 세포 외부 Vax1의 역할. 배측 시상하부 (ventral hypothalamus)에서 분비되는 Vax1 단백질의 생체 내 역할을 규명하기 위해 시상하부와 인접한 수정 후 13일 생쥐 배아 제3뇌실 (third ventricle) 내에 비면역항체 또는 Vax1을 인식하는 항체를 분비하는 콜라겐 구조체를 이식함. 구조체를 이식한 생쥐 배아 안구에 세포막을 표지하는 형광시약인 DiI를 주입하여 해당 안구에서 유래하는 시신경의 분포를 추적함. 24시간 후 해당 배아의 절편을 획득하여 DiI에 의해 표지된 왼쪽 안구에서 유래한 시신경의 분포를 조사한 결과 비면역항체를 이식한 생쥐 배아는 정상적인 중심선으로의 성장을 보인 반면, Vax1 항체를 이식한 생쥐 배아에서는 시신경의 성장이 저하되어 중심선으로의 접근이 억제됨. 중심선으로의 성장이 억제된 시신경은 시신경 축삭 내 Vax1의 분포가 줄어들어 있음
표
시신경 교차점 형성을 위한 세포 외부 Vax1의 역할. 배측 시상하부 (ventral hypothalamus)에서 분비되는 Vax1 단백질의 생체 내 역할을 규명하기 위해 시상하부와 인접한 수정 후 13일 생쥐 배아 제3뇌실 (third ventricle) 내에 비면역항체 또는 Vax1을 인식하는 항체를 분비하는 콜라겐 구조체를 이식함. 구조체를 이식한 생쥐 배아 안구에 세포막을 표지하는 형광시약인 DiI를 주입하여 해당 안구에서 유래하는 시신경의 분포를 추적함. 24시간 후 해당 배아의 절편을 획득하여 DiI에 의해 표지된 왼쪽 안구에서 유래한 시신경의 분포를 조사한 결과 비면역항체를 이식한 생쥐 배아는 정상적인 중심선으로의 성장을 보인 반면, Vax1 항체를 이식한 생쥐 배아에서는 시신경의 성장이 저하되어 중심선으로의 접근이 억제됨. 중심선으로의 성장이 억제된 시신경은 시신경 축삭 내 Vax1의 분포가 줄어들어 있음
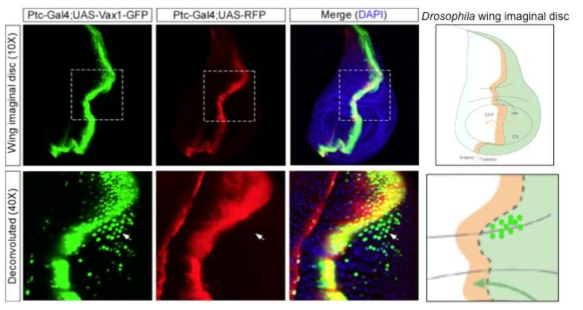 표
Vax1 단백질의 생체 내 세포 간 이동. Vax1-GFP를 GAL4 전사촉진인자의 존재 하에 발현할 수 있는 UAS-Vax1-GFP 형질전환 초파리를 제작한 후, 이 초파리를 wing imaginal disc의 중심축 부위에서 GAL4가 특이적으로 발현되는 Ptc-Gal4 초파리와 교배해서 Vax1-GFP 단백질을 wing imaginal disc 중심부에서 발현하였다. 또한, Ptc-Gal4에 의해 Vax1-GFP와 마찬가지로 UAS-RFP에서 RFP 단백질이 발현이 되도록 만들어 주어 Vax1-GFP의 분포와 상호 비교하였다. 아래쪽 확대 그림에서 보듯이, Vax1-GFP 단백질은 RFP와 마찬가지로 원래 발현이 되는 지역인 wing imaginal disc 중심축 세포들뿐만 아니라 anterior (A) part에 RFP를 발현하지 않는 세포들에서도 관찰이 되었다. 이는 Vax1-GFP 단백질이 주변 세포들로 이동을 할 수 있음을 알 수 있었다
표
Vax1 단백질의 생체 내 세포 간 이동. Vax1-GFP를 GAL4 전사촉진인자의 존재 하에 발현할 수 있는 UAS-Vax1-GFP 형질전환 초파리를 제작한 후, 이 초파리를 wing imaginal disc의 중심축 부위에서 GAL4가 특이적으로 발현되는 Ptc-Gal4 초파리와 교배해서 Vax1-GFP 단백질을 wing imaginal disc 중심부에서 발현하였다. 또한, Ptc-Gal4에 의해 Vax1-GFP와 마찬가지로 UAS-RFP에서 RFP 단백질이 발현이 되도록 만들어 주어 Vax1-GFP의 분포와 상호 비교하였다. 아래쪽 확대 그림에서 보듯이, Vax1-GFP 단백질은 RFP와 마찬가지로 원래 발현이 되는 지역인 wing imaginal disc 중심축 세포들뿐만 아니라 anterior (A) part에 RFP를 발현하지 않는 세포들에서도 관찰이 되었다. 이는 Vax1-GFP 단백질이 주변 세포들로 이동을 할 수 있음을 알 수 있었다
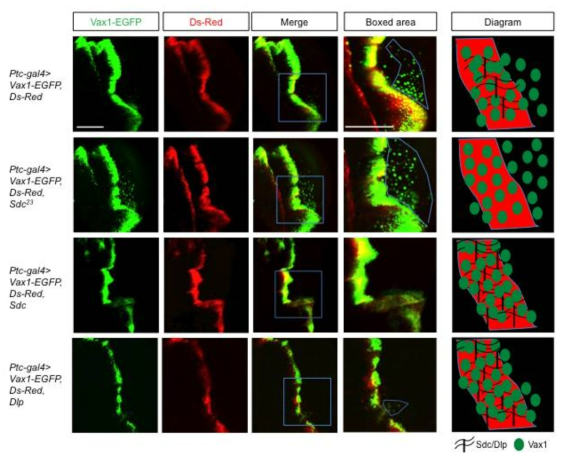 표
Heparin sulfate proteoglycan 분포 조절을 통한 생체 내 Vax1 이동 변화. Heparin sulfate proteoglycan에 의한 Vax1의 세포 간 이동을 생체 내에서 검증하기 위해, transmembrane heparin sulfate proteoglycan인 syndecan (Sdc)과 GPI-anchoring proteoglycan인 glypican의 초파리 homolog dally-like protein (Dlp)의 mutant와 overexpression line들을 확보함. 이들 중 dally와 dlp는 hedgehog, wingless, dpp 등의 필수적인 발달 조절인자들의 분포를 조절하는 유전자이므로 mutant들은 대부분 초기 발달에서 성장을 멈추어 Vax1 분비에 대한 조사를 하기가 불가능함. 따라서, 비교적 초기 발달 이상이 미약한 Sdc mutant인 Sdc23 line에서의 Vax1 이동과 UAS-Dlp 초파리를 이용하여 Vax1을 발현하는 세포에서 함께 Dlp를 과발현하여 local heparin sulfate proteoglycan 농도를 높이는 방식으로 Vax1의 세포 간 이동에 미치는 heparin sulfate proteoglycan들의 효과를 조사함. 그림에 보는 것처럼 Vax1을 Ds-Red와 동시에 Ptc-gal4를 이용하여 wing imaginal disc의 중간에서 발현하면, 발현하는 세포뿐만 아니라 posterior part의 Ptc-negative 세포들에까지 이동하여 분포함을 이미 증명한 바 있다. 하지만, Ptc-gal4를 발현하는 세포에 Vax1, Ds-Red를 Dlp와 함께 발현하면, Vax1이 이동하지 못하고 발현하는 세포에만 머무는 것을 알 수 있다. 따라서, 세포 외부로 분비된 Vax1 단백질이 과발현된 Dlp glypican heparin sulfate proteoglycan에 포집되어 주변으로의 이동이 저해되었다고 유추할 수 있다
표
Heparin sulfate proteoglycan 분포 조절을 통한 생체 내 Vax1 이동 변화. Heparin sulfate proteoglycan에 의한 Vax1의 세포 간 이동을 생체 내에서 검증하기 위해, transmembrane heparin sulfate proteoglycan인 syndecan (Sdc)과 GPI-anchoring proteoglycan인 glypican의 초파리 homolog dally-like protein (Dlp)의 mutant와 overexpression line들을 확보함. 이들 중 dally와 dlp는 hedgehog, wingless, dpp 등의 필수적인 발달 조절인자들의 분포를 조절하는 유전자이므로 mutant들은 대부분 초기 발달에서 성장을 멈추어 Vax1 분비에 대한 조사를 하기가 불가능함. 따라서, 비교적 초기 발달 이상이 미약한 Sdc mutant인 Sdc23 line에서의 Vax1 이동과 UAS-Dlp 초파리를 이용하여 Vax1을 발현하는 세포에서 함께 Dlp를 과발현하여 local heparin sulfate proteoglycan 농도를 높이는 방식으로 Vax1의 세포 간 이동에 미치는 heparin sulfate proteoglycan들의 효과를 조사함. 그림에 보는 것처럼 Vax1을 Ds-Red와 동시에 Ptc-gal4를 이용하여 wing imaginal disc의 중간에서 발현하면, 발현하는 세포뿐만 아니라 posterior part의 Ptc-negative 세포들에까지 이동하여 분포함을 이미 증명한 바 있다. 하지만, Ptc-gal4를 발현하는 세포에 Vax1, Ds-Red를 Dlp와 함께 발현하면, Vax1이 이동하지 못하고 발현하는 세포에만 머무는 것을 알 수 있다. 따라서, 세포 외부로 분비된 Vax1 단백질이 과발현된 Dlp glypican heparin sulfate proteoglycan에 포집되어 주변으로의 이동이 저해되었다고 유추할 수 있다
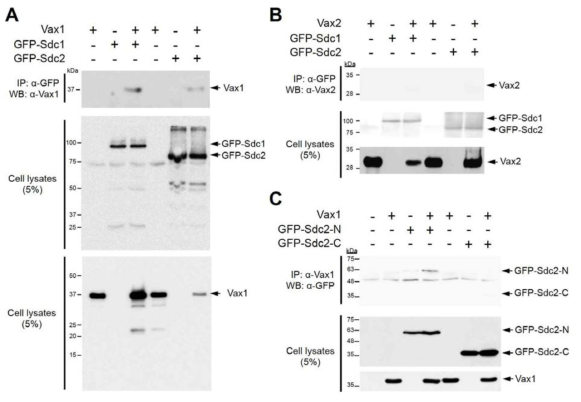 표
Sdc N-말단 특이적 Vax1의 결합. (A) HEK293T 세포에 Vax1과 GFP-Sdc1, GFP-Sdc2를 발현하고 GFP에 대한 항체를 이용하여 Sdc 단백질을 면역침강하였다. 침강된 면역복합체에 Vax1 단백질이 함께 존재하는지를 Vax1에 대한 항체를 이용하여 Western blot으로 확인하였다. (B) Vax1 대신 Vax2를 GFP-Sdc와 발현 후 동일한 방법으로 Vax2의 Sdc에 대한 상호작용을 조사하였다. (C) Vax1의 Sdc2의 N-말단 부위 (GFP-Sdc2-N) 또는 C-말단 (GFP-Sdc2-C) 에 대한 선택적 결합을 Vax1 면역침강법으로 조사하였다
표
Sdc N-말단 특이적 Vax1의 결합. (A) HEK293T 세포에 Vax1과 GFP-Sdc1, GFP-Sdc2를 발현하고 GFP에 대한 항체를 이용하여 Sdc 단백질을 면역침강하였다. 침강된 면역복합체에 Vax1 단백질이 함께 존재하는지를 Vax1에 대한 항체를 이용하여 Western blot으로 확인하였다. (B) Vax1 대신 Vax2를 GFP-Sdc와 발현 후 동일한 방법으로 Vax2의 Sdc에 대한 상호작용을 조사하였다. (C) Vax1의 Sdc2의 N-말단 부위 (GFP-Sdc2-N) 또는 C-말단 (GFP-Sdc2-C) 에 대한 선택적 결합을 Vax1 면역침강법으로 조사하였다
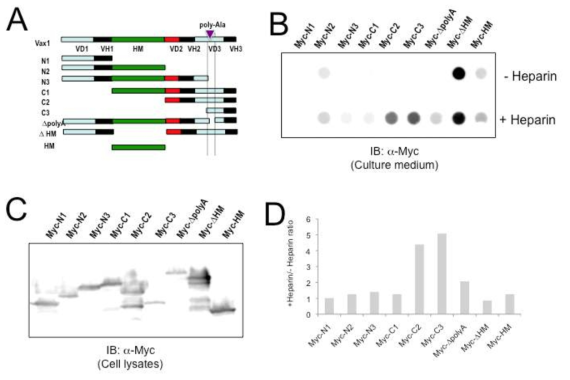 표
Vax1의 세포 외부 분비 및 당 결합에 관여하는 부위 검증. 앞의 결과들에 의하면 분비된 Vax1은 주변 세포의 proteoglycan의 당 사슬에 결합을 한 후 주변세포로의 이동 및 해당 세포에 신호를 전달할 가능성이 있다. 이러한 Vax1의 분비와 주변세포의 proteoglycan 당 사슬에 결합하는 부위에 대한 정보를 얻고자 Vax1 단백질의 절편을 293T 세포에 발현 한 후 배양액 내 Vax1 절편의 양과 heparin에 의해 증가되는 배양액 내 Vax1 절편의 양을 조사함으로써 세포 외부로의 분비에 관여하는 Vax1 부위와 당사슬에 결합하는 부위를 검증하려고 함 (A&B). 그 결과 Vax1의 N-말단이 없는 경우 세포 외부로 분비는 가능하나 수용성으로 있지 못하고 당사슬을 포함한 proteoglycan에 결합하여 있는 것으로 나타남 (heparin 처리 시에만 확인된 C1, C2, C3 절편들). 이와는 반대로 homeodomain이 없는 경우는 그림 24와 마찬가지로 세포 외부에서 대부분 수용성으로 존재함을 알 수 있음. 따라서, 세포외부로의 분비 이후 Vax1은 homeodomain과 C-말단을 통해 세포막 및 proteoglycan에 결합함을 알 수 있음
표
Vax1의 세포 외부 분비 및 당 결합에 관여하는 부위 검증. 앞의 결과들에 의하면 분비된 Vax1은 주변 세포의 proteoglycan의 당 사슬에 결합을 한 후 주변세포로의 이동 및 해당 세포에 신호를 전달할 가능성이 있다. 이러한 Vax1의 분비와 주변세포의 proteoglycan 당 사슬에 결합하는 부위에 대한 정보를 얻고자 Vax1 단백질의 절편을 293T 세포에 발현 한 후 배양액 내 Vax1 절편의 양과 heparin에 의해 증가되는 배양액 내 Vax1 절편의 양을 조사함으로써 세포 외부로의 분비에 관여하는 Vax1 부위와 당사슬에 결합하는 부위를 검증하려고 함 (A&B). 그 결과 Vax1의 N-말단이 없는 경우 세포 외부로 분비는 가능하나 수용성으로 있지 못하고 당사슬을 포함한 proteoglycan에 결합하여 있는 것으로 나타남 (heparin 처리 시에만 확인된 C1, C2, C3 절편들). 이와는 반대로 homeodomain이 없는 경우는 그림 24와 마찬가지로 세포 외부에서 대부분 수용성으로 존재함을 알 수 있음. 따라서, 세포외부로의 분비 이후 Vax1은 homeodomain과 C-말단을 통해 세포막 및 proteoglycan에 결합함을 알 수 있음
 표
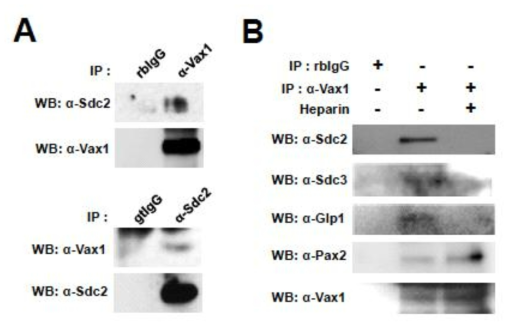
시신경에서 Vax1과 Sdc2 사이의 상호 작용. (A) Vax1과 Sdc 단백질 간 상호작용을 P0 생쥐 시신경 cell lysate를 Vax1 단백질에 대한 항체로 면역침강한 후 Vax1과 결합하여 함께 분리된 Sdc2, Sdc3, Glp1 등의 HSPG 단백질을 WB로 검출함. (B) 또한, 이 과정 중 면역침강 용액에 heparin을 추가하여 HSPG 단백질의 heparin 당 부위에 결합된 단백질들을 해리 시킨 경우 Vax1과 Sdc2, Sdc3, Glp1 등 HSPG 단백질과의 결합이 억제되었지만, 세포 핵 내에서 Vax1과 상호결합하는 것으로 확인된 Pax2의 경우는 heparin의 존재 유무에 상관 없이 결합을 하고 있음을 알 수 있다. 이는 Vax1이 HSPG의 heparin 당 부위와 특이적 결합을 함을 시사함
표
시신경에서 Vax1과 Sdc2 사이의 상호 작용. (A) Vax1과 Sdc 단백질 간 상호작용을 P0 생쥐 시신경 cell lysate를 Vax1 단백질에 대한 항체로 면역침강한 후 Vax1과 결합하여 함께 분리된 Sdc2, Sdc3, Glp1 등의 HSPG 단백질을 WB로 검출함. (B) 또한, 이 과정 중 면역침강 용액에 heparin을 추가하여 HSPG 단백질의 heparin 당 부위에 결합된 단백질들을 해리 시킨 경우 Vax1과 Sdc2, Sdc3, Glp1 등 HSPG 단백질과의 결합이 억제되었지만, 세포 핵 내에서 Vax1과 상호결합하는 것으로 확인된 Pax2의 경우는 heparin의 존재 유무에 상관 없이 결합을 하고 있음을 알 수 있다. 이는 Vax1이 HSPG의 heparin 당 부위와 특이적 결합을 함을 시사함
 표
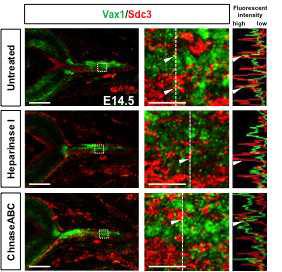
시신경 내 Vax1 단백질의 heparin 민감성 분포. Heparin에 민감하게 Sdc3 등의 HSPG와 면역침강되었던 Vax1 단백질이 실재로 시신경 내에서 망막 신경 축삭 부위에 존재하는 Sdc3와 같이 위치를 하는지를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. 그 결과 Sdc3와 Vax1은 망막 신경 축삭에서만 특이적으로 공통의 분포를 나타 내었으며, 이러한 면역형광염색 신호는 heparin 당을 분해하는 heparitinase의 처리에 의해 사라졌다. 하지만, chondroitinase처럼 heparin 당을 분해하지 못하는 효소에 의해서는 영향을 받지 않음
표
시신경 내 Vax1 단백질의 heparin 민감성 분포. Heparin에 민감하게 Sdc3 등의 HSPG와 면역침강되었던 Vax1 단백질이 실재로 시신경 내에서 망막 신경 축삭 부위에 존재하는 Sdc3와 같이 위치를 하는지를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. 그 결과 Sdc3와 Vax1은 망막 신경 축삭에서만 특이적으로 공통의 분포를 나타 내었으며, 이러한 면역형광염색 신호는 heparin 당을 분해하는 heparitinase의 처리에 의해 사라졌다. 하지만, chondroitinase처럼 heparin 당을 분해하지 못하는 효소에 의해서는 영향을 받지 않음
 표
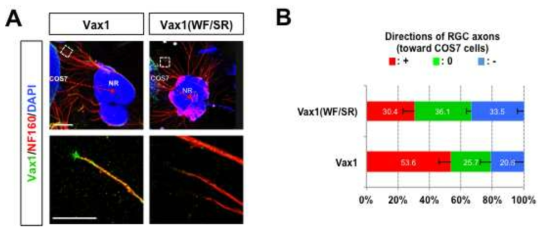
Vax1에 의한 망막 신경 축삭 성장 유도에 세포막 투과가 필요함. Vax1의 경우 망막 신경 축삭 세포막 외부 뿐만 아니라 세포 내부에서도 관찰이 되었으므로, Vax1의 작용점이 세포막에서 Sdc2와의 결합을 통해 축삭의 성장을 유도할 수도 있고 세포 내부로 이동하여 세포 내부에 존재하는 단백질들을 통해 축삭 성장을 유도할 가능성도 있다. 이를 증명하기 위해 세포막 투과성이 떨어진 Vax1(WF/SR) 변이 단백질을 발현하는 COS7 세포의 망막 신경 축삭 성장 유도 효과를 정상 Vax1을 발현하는 COS7 세포와 비교하였다. 그 결과 Vax1(WF/SR) 단백질은 Vax1과 달리 선택적 망막 신경 성장 유도를 하지 못하는 것을 확인되었다. 이는 Vax1의 Sdc를 비롯한 HSPG에의 결합뿐만 아니라 축삭 세포 내로의 이동이 중요하다는 사실을 시사함
표
Vax1에 의한 망막 신경 축삭 성장 유도에 세포막 투과가 필요함. Vax1의 경우 망막 신경 축삭 세포막 외부 뿐만 아니라 세포 내부에서도 관찰이 되었으므로, Vax1의 작용점이 세포막에서 Sdc2와의 결합을 통해 축삭의 성장을 유도할 수도 있고 세포 내부로 이동하여 세포 내부에 존재하는 단백질들을 통해 축삭 성장을 유도할 가능성도 있다. 이를 증명하기 위해 세포막 투과성이 떨어진 Vax1(WF/SR) 변이 단백질을 발현하는 COS7 세포의 망막 신경 축삭 성장 유도 효과를 정상 Vax1을 발현하는 COS7 세포와 비교하였다. 그 결과 Vax1(WF/SR) 단백질은 Vax1과 달리 선택적 망막 신경 성장 유도를 하지 못하는 것을 확인되었다. 이는 Vax1의 Sdc를 비롯한 HSPG에의 결합뿐만 아니라 축삭 세포 내로의 이동이 중요하다는 사실을 시사함
 표
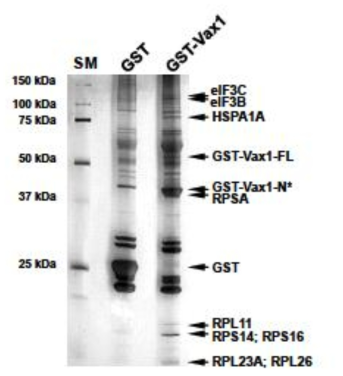
Vax1의 세포질 내 결합단백질 발굴. Vax1의 세포질 내로의 이동이 망막 신경 축삭 성장에 필요하다는 사실에 기반하여, GST-Vax1이 과발현된 293T 세포의 세포질에서 Vax1의 세포질 내 작용 단백질을 GST full-down을 통해 포집하고, 이를 MALDI-TOF를 이용하여 분석하였다. 그 결과 대부분의 세포질 내 Vax1 결합단백질들이 리보좀에 존재하는 단백질들 (ribosomal protein S (RPS) 또는 RPL)이나 단백질 합성에 관여하는 단백질 (eIF3B/C, Hsp70)로 확인되었다. 이는 Vax1이 세포질에서 단백질 합성에 관여할 것이라는 것을 의미하는 결과로 해석된다
표
Vax1의 세포질 내 결합단백질 발굴. Vax1의 세포질 내로의 이동이 망막 신경 축삭 성장에 필요하다는 사실에 기반하여, GST-Vax1이 과발현된 293T 세포의 세포질에서 Vax1의 세포질 내 작용 단백질을 GST full-down을 통해 포집하고, 이를 MALDI-TOF를 이용하여 분석하였다. 그 결과 대부분의 세포질 내 Vax1 결합단백질들이 리보좀에 존재하는 단백질들 (ribosomal protein S (RPS) 또는 RPL)이나 단백질 합성에 관여하는 단백질 (eIF3B/C, Hsp70)로 확인되었다. 이는 Vax1이 세포질에서 단백질 합성에 관여할 것이라는 것을 의미하는 결과로 해석된다
 표
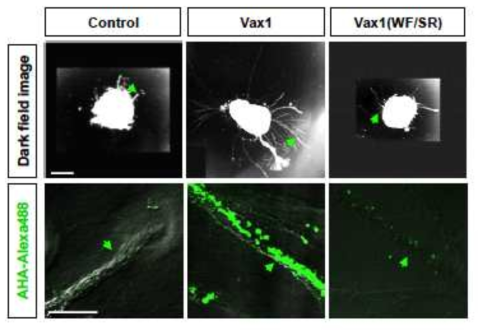
Vax1의 망막 신경 축삭 내 단백질 생합성 촉진 효과. Vax1의 리보좀 및 단백질 생합성 조절 단백질과의 상호작용이 가지는 의미를 확인하기 위해, metionine이 제거된 망막 배양액에 L-azidohonoalanine (AHA)를 첨가한 후 Vax1을 6시간 동안 첨가하여 Vax1이 작용하는 망막 신경 축삭과 망막 신경 세포에서 생합성되는 단백질들에 AHA가 들어가도록 하였다. 그 후 망막조직을 고정한 후 세포 내부에 생성된 AHA를 포함한 단백질을 DIBO-fluor Alexa488과의 Click chemistry를 통해 형광 표지한 후 현미경 하에서 관찰함. 그 결과, Vax1이 처리된 망막 신경 축삭 부위에 단백질 생합성이 비처리 망막 신경이나 세포막 비투과 Vax1(WF/SR) 단백질과 비교해서 급격하게 증가한 것을 알 수 있음. 하지만, 이러한 증가는 세포 본체에서는 두드러지지 않는 것으로 보아 Vax1의 타겟이 축삭에 집중되어 있음을 알 수 있음
표
Vax1의 망막 신경 축삭 내 단백질 생합성 촉진 효과. Vax1의 리보좀 및 단백질 생합성 조절 단백질과의 상호작용이 가지는 의미를 확인하기 위해, metionine이 제거된 망막 배양액에 L-azidohonoalanine (AHA)를 첨가한 후 Vax1을 6시간 동안 첨가하여 Vax1이 작용하는 망막 신경 축삭과 망막 신경 세포에서 생합성되는 단백질들에 AHA가 들어가도록 하였다. 그 후 망막조직을 고정한 후 세포 내부에 생성된 AHA를 포함한 단백질을 DIBO-fluor Alexa488과의 Click chemistry를 통해 형광 표지한 후 현미경 하에서 관찰함. 그 결과, Vax1이 처리된 망막 신경 축삭 부위에 단백질 생합성이 비처리 망막 신경이나 세포막 비투과 Vax1(WF/SR) 단백질과 비교해서 급격하게 증가한 것을 알 수 있음. 하지만, 이러한 증가는 세포 본체에서는 두드러지지 않는 것으로 보아 Vax1의 타겟이 축삭에 집중되어 있음을 알 수 있음
 표
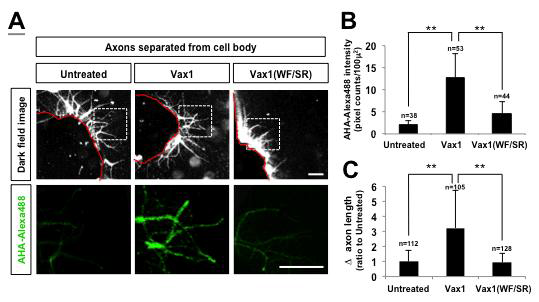
Vax1에 의한 시신경 축삭 특이적 단백질 합성 촉진 효과 검증. 세포 내 단백질 합성 촉진을 통해 시신경 축삭 성장을 유도하는 Vax1의 효과가 세포핵과 세포 본체 (cell body)에서 일어나는 현상인지 실재 성장이 일어나는 축삭에서 나타나는 현상인지를 검증하기 위해 세포 본체가 포함된 망막 이식체와 축삭을 분리 후 축삭 부위에만 Vax1 단백질을 처리하고 새롭게 합성되는 단백질들을 AHA-Alexa488을 이용해 표지함. 그 결과 축삭 부위에만 Vax1을 처리해도 축삭 성장과 신규 단백질 합성이 촉진되는 것을 통해 Vax1은 축삭 특이적 단백질 합성 유도를 통해 축삭 성장을 유도함을 알 수 있음
표
Vax1에 의한 시신경 축삭 특이적 단백질 합성 촉진 효과 검증. 세포 내 단백질 합성 촉진을 통해 시신경 축삭 성장을 유도하는 Vax1의 효과가 세포핵과 세포 본체 (cell body)에서 일어나는 현상인지 실재 성장이 일어나는 축삭에서 나타나는 현상인지를 검증하기 위해 세포 본체가 포함된 망막 이식체와 축삭을 분리 후 축삭 부위에만 Vax1 단백질을 처리하고 새롭게 합성되는 단백질들을 AHA-Alexa488을 이용해 표지함. 그 결과 축삭 부위에만 Vax1을 처리해도 축삭 성장과 신규 단백질 합성이 촉진되는 것을 통해 Vax1은 축삭 특이적 단백질 합성 유도를 통해 축삭 성장을 유도함을 알 수 있음
 표
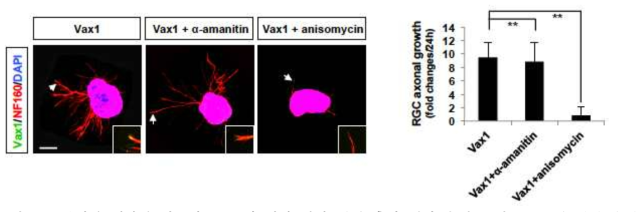
단백질 생합성 의존적 Vax1에 의한 망막 신경 축삭 성장 촉진 효과. Vax1에 의한 축삭 내 단백질 생합성 촉진이 실재 Vax1에 의한 망막 신경 축삭 성장과 어떤 연관성이 있는지를 조사하기 위해, 망막 배양액에 Vax1을 처리 시 유전자 발현 억제제인 alpha-amanitin과 단백질 생합성 억제제인 anisomycin을 각각 처리하고 축삭 내 Vax1의 침투와 축삭의 성장 정도를 측정함. 그 결과 Vax1의 침투에는 이상이 없지만 Vax1에 의해 촉진되는 축삭 성장은 anisomycin 처리 시에 억제됨을 관찰함. 따라서 Vax1이 세포 내로 이동 후 세포 내 단백질 생합성을 통해 망막 신경 축삭 성장을 유도하는 것으로 결론을 내릴 수 있었음
표
단백질 생합성 의존적 Vax1에 의한 망막 신경 축삭 성장 촉진 효과. Vax1에 의한 축삭 내 단백질 생합성 촉진이 실재 Vax1에 의한 망막 신경 축삭 성장과 어떤 연관성이 있는지를 조사하기 위해, 망막 배양액에 Vax1을 처리 시 유전자 발현 억제제인 alpha-amanitin과 단백질 생합성 억제제인 anisomycin을 각각 처리하고 축삭 내 Vax1의 침투와 축삭의 성장 정도를 측정함. 그 결과 Vax1의 침투에는 이상이 없지만 Vax1에 의해 촉진되는 축삭 성장은 anisomycin 처리 시에 억제됨을 관찰함. 따라서 Vax1이 세포 내로 이동 후 세포 내 단백질 생합성을 통해 망막 신경 축삭 성장을 유도하는 것으로 결론을 내릴 수 있었음
 표
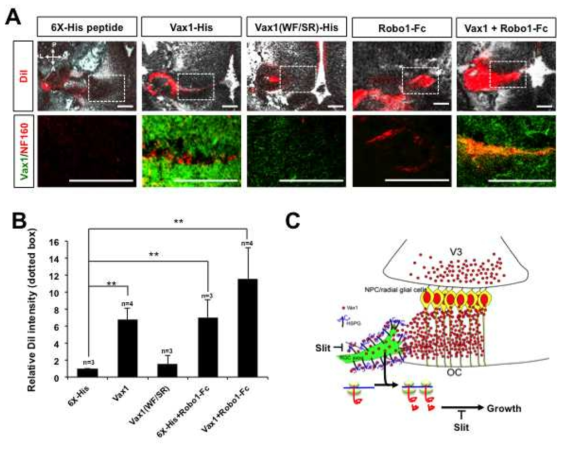
Vax1 이식을 통한 Vax1-ko 생쥐의 시신경 재성장 유도. (A&B) 시상하부 배측 중심선으로의 시신경 성장이 저해된 Vax1-ko 생쥐 배아 제3뇌실 내에 6X-His 펩티드, Vax1-His 단백질, 세포 침투능이 상실된 Vax1(WF/SR)-His 단백질을 분비하는 콜라겐 구조체를 이식하고 시신경의 성장을 우측 안구에 주입한 DiI 형광 염색시약에 의해 표지된 시신경의 분포를 통해 조사함. 이 중 Vax1-His 단백질만이 Vax1-ko 생쥐 시신경의 재성장을 유도할 수 있음. Vax1-ko 생쥐 배아 시 신경 성장 이상이 시상하부 측면에 발현되어 시신경 축삭 성장을 억제하는 Slit에 의한 것인지를 확인하기 위해 Slit 단백질의 수용체인 Robo1의 Slit 결합부위를 포함하는 Robo1-Fc 단백질 분비하는 콜라겐 구조체를 제3뇌실에 이식함. 그 결과 부분적인 시신경의 재성장이 일어났고, 이러한 효과는 Vax1과 Robo1-Fc를 함께 분비하는 콜라겐 구조체의 이식 시에 극대화되었음. (C) 이를 통해 시신경의 시상하부 중심축으로의 성장이 성장 촉진인자인 Vax1과 성장 억제인자인 Slit 사이의 상호 견재를 통해 일어난다는 모델을 구축하였음
표
Vax1 이식을 통한 Vax1-ko 생쥐의 시신경 재성장 유도. (A&B) 시상하부 배측 중심선으로의 시신경 성장이 저해된 Vax1-ko 생쥐 배아 제3뇌실 내에 6X-His 펩티드, Vax1-His 단백질, 세포 침투능이 상실된 Vax1(WF/SR)-His 단백질을 분비하는 콜라겐 구조체를 이식하고 시신경의 성장을 우측 안구에 주입한 DiI 형광 염색시약에 의해 표지된 시신경의 분포를 통해 조사함. 이 중 Vax1-His 단백질만이 Vax1-ko 생쥐 시신경의 재성장을 유도할 수 있음. Vax1-ko 생쥐 배아 시 신경 성장 이상이 시상하부 측면에 발현되어 시신경 축삭 성장을 억제하는 Slit에 의한 것인지를 확인하기 위해 Slit 단백질의 수용체인 Robo1의 Slit 결합부위를 포함하는 Robo1-Fc 단백질 분비하는 콜라겐 구조체를 제3뇌실에 이식함. 그 결과 부분적인 시신경의 재성장이 일어났고, 이러한 효과는 Vax1과 Robo1-Fc를 함께 분비하는 콜라겐 구조체의 이식 시에 극대화되었음. (C) 이를 통해 시신경의 시상하부 중심축으로의 성장이 성장 촉진인자인 Vax1과 성장 억제인자인 Slit 사이의 상호 견재를 통해 일어난다는 모델을 구축하였음
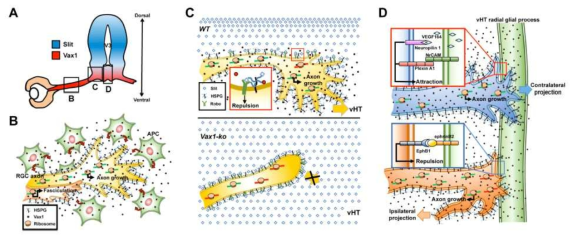 표
Vax1에 의한 시신경 축삭 성장 조절 모식도. (A) Vax1(붉은색)은 전뇌 배부위 중심부에서 강하게 발현되고 외곽으로 갈수록 그 농도가 줄어드는 반면, Slit은 전뇌 등부위에서 높고 배부위에서는 낮은 발현 양상을 보인다. (B) 시신경 축삭이 안구를 나와서 뇌 중심선을 향하여 성장하는 동안 시신경 성장부 주변에서 분비된 Vax1이 지속적으로 시신경 축삭의 성장을 유도한다. (C) 시신경이 전뇌 배부위 주변에 접근하면 이곳에 높은 농도로 존재하는 Slit의 작용으로 등부위로의 성장은 억제되는 반면 배부위 중심부에서 분비되는 Vax1에 의해 배부위 중심부로의 성장은 지속된다. 하지만 Vax1이 없는 생쥐의 경우는 배부위 중심부로의 이동이 저하되어 뇌 주변부에서 시신경이 성장을 멈춘다. (D) 뇌 중심선까지 성장한 시신경 축삭은 그곳에 특이적으로 발현된 ephrinB2에 시신경 축삭에 EphB1이 반응하여 시신경 축삭 성장을 멈추고 되돌아 온다. 하지만, EphB1이 없는 시신경 축삭은 그대로 그 부위를 통과하여 반대편 뇌로 성장을 하게 된다. 이 모든 과정에서 Vax1은 시 신경 축삭의 방향과는 상관 없이 축삭 내 단백질 합성 촉진을 통해 시신경 축삭의 성장 속도를 높이는 역할을 한다
표
Vax1에 의한 시신경 축삭 성장 조절 모식도. (A) Vax1(붉은색)은 전뇌 배부위 중심부에서 강하게 발현되고 외곽으로 갈수록 그 농도가 줄어드는 반면, Slit은 전뇌 등부위에서 높고 배부위에서는 낮은 발현 양상을 보인다. (B) 시신경 축삭이 안구를 나와서 뇌 중심선을 향하여 성장하는 동안 시신경 성장부 주변에서 분비된 Vax1이 지속적으로 시신경 축삭의 성장을 유도한다. (C) 시신경이 전뇌 배부위 주변에 접근하면 이곳에 높은 농도로 존재하는 Slit의 작용으로 등부위로의 성장은 억제되는 반면 배부위 중심부에서 분비되는 Vax1에 의해 배부위 중심부로의 성장은 지속된다. 하지만 Vax1이 없는 생쥐의 경우는 배부위 중심부로의 이동이 저하되어 뇌 주변부에서 시신경이 성장을 멈춘다. (D) 뇌 중심선까지 성장한 시신경 축삭은 그곳에 특이적으로 발현된 ephrinB2에 시신경 축삭에 EphB1이 반응하여 시신경 축삭 성장을 멈추고 되돌아 온다. 하지만, EphB1이 없는 시신경 축삭은 그대로 그 부위를 통과하여 반대편 뇌로 성장을 하게 된다. 이 모든 과정에서 Vax1은 시 신경 축삭의 방향과는 상관 없이 축삭 내 단백질 합성 촉진을 통해 시신경 축삭의 성장 속도를 높이는 역할을 한다
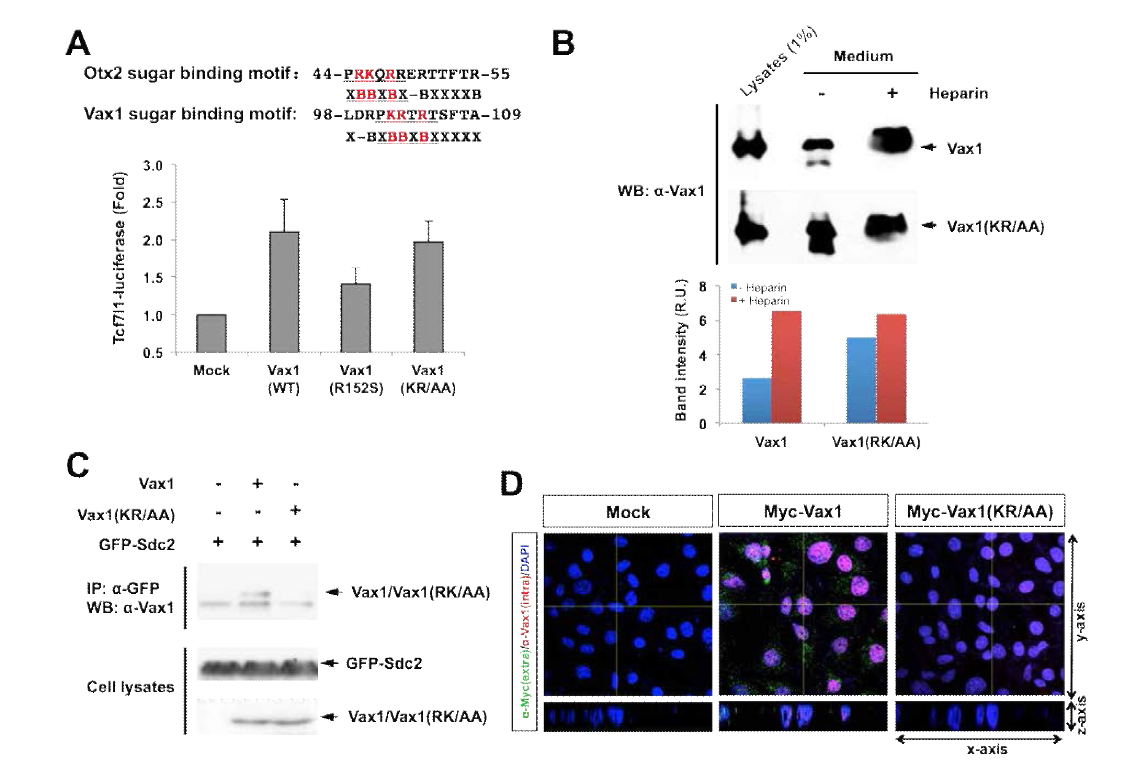 표
세포 표면 부착 이상 Vax1(KR/AA) 변이형. (A) (위) Otx2와 Vax1의 당사슬 결합 부위. (아래)293T 세포에 정상 Vax1, 전사활성 저하형 Vax1(R152S), Vax1(RK/AA) 변이형을 발현 후 함께 발현한 Vax1 타겟인 Tcf7l1-luciferase 활성을 조사하여 Vax1 비발현 세포 (Mock)의 luciferase 값과 비교함. (B) 293T 세포에 Vax1 또는 Vax1(KR/AA)를 발현 후 세포 배양액에 10% heparin을 3시간 동안 처리하여 세포막의 HS에 결합한 Vax1 단백질을 배양액으로 이동시킨 다음 배양액 단백질을 WB로 분석하여 배양액에 존재하는 Vax1 단백질의 상대량을 heparin 비처리군과 상호 비교함. (C) 293T 세포에 Vax1과 GFP-Sdc2를 함께 발현 후 GFP에 대한 항체로 면역침강 후 함께 분리된 Vax1의 양을 WB으로 조사함. (D) COS7 세포에 Myc/His 표지된 Vax1 또는 Vax1(KR/AA) 재조합단백질을 처리하고 12시간 이후에 세포에 존재하는 Vax1 단백질들을 Myc 항체를 이용한 면역염색으로 조사함
표
세포 표면 부착 이상 Vax1(KR/AA) 변이형. (A) (위) Otx2와 Vax1의 당사슬 결합 부위. (아래)293T 세포에 정상 Vax1, 전사활성 저하형 Vax1(R152S), Vax1(RK/AA) 변이형을 발현 후 함께 발현한 Vax1 타겟인 Tcf7l1-luciferase 활성을 조사하여 Vax1 비발현 세포 (Mock)의 luciferase 값과 비교함. (B) 293T 세포에 Vax1 또는 Vax1(KR/AA)를 발현 후 세포 배양액에 10% heparin을 3시간 동안 처리하여 세포막의 HS에 결합한 Vax1 단백질을 배양액으로 이동시킨 다음 배양액 단백질을 WB로 분석하여 배양액에 존재하는 Vax1 단백질의 상대량을 heparin 비처리군과 상호 비교함. (C) 293T 세포에 Vax1과 GFP-Sdc2를 함께 발현 후 GFP에 대한 항체로 면역침강 후 함께 분리된 Vax1의 양을 WB으로 조사함. (D) COS7 세포에 Myc/His 표지된 Vax1 또는 Vax1(KR/AA) 재조합단백질을 처리하고 12시간 이후에 세포에 존재하는 Vax1 단백질들을 Myc 항체를 이용한 면역염색으로 조사함
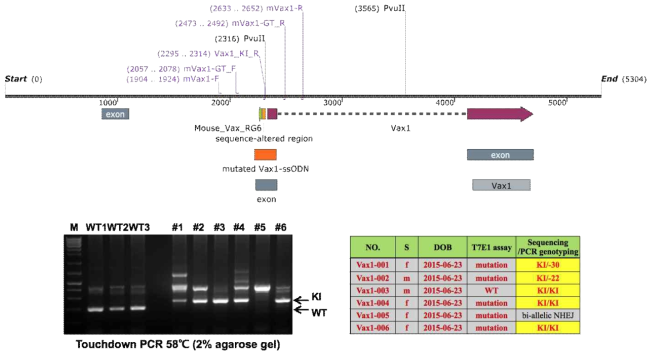 표
Vax1(KR/AA) 생쥐 제작을 위한 CRISPR/Cas9 실험. (위) 생쥐 Vax1 유전자 구성도 및 genotyping PCR primer 위치 표시. Vax1 exon 2번에 해당하는 DNA 염기서열 내 K101, R102 부위가 A101, A102로 변환한 ssDNA를 합성하여 (오렌지색) K101 부위 DNA 앞 17bp 부위를 타겟으로 하는 gRNA와 함께 생쥐 수정란에 주입함. (아래 왼쪽) mVax1-F/Vax1-KI_R primer로 KI Vax1 부위를 증폭하고, mVax1-GT_F/mVax1-GT_R primer로 WT Vax1 부위를 증폭함. 그 결과 6마리의 배아 중 총 5마리에서 KI Vax1이 관찰이 되었고, 이들 유전자 Vax1 exon2 부위를 분리하여 유전자 염기서열을 분석한 결과 3마리는 KI/KI homozygote, 2마리는 KI/del로 확인되었다
표
Vax1(KR/AA) 생쥐 제작을 위한 CRISPR/Cas9 실험. (위) 생쥐 Vax1 유전자 구성도 및 genotyping PCR primer 위치 표시. Vax1 exon 2번에 해당하는 DNA 염기서열 내 K101, R102 부위가 A101, A102로 변환한 ssDNA를 합성하여 (오렌지색) K101 부위 DNA 앞 17bp 부위를 타겟으로 하는 gRNA와 함께 생쥐 수정란에 주입함. (아래 왼쪽) mVax1-F/Vax1-KI_R primer로 KI Vax1 부위를 증폭하고, mVax1-GT_F/mVax1-GT_R primer로 WT Vax1 부위를 증폭함. 그 결과 6마리의 배아 중 총 5마리에서 KI Vax1이 관찰이 되었고, 이들 유전자 Vax1 exon2 부위를 분리하여 유전자 염기서열을 분석한 결과 3마리는 KI/KI homozygote, 2마리는 KI/del로 확인되었다
 표
변이형 Vax1 생쥐의 성체시기 해부학적 뇌 분석. (A) 생후 30일 된 생쥐에 뇌를 위쪽(왼쪽)과 아래쪽(오른쪽)에서 바라본 모습. 정상 Vax1 생쥐에 뇌에서는 시신경 교차가 일어나나, 변이형 Vax1 생쥐에 뇌에서는 시신경 교차가 일어나지 않음 (오른쪽). (B) 동결절편기를 이용하여 뇌를 절단 한 후, H&E 염색을 통해 해부학적 구조 관철 결과함. 태아시기와 마찬가지고 변이형에서 뇌교 (corpus callosum, 중간의 백색질) 가 형성되지 않았으며, septum 부위에 비정상적 구조로 인해 뇌실(ventricle) 부위가 확장된 모습도 보임. septum 부위에서 변이형 Vax1 의 전사 활성 이상으로 구조적 변화를 일으킨 것으로 예상됨. (C) 면역 형광 염색법을 이용하여 뇌교를 관찰 한 결과, 정상 Vax1 생쥐의 뇌교에서는 Vax1 단백질의 염색과 신경축삭 표지자인 NF160 이 함께 관찰 되었으나 변이형에서는 뇌교가 형성되지 않았으며, NF160 의 표지 및 Vax1 이 관찰되지 않았음
표
변이형 Vax1 생쥐의 성체시기 해부학적 뇌 분석. (A) 생후 30일 된 생쥐에 뇌를 위쪽(왼쪽)과 아래쪽(오른쪽)에서 바라본 모습. 정상 Vax1 생쥐에 뇌에서는 시신경 교차가 일어나나, 변이형 Vax1 생쥐에 뇌에서는 시신경 교차가 일어나지 않음 (오른쪽). (B) 동결절편기를 이용하여 뇌를 절단 한 후, H&E 염색을 통해 해부학적 구조 관철 결과함. 태아시기와 마찬가지고 변이형에서 뇌교 (corpus callosum, 중간의 백색질) 가 형성되지 않았으며, septum 부위에 비정상적 구조로 인해 뇌실(ventricle) 부위가 확장된 모습도 보임. septum 부위에서 변이형 Vax1 의 전사 활성 이상으로 구조적 변화를 일으킨 것으로 예상됨. (C) 면역 형광 염색법을 이용하여 뇌교를 관찰 한 결과, 정상 Vax1 생쥐의 뇌교에서는 Vax1 단백질의 염색과 신경축삭 표지자인 NF160 이 함께 관찰 되었으나 변이형에서는 뇌교가 형성되지 않았으며, NF160 의 표지 및 Vax1 이 관찰되지 않았음
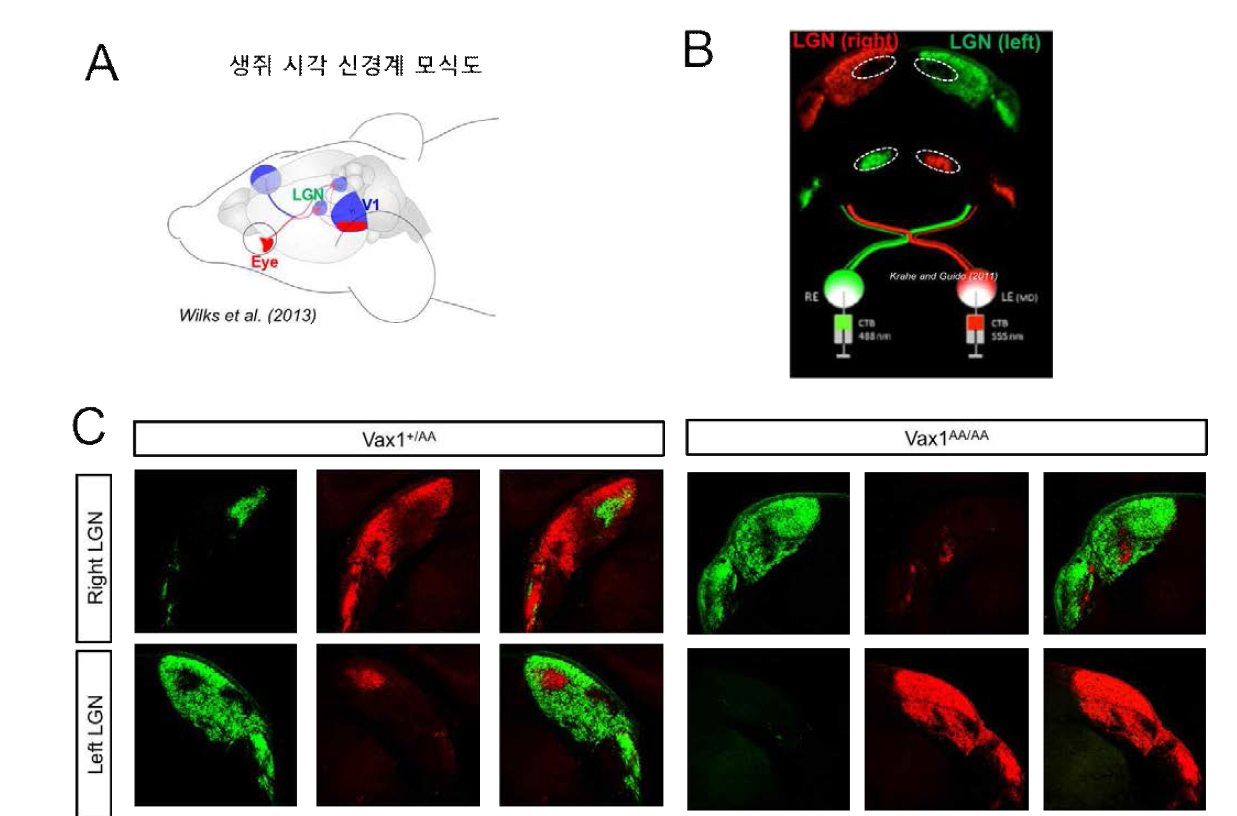 표
Vax1 (KR/AA) 생쥐에서 나타나는 시신경 교차 장애. 앞의 그림 ?에 따르면 정상 Vax1 유전자를 발현하는 생쥐에서는 시신경교차가 정상적인 구조인 반면, 변이형 Vax1 (AA) 유전자를 발현하는 생쥐에서는 시신경 교차의 구조가 나타나지 않음. (A) 생쥐 시각계에서 시신경의 95% 이상은 눈과 반대쪽에 위치한 뇌 부위로 연결되고 5% 이내의 시신경이 동일한 쪽의 뇌 부위로 연결이 됨. 특히, 이 중 측시상핵(lateral geniculate nucleus, LGN)으로 연결된 시신경은 망막의 이미지를 전달하고 이 정보가 대뇌의 시각중추 (visual cortex 1, V1) 영역으로 전달되는 특징이 있음. (B) 이러한 시신경 교차 여부를 확인하는 방법은 생쥐의 좌우측 눈에 각각 다른 색깔을 나타내는 시신경 염색 형광물질을 주입한 후 이들 형광물질이 좌우측 LGN에 분포하는 양상을 통해 알 수 있음. 즉, 오른쪽 눈(right eye, RE)에 주입한 녹색 형광물질에 염색된 시신경의 대부분은 왼쪽 LGN에서 검출되고, 왼쪽 눈(left eye, LR)에 주입한 적색 형광물질에 염색된 시신영은 오른쪽 LGN에서 주로 검출됨. (C) 생후 60일 된 생쥐에 눈에 각각 녹색과 붉은색 형광을 나타내는 Cholera Toxin B (CTB)를 주입함. Vax1(+/AA) 생쥐에서는 시신경교차로 인해 CTB를 주입한 대부분 반대쪽 뇌의 LGN 영역에서 염색되었으나, Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐에서는 시신경 교차의 상실로 인해 CTB가 주입한 눈과 같은 쪽 뇌 영역에서 염색되었음. 이는 Vax1의 세포 간 이동이 저해되면 시신경이 뇌 중간선 부위를 통과하지 못하고 같은 쪽 뇌로 진행을 함을 의미함
표
Vax1 (KR/AA) 생쥐에서 나타나는 시신경 교차 장애. 앞의 그림 ?에 따르면 정상 Vax1 유전자를 발현하는 생쥐에서는 시신경교차가 정상적인 구조인 반면, 변이형 Vax1 (AA) 유전자를 발현하는 생쥐에서는 시신경 교차의 구조가 나타나지 않음. (A) 생쥐 시각계에서 시신경의 95% 이상은 눈과 반대쪽에 위치한 뇌 부위로 연결되고 5% 이내의 시신경이 동일한 쪽의 뇌 부위로 연결이 됨. 특히, 이 중 측시상핵(lateral geniculate nucleus, LGN)으로 연결된 시신경은 망막의 이미지를 전달하고 이 정보가 대뇌의 시각중추 (visual cortex 1, V1) 영역으로 전달되는 특징이 있음. (B) 이러한 시신경 교차 여부를 확인하는 방법은 생쥐의 좌우측 눈에 각각 다른 색깔을 나타내는 시신경 염색 형광물질을 주입한 후 이들 형광물질이 좌우측 LGN에 분포하는 양상을 통해 알 수 있음. 즉, 오른쪽 눈(right eye, RE)에 주입한 녹색 형광물질에 염색된 시신경의 대부분은 왼쪽 LGN에서 검출되고, 왼쪽 눈(left eye, LR)에 주입한 적색 형광물질에 염색된 시신영은 오른쪽 LGN에서 주로 검출됨. (C) 생후 60일 된 생쥐에 눈에 각각 녹색과 붉은색 형광을 나타내는 Cholera Toxin B (CTB)를 주입함. Vax1(+/AA) 생쥐에서는 시신경교차로 인해 CTB를 주입한 대부분 반대쪽 뇌의 LGN 영역에서 염색되었으나, Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐에서는 시신경 교차의 상실로 인해 CTB가 주입한 눈과 같은 쪽 뇌 영역에서 염색되었음. 이는 Vax1의 세포 간 이동이 저해되면 시신경이 뇌 중간선 부위를 통과하지 못하고 같은 쪽 뇌로 진행을 함을 의미함
 표
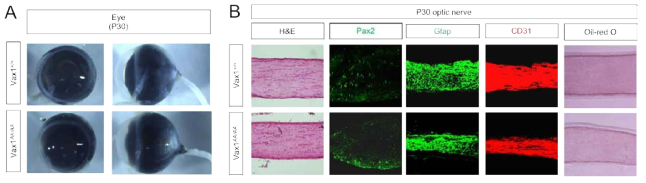
Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 시신경 분석. (A) 생후 60일 생쥐 안구의 정면 사진(왼쪽)과 측면 사진(오른쪽). Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 경우 정상 Vax1(+/+) 생쥐와 비교해 안구의 형태와 크기가 크게 다르지 않음. (B) 생후 60일 Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐와 정상 Vax1(+/+) 생쥐의 시신경 절편을 H&E 염색하여 축삭(옅은 부위)과 시신경을 구성하는 다양한 세포들의 핵(진한 부위)을 염색함. 그 결과 축삭 주변에 시신경 세포들이 흩어져 분포하고 있음을 알 수 있음. 이는 Vax1(-/-) 생쥐에서 보고된 축삭과 시신경세포들의 상호작용 실패에 따른 망막 신경 축삭 노출 현상(defasciclation)과 차이가 있는 결과임. 시신경 내 성상세포(astrocyte) 핵를 표지하는 Pax2와 세포질을 표시하는 Gfap 역시 시신경에 골고루 분포함. 또한, 시신경을 통해 망막으로 연결된 혈관세포를 표지하는 CD31 역시 시신경에 정상적으로 분포함. 시신경 축삭을 둘러싸는 oligodendrocyte의 백색질에 집중된 지질을 Oil-Red O 염색으로 조사한 결과 백색질의 분포도 정상으로 판별됨
표
Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 시신경 분석. (A) 생후 60일 생쥐 안구의 정면 사진(왼쪽)과 측면 사진(오른쪽). Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 경우 정상 Vax1(+/+) 생쥐와 비교해 안구의 형태와 크기가 크게 다르지 않음. (B) 생후 60일 Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐와 정상 Vax1(+/+) 생쥐의 시신경 절편을 H&E 염색하여 축삭(옅은 부위)과 시신경을 구성하는 다양한 세포들의 핵(진한 부위)을 염색함. 그 결과 축삭 주변에 시신경 세포들이 흩어져 분포하고 있음을 알 수 있음. 이는 Vax1(-/-) 생쥐에서 보고된 축삭과 시신경세포들의 상호작용 실패에 따른 망막 신경 축삭 노출 현상(defasciclation)과 차이가 있는 결과임. 시신경 내 성상세포(astrocyte) 핵를 표지하는 Pax2와 세포질을 표시하는 Gfap 역시 시신경에 골고루 분포함. 또한, 시신경을 통해 망막으로 연결된 혈관세포를 표지하는 CD31 역시 시신경에 정상적으로 분포함. 시신경 축삭을 둘러싸는 oligodendrocyte의 백색질에 집중된 지질을 Oil-Red O 염색으로 조사한 결과 백색질의 분포도 정상으로 판별됨
 표
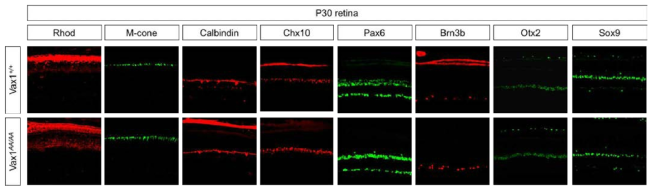
Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐 망막의 해부학적 분석. 생후 30일 된 생쥐 망막에 해부학적 분석. 생후 30일 된 Vax1 생쥐와 Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 망막세포를 면역형광염색법을 이용하여 망막을 구성하는 각각의 세포를 확인함. 광수용체 세포(photoreceptor)를 표지하는 Rhod,,M-cone 과 수평세포(horizontal cell)를 표지하는 Calbindin, 무축삭세포(amacrine cell)을 표지하는 Chx10, Pax6, 신경결세포(ganglion cell)을 표지하는 Brn3b 등을 이용하여 확인한 결과, 정상 생쥐와 Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐에서 망막에서 발현되는 단백질의 큰 변화는 보이지 않음. 이는 Vax1 단백질이 망막구조의 발생에는 직접적인 영향을 미치지 않음을 의미함
표
Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐 망막의 해부학적 분석. 생후 30일 된 생쥐 망막에 해부학적 분석. 생후 30일 된 Vax1 생쥐와 Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 망막세포를 면역형광염색법을 이용하여 망막을 구성하는 각각의 세포를 확인함. 광수용체 세포(photoreceptor)를 표지하는 Rhod,,M-cone 과 수평세포(horizontal cell)를 표지하는 Calbindin, 무축삭세포(amacrine cell)을 표지하는 Chx10, Pax6, 신경결세포(ganglion cell)을 표지하는 Brn3b 등을 이용하여 확인한 결과, 정상 생쥐와 Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐에서 망막에서 발현되는 단백질의 큰 변화는 보이지 않음. 이는 Vax1 단백질이 망막구조의 발생에는 직접적인 영향을 미치지 않음을 의미함
 표
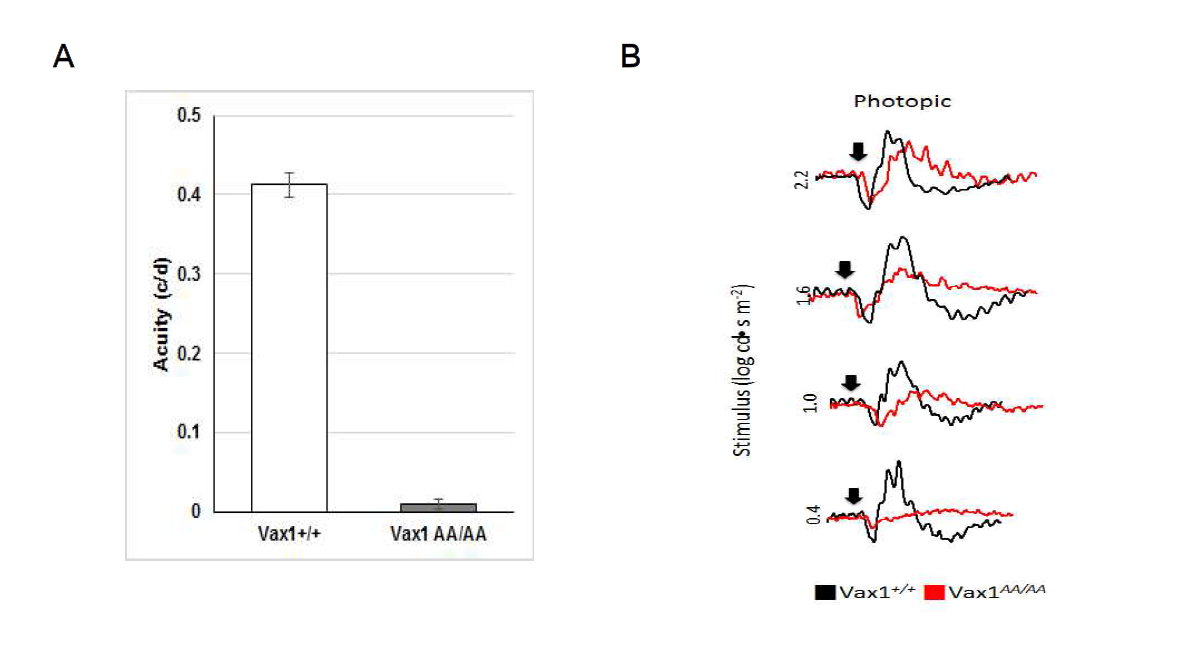
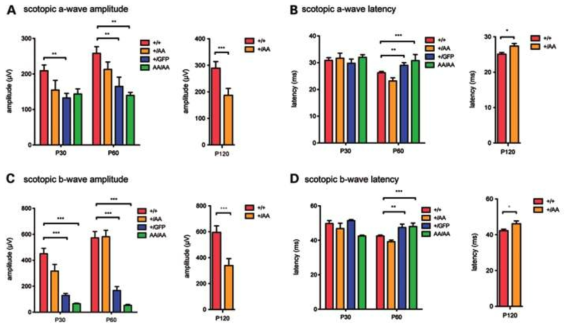
Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 시각 기능 검사. (A) 시신경 교차가 일어나지 못한 Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐는 정상 생쥐와 비교해 눈에서 뇌로의 시신경 연결은 반전이 된 반면, 뇌에서 다양한 운동 신경들로 전달되는 경로는 정상과 유사하게 되어 있을 가능성이 높음. 이는 눈에서 감지한 이미지가 뇌로 전달이 되더라도 해당 이미지를 인식한 뇌가 운동을 유도하는 과정에서 방향성이 반전될 가능성이 있음 (모식도로 그리기). (B) 이러한 시각 정보와 운동의 반전 여부를 확인하기 위해, 시각운동 반응(optokinetic response, OKR)을 Optomotry를 이용하여 조사함. Vax1(+/AA) 생쥐는 좌우 방향으로 움직이는 세로축 선들에 반응해 머리를 같은 방향으로 움직이며, 그 정확도가 약 0.4로 정상 생쥐와 유사한 반면, Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐는 거의 반응을 하지 못하는 것을 알 수 있음 (n=3). (C) Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 비정상적 시각 반응이 망막 기능의 이상에서 나타나는지를 망막전위도 (electroretinogram, ERG) 측정을 통해 조사함. Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐는 정상 Vax1(+/+) 생쥐에 비해 명반응 자극에 대한 망막 전위도 (photopic ERG)의 a-wave에는 큰 차이를 나타내지 않았지만 b-wave는 정상보다 지연된 반응 양상을 보임
표
Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 시각 기능 검사. (A) 시신경 교차가 일어나지 못한 Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐는 정상 생쥐와 비교해 눈에서 뇌로의 시신경 연결은 반전이 된 반면, 뇌에서 다양한 운동 신경들로 전달되는 경로는 정상과 유사하게 되어 있을 가능성이 높음. 이는 눈에서 감지한 이미지가 뇌로 전달이 되더라도 해당 이미지를 인식한 뇌가 운동을 유도하는 과정에서 방향성이 반전될 가능성이 있음 (모식도로 그리기). (B) 이러한 시각 정보와 운동의 반전 여부를 확인하기 위해, 시각운동 반응(optokinetic response, OKR)을 Optomotry를 이용하여 조사함. Vax1(+/AA) 생쥐는 좌우 방향으로 움직이는 세로축 선들에 반응해 머리를 같은 방향으로 움직이며, 그 정확도가 약 0.4로 정상 생쥐와 유사한 반면, Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐는 거의 반응을 하지 못하는 것을 알 수 있음 (n=3). (C) Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 비정상적 시각 반응이 망막 기능의 이상에서 나타나는지를 망막전위도 (electroretinogram, ERG) 측정을 통해 조사함. Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐는 정상 Vax1(+/+) 생쥐에 비해 명반응 자극에 대한 망막 전위도 (photopic ERG)의 a-wave에는 큰 차이를 나타내지 않았지만 b-wave는 정상보다 지연된 반응 양상을 보임
 표
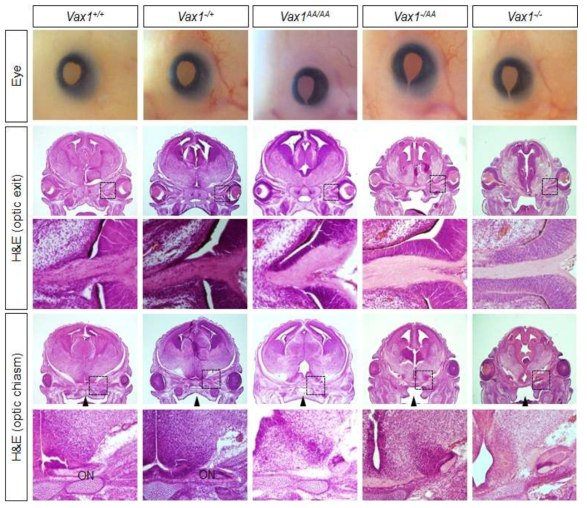
Vax1(KR/AA) 생쥐의 해부학적 분석. (위) 수정 후 15일 생쥐 배아 사진. 정상 및 Vax1(+/-) 생쥐와 달리 나머지 생쥐들에서는 안구 하부에 틈이 생기는 coloboma가 관찰됨. 해당 생쥐 뇌 절편을 조사한 결과 해당 생쥐의 optic stalk의 하부가 완전히 닫히지 않아 시신경 성장이 정상적으로 일어나지 못해 optic chiasm 형성이 일어나지 않음. ON, optic nerve. 다만, 변이형 Vax1 단백질만을 가지는 Vax1 AA/AA 생쥐에서는 입 천장이 열리는 구개열이 나타나지는 않음. 입천장 뼈를 만드는 신경능세포(Neural crest cell) 에서는 Vax1에 역할에 대한 규명이 필요함
표
Vax1(KR/AA) 생쥐의 해부학적 분석. (위) 수정 후 15일 생쥐 배아 사진. 정상 및 Vax1(+/-) 생쥐와 달리 나머지 생쥐들에서는 안구 하부에 틈이 생기는 coloboma가 관찰됨. 해당 생쥐 뇌 절편을 조사한 결과 해당 생쥐의 optic stalk의 하부가 완전히 닫히지 않아 시신경 성장이 정상적으로 일어나지 못해 optic chiasm 형성이 일어나지 않음. ON, optic nerve. 다만, 변이형 Vax1 단백질만을 가지는 Vax1 AA/AA 생쥐에서는 입 천장이 열리는 구개열이 나타나지는 않음. 입천장 뼈를 만드는 신경능세포(Neural crest cell) 에서는 Vax1에 역할에 대한 규명이 필요함
 표
Vax1(AA) 단백질의 세포 간 이동 저하. 1차년도에 제작 완료한 Vax1(AA) 단백질을 발현하는 생쥐 시신경에서 세포 간 이동을 검증하기 위하여 각기 정상 Vax1 및 변이형 Vax1(AA) 유전자를 0, 1, 2개 씩 발현하는 수정 후 14.5일 생쥐 시신경 내 Vax1을 시신경축삭 표지자인 Nf160 과의 면역형광염색을 통해 조사함. 그 결과, 정상 생쥐 시신경 축삭에서 관찰되던 Vax1 단백질이 Vax1(AA)만을 발현하는 생쥐 시신경축삭에서는 관찰되지 않음. 이는 시신경을 둘러싸고 있는 astrocyte precursor cell (APC)에서 발현된 Vax1이 시신경축삭으로 이동이 되지 못했음을 의미함
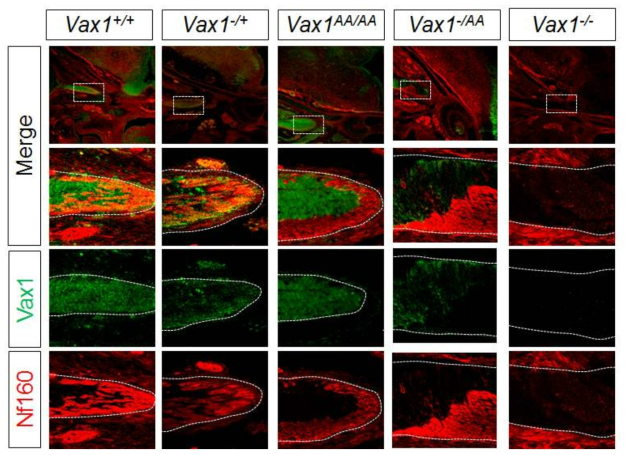
표
Vax1(AA) 단백질의 세포 간 이동 저하. 1차년도에 제작 완료한 Vax1(AA) 단백질을 발현하는 생쥐 시신경에서 세포 간 이동을 검증하기 위하여 각기 정상 Vax1 및 변이형 Vax1(AA) 유전자를 0, 1, 2개 씩 발현하는 수정 후 14.5일 생쥐 시신경 내 Vax1을 시신경축삭 표지자인 Nf160 과의 면역형광염색을 통해 조사함. 그 결과, 정상 생쥐 시신경 축삭에서 관찰되던 Vax1 단백질이 Vax1(AA)만을 발현하는 생쥐 시신경축삭에서는 관찰되지 않음. 이는 시신경을 둘러싸고 있는 astrocyte precursor cell (APC)에서 발현된 Vax1이 시신경축삭으로 이동이 되지 못했음을 의미함
 표
Vax1(AA) 생쥐에서 관찰된 hypomorphic phenotype. 선행연구를 통해 Vax1(AA) 변이 단백질은 세포 간 이동 뿐만 아니라 Vax1 타겟 유전자에 대한 전사 활성 역시 정상의 80% 정도로 감소함을 발견하였다. 이는 Vax1(AA) 생쥐에서 나타난 변화들이 단백질이 세포 간 이동 실패로 인해 나타나는 것과 동시에 Vax1 타겟 유전자 발현의 저하에 의해서도 나타날 가능성이 있다. 이를 확인하기 위해 Vax1 전사 기능에 의존적인 것으로 알려진 망막과 시축(optic stalk) 사이의 경계 형성을 망막과 시축의 마커인 Pax6와 Pax2의 분포를 통해 조사하였다. Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐에서 망막 부위가 시축 영역으로 확장되어 있으며, 이 부위는 두 영역의 세포들이 섞여 있는 특징을 보인다. 다만, 이 현상은 Vax1(-/-) 생쥐에서 보이는 망막 영역의 전반적 확장 현상 보다는 다소 약한 특징을 보임
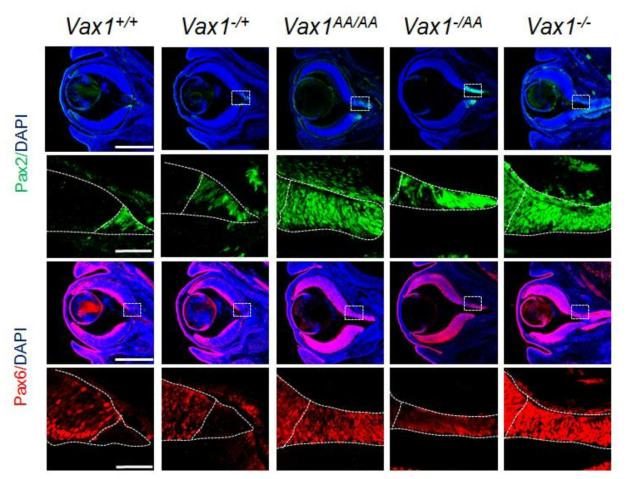
표
Vax1(AA) 생쥐에서 관찰된 hypomorphic phenotype. 선행연구를 통해 Vax1(AA) 변이 단백질은 세포 간 이동 뿐만 아니라 Vax1 타겟 유전자에 대한 전사 활성 역시 정상의 80% 정도로 감소함을 발견하였다. 이는 Vax1(AA) 생쥐에서 나타난 변화들이 단백질이 세포 간 이동 실패로 인해 나타나는 것과 동시에 Vax1 타겟 유전자 발현의 저하에 의해서도 나타날 가능성이 있다. 이를 확인하기 위해 Vax1 전사 기능에 의존적인 것으로 알려진 망막과 시축(optic stalk) 사이의 경계 형성을 망막과 시축의 마커인 Pax6와 Pax2의 분포를 통해 조사하였다. Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐에서 망막 부위가 시축 영역으로 확장되어 있으며, 이 부위는 두 영역의 세포들이 섞여 있는 특징을 보인다. 다만, 이 현상은 Vax1(-/-) 생쥐에서 보이는 망막 영역의 전반적 확장 현상 보다는 다소 약한 특징을 보임
 표
Otx2-AA 단백질의 세포 간 이동 능력 측정. 1단계 연구를 통해 cortical PV cell 외부의 perineural network (PNN)의 chondroitin sulfate (CS)에 결합하는 부위로 판명된 Otx2의 44-45번에 있는 Arg-Lys (RK) 부위를 Alanine으로 치환한 Otx2-AA 단백질의 세포 간 이동 능력을 배양세포에서 조사함. (A) Otx2를 과발현하는 293T 세포의 배양액 (growth medium (GM))을 heparin 존재 여부에 따라 분리한 후 각 배양액에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질의 양을 조사함. 그 결과 정상 Otx2 단백질은 heparin 처리 없이는 배양액에서 거의 검출이 되지 않았지만, Otx2-AA는 heparin 처리 없이도 정상보다 3배 이상의 단백질이 배양액에 존재함. 이는 Otx2-AA 단백질의 세포막 부착력이 약화되었음을 의미함. (B) Otx2-AA 단백질의 세포 간 이동을 조사하기 위해 Otx2-myc/His 재조합단백질을 COS7 세포에 처리 후 세포 배양액을 포집하여 세포에 결합하지 못하고 배양액에 남은 단백질과 넣어 준 단백질 양을 상호 비교함. 그 결과, Otx2의 경우는 약 60% 단백질이 세포로 이동하지 못하고 남아 있지만 Otx2-AA는 거의 대부분 단백질이 세포로 이동하지 못하고 배양액에 남아 있음을 확인함. (C) 마찬가지로 COS7 세포 내부로 이동한 Otx2 단백질의 양을 면역형광염색으로 조사한 결과 세포의 핵까지 이동한 정상 Otx2보다 Otx2-AA 단백질은 세포막에만 일부 검출될 뿐 세포 내부로 이동이 거의 이루어지지 않음
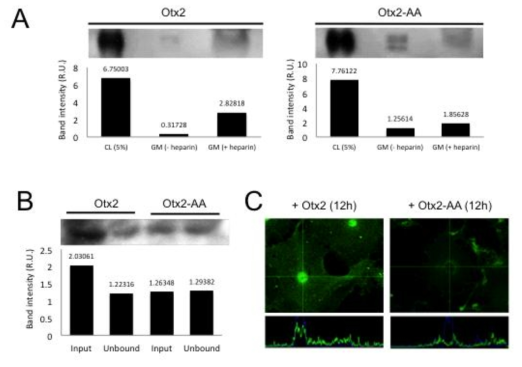
표
Otx2-AA 단백질의 세포 간 이동 능력 측정. 1단계 연구를 통해 cortical PV cell 외부의 perineural network (PNN)의 chondroitin sulfate (CS)에 결합하는 부위로 판명된 Otx2의 44-45번에 있는 Arg-Lys (RK) 부위를 Alanine으로 치환한 Otx2-AA 단백질의 세포 간 이동 능력을 배양세포에서 조사함. (A) Otx2를 과발현하는 293T 세포의 배양액 (growth medium (GM))을 heparin 존재 여부에 따라 분리한 후 각 배양액에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질의 양을 조사함. 그 결과 정상 Otx2 단백질은 heparin 처리 없이는 배양액에서 거의 검출이 되지 않았지만, Otx2-AA는 heparin 처리 없이도 정상보다 3배 이상의 단백질이 배양액에 존재함. 이는 Otx2-AA 단백질의 세포막 부착력이 약화되었음을 의미함. (B) Otx2-AA 단백질의 세포 간 이동을 조사하기 위해 Otx2-myc/His 재조합단백질을 COS7 세포에 처리 후 세포 배양액을 포집하여 세포에 결합하지 못하고 배양액에 남은 단백질과 넣어 준 단백질 양을 상호 비교함. 그 결과, Otx2의 경우는 약 60% 단백질이 세포로 이동하지 못하고 남아 있지만 Otx2-AA는 거의 대부분 단백질이 세포로 이동하지 못하고 배양액에 남아 있음을 확인함. (C) 마찬가지로 COS7 세포 내부로 이동한 Otx2 단백질의 양을 면역형광염색으로 조사한 결과 세포의 핵까지 이동한 정상 Otx2보다 Otx2-AA 단백질은 세포막에만 일부 검출될 뿐 세포 내부로 이동이 거의 이루어지지 않음
 표
Otx2-AA 단백질의 생화학적 활성 검증. (A) Otx2와 Otx2-AA 단백질을 각각 Otx2의 타겟 유전자인 IRBP의 promoter 부위에 해당되는 DNA oligomer probe와 섞어서 타겟 DNA 서열에 대한 결합력을 측정함. 그 결과 Otx2-AA는 Otx2와 비교해 약간 감소하였지만 여전히 정상적인 DNA 결합능력을 가지고 있음을 확인함. (B) DNA에 정상적 결합을 하는 Otx2-AA의 전사촉진 활성을 망막 내 Otx2 타겟 유전자인 Crx와 PKCalpha promoter에 의해 발현되는 luciferase의 활성을 조사함으로써 확인함. 그 결과 Otx2-AA는 Otx2에 비해 약 70~80% 정도의 전사활성을 가지는 것으로 확인됨
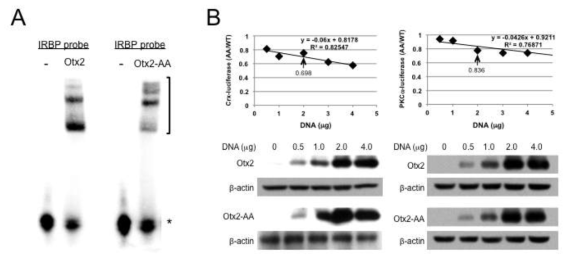
표
Otx2-AA 단백질의 생화학적 활성 검증. (A) Otx2와 Otx2-AA 단백질을 각각 Otx2의 타겟 유전자인 IRBP의 promoter 부위에 해당되는 DNA oligomer probe와 섞어서 타겟 DNA 서열에 대한 결합력을 측정함. 그 결과 Otx2-AA는 Otx2와 비교해 약간 감소하였지만 여전히 정상적인 DNA 결합능력을 가지고 있음을 확인함. (B) DNA에 정상적 결합을 하는 Otx2-AA의 전사촉진 활성을 망막 내 Otx2 타겟 유전자인 Crx와 PKCalpha promoter에 의해 발현되는 luciferase의 활성을 조사함으로써 확인함. 그 결과 Otx2-AA는 Otx2에 비해 약 70~80% 정도의 전사활성을 가지는 것으로 확인됨
 표
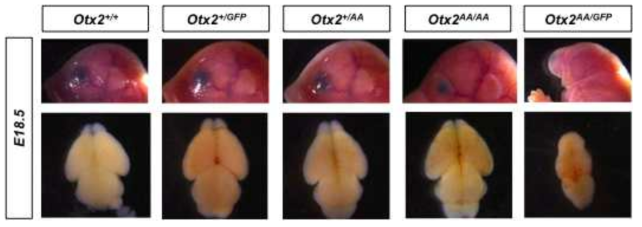
Otx2-AA 생쥐의 뇌 발달 유지 효과. Otx2의 활성이 정상에 비해 약 70% 정도인 Otx2-AA의 기능이 실재로 생체 내에서 어떤 발달 이상을 가지고 올지를 조사하기 위해, Otx2가 2개 모두 정상인 경우 (Otx2+/+), 하나의 정상 Otx2와 하나의 Otx2-AA를 가지는 경우 (Otx2+/AA), Otx2-AA만 두 개 가지는 경우 (Otx2AA/AA), Otx2 하나만 가지는 경우 (Otx2+/GFP), Otx2-AA만 하나 가지는 경우 (Otx2AA/GFP)로 나누어 뇌와 안구 발달을 조사함. 그 결과, Otx2가 하나만 있을 때는 뇌와 안구 발달 모두 정상이지만, Otx2-AA만 하나 가진 경우는 안구 발달이 전혀 이루어지지 않고 뇌의 크기도 줄어들어 있음을 알 수 있다. 이는 Otx2-AA가 정 상적인 Otx2에 비해 그 기능이 심각히 약함을 알 수 있음. 또한, Otx2-AA만 두 개 있는 경우, 뇌 발달은 정상이지만 안구의 발달에 약한 이상이 있는 것을 알 수 있음. 이는 Otx2-AA 두 개가 Otx2하나보다 그 활성이 부족함을 시사함. 따라서, 정상 Otx2 하나만 가질 경우 생체는 최소 70% 이상의 전사활성을 가지거나, 70% 이하의 전사활성을 가지더라도 세포 간 이동을 함으로써 이를 보정할 수 있다고 판단할 수 있음
표
Otx2-AA 생쥐의 뇌 발달 유지 효과. Otx2의 활성이 정상에 비해 약 70% 정도인 Otx2-AA의 기능이 실재로 생체 내에서 어떤 발달 이상을 가지고 올지를 조사하기 위해, Otx2가 2개 모두 정상인 경우 (Otx2+/+), 하나의 정상 Otx2와 하나의 Otx2-AA를 가지는 경우 (Otx2+/AA), Otx2-AA만 두 개 가지는 경우 (Otx2AA/AA), Otx2 하나만 가지는 경우 (Otx2+/GFP), Otx2-AA만 하나 가지는 경우 (Otx2AA/GFP)로 나누어 뇌와 안구 발달을 조사함. 그 결과, Otx2가 하나만 있을 때는 뇌와 안구 발달 모두 정상이지만, Otx2-AA만 하나 가진 경우는 안구 발달이 전혀 이루어지지 않고 뇌의 크기도 줄어들어 있음을 알 수 있다. 이는 Otx2-AA가 정 상적인 Otx2에 비해 그 기능이 심각히 약함을 알 수 있음. 또한, Otx2-AA만 두 개 있는 경우, 뇌 발달은 정상이지만 안구의 발달에 약한 이상이 있는 것을 알 수 있음. 이는 Otx2-AA 두 개가 Otx2하나보다 그 활성이 부족함을 시사함. 따라서, 정상 Otx2 하나만 가질 경우 생체는 최소 70% 이상의 전사활성을 가지거나, 70% 이하의 전사활성을 가지더라도 세포 간 이동을 함으로써 이를 보정할 수 있다고 판단할 수 있음
 표
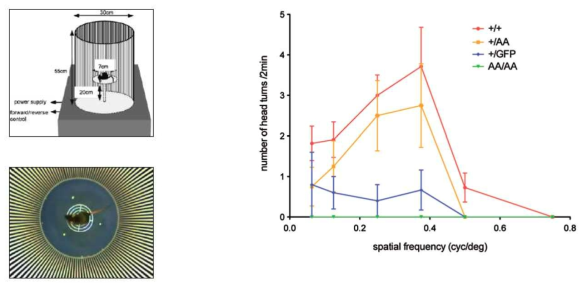
Otx2-AA 생쥐의 시력 테스트. 각기 다른 Otx2 유전자의 변이를 가진 생쥐들의 시력을 검증하기 위하여 생후 60일 생쥐들을 Optomotry를 이용하여 생쥐 정면에 각기 흑백의 세로띠를 반시계 방향으로 속도를 변화시키며 이동할 때 (cyc/deg) 나타나는 생쥐의 머리 돌림 반응도 (head turns) 측정으로 시력을 검증함. 그 결과 Otx2(+/AA) 생쥐는 정상과 비교하여 약간 감소한 시력이지만 여전히 정상 수준의 시각을 가지고 있었지만, Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐는 시력이 심각한 정도로 손상되어 있었고, Otx2(AA/AA) 생쥐는 시력이 거의 존재하지 않는 상태로 판명됨
표
Otx2-AA 생쥐의 시력 테스트. 각기 다른 Otx2 유전자의 변이를 가진 생쥐들의 시력을 검증하기 위하여 생후 60일 생쥐들을 Optomotry를 이용하여 생쥐 정면에 각기 흑백의 세로띠를 반시계 방향으로 속도를 변화시키며 이동할 때 (cyc/deg) 나타나는 생쥐의 머리 돌림 반응도 (head turns) 측정으로 시력을 검증함. 그 결과 Otx2(+/AA) 생쥐는 정상과 비교하여 약간 감소한 시력이지만 여전히 정상 수준의 시각을 가지고 있었지만, Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐는 시력이 심각한 정도로 손상되어 있었고, Otx2(AA/AA) 생쥐는 시력이 거의 존재하지 않는 상태로 판명됨
 표
Otx2-AA 생쥐 망막의 시각 반응도 테스트. 그림 92에서 확인한 Otx2(+/GFP) 및 Otx2(AA/AA) 생쥐의 시력 상실의 원인이 망막 수준의 활성도 감소에서 나타나는지를 검증하기 위하여 생후 30일 및 60일 생쥐 망막의 빛에 대한 반응도를 electroretinogram (ERG)를 이용하여 측정하였다. 그 결과 약한 빛에 반응하는 관상세포 (rod photoreceptor)와 이와 연결된 양극세포의 반응을 측정하는 scotopic ERG 반응에서 관상세포 반응도를 나타내는 a-wave의 경우 Otx2(+/GFP)와 Otx2(AA/AA) 생쥐가 정상에 비해 약 70% 수준의 반응도를 나타내는 반면 (A), b-wave 반응은 거의 30% 이하로 나타나 (C) 이들 생쥐 시력 약화의 원인은 양극세포의 수준에서 주로 나타남을 확인함
표
Otx2-AA 생쥐 망막의 시각 반응도 테스트. 그림 92에서 확인한 Otx2(+/GFP) 및 Otx2(AA/AA) 생쥐의 시력 상실의 원인이 망막 수준의 활성도 감소에서 나타나는지를 검증하기 위하여 생후 30일 및 60일 생쥐 망막의 빛에 대한 반응도를 electroretinogram (ERG)를 이용하여 측정하였다. 그 결과 약한 빛에 반응하는 관상세포 (rod photoreceptor)와 이와 연결된 양극세포의 반응을 측정하는 scotopic ERG 반응에서 관상세포 반응도를 나타내는 a-wave의 경우 Otx2(+/GFP)와 Otx2(AA/AA) 생쥐가 정상에 비해 약 70% 수준의 반응도를 나타내는 반면 (A), b-wave 반응은 거의 30% 이하로 나타나 (C) 이들 생쥐 시력 약화의 원인은 양극세포의 수준에서 주로 나타남을 확인함
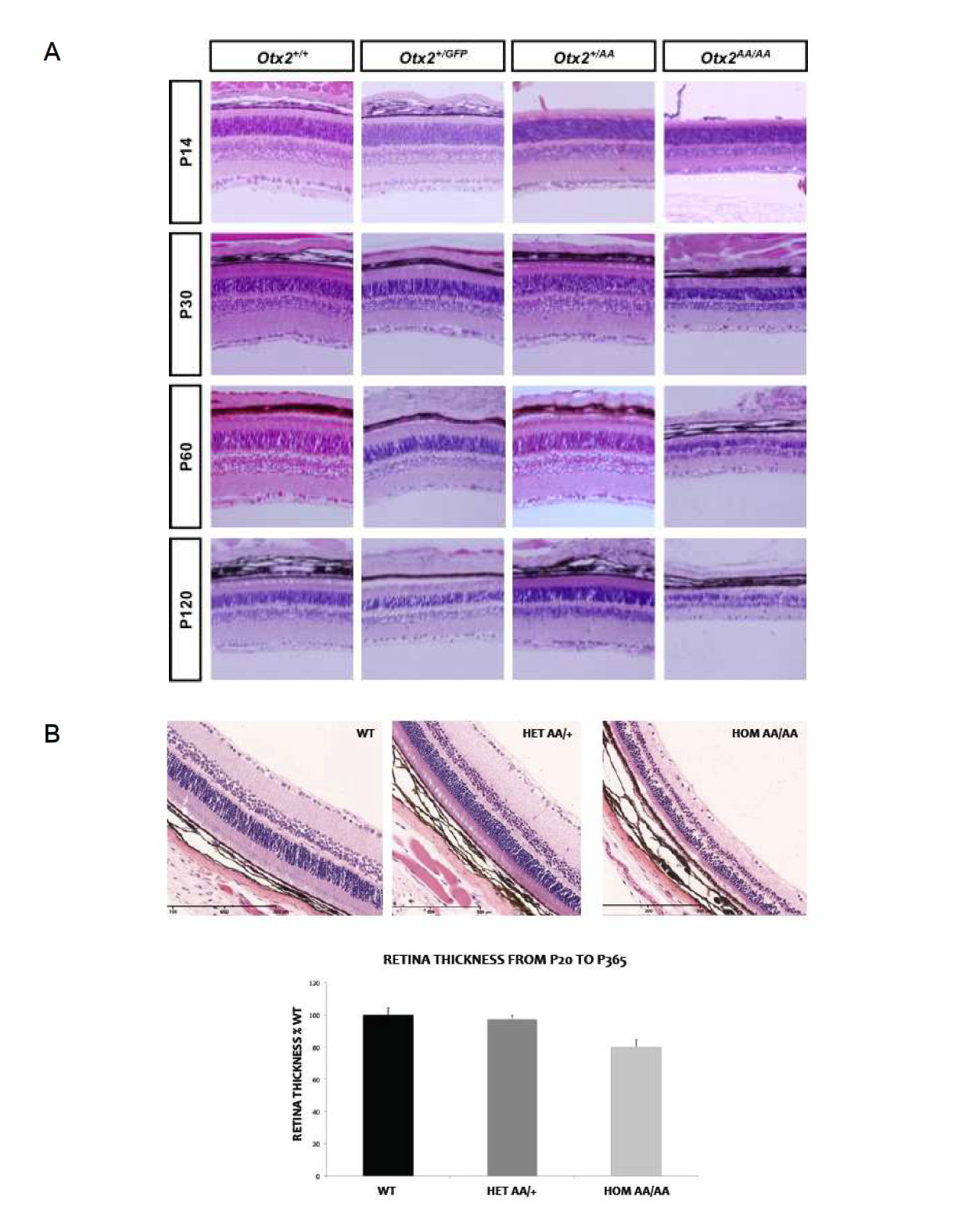 표
Otx2 활성에 따른 망막신경 발달 및 퇴화. (A) 뇌와 안구발달을 통해 추정한 Otx2와 Otx2-AA의 상대적 활성을 안구 발달이 정상인 생쥐 망막에서 추가로 검증함. 안구 크기가 정상인 Otx2+/GFP와 Otx2AA/AA의 경우 생후 2주 (P14)부터 이미 INL을 구성하는 세포의 수가 감소되어 있음을 보아, Otx2가 하나만 있거나 활성이 떨어진 Otx2-AA 두 개를 가지는 경우는 망막 신경 발달이 정상적으로 이루어 질 수 없음을 증명함. 또한, 더 나아가 이 망막조직들은 시간이 지남에 따라 망막신경들의 퇴화가 일어나는 것으로 보아 Otx2의 기능이 망막발달 뿐만 아니라 망막신경세포의 유지에도 중요함을 알 수 있음. (B) 구조적으로 정상인 Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막의 경우도 두께가 정상에 비해 약 20% 이상 감소해 있었으며, 광수용세포가 위치한 outer nuclear layer (ONL) 뿐만 아니라 interneuron들이 위치한 inner nuclear layer (INL)에 걸쳐 광범위한 세포의 감소가 나타났다
표
Otx2 활성에 따른 망막신경 발달 및 퇴화. (A) 뇌와 안구발달을 통해 추정한 Otx2와 Otx2-AA의 상대적 활성을 안구 발달이 정상인 생쥐 망막에서 추가로 검증함. 안구 크기가 정상인 Otx2+/GFP와 Otx2AA/AA의 경우 생후 2주 (P14)부터 이미 INL을 구성하는 세포의 수가 감소되어 있음을 보아, Otx2가 하나만 있거나 활성이 떨어진 Otx2-AA 두 개를 가지는 경우는 망막 신경 발달이 정상적으로 이루어 질 수 없음을 증명함. 또한, 더 나아가 이 망막조직들은 시간이 지남에 따라 망막신경들의 퇴화가 일어나는 것으로 보아 Otx2의 기능이 망막발달 뿐만 아니라 망막신경세포의 유지에도 중요함을 알 수 있음. (B) 구조적으로 정상인 Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막의 경우도 두께가 정상에 비해 약 20% 이상 감소해 있었으며, 광수용세포가 위치한 outer nuclear layer (ONL) 뿐만 아니라 interneuron들이 위치한 inner nuclear layer (INL)에 걸쳐 광범위한 세포의 감소가 나타났다
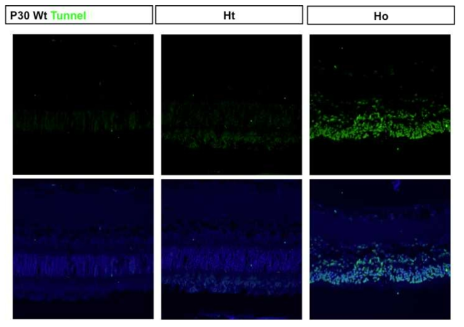 표
Otx2-AA/AA 망막에서 줄어든 INL과 ONL의 두께가 세포의 발달 이상인지 아니면 세포의 과도한 사멸 때문에 일어나는지를 검증하기 위해 4주령 정상 생쥐 (WT)와 Otx2-AA/+ (Ht), Otx2-AA/AA (Ho) 망막에서 apoptosis로 죽어가는 세포의 분포를 TUNEL 염색으로 조사함. 그 결과 Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막 내 ONL 및 INL 상층부 세포에서 TUNEL에 의해 염색되는 세포의 수가 증가되어 있음을 알 수 있다. Otx2-AA/+ 생쥐 망막에도 일부 ONL 세포에서 TUNEL 신호가 관찰된 것으로 보아 Otx2의 세포 간 이동이 광수용세포의 생존에 중요할 것으로 예측함
표
Otx2-AA/AA 망막에서 줄어든 INL과 ONL의 두께가 세포의 발달 이상인지 아니면 세포의 과도한 사멸 때문에 일어나는지를 검증하기 위해 4주령 정상 생쥐 (WT)와 Otx2-AA/+ (Ht), Otx2-AA/AA (Ho) 망막에서 apoptosis로 죽어가는 세포의 분포를 TUNEL 염색으로 조사함. 그 결과 Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막 내 ONL 및 INL 상층부 세포에서 TUNEL에 의해 염색되는 세포의 수가 증가되어 있음을 알 수 있다. Otx2-AA/+ 생쥐 망막에도 일부 ONL 세포에서 TUNEL 신호가 관찰된 것으로 보아 Otx2의 세포 간 이동이 광수용세포의 생존에 중요할 것으로 예측함
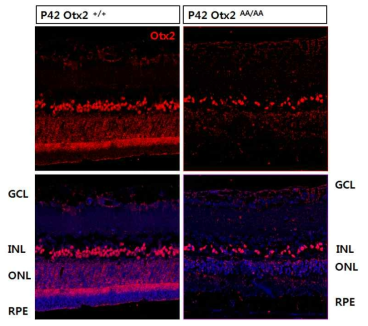 표
망막 내 Otx2-AA 발현양 저하와 양극세포 감소. 6주령 Otx2-AA/AA 망막에서 Otx2를 발현하는 INL 내 세포의 수가 정상의 30% 수준으로 급감한 것을 알 수 있다. 이는 Otx2를 발현하는 INL 세포 수의 감소와 일치하는 것으로 세포 간 이동 기능이 저하된 Otx2-AA는 Otx2 발달 및 유지를 지원하지 못하는 것으로 판명됨. 양극세포에서 발현된 Otx2가 이동하여 분포하는 RGC에도 Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막에서는 Otx2가 거의 상실이 되어, Otx2-AA 단백질은 세포 간 이동이 결여되었음을 다시 한 번 증명함. 또한, ONL의 광수용세포 세포질과 inner segment에서 관찰되던 Otx2 단백질 역시 거의 사라짐을 알 수 있다. 그 결과 ONL에 위치하는 광수용세포의 전체 숫자도 정상의 60% 정도로 줄어들어 있음을 알 수 있다
표
망막 내 Otx2-AA 발현양 저하와 양극세포 감소. 6주령 Otx2-AA/AA 망막에서 Otx2를 발현하는 INL 내 세포의 수가 정상의 30% 수준으로 급감한 것을 알 수 있다. 이는 Otx2를 발현하는 INL 세포 수의 감소와 일치하는 것으로 세포 간 이동 기능이 저하된 Otx2-AA는 Otx2 발달 및 유지를 지원하지 못하는 것으로 판명됨. 양극세포에서 발현된 Otx2가 이동하여 분포하는 RGC에도 Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막에서는 Otx2가 거의 상실이 되어, Otx2-AA 단백질은 세포 간 이동이 결여되었음을 다시 한 번 증명함. 또한, ONL의 광수용세포 세포질과 inner segment에서 관찰되던 Otx2 단백질 역시 거의 사라짐을 알 수 있다. 그 결과 ONL에 위치하는 광수용세포의 전체 숫자도 정상의 60% 정도로 줄어들어 있음을 알 수 있다
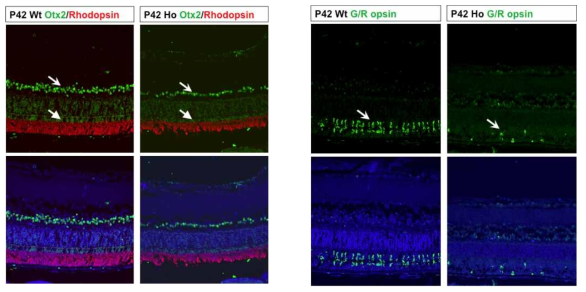 표
Otx2-AA/AA 망막 내 원추세포 특이적 광수용세포 사멸. Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막에서 INL과 더불어 ONL에서도 세포의 유실이 일어났으므로, ONL 세포 유실이 관상세포 (rod photoreceptor)와 원추세포 (cone photoreceptor) 중 어느 세포 군에서 주로 일어났는지를 조사하기 위하여, 6주령의 WT 생쥐와 Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막을 관상세포 특이적 rodopsin과 원추세포 특이적 G/R opsin을 이용하여 면역형광염색을 수행함. 그 결과 관상세포의 수에는 큰 차이가 없었지만, 원추세포의 경우는 심각한 세포수의 감소가 나타남. 따라서, Otx2-AA/AA 망막 ONL에서의 세포 유실은 주로 원추세포의 유실에 의한 것인 것으로 예측함
표
Otx2-AA/AA 망막 내 원추세포 특이적 광수용세포 사멸. Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막에서 INL과 더불어 ONL에서도 세포의 유실이 일어났으므로, ONL 세포 유실이 관상세포 (rod photoreceptor)와 원추세포 (cone photoreceptor) 중 어느 세포 군에서 주로 일어났는지를 조사하기 위하여, 6주령의 WT 생쥐와 Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막을 관상세포 특이적 rodopsin과 원추세포 특이적 G/R opsin을 이용하여 면역형광염색을 수행함. 그 결과 관상세포의 수에는 큰 차이가 없었지만, 원추세포의 경우는 심각한 세포수의 감소가 나타남. 따라서, Otx2-AA/AA 망막 ONL에서의 세포 유실은 주로 원추세포의 유실에 의한 것인 것으로 예측함
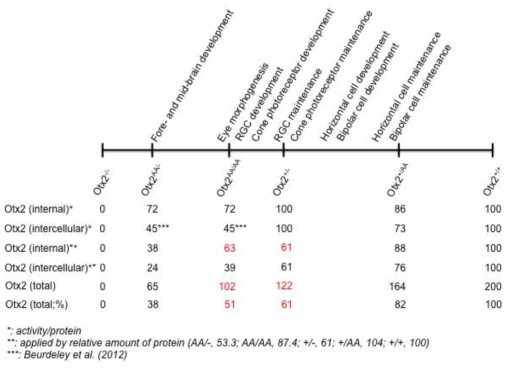 표
내부 Otx2와 외부 Otx2의 기능 예측. 위의 결과들을 기반으로 각 신경 조직의 정상적 발달 및 유지에 필요한 Otx2 활성을 도식화 함. 결과에 의하면 Otx2의 기능은 세포 내부에서 발현되어 작용하는 내부 Otx2 단백질과 외부로부터 이동하여 세포 내 기능에 참여하는 외부 Otx2 단백질로 나누어 볼 수 있다. 이들 두 종류의 Otx2 단백질 기능의 총합이 세포가 가지는 Otx2 활성이 총합이라고 볼 수 있다. 정상적 뇌의 발달을 위해서는 최소한 정상에 비해 38%의 Otx2 기능이 요구됨을 알 수 있고, 이는 Otx2AA/GFP에서 처럼 주로 세포 내부에서 작용하는 Otx2의 활성과 유사한 양상을 보인다. 망막 발달을 위한 최소의 Otx2 활성은 약 51%이며 이는 세포 내부의 기능 뿐만 아니라 세포 외부에서 영입되는 단백질 또한 필요로 함을 알 수 있다. 즉, 세포 내부 단백질의 총량이 정상에 비해 약 63%이지만 세포 외부로부터 영입되는 단백질의 양이 정상의 39% 밖에 되지 않는 Otx2AA/AA의 경우에는 약한 눈 발생의 이상과 더불어 망막 내 양극세포의 발달 이상을 나타낸다. Otx2+/GFP의 경우는 세포 내부 단백질 총량은 Otx2AA/AA에 비해 오히려 약간 낮지만 세포 간이동에 의해 획득한 외부 단백질이 오히려 높아 총량 역시 61% 정도가 되어 안구 발달은 정상이고 약한 양극세포의 발달 이상만 보인다
표
내부 Otx2와 외부 Otx2의 기능 예측. 위의 결과들을 기반으로 각 신경 조직의 정상적 발달 및 유지에 필요한 Otx2 활성을 도식화 함. 결과에 의하면 Otx2의 기능은 세포 내부에서 발현되어 작용하는 내부 Otx2 단백질과 외부로부터 이동하여 세포 내 기능에 참여하는 외부 Otx2 단백질로 나누어 볼 수 있다. 이들 두 종류의 Otx2 단백질 기능의 총합이 세포가 가지는 Otx2 활성이 총합이라고 볼 수 있다. 정상적 뇌의 발달을 위해서는 최소한 정상에 비해 38%의 Otx2 기능이 요구됨을 알 수 있고, 이는 Otx2AA/GFP에서 처럼 주로 세포 내부에서 작용하는 Otx2의 활성과 유사한 양상을 보인다. 망막 발달을 위한 최소의 Otx2 활성은 약 51%이며 이는 세포 내부의 기능 뿐만 아니라 세포 외부에서 영입되는 단백질 또한 필요로 함을 알 수 있다. 즉, 세포 내부 단백질의 총량이 정상에 비해 약 63%이지만 세포 외부로부터 영입되는 단백질의 양이 정상의 39% 밖에 되지 않는 Otx2AA/AA의 경우에는 약한 눈 발생의 이상과 더불어 망막 내 양극세포의 발달 이상을 나타낸다. Otx2+/GFP의 경우는 세포 내부 단백질 총량은 Otx2AA/AA에 비해 오히려 약간 낮지만 세포 간이동에 의해 획득한 외부 단백질이 오히려 높아 총량 역시 61% 정도가 되어 안구 발달은 정상이고 약한 양극세포의 발달 이상만 보인다
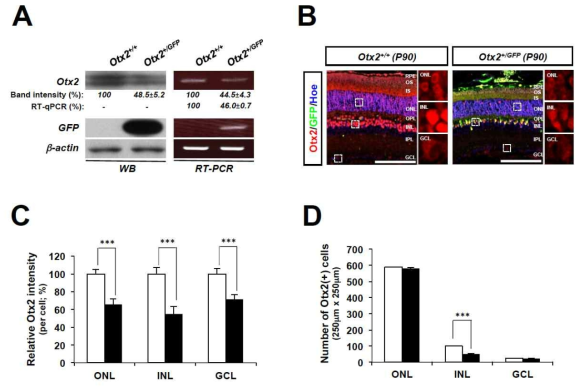 표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 Otx2의 양적 변화. 망막의 발달 및 퇴화가 관찰된 P90 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막 내 Otx2 단백질과 mRNA 양을 정상생쥐와 Western blot (WB)와 RT-qPCR을 통해 비교함. 그 결과 단백질의 경우 정상에 비해 약 44.5%, mRNA는 정상에 비해 약 48.5% 수준을 나타냄. 이 값이 전체 망막 세포 중 Otx2 발현 세포의 수의 감소에 의한 것인지 아니면 전체 Otx2 발현 세포 수의 변화는 없이 단위세포 당 양적 변화에 의한 것인지를 조사하기 위해 P90 Otx2(+/GFP) 망막 내 Otx2 발현 세포를 면역형광염색을 통해 조사함. 그 결과 Otx2를 발현하는 ONL 세포 수는 정상의 94.5%로 큰 변화가 없지만 Otx2를 발현하는 INL 세포 수는 정상의 40.3% 정도 밖에 되지 않았다. 이와는 달리 ONL과 INL 단위세포 당 Otx2 면역형광염색 강도는 61%와 58%로 좀 더 높았다. 이는 WB와 RT-qPCR에서 확인된 Otx2의 양의 감소는 단위세포 당발현량 감소와 INL의 Otx2 발현 세포 수의 감소의 복합적 요인으로 나타난 것으로 파악됨
표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 Otx2의 양적 변화. 망막의 발달 및 퇴화가 관찰된 P90 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막 내 Otx2 단백질과 mRNA 양을 정상생쥐와 Western blot (WB)와 RT-qPCR을 통해 비교함. 그 결과 단백질의 경우 정상에 비해 약 44.5%, mRNA는 정상에 비해 약 48.5% 수준을 나타냄. 이 값이 전체 망막 세포 중 Otx2 발현 세포의 수의 감소에 의한 것인지 아니면 전체 Otx2 발현 세포 수의 변화는 없이 단위세포 당 양적 변화에 의한 것인지를 조사하기 위해 P90 Otx2(+/GFP) 망막 내 Otx2 발현 세포를 면역형광염색을 통해 조사함. 그 결과 Otx2를 발현하는 ONL 세포 수는 정상의 94.5%로 큰 변화가 없지만 Otx2를 발현하는 INL 세포 수는 정상의 40.3% 정도 밖에 되지 않았다. 이와는 달리 ONL과 INL 단위세포 당 Otx2 면역형광염색 강도는 61%와 58%로 좀 더 높았다. 이는 WB와 RT-qPCR에서 확인된 Otx2의 양의 감소는 단위세포 당발현량 감소와 INL의 Otx2 발현 세포 수의 감소의 복합적 요인으로 나타난 것으로 파악됨
 표
Otx2 heterozygote 생쥐의 시각 이상. 위의 결과들에 따르면 Otx2의 양적, 질적 감소는 생쥐 망막 발달 및 유지에 심각한 영향을 주는 것으로 파악됨. 따라서, Otx2 유전자를 하나만 가지는 3개월령 (P90) Otx2 heterozygote (Otx2(+/GFP); 검은색 막대) 생쥐의 시력 (visual acuity; A)와 망막의 빛에 의한 반응을 측정하는 electroretinogram (ERG; B-E)를 통해 검증함. 그 결과 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐는 시력이 약화되어 있으며 망막의 강한 빛 반응도가 심각하게 약화되어 있음을 알 수 있음
표
Otx2 heterozygote 생쥐의 시각 이상. 위의 결과들에 따르면 Otx2의 양적, 질적 감소는 생쥐 망막 발달 및 유지에 심각한 영향을 주는 것으로 파악됨. 따라서, Otx2 유전자를 하나만 가지는 3개월령 (P90) Otx2 heterozygote (Otx2(+/GFP); 검은색 막대) 생쥐의 시력 (visual acuity; A)와 망막의 빛에 의한 반응을 측정하는 electroretinogram (ERG; B-E)를 통해 검증함. 그 결과 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐는 시력이 약화되어 있으며 망막의 강한 빛 반응도가 심각하게 약화되어 있음을 알 수 있음
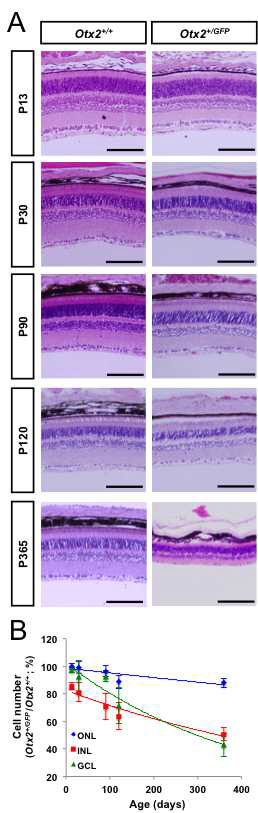 표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막의 점진적 퇴화. 시력과 시각반응의 이상을 보인 P90 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막의 이상이 망막의 퇴화에 의한 것인지를 조사하기 위해 각 시기별로 생쥐 망막절편을 분리하여 H&E 염색으로 망막 내 신경세포 수를 조사함 (A). 그 결과, Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐의 광수용세포가 위치한 ONL은 큰 변화가 없는 반면, 시신경을 이루는 갱글리온세포가 위치한 GCL의 경우는 발달이 완료되는 생후 2주 시점에는 큰 이상이 없다가 갱글리온세포는 시간이 지남에 따라 퇴화함을 알 수 있음. 또한, 이들 두 세포들을 연결하는 세포들이 집중적으로 위치한 INL의 수는 이미 발달과정에도 감소를 하였고, 시간이 지남에 따라 역시 심각한 퇴화를 나타냄. 이 결과를 통해, Otx2 유전자 하나 만으로 INL 세포의 발달이 온전하게 이루어지지 못하고, 갱글리온세포의 유지가 정상적이지 못함을 확인함
표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막의 점진적 퇴화. 시력과 시각반응의 이상을 보인 P90 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막의 이상이 망막의 퇴화에 의한 것인지를 조사하기 위해 각 시기별로 생쥐 망막절편을 분리하여 H&E 염색으로 망막 내 신경세포 수를 조사함 (A). 그 결과, Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐의 광수용세포가 위치한 ONL은 큰 변화가 없는 반면, 시신경을 이루는 갱글리온세포가 위치한 GCL의 경우는 발달이 완료되는 생후 2주 시점에는 큰 이상이 없다가 갱글리온세포는 시간이 지남에 따라 퇴화함을 알 수 있음. 또한, 이들 두 세포들을 연결하는 세포들이 집중적으로 위치한 INL의 수는 이미 발달과정에도 감소를 하였고, 시간이 지남에 따라 역시 심각한 퇴화를 나타냄. 이 결과를 통해, Otx2 유전자 하나 만으로 INL 세포의 발달이 온전하게 이루어지지 못하고, 갱글리온세포의 유지가 정상적이지 못함을 확인함
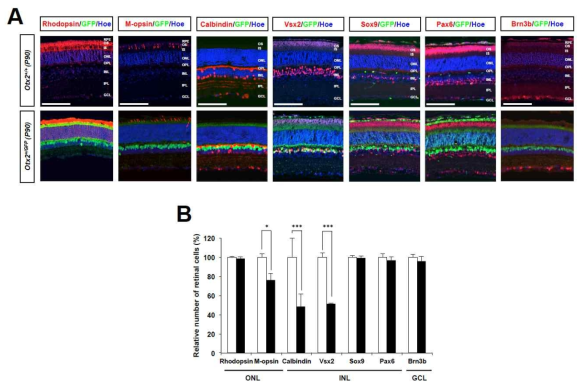 표
Otx2(+/GFP) 망막에서 양극세포와 평행세포의 감소. Otx2 발현 세포 수의 감소가 나타난 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 감소한 INL 세포의 정체를 규명하기 위해, 각 INL 신경세포 특이적 마커의 분포를 통해 조사함. 그 결과 양극세포에서 발현되는 Vsx2를 가지는 세포의 수가 Otx2 경우처럼 정상의 40% 수준으로 감소 함. 특히, Vsx2는 Otx2 유전자 부위에서 발현되는 GFP와 동일한 세포에서 나타나는 것으로 보아, Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐에서 감소한 Otx2 발현 세포는 양극세포로 추정됨. Calbinin에 의해 표지되는 INL 상부의 평행세포도 그 수가 감소하였으나, 이 세포는 Otx2 및 GFP를 발현하지 않는 것으로 보아 2차적 결과로 판단됨
표
Otx2(+/GFP) 망막에서 양극세포와 평행세포의 감소. Otx2 발현 세포 수의 감소가 나타난 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 감소한 INL 세포의 정체를 규명하기 위해, 각 INL 신경세포 특이적 마커의 분포를 통해 조사함. 그 결과 양극세포에서 발현되는 Vsx2를 가지는 세포의 수가 Otx2 경우처럼 정상의 40% 수준으로 감소 함. 특히, Vsx2는 Otx2 유전자 부위에서 발현되는 GFP와 동일한 세포에서 나타나는 것으로 보아, Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐에서 감소한 Otx2 발현 세포는 양극세포로 추정됨. Calbinin에 의해 표지되는 INL 상부의 평행세포도 그 수가 감소하였으나, 이 세포는 Otx2 및 GFP를 발현하지 않는 것으로 보아 2차적 결과로 판단됨
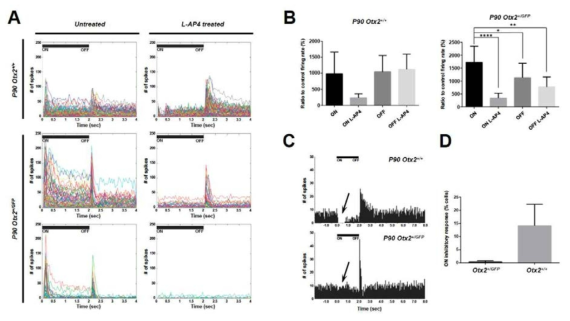 표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막 내 ON 및 OFF 신경세포 분포 및 반응도. (A) 생후 90일의 정상 생쥐와 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막의 망막 갱글리온세포에 64개에 전극을 비선택적으로 위치한 후 망막에 2초간 빛을 점멸하면서 각 신경 세포들의 전기적 활성도를 측정하였다. 이들 중 빛이 켜졌을때와 빛이 꺼졌을 때 모두 반응하는 ON/OFF 갱글리온세포들의 반응만을 별도로 분리한 후 이들을 반응도 그래프를 하나로 나타냄. 이 과정에서 초기 측정 후 해당 망막에 ON 양극세포에서만 발현되는 mGluR의 억제제인 L-AP4를 처리하면 ON/OFF 갱글리온세포의 ON 반응만이 선택적으로 사라져 OFF 반응의 정도만 측정할 수 있다. 이 조건에서 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막의 상당수 ON/OFF 갱글리온세포는 OFF 반응이 측정이 되지 않는 것을 보아 해당 세포들의 OFF 반응에 이상이 있음을 알 수 있음. (B) 위의 측정 결과들을 도표로 나타내었다. (C,D) 이들 중 일부는 빛이 켜지면 빛이 없을 때 활성화된 OFF 회로의 ON 회로 억제의 결과로 ON 반응의 급격한 감소가 동반되는 효과가 정상 생쥐에서는 나오는 반면 Otx(+/GFP) 생쥐에서는 나오지 않는 것으로 보아 해당 생쥐에서 OFF 양극세포의 활성도가 감소됨을 알 수 있음
표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막 내 ON 및 OFF 신경세포 분포 및 반응도. (A) 생후 90일의 정상 생쥐와 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막의 망막 갱글리온세포에 64개에 전극을 비선택적으로 위치한 후 망막에 2초간 빛을 점멸하면서 각 신경 세포들의 전기적 활성도를 측정하였다. 이들 중 빛이 켜졌을때와 빛이 꺼졌을 때 모두 반응하는 ON/OFF 갱글리온세포들의 반응만을 별도로 분리한 후 이들을 반응도 그래프를 하나로 나타냄. 이 과정에서 초기 측정 후 해당 망막에 ON 양극세포에서만 발현되는 mGluR의 억제제인 L-AP4를 처리하면 ON/OFF 갱글리온세포의 ON 반응만이 선택적으로 사라져 OFF 반응의 정도만 측정할 수 있다. 이 조건에서 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막의 상당수 ON/OFF 갱글리온세포는 OFF 반응이 측정이 되지 않는 것을 보아 해당 세포들의 OFF 반응에 이상이 있음을 알 수 있음. (B) 위의 측정 결과들을 도표로 나타내었다. (C,D) 이들 중 일부는 빛이 켜지면 빛이 없을 때 활성화된 OFF 회로의 ON 회로 억제의 결과로 ON 반응의 급격한 감소가 동반되는 효과가 정상 생쥐에서는 나오는 반면 Otx(+/GFP) 생쥐에서는 나오지 않는 것으로 보아 해당 생쥐에서 OFF 양극세포의 활성도가 감소됨을 알 수 있음
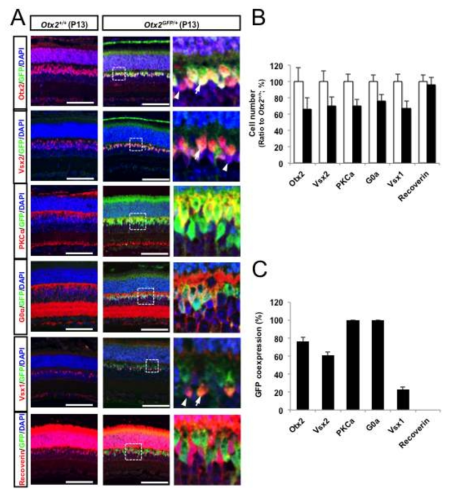 표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 양극세포 발달 이상. P90 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 나타난 Otx2 발현 양극세포의 감소 원인이 발달의 문제인지 아니면 퇴화에 의한 것인지를 규명하기위해 망막발달이 완성되는 생후 2주 (P13) 망막 절편에서 Otx2 발현 세포와 전체 양극세포를 표지하는 Vsx2, rod 양극세포를 표지하는 PKCalpha, ON-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 G0alpha, OFF-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 Vsx1, 제 2형 (Type-2; T2) OFF-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 Recoverin 등의 분포를 조사함 (A). 그 결과 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포를 제외한 전체 양극세포의 수와 rod, ON-cone, OFF-cone 양극세포 수가 모두가 Otx2 수의 감소와 유사하게 정상 망막에 비해 약 20-30% 정도 감소한 것으로 나타남 (B). 이는 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 양극세포의 발달이 감소함을 시사함. 이들 다양한 양극세포들 중 Otx2를 발현하는 세포를 간접적으로 Otx2 부위에서 발현되는 GFP의 분포와 비교하여 조사한 결과, rod와 ON-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 PKCalpha와 G0alpha는 100% GFP를 발현하고 있지만, OFF-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 Vsx1의 경우는 약 22% 정도만 GFP와 공동발현되고 있었고, T2 OFF-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 Recoverin은 전혀 GFP와 겹치지 않음. 흥미로운 것은 이론적으로 GFP와 완벽하게 겹쳐야하는 Otx2 조차도 약 24%는 GFP와 겹치지 않고 있는 것으로 보아 이들 GFP(-) 세포들에 존재하는 Otx2와 이들의 기능에 대한 의문점이 들었다
표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 양극세포 발달 이상. P90 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 나타난 Otx2 발현 양극세포의 감소 원인이 발달의 문제인지 아니면 퇴화에 의한 것인지를 규명하기위해 망막발달이 완성되는 생후 2주 (P13) 망막 절편에서 Otx2 발현 세포와 전체 양극세포를 표지하는 Vsx2, rod 양극세포를 표지하는 PKCalpha, ON-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 G0alpha, OFF-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 Vsx1, 제 2형 (Type-2; T2) OFF-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 Recoverin 등의 분포를 조사함 (A). 그 결과 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포를 제외한 전체 양극세포의 수와 rod, ON-cone, OFF-cone 양극세포 수가 모두가 Otx2 수의 감소와 유사하게 정상 망막에 비해 약 20-30% 정도 감소한 것으로 나타남 (B). 이는 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 양극세포의 발달이 감소함을 시사함. 이들 다양한 양극세포들 중 Otx2를 발현하는 세포를 간접적으로 Otx2 부위에서 발현되는 GFP의 분포와 비교하여 조사한 결과, rod와 ON-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 PKCalpha와 G0alpha는 100% GFP를 발현하고 있지만, OFF-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 Vsx1의 경우는 약 22% 정도만 GFP와 공동발현되고 있었고, T2 OFF-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 Recoverin은 전혀 GFP와 겹치지 않음. 흥미로운 것은 이론적으로 GFP와 완벽하게 겹쳐야하는 Otx2 조차도 약 24%는 GFP와 겹치지 않고 있는 것으로 보아 이들 GFP(-) 세포들에 존재하는 Otx2와 이들의 기능에 대한 의문점이 들었다
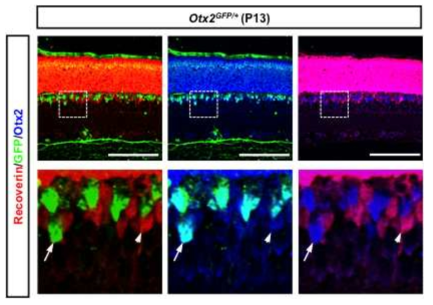 표
T2 OFF-cone 양극세포의 외부 Otx2 발현. Otx2 유전자 부위에서 발현되는 GFP와 전혀 겹치지 않는 Recoverin 발현 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포의 발달과 유지에 대한 Otx2의 기능을 조사하기 위해 Otx2(푸른색), Recoverin (붉은색), GFP (녹색)을 동시에 면역형광염색을 통해 검출하였다. 그 결과 흥미롭게 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포는 GFP가 없음에도 불구하고 Otx2 단백질은 포함하고 있었다. 이는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포에 분포하는 Otx2 단백질은 세포 내부에서 발현되었다기 보다는 세포 외부로부터 이동되어 왔음을 시사한다
표
T2 OFF-cone 양극세포의 외부 Otx2 발현. Otx2 유전자 부위에서 발현되는 GFP와 전혀 겹치지 않는 Recoverin 발현 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포의 발달과 유지에 대한 Otx2의 기능을 조사하기 위해 Otx2(푸른색), Recoverin (붉은색), GFP (녹색)을 동시에 면역형광염색을 통해 검출하였다. 그 결과 흥미롭게 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포는 GFP가 없음에도 불구하고 Otx2 단백질은 포함하고 있었다. 이는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포에 분포하는 Otx2 단백질은 세포 내부에서 발현되었다기 보다는 세포 외부로부터 이동되어 왔음을 시사한다
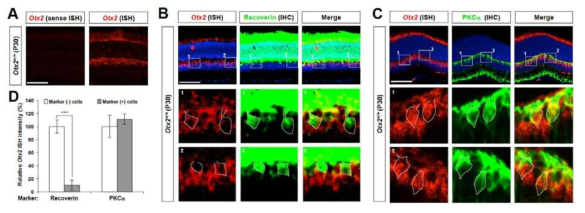 표
제 2형 양극세포 내 Otx2 유전자 발현의 부재. (A) 앞의 그림에서 Otx2 유전자 부위에서 발현되는 GFP 존재 없이 Otx2 단백질만을 포함하는 제 2형 양극세포 내 Otx2가 외부에서 유래한 것인지를 증명하기 위하여 Otx2 mRNA 발현을 직접 조사함. Otx2 mRNA와 동일한 염기서열 (sense) 또는 상보적 염기서열 (antisense, Otx2)을 가지는 RNA를 합성 후 DIG로 표지하고 이를 생후 30일 생쥐 망막에 hybridization 후 이들 RNA들과 상보 결합을 하는 mRNA를 포함하는 세포의 위치를 형광표지된 anti-DIG 항체를 이용하여 조사함. 그 결과 sense RNA는 전혀 망막에 특이적 신호를 제공하지 않았지만, Otx2는 Otx2 단백질이 나타났던 INL과 ONL 위치에 특이적 신호를 보임. (B) Otx2 유전자의 제2형 양극세포 내 발현 여부를 조사하기 위하여 제2형 양극세포 표지자인 Recoverin에 대한 면역형광염색을 Otx2 ISH와 동시에 수행한 결과 제2형 양극세포는 Otx2 유전자 발현이 거의 검출되지 않음. (C) 이와는 반대로 관상 양극세포 표지자인 PKCalpha에 대한 면역 형광염색을 동시에 수행하였을 때는 Otx2 mRNA와 Otx2 단백질 모두 이들 세포에서 발현됨을 알수 있음. (D) 이를 통하여 관상 양극세포는 Otx2 mRNA를 통해 Otx2 단백질을 발현하고, 제2형 양극세포는 Otx2 mRNA 발현 없이 Otx2 단백질을 발현함을 알 수 있음
표
제 2형 양극세포 내 Otx2 유전자 발현의 부재. (A) 앞의 그림에서 Otx2 유전자 부위에서 발현되는 GFP 존재 없이 Otx2 단백질만을 포함하는 제 2형 양극세포 내 Otx2가 외부에서 유래한 것인지를 증명하기 위하여 Otx2 mRNA 발현을 직접 조사함. Otx2 mRNA와 동일한 염기서열 (sense) 또는 상보적 염기서열 (antisense, Otx2)을 가지는 RNA를 합성 후 DIG로 표지하고 이를 생후 30일 생쥐 망막에 hybridization 후 이들 RNA들과 상보 결합을 하는 mRNA를 포함하는 세포의 위치를 형광표지된 anti-DIG 항체를 이용하여 조사함. 그 결과 sense RNA는 전혀 망막에 특이적 신호를 제공하지 않았지만, Otx2는 Otx2 단백질이 나타났던 INL과 ONL 위치에 특이적 신호를 보임. (B) Otx2 유전자의 제2형 양극세포 내 발현 여부를 조사하기 위하여 제2형 양극세포 표지자인 Recoverin에 대한 면역형광염색을 Otx2 ISH와 동시에 수행한 결과 제2형 양극세포는 Otx2 유전자 발현이 거의 검출되지 않음. (C) 이와는 반대로 관상 양극세포 표지자인 PKCalpha에 대한 면역 형광염색을 동시에 수행하였을 때는 Otx2 mRNA와 Otx2 단백질 모두 이들 세포에서 발현됨을 알수 있음. (D) 이를 통하여 관상 양극세포는 Otx2 mRNA를 통해 Otx2 단백질을 발현하고, 제2형 양극세포는 Otx2 mRNA 발현 없이 Otx2 단백질을 발현함을 알 수 있음
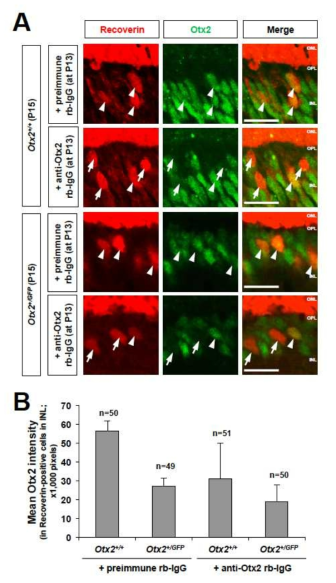 표
T2 OFF-cone 양극세포에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질의 유래 검증. T2 OFF-cone 양극세포에서 존재하는 Otx2가 실재로 세포 간 이동을 통해 획득한 것인지를 증명하기 위해 생후 13일째 생쥐 안구 내에 일반 생쥐 항체 (preimmune IgG) 또는 Otx2에 대한 단일항체 (anti-Otx2 IgG)를 주입하여 세포 외부에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질과 결합하여 Otx2 단백질의 세포 간 이동을 억제함. 2일후인 생후 15일에 해당 생쥐들의 안구를 적출하여 망막 절편 내 Recovrin-positive T2 OFF-cone 양극세포에서 Otx2 단백질의 존재 여부를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. 그 결고, Otx2에 대한 단일항체를 주사한 안구 내 망막의 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포 내 Otx2 단백질의 양이 급격히 감소함을 알 수 있음. 이는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포 내에 존재하는 Otx2가 세포 간 이동을 통해 획득된 것이라는 사실을 반증함
표
T2 OFF-cone 양극세포에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질의 유래 검증. T2 OFF-cone 양극세포에서 존재하는 Otx2가 실재로 세포 간 이동을 통해 획득한 것인지를 증명하기 위해 생후 13일째 생쥐 안구 내에 일반 생쥐 항체 (preimmune IgG) 또는 Otx2에 대한 단일항체 (anti-Otx2 IgG)를 주입하여 세포 외부에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질과 결합하여 Otx2 단백질의 세포 간 이동을 억제함. 2일후인 생후 15일에 해당 생쥐들의 안구를 적출하여 망막 절편 내 Recovrin-positive T2 OFF-cone 양극세포에서 Otx2 단백질의 존재 여부를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. 그 결고, Otx2에 대한 단일항체를 주사한 안구 내 망막의 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포 내 Otx2 단백질의 양이 급격히 감소함을 알 수 있음. 이는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포 내에 존재하는 Otx2가 세포 간 이동을 통해 획득된 것이라는 사실을 반증함
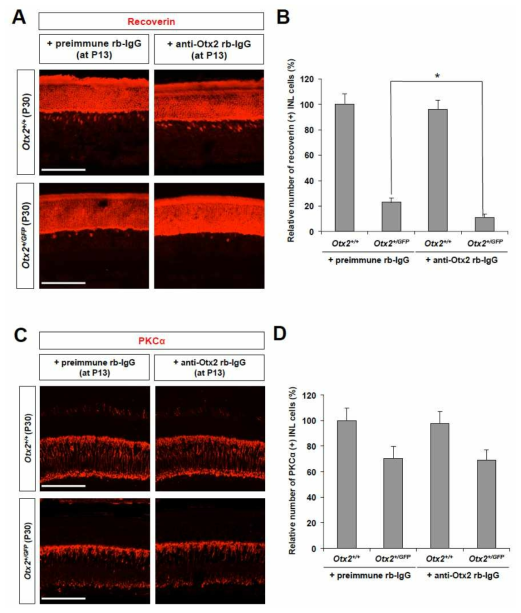 표
Otx2 항체 주입에 의한 제2형 양극세포의 퇴화. 그림 59에서와 마찬가지로 Otx2에 대한 항체를 생후 13일 정상 생쥐 또는 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에 투여 후 2주 후인 생후 30일에 해당 생쥐 망막을 포집 후 그 안에 존재하는 제2형 양극세포(A,B) 및 관상 양극세포(C,D)의 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. 그 결과 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에 Otx2 항체를 투여한 결과 제2형 양극 세포의 수가 감소함을 알 수 있음. 이는 해당 생쥐 망막의 세포 외부에 존재하는 Otx2가 제2형 양극세포의 유지에 필요함을 시사함
표
Otx2 항체 주입에 의한 제2형 양극세포의 퇴화. 그림 59에서와 마찬가지로 Otx2에 대한 항체를 생후 13일 정상 생쥐 또는 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에 투여 후 2주 후인 생후 30일에 해당 생쥐 망막을 포집 후 그 안에 존재하는 제2형 양극세포(A,B) 및 관상 양극세포(C,D)의 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. 그 결과 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에 Otx2 항체를 투여한 결과 제2형 양극 세포의 수가 감소함을 알 수 있음. 이는 해당 생쥐 망막의 세포 외부에 존재하는 Otx2가 제2형 양극세포의 유지에 필요함을 시사함
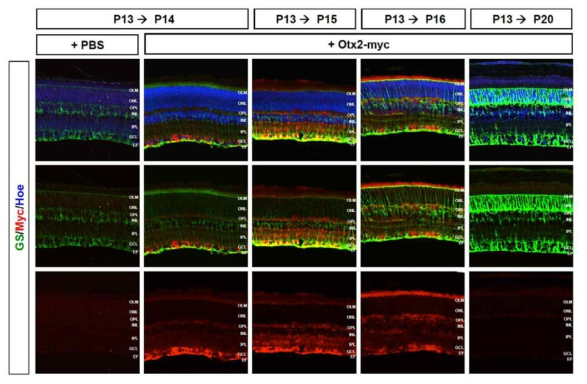 표
Otx2 단백질의 망막 신경 내 침투. 생후 13일 생쥐 안구 내에 Otx2-myc 단백질을 200ng 주입 후 각 시간에 따른 망막 내 단백질 분포를 Myc tag에 대한 항체를 이용하여 조사함. 그 결과 주입 후 하루 후부터 Otx2-myc 단백질이 주로 망막갱글리온세포에서 관찰되다 이틀 후부터는 INL, 3일후부터는 ONL까지 침투하였음. 하지만, 주입 후 7일 이후에는 해당 단백질들이 망막에 거의 존재하지 않는 것으로 보아, Otx2-myc 단백질은 주입 후 2일 이후 망막 양극세포들에 침투하고 1주일 이내에 소멸됨을 알 수 있음
표
Otx2 단백질의 망막 신경 내 침투. 생후 13일 생쥐 안구 내에 Otx2-myc 단백질을 200ng 주입 후 각 시간에 따른 망막 내 단백질 분포를 Myc tag에 대한 항체를 이용하여 조사함. 그 결과 주입 후 하루 후부터 Otx2-myc 단백질이 주로 망막갱글리온세포에서 관찰되다 이틀 후부터는 INL, 3일후부터는 ONL까지 침투하였음. 하지만, 주입 후 7일 이후에는 해당 단백질들이 망막에 거의 존재하지 않는 것으로 보아, Otx2-myc 단백질은 주입 후 2일 이후 망막 양극세포들에 침투하고 1주일 이내에 소멸됨을 알 수 있음
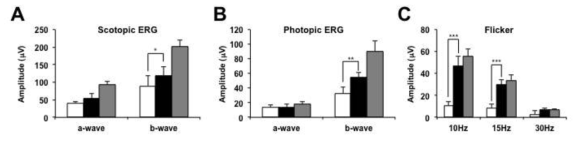 표
Otx2 투여를 통한 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막퇴화 억제. (A) Otx2 단백질을 생후 13일째 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐의 우측 안구 내에 투여한 후 2주 후인 생후 28일에 생쥐의 ERG 반응을 조사 함. (B) Otx2를 투여한 생쥐의 경우 주로 광수용세포의 반응에 의해 나타나는 a-wave와 rod 또는 ON-cone 양극세포에 의해 나타나는 b-wave의 크기가 비투여한 왼쪽 안구에 비해 확연하게 차이 를 보이는 것을 알 수 있음. (C) 위의 PBS를 투여한 정상 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막과 Otx2를 투여 한 생쥐 망막 내 신경세포의 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사한 결과, PBS 투여 생쥐보다 Otx2 투여 생쥐 망막 내 Otx2 및 GFP 발현 세포 수가 급격하게 늘어나 있음을 알 수 있음. 이는 외부에서 투 여한 Otx2가 Otx2를 발현하는 세포의 퇴화를 억제할 수 있음을 시사함. 또한, 양극세포를 표지하는 Vsx2 수 역시 증가한 것을 알 수 있음. PKCalpha를 발현하는 rod 양극세포의 수도 비록 Otx2나 Chx10 발현 세포보다 낮기는 하지만 유의미한 증가를 보였다. 특히, Recoverin을 발현하는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포의 경우는 PBS 투여 망막에서는 완전히 퇴화가 되었지만, Otx2 투여 망막에서 는 여전히 많은 수의 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포가 남아 있음. 이는 Vsx1을 발현하는 전체 OFF-cone 양극세포에도 적용되는 사실이었다. 실재로 a-wave의 증가는 hyperpolarization에 의해 나타나는 것으로 일반적으로 빛에 의해 hyperpolarization 되는 photoreceptor의 활성 증가 뿐만 아니라 OFF cone 양극세포의 활성 강화에 의해서도 나타날 가능성이 높은 것으로 알려져 있다. 따라서, rod 및 cone 광수용세포의 수는 크게 변화가 없는 반면 T2 OFF-cone을 포함한 전체적인 OFF cone 양극세포 수의 증가가 Otx2 투여 망막에서 그 퇴화가 억제되었음을 알 수 있다
표
Otx2 투여를 통한 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막퇴화 억제. (A) Otx2 단백질을 생후 13일째 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐의 우측 안구 내에 투여한 후 2주 후인 생후 28일에 생쥐의 ERG 반응을 조사 함. (B) Otx2를 투여한 생쥐의 경우 주로 광수용세포의 반응에 의해 나타나는 a-wave와 rod 또는 ON-cone 양극세포에 의해 나타나는 b-wave의 크기가 비투여한 왼쪽 안구에 비해 확연하게 차이 를 보이는 것을 알 수 있음. (C) 위의 PBS를 투여한 정상 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막과 Otx2를 투여 한 생쥐 망막 내 신경세포의 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사한 결과, PBS 투여 생쥐보다 Otx2 투여 생쥐 망막 내 Otx2 및 GFP 발현 세포 수가 급격하게 늘어나 있음을 알 수 있음. 이는 외부에서 투 여한 Otx2가 Otx2를 발현하는 세포의 퇴화를 억제할 수 있음을 시사함. 또한, 양극세포를 표지하는 Vsx2 수 역시 증가한 것을 알 수 있음. PKCalpha를 발현하는 rod 양극세포의 수도 비록 Otx2나 Chx10 발현 세포보다 낮기는 하지만 유의미한 증가를 보였다. 특히, Recoverin을 발현하는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포의 경우는 PBS 투여 망막에서는 완전히 퇴화가 되었지만, Otx2 투여 망막에서 는 여전히 많은 수의 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포가 남아 있음. 이는 Vsx1을 발현하는 전체 OFF-cone 양극세포에도 적용되는 사실이었다. 실재로 a-wave의 증가는 hyperpolarization에 의해 나타나는 것으로 일반적으로 빛에 의해 hyperpolarization 되는 photoreceptor의 활성 증가 뿐만 아니라 OFF cone 양극세포의 활성 강화에 의해서도 나타날 가능성이 높은 것으로 알려져 있다. 따라서, rod 및 cone 광수용세포의 수는 크게 변화가 없는 반면 T2 OFF-cone을 포함한 전체적인 OFF cone 양극세포 수의 증가가 Otx2 투여 망막에서 그 퇴화가 억제되었음을 알 수 있다
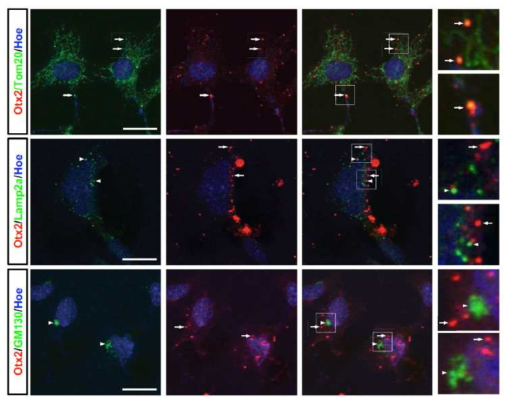 표
외래 Otx2 단백질의 미토콘드리아 침투. 세포 외부에서 세포 내부로 침투한 Otx2 단백질의 세포 내 작용 위치를 세포 소기관의 표지자들의 분포와 비교하여 조사함. 망막세포인 RGC5 세포의 배양액에 순수 분리한 Otx2 단백질 (200 ng/ml)을 첨가하고 4시간 후 세포를 고정 후 미토콘드리아 단백질인 Tom20, 리소좀 단백질인 Lamp2, 골지체 단백질인 GM130과 Otx2와의 공동 면역 형광염색을 통해 비교함. 그 결과 Otx2 단백질은 미토콘드리아 단백질인 Tom20와 같은 위치에 발견되지만, 리소좀이나 골지체에는 위치하지 않음
표
외래 Otx2 단백질의 미토콘드리아 침투. 세포 외부에서 세포 내부로 침투한 Otx2 단백질의 세포 내 작용 위치를 세포 소기관의 표지자들의 분포와 비교하여 조사함. 망막세포인 RGC5 세포의 배양액에 순수 분리한 Otx2 단백질 (200 ng/ml)을 첨가하고 4시간 후 세포를 고정 후 미토콘드리아 단백질인 Tom20, 리소좀 단백질인 Lamp2, 골지체 단백질인 GM130과 Otx2와의 공동 면역 형광염색을 통해 비교함. 그 결과 Otx2 단백질은 미토콘드리아 단백질인 Tom20와 같은 위치에 발견되지만, 리소좀이나 골지체에는 위치하지 않음
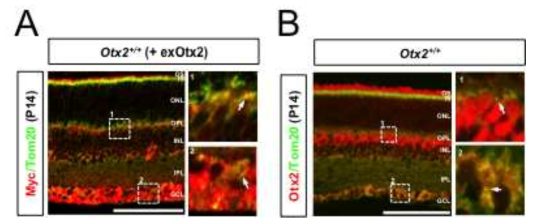 표
Otx2 단백질의 망막 신경 세포 내 미토콘드리아로의 이동. (A) 생후 13일째 생쥐 안구내에 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질 (200 ng)을 주입하고 24시간 후 생쥐 안구를 적출 후 안구 절편을 Myc에 대한 항체와 미토콘드리아 단백질인 Tom20에 대한 항체를 이용하여 면역형광염색을 수행함. 그 결과 외부에서 주입한 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질은 망막갱글리온세포와 INL 내의 신경세포에서 관찰이 되었으며 이들 세포 내에 있는 미토콘드리아에서도 관찰됨. (B) 외부에서 주입한 Otx2 단백질뿐만 아니라 생체 내에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질 역시 미토콘드리아에서 관찰이 됨
표
Otx2 단백질의 망막 신경 세포 내 미토콘드리아로의 이동. (A) 생후 13일째 생쥐 안구내에 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질 (200 ng)을 주입하고 24시간 후 생쥐 안구를 적출 후 안구 절편을 Myc에 대한 항체와 미토콘드리아 단백질인 Tom20에 대한 항체를 이용하여 면역형광염색을 수행함. 그 결과 외부에서 주입한 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질은 망막갱글리온세포와 INL 내의 신경세포에서 관찰이 되었으며 이들 세포 내에 있는 미토콘드리아에서도 관찰됨. (B) 외부에서 주입한 Otx2 단백질뿐만 아니라 생체 내에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질 역시 미토콘드리아에서 관찰이 됨
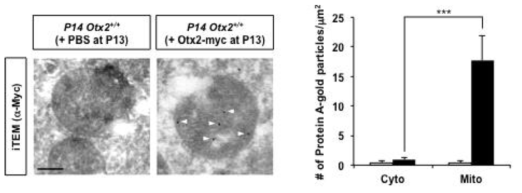 표
망막 신경 미토콘드리아 내 Otx2의 존재 규명. 생후 13일 생쥐 안구 내에 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질 (100ng)을 주입하고 24시간 후 안구를 적출하여 망막 절편을 토끼 Myc 항체를 이용하여 면역염색 후 금입자가 표지된 토끼항체에 대한 2차항체를 이용해 Myc 항체의 분포를 전자현미경으로 검출함. 단백질을 투여하지 않은 안구의 망막신경세포 미토콘드리아에는 금입자가 검출되지 않지만 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질을 투여한 안구의 신경세포 미토콘드리아에서는 금입자가 검출됨. 이는 외부에서 주입한 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질이 망막신경 내 미토콘드리아로 이동하였음을 증명하는 결과임
표
망막 신경 미토콘드리아 내 Otx2의 존재 규명. 생후 13일 생쥐 안구 내에 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질 (100ng)을 주입하고 24시간 후 안구를 적출하여 망막 절편을 토끼 Myc 항체를 이용하여 면역염색 후 금입자가 표지된 토끼항체에 대한 2차항체를 이용해 Myc 항체의 분포를 전자현미경으로 검출함. 단백질을 투여하지 않은 안구의 망막신경세포 미토콘드리아에는 금입자가 검출되지 않지만 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질을 투여한 안구의 신경세포 미토콘드리아에서는 금입자가 검출됨. 이는 외부에서 주입한 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질이 망막신경 내 미토콘드리아로 이동하였음을 증명하는 결과임
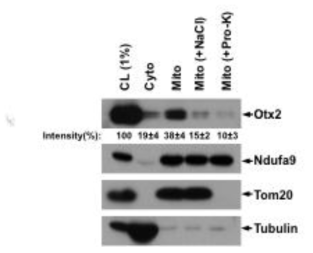 표
망막신경 세포 내 미토콘드리아에 있는 Otx2의 특징. 생후 14일 생쥐 망막을 적출 후 세포 내 미토콘드리아를 분리하고 (mito) 이를 0.5M NaCl이 포함된 PBS 또는 proteinase-K (1U/ul)이 포함된 PBS에 30분 동안 보관하여 미토콘드리아 외막 지질 또는 단백질과 Otx2 단백질과의 상호작용을 파괴함. 그 결과 미처리 미토콘드리아에 비해 NaCl 처리군은 약 40% 정도만 Otx2 단백질이 남아 있었고, 27%만이 proteinase-K 처리 이후에 남아 있었음. 이는 대부분의 미토콘드리아 Otx2 단백질은 미토콘드리아 외막에 있고 1/3 정도만 내부에 존재함을 알 수 있음
표
망막신경 세포 내 미토콘드리아에 있는 Otx2의 특징. 생후 14일 생쥐 망막을 적출 후 세포 내 미토콘드리아를 분리하고 (mito) 이를 0.5M NaCl이 포함된 PBS 또는 proteinase-K (1U/ul)이 포함된 PBS에 30분 동안 보관하여 미토콘드리아 외막 지질 또는 단백질과 Otx2 단백질과의 상호작용을 파괴함. 그 결과 미처리 미토콘드리아에 비해 NaCl 처리군은 약 40% 정도만 Otx2 단백질이 남아 있었고, 27%만이 proteinase-K 처리 이후에 남아 있었음. 이는 대부분의 미토콘드리아 Otx2 단백질은 미토콘드리아 외막에 있고 1/3 정도만 내부에 존재함을 알 수 있음
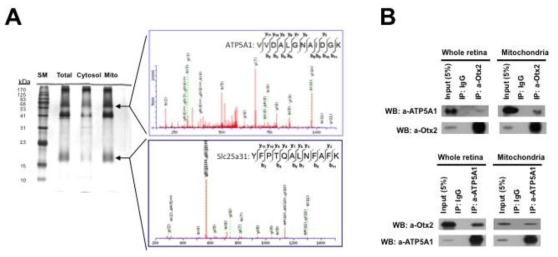 표
Otx2와 미토콘드리아 ATP 합성효소 ATP5A1과의 상호작용. (A) 미토콘드리아에 분포하는 Otx2 단백질의 기능을 검증하기 위해 망막신경세포에서 세포질을 미토콘드리아를 분리하고 이들 분획에 존재하는 Otx2를 Otx2 항체를 이용하여 분리함. 분리된 면역복합체에 함께 분리된 단백질체를 MALDI-TOF MS/MS를 이용해 검증한 결과 미토콘드리아 ATP 합성효소인 ATP5A1과 미토콘드리아에서 합성된 ATP를 미토콘드리아 외부로 수송하는 solute carrier 25a31 (Slc25a31)가 검출됨. (B) 이를 추가로 검증하기 위해 망막신경세포 및 순수 분리된 생쥐 망막 신경 미토콘드리아에 Otx2 또는 ATP5A1에 대한 항체를 투여하여 Otx2 및 ATP5A1를 면역침강 후 함께 분리된 ATP5A1과 Otx2를 Western blot으로 확인함. 이 결과들은 미토콘드리아 내 Otx2가 미토콘드리아 ATP5A1 등과의 상호작용을 통해 ATP 합성에 관여하고 있다는 것을 시사함
표
Otx2와 미토콘드리아 ATP 합성효소 ATP5A1과의 상호작용. (A) 미토콘드리아에 분포하는 Otx2 단백질의 기능을 검증하기 위해 망막신경세포에서 세포질을 미토콘드리아를 분리하고 이들 분획에 존재하는 Otx2를 Otx2 항체를 이용하여 분리함. 분리된 면역복합체에 함께 분리된 단백질체를 MALDI-TOF MS/MS를 이용해 검증한 결과 미토콘드리아 ATP 합성효소인 ATP5A1과 미토콘드리아에서 합성된 ATP를 미토콘드리아 외부로 수송하는 solute carrier 25a31 (Slc25a31)가 검출됨. (B) 이를 추가로 검증하기 위해 망막신경세포 및 순수 분리된 생쥐 망막 신경 미토콘드리아에 Otx2 또는 ATP5A1에 대한 항체를 투여하여 Otx2 및 ATP5A1를 면역침강 후 함께 분리된 ATP5A1과 Otx2를 Western blot으로 확인함. 이 결과들은 미토콘드리아 내 Otx2가 미토콘드리아 ATP5A1 등과의 상호작용을 통해 ATP 합성에 관여하고 있다는 것을 시사함
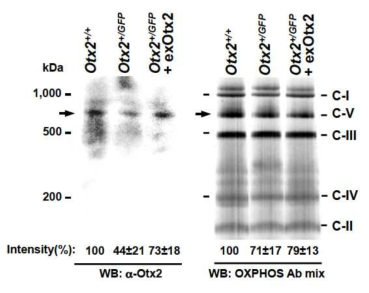 표
생쥐 망막 신경 미토콘드리아의 ATP 합성복합체 구성체로의 Otx2. Otx2가 ATP5A1과 상호작용을 통하여 미토콘드리아 ATP 합성복합체에 참여할 가능성을 확인하기 위해 생후 15일 생쥐 망막 미토콘드리아를 분리 후 이를 blue native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (BN-PAGE) 및 Otx2 항체를 이용한 Western blot을 이용하여 Otx2가 포함된 미토콘드리아의 단백질 복합체의 크기를 측정함. 그 결과 Otx2는 약 700kDa 근방에서 관찰되고, 이는 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서는 감소하고, Otx2-Myc/His를 투여한 생쥐 망막에서는 그 양이 증가함. 이는 Otx2가 결합하는 ATP5A1이 포함된 ATP 합성복합체인 전자전달 복합체 V와 크기가 유사함. 따라서 Otx2는 ATP5A1과 직,간접적으로 결합하여 미토콘드리아 ATP 합성복합체에 참여함을 의미함
표
생쥐 망막 신경 미토콘드리아의 ATP 합성복합체 구성체로의 Otx2. Otx2가 ATP5A1과 상호작용을 통하여 미토콘드리아 ATP 합성복합체에 참여할 가능성을 확인하기 위해 생후 15일 생쥐 망막 미토콘드리아를 분리 후 이를 blue native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (BN-PAGE) 및 Otx2 항체를 이용한 Western blot을 이용하여 Otx2가 포함된 미토콘드리아의 단백질 복합체의 크기를 측정함. 그 결과 Otx2는 약 700kDa 근방에서 관찰되고, 이는 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서는 감소하고, Otx2-Myc/His를 투여한 생쥐 망막에서는 그 양이 증가함. 이는 Otx2가 결합하는 ATP5A1이 포함된 ATP 합성복합체인 전자전달 복합체 V와 크기가 유사함. 따라서 Otx2는 ATP5A1과 직,간접적으로 결합하여 미토콘드리아 ATP 합성복합체에 참여함을 의미함
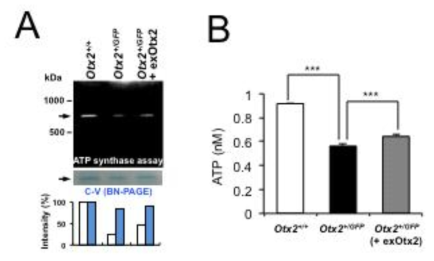 표
Otx2 투여에 의한 망막신경 내 ATP 합성 촉진. (A) Otx2의 ATP 합성복합체의 구성인자로써 기능을 확인하기 위해, 생후 15일 정상 생쥐 또는 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐와 생후 13일에 Otx2 단백질을 투여한 생쥐 망막 신경 미토콘드리아를 분리 후 in gel ATP synthase assay를 통하여 해당 미토콘드리아의 활성을 조사함. Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐는 정상 생쥐 망막에 비해 분석에 이용한 미토콘드리아 전자전달계 V의 양적인 변화는 크지 않으나 ATP 합성 복합체의 ATP 합성 능력은 정상의 1/4로 줄어들어 있음. 이와는 달리 Otx2를 투여한 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막 미토콘드리아의 활성도는 정상의 1/2 수준으로 복구가 됨. 이는 세포 내 ATP 농도의 변화로 나타남 (B)
표
Otx2 투여에 의한 망막신경 내 ATP 합성 촉진. (A) Otx2의 ATP 합성복합체의 구성인자로써 기능을 확인하기 위해, 생후 15일 정상 생쥐 또는 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐와 생후 13일에 Otx2 단백질을 투여한 생쥐 망막 신경 미토콘드리아를 분리 후 in gel ATP synthase assay를 통하여 해당 미토콘드리아의 활성을 조사함. Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐는 정상 생쥐 망막에 비해 분석에 이용한 미토콘드리아 전자전달계 V의 양적인 변화는 크지 않으나 ATP 합성 복합체의 ATP 합성 능력은 정상의 1/4로 줄어들어 있음. 이와는 달리 Otx2를 투여한 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막 미토콘드리아의 활성도는 정상의 1/2 수준으로 복구가 됨. 이는 세포 내 ATP 농도의 변화로 나타남 (B)
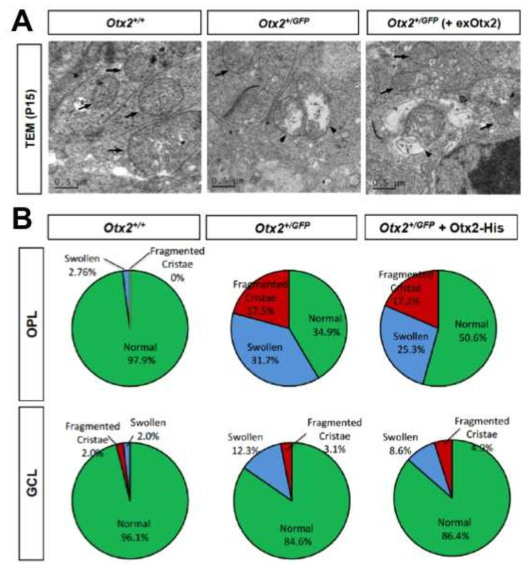 표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막 내 미토콘드리아 구조 이상 (P15). (A) 생후 15일 정상 망막 및 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막과 생후 13일에 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질을 투여한 안구 내 망막 신경세포 내 미토콘드리아의 구조를 전자현미경으로 조사함. 정상 망막신경세포 내 미토콘드리아는 내막이 겹으로 접힌 cristae 구조를 잘 유지하고 있는 반면, Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막신경세포 내 미토콘드리아는 cristae 겹의 수가 적고 풀린 구조를 가지는 경우가 많음. 이에 반해 Otx2를 주입한 안구 내 망막 신경 미토콘드리아는 cristae 접힘 구조가 회복되는 경향을 보임. (B) 이러한 미토콘드리아의 특징을 정량화하여 그래프로 나타냄
표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막 내 미토콘드리아 구조 이상 (P15). (A) 생후 15일 정상 망막 및 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막과 생후 13일에 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질을 투여한 안구 내 망막 신경세포 내 미토콘드리아의 구조를 전자현미경으로 조사함. 정상 망막신경세포 내 미토콘드리아는 내막이 겹으로 접힌 cristae 구조를 잘 유지하고 있는 반면, Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막신경세포 내 미토콘드리아는 cristae 겹의 수가 적고 풀린 구조를 가지는 경우가 많음. 이에 반해 Otx2를 주입한 안구 내 망막 신경 미토콘드리아는 cristae 접힘 구조가 회복되는 경향을 보임. (B) 이러한 미토콘드리아의 특징을 정량화하여 그래프로 나타냄
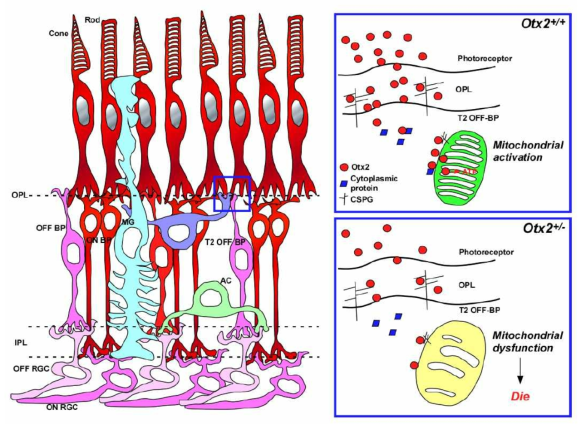 표
Otx2 단백질의 세포 간 이동에 의한 망막신경퇴화 억제 기전. 정상 망막조직에서 Otx2 유전자를 발현하는 photoreceptor나 rod/ON-cone 양극세포는 해당 세포의 발달과 유지를 위해 Otx2를 사용할 뿐만 아니라 세포 외부로 Otx2 단백질을 분비함. 따라서 이들 세포의 주변에 존재하는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포나 RGC등은 세포 외부에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질을 획득하여 해당 세포 내부로 이동 후 세포의 유지에 사용하게 됨. 따라서, Otx2 유전자 하나의 결실은 Otx2를 발현하는 rod/ON-cone 양극세포의 발달 저하 뿐만 아니라 이들 세포에서 분비되는 Otx2의 양적 저하로 인해 세포 외부로부터 Otx2를 공급받는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포와 RGC 등에 Otx2의 양적 감소를 유도함. 따라서, 이들 세포는 외부에서 공급되는 Otx2가 담당하는 세포 유지의 기능이 약화되어 망막 신경퇴화로 이어지고, 이것은 결국 ERG b-wave 반응 저하를 동반한 시력 저하를 유도함
표
Otx2 단백질의 세포 간 이동에 의한 망막신경퇴화 억제 기전. 정상 망막조직에서 Otx2 유전자를 발현하는 photoreceptor나 rod/ON-cone 양극세포는 해당 세포의 발달과 유지를 위해 Otx2를 사용할 뿐만 아니라 세포 외부로 Otx2 단백질을 분비함. 따라서 이들 세포의 주변에 존재하는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포나 RGC등은 세포 외부에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질을 획득하여 해당 세포 내부로 이동 후 세포의 유지에 사용하게 됨. 따라서, Otx2 유전자 하나의 결실은 Otx2를 발현하는 rod/ON-cone 양극세포의 발달 저하 뿐만 아니라 이들 세포에서 분비되는 Otx2의 양적 저하로 인해 세포 외부로부터 Otx2를 공급받는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포와 RGC 등에 Otx2의 양적 감소를 유도함. 따라서, 이들 세포는 외부에서 공급되는 Otx2가 담당하는 세포 유지의 기능이 약화되어 망막 신경퇴화로 이어지고, 이것은 결국 ERG b-wave 반응 저하를 동반한 시력 저하를 유도함
 표
Keton body 투여를 통한 망막 퇴화 억제 시도. 생후 13일부터 29일까지 매일 sodium β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB, 72.8 mg/kg)를 복강으로 주사하였다. (A) 생후 30일째 생쥐의 모습과 혈관 이상을 보이는 BHB 투여 생쥐 내장. (B) 매일 생쥐들의 몸무게를 측정한 결과 BHB를 투여한 생쥐 그룹들은 현저한 체중 감소를 동반함을 알 수 있음. (C & D) 이들 생쥐의 망막 내에 존재하는 Otx2 발현 세포의 수와 Recoverin 발현 제2형 양극세포의 수를 측정한 결과 BHB 투여에 의한 뚜렷한 차이를 관찰하기는 어려움
표
Keton body 투여를 통한 망막 퇴화 억제 시도. 생후 13일부터 29일까지 매일 sodium β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB, 72.8 mg/kg)를 복강으로 주사하였다. (A) 생후 30일째 생쥐의 모습과 혈관 이상을 보이는 BHB 투여 생쥐 내장. (B) 매일 생쥐들의 몸무게를 측정한 결과 BHB를 투여한 생쥐 그룹들은 현저한 체중 감소를 동반함을 알 수 있음. (C & D) 이들 생쥐의 망막 내에 존재하는 Otx2 발현 세포의 수와 Recoverin 발현 제2형 양극세포의 수를 측정한 결과 BHB 투여에 의한 뚜렷한 차이를 관찰하기는 어려움
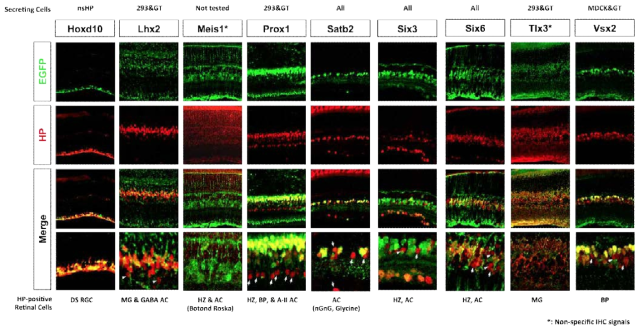 표
EGFP-BAC 생쥐 망막에서 호메오도메인 전사인자와 EGFP 분포 비교. 기존 논문과 데이터베이스를 기반으로 생쥐 망막에서 발현이 되는 것으로 알려진 HP들 중 BAC-EGFP 생쥐로 제작된 16종을 도입한 후, 이들 중 성공적으로 GFP 형광을 보이는 것으로 확인된 9종의 생쥐를 분석에 이용함. 이들 생쥐들이 생후 30일 망막 절편을 각각의 HP에 대한 항체와 GFP에 대한 항체로 면역형광염색을 수행함. 해당 조직에서 GFP 형광을 동반하지 않고 HP만을 발현하는 세포들을 화살표로 표시함. 위의 BAC-EGFP 생쥐 망막을 이용한 면역형광염색을 통해 세포 간 이동을 할 것으로 예측된 호메오도메인 전사인자들 중 Prox1에 집중하여 이의 유의성 검증을 하였다. 이론적으로 단백질은 mRNA과 동일한 세포에서 발현이 되어야 하고, 생쥐 Prox1은 alternative spliced varient나 isotype이 발견이 되지 않았기 때문에 Prox1 단백질과 Prox1 mRNA는 동일한 세포에서 관찰이 되어야 한다. 하지만, 생쥐 망막에서 Prox1 mRNA는 주로 INL의 윗부분에 집중되어 분포하는 반면, Prox1 단백질은 이 부분 이외에 INL의 아랫부분에도 존재하였다
표
EGFP-BAC 생쥐 망막에서 호메오도메인 전사인자와 EGFP 분포 비교. 기존 논문과 데이터베이스를 기반으로 생쥐 망막에서 발현이 되는 것으로 알려진 HP들 중 BAC-EGFP 생쥐로 제작된 16종을 도입한 후, 이들 중 성공적으로 GFP 형광을 보이는 것으로 확인된 9종의 생쥐를 분석에 이용함. 이들 생쥐들이 생후 30일 망막 절편을 각각의 HP에 대한 항체와 GFP에 대한 항체로 면역형광염색을 수행함. 해당 조직에서 GFP 형광을 동반하지 않고 HP만을 발현하는 세포들을 화살표로 표시함. 위의 BAC-EGFP 생쥐 망막을 이용한 면역형광염색을 통해 세포 간 이동을 할 것으로 예측된 호메오도메인 전사인자들 중 Prox1에 집중하여 이의 유의성 검증을 하였다. 이론적으로 단백질은 mRNA과 동일한 세포에서 발현이 되어야 하고, 생쥐 Prox1은 alternative spliced varient나 isotype이 발견이 되지 않았기 때문에 Prox1 단백질과 Prox1 mRNA는 동일한 세포에서 관찰이 되어야 한다. 하지만, 생쥐 망막에서 Prox1 mRNA는 주로 INL의 윗부분에 집중되어 분포하는 반면, Prox1 단백질은 이 부분 이외에 INL의 아랫부분에도 존재하였다
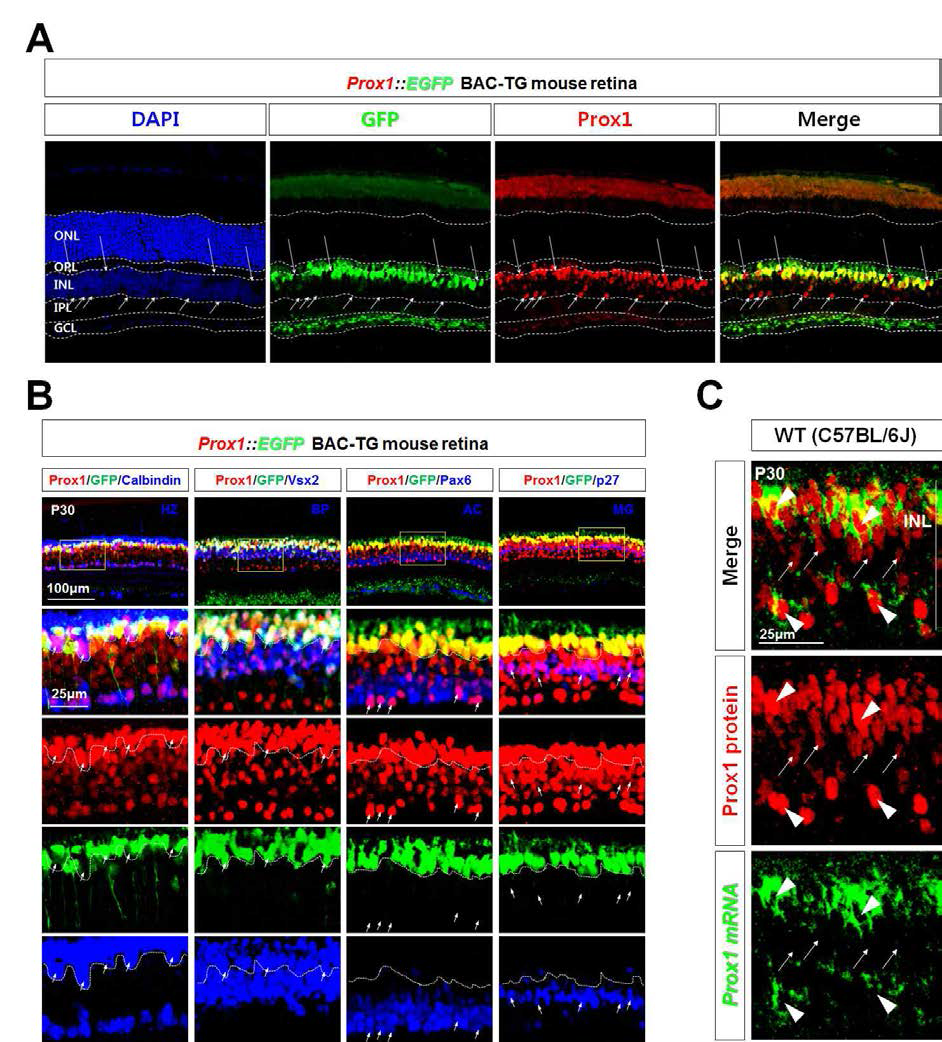 표
분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1의 생체 내 세포간 이동 검증. (A) 세포 외부로의 분비능 및 주변세포로의 침투능이 검증된 호메오도메인 전사인자인 Prox1이 발현되는 곳에서 그와 동시에 GFP가 발현되도록 만든 Prox1-GFP 유전자변형마우스를 이용하여 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자의 생체 내에서의 세포간 이동을 검증하였음. (B) 생후 30일 된 Prox1-GFP 유전자변형 마우스의 망막절편을 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1에 특이적인 항체를 이용하여 면역형광염색하고 형광현미경하에서 관찰한 결과, Calbindin으로 표지된 망막 수평 세포(Horizontal cell, HZC)와 Vsx2로 표지된 망막 양극 세포(bipolar cell, BPC)에서는 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1과 GFP가 같은 위치에 존재하고 있는 반면, Pax6로 표지된 망막 무축색 세포(amacrine cell, ACC)와 p27로 표지된 뮬러 세포(Muller cell, MC)에서는 오로지 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1만 홀로 존재하고 있음을 확인할 수 있었음. 이는 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1의 세포외부로의 분비능 및 주변세포로의 침투능에 의한 BPC로부터 ACC와 MC로의 이동 가능성을 시사함. (C) FITC-labeled Prox1 RNA probe를 이용한 in situ hybridization (ISH) 후 Prox1에 대한 항체를 이용한 면역형광염색을 통해 생쥐 망막 절편에서의 Prox1 단백질과 mRNA의 분포를 조사함으로써 endogenous Prox1의 망막 신경 세포에서의 세포간 이동을 검증함
표
분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1의 생체 내 세포간 이동 검증. (A) 세포 외부로의 분비능 및 주변세포로의 침투능이 검증된 호메오도메인 전사인자인 Prox1이 발현되는 곳에서 그와 동시에 GFP가 발현되도록 만든 Prox1-GFP 유전자변형마우스를 이용하여 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자의 생체 내에서의 세포간 이동을 검증하였음. (B) 생후 30일 된 Prox1-GFP 유전자변형 마우스의 망막절편을 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1에 특이적인 항체를 이용하여 면역형광염색하고 형광현미경하에서 관찰한 결과, Calbindin으로 표지된 망막 수평 세포(Horizontal cell, HZC)와 Vsx2로 표지된 망막 양극 세포(bipolar cell, BPC)에서는 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1과 GFP가 같은 위치에 존재하고 있는 반면, Pax6로 표지된 망막 무축색 세포(amacrine cell, ACC)와 p27로 표지된 뮬러 세포(Muller cell, MC)에서는 오로지 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1만 홀로 존재하고 있음을 확인할 수 있었음. 이는 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1의 세포외부로의 분비능 및 주변세포로의 침투능에 의한 BPC로부터 ACC와 MC로의 이동 가능성을 시사함. (C) FITC-labeled Prox1 RNA probe를 이용한 in situ hybridization (ISH) 후 Prox1에 대한 항체를 이용한 면역형광염색을 통해 생쥐 망막 절편에서의 Prox1 단백질과 mRNA의 분포를 조사함으로써 endogenous Prox1의 망막 신경 세포에서의 세포간 이동을 검증함
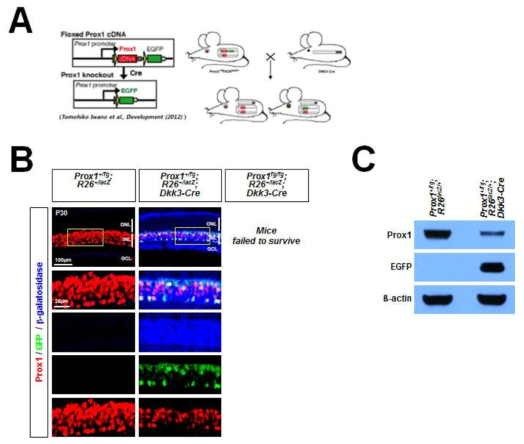 표
망막 특이적 Prox1-cko 마우스 제작. (A) MC에 존재하는 Prox1 단백질이 세포자체 내 전사를 동반하지 않고 외부에서 유입된 것인지를 확인하기 위해 Prox1 유전자 부위에 EGFP가 Cre recombinase에 의존적으로 발현되는 Prox1-floxed GFP (Prox1fg/fg) knock-in 생쥐와, 망막 전체 세포에서 Cre recombinase 활성이 나타나는 Dkk3-Cre 생쥐를 교배하여 Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐를 제작함. 이 생쥐 망막에서 Cre recombinase 활성이 나타난 세포를 표지하기 위해 R26R Cre reporter를 함께 가진 생쥐를 제작함. (B) 그 결과, 망막 전체에서 Cre recombinase의 활성에 의해 β-galactosidase가 발현됨과 동시에 망막내에서 Prox1 유전자 부위의 전사 활성을 나타내는 부위에서 EGFP 신호가 나타남을 확인함. (C) Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐 망막 내 Prox1 단백질의 양을 Western blot (WB)을 통해 비교함. 그 결과 정상 생쥐에 비해 Prox1단백질의 양이 현저히 줄어들어 있음을 확인하였으며, Prox1 단백질을 대신해서 EGFP 단백질이 발현되었음을 확인함
표
망막 특이적 Prox1-cko 마우스 제작. (A) MC에 존재하는 Prox1 단백질이 세포자체 내 전사를 동반하지 않고 외부에서 유입된 것인지를 확인하기 위해 Prox1 유전자 부위에 EGFP가 Cre recombinase에 의존적으로 발현되는 Prox1-floxed GFP (Prox1fg/fg) knock-in 생쥐와, 망막 전체 세포에서 Cre recombinase 활성이 나타나는 Dkk3-Cre 생쥐를 교배하여 Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐를 제작함. 이 생쥐 망막에서 Cre recombinase 활성이 나타난 세포를 표지하기 위해 R26R Cre reporter를 함께 가진 생쥐를 제작함. (B) 그 결과, 망막 전체에서 Cre recombinase의 활성에 의해 β-galactosidase가 발현됨과 동시에 망막내에서 Prox1 유전자 부위의 전사 활성을 나타내는 부위에서 EGFP 신호가 나타남을 확인함. (C) Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐 망막 내 Prox1 단백질의 양을 Western blot (WB)을 통해 비교함. 그 결과 정상 생쥐에 비해 Prox1단백질의 양이 현저히 줄어들어 있음을 확인하였으며, Prox1 단백질을 대신해서 EGFP 단백질이 발현되었음을 확인함
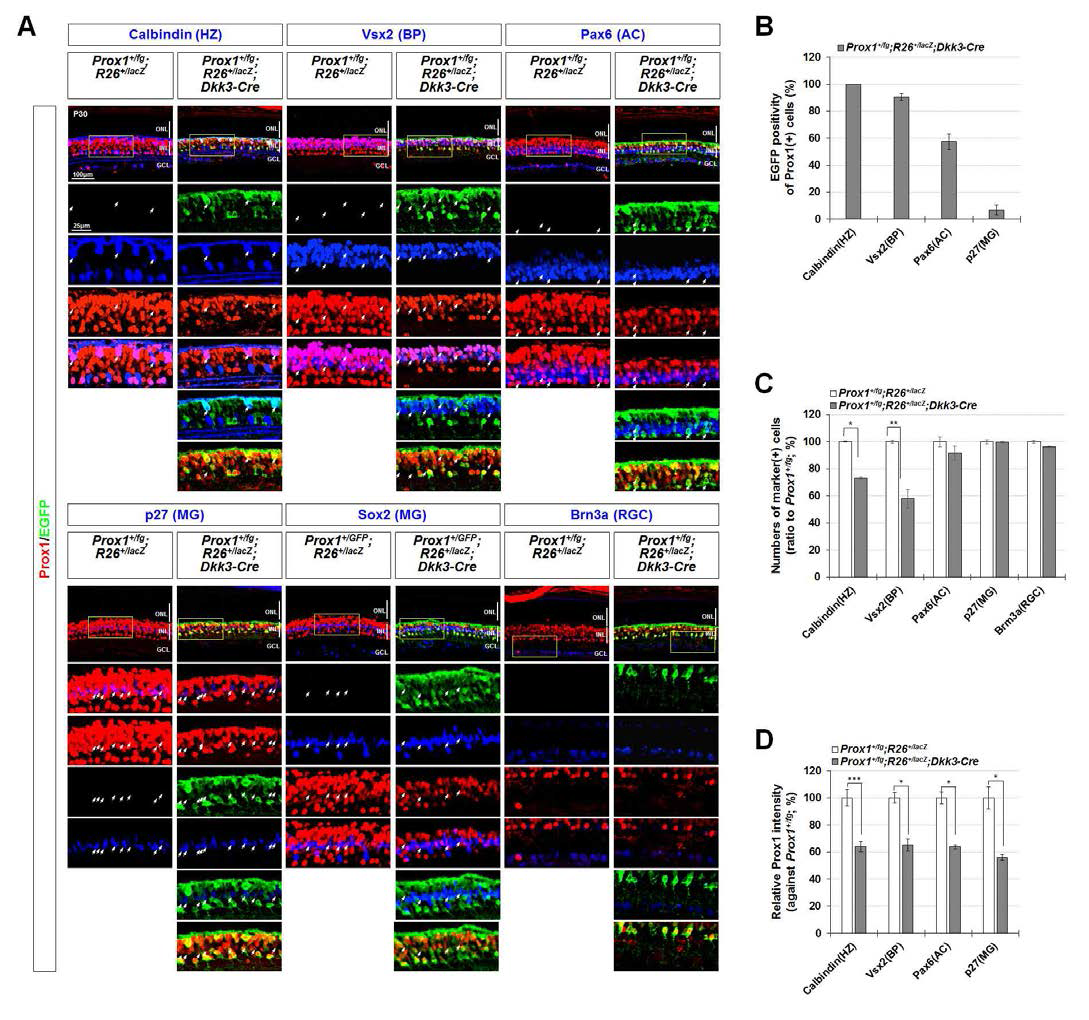 표
Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐를 이용한 망막 세포 내 Prox1 단백질의 자발적 비자발적 발현 판명. (A, B) Prox1 BAX TG 생쥐 망막에서 Prox1 유전자를 발현할 것으로 예상된 Calbindin으로 표지된 HZC과 Vsx2로 표지된 BPC는 물론, Prox1 유전자를 발현하지 않을 것으로 예측되었던 Pax6로 표지된 ACC에서 역시 Prox1 유전자 부위의 전사 활성을 나타내는 EGFP 신호가 관찰됨. 이를 통하여 ACC에서 관찰된 Prox1 단백질 역시 자체 내 Prox1 전사를 통해 생성된 것임을 확인 하였음. 그러나 p27과 Sox2에 의해 표지되는 MC은 EGFP의 발현 없이 Prox1 단백질을 나타냄을 확인함. 이는 MC에 존재하는 Prox1이 외부에서 유입되었을 가능성을 시사함. (C) Prox1 단백질을 자발적으로 발현하는 것으로 검증된 HZC, BPC, 그리고 AC의 경우에는 Prox1 유전자가 하나 제거된 Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐의 망막에서 그 수가 현저히 줄어들었으나, Prox1단백질이 외부에서 유입되었을것이라 판단되는 MC의 경우에는 그 수의 변화가 나타나지 않았음. (D) Prox1 유전자가 하나 제거된 경우에 MC의 전체 세포의 숫자는 변하지 않았지만, MC내에 존재하는 Prox1의 양은 Prox1 유전자의 제거에 동반되어 감소하는 특징을 보임. 이는 Prox1을 발현하는 세포에서 Prox1의 생산량이 감소하면 Prox1을 받아들이는 MC내의 Prox1 단백질의 양 또한 감소하였을 가능성을 시사함
표
Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐를 이용한 망막 세포 내 Prox1 단백질의 자발적 비자발적 발현 판명. (A, B) Prox1 BAX TG 생쥐 망막에서 Prox1 유전자를 발현할 것으로 예상된 Calbindin으로 표지된 HZC과 Vsx2로 표지된 BPC는 물론, Prox1 유전자를 발현하지 않을 것으로 예측되었던 Pax6로 표지된 ACC에서 역시 Prox1 유전자 부위의 전사 활성을 나타내는 EGFP 신호가 관찰됨. 이를 통하여 ACC에서 관찰된 Prox1 단백질 역시 자체 내 Prox1 전사를 통해 생성된 것임을 확인 하였음. 그러나 p27과 Sox2에 의해 표지되는 MC은 EGFP의 발현 없이 Prox1 단백질을 나타냄을 확인함. 이는 MC에 존재하는 Prox1이 외부에서 유입되었을 가능성을 시사함. (C) Prox1 단백질을 자발적으로 발현하는 것으로 검증된 HZC, BPC, 그리고 AC의 경우에는 Prox1 유전자가 하나 제거된 Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐의 망막에서 그 수가 현저히 줄어들었으나, Prox1단백질이 외부에서 유입되었을것이라 판단되는 MC의 경우에는 그 수의 변화가 나타나지 않았음. (D) Prox1 유전자가 하나 제거된 경우에 MC의 전체 세포의 숫자는 변하지 않았지만, MC내에 존재하는 Prox1의 양은 Prox1 유전자의 제거에 동반되어 감소하는 특징을 보임. 이는 Prox1을 발현하는 세포에서 Prox1의 생산량이 감소하면 Prox1을 받아들이는 MC내의 Prox1 단백질의 양 또한 감소하였을 가능성을 시사함
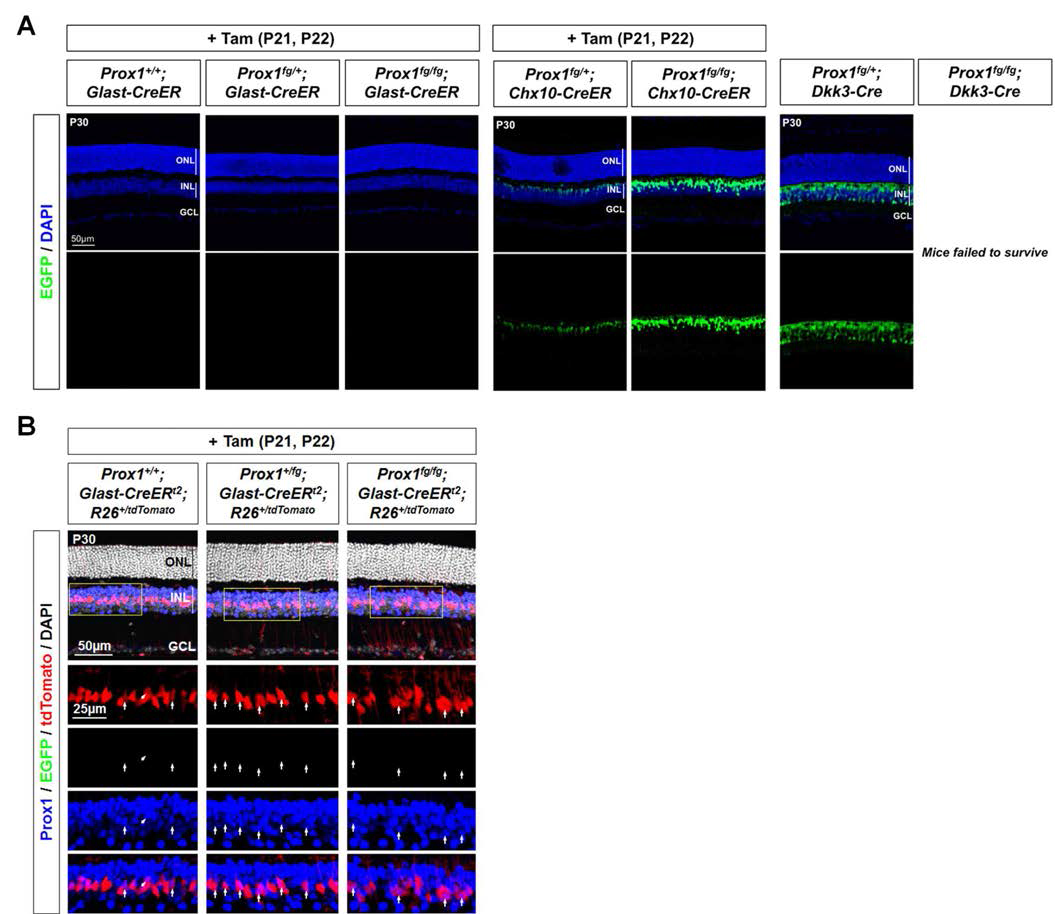 표
Prox1 유전자를 제거한 Muller glia 세포에서 외부 유래 Prox1 단백질의 검출. (A) MG 내에 존재하는 Prox1 단백질의 비자발적 발현을 다시한번 검증하기 위하여 Prox1fg/fg knock-in 생 쥐와 MG에서 특이적 활성을 보이는 Glast 유전자 부위의 발현 조절을 받는 CreERt2를 발현하는 Glast-CreERt2 생쥐를 교배하여 Prox1fg/+;Glast-CreERt2 생쥐를 제작함. 이 생쥐에서 CreERt2 단 백질은 estrogen analog인 tamoxifen에 의해 활성화 되는 특징이 있으므로, 생후 21일과 22일 양일 간에 걸쳐 생쥐 복강 내 10mg/kg으로 tamoxifen을 주입 후 생후 30일에 생쥐 안구를 적출하여 Cre recombinase에 의해 유전자 재조합이 일어나 Prox1 대신 EGFP를 발현한 망막 세포의 존재 여부를 확인함. 그 결과 생쥐의 망막내 MG에서 Prox1 유전자 부위의 전사 활성을 나타내는 EGFP 신호가 검출되지 않았음. 그러나 Prox1fg/fg knock-in 생쥐와 BPC에서 특이적 활성을 보이는 Chx10 유전자 부위의 발현 조절을 받는 CreERt2를 발현하는 Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐를 교배하여 제작한 Prox1fg/+;Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐의 망막에서는 BPC에서 Prox1 유전자 부위의 전사 활성을 나타내는 EGFP 신호가 검출되었음. 이는 Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐를 통해 확인한바와 일치하는 결과임. (B) 앞서 제작한 Prox1fg/+;Glast-CreERt2 생쥐 망막의 MG에서 Prox1 유전자가 확실하게 제거되었음 을 검증하기위해 Cre recombinase 활성이 나타난 세포를 표지하는 Rosa-tdTomato Cre reporter를 함께 가진 Prox1fg/+;Glast-CreERt2;Rosa-tdTomato생쥐를 제작하고, 이 생쥐의 MG에 여전히 Prox1 단백질이 존재하는지의 여부를 검사함
표
Prox1 유전자를 제거한 Muller glia 세포에서 외부 유래 Prox1 단백질의 검출. (A) MG 내에 존재하는 Prox1 단백질의 비자발적 발현을 다시한번 검증하기 위하여 Prox1fg/fg knock-in 생 쥐와 MG에서 특이적 활성을 보이는 Glast 유전자 부위의 발현 조절을 받는 CreERt2를 발현하는 Glast-CreERt2 생쥐를 교배하여 Prox1fg/+;Glast-CreERt2 생쥐를 제작함. 이 생쥐에서 CreERt2 단 백질은 estrogen analog인 tamoxifen에 의해 활성화 되는 특징이 있으므로, 생후 21일과 22일 양일 간에 걸쳐 생쥐 복강 내 10mg/kg으로 tamoxifen을 주입 후 생후 30일에 생쥐 안구를 적출하여 Cre recombinase에 의해 유전자 재조합이 일어나 Prox1 대신 EGFP를 발현한 망막 세포의 존재 여부를 확인함. 그 결과 생쥐의 망막내 MG에서 Prox1 유전자 부위의 전사 활성을 나타내는 EGFP 신호가 검출되지 않았음. 그러나 Prox1fg/fg knock-in 생쥐와 BPC에서 특이적 활성을 보이는 Chx10 유전자 부위의 발현 조절을 받는 CreERt2를 발현하는 Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐를 교배하여 제작한 Prox1fg/+;Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐의 망막에서는 BPC에서 Prox1 유전자 부위의 전사 활성을 나타내는 EGFP 신호가 검출되었음. 이는 Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐를 통해 확인한바와 일치하는 결과임. (B) 앞서 제작한 Prox1fg/+;Glast-CreERt2 생쥐 망막의 MG에서 Prox1 유전자가 확실하게 제거되었음 을 검증하기위해 Cre recombinase 활성이 나타난 세포를 표지하는 Rosa-tdTomato Cre reporter를 함께 가진 Prox1fg/+;Glast-CreERt2;Rosa-tdTomato생쥐를 제작하고, 이 생쥐의 MG에 여전히 Prox1 단백질이 존재하는지의 여부를 검사함
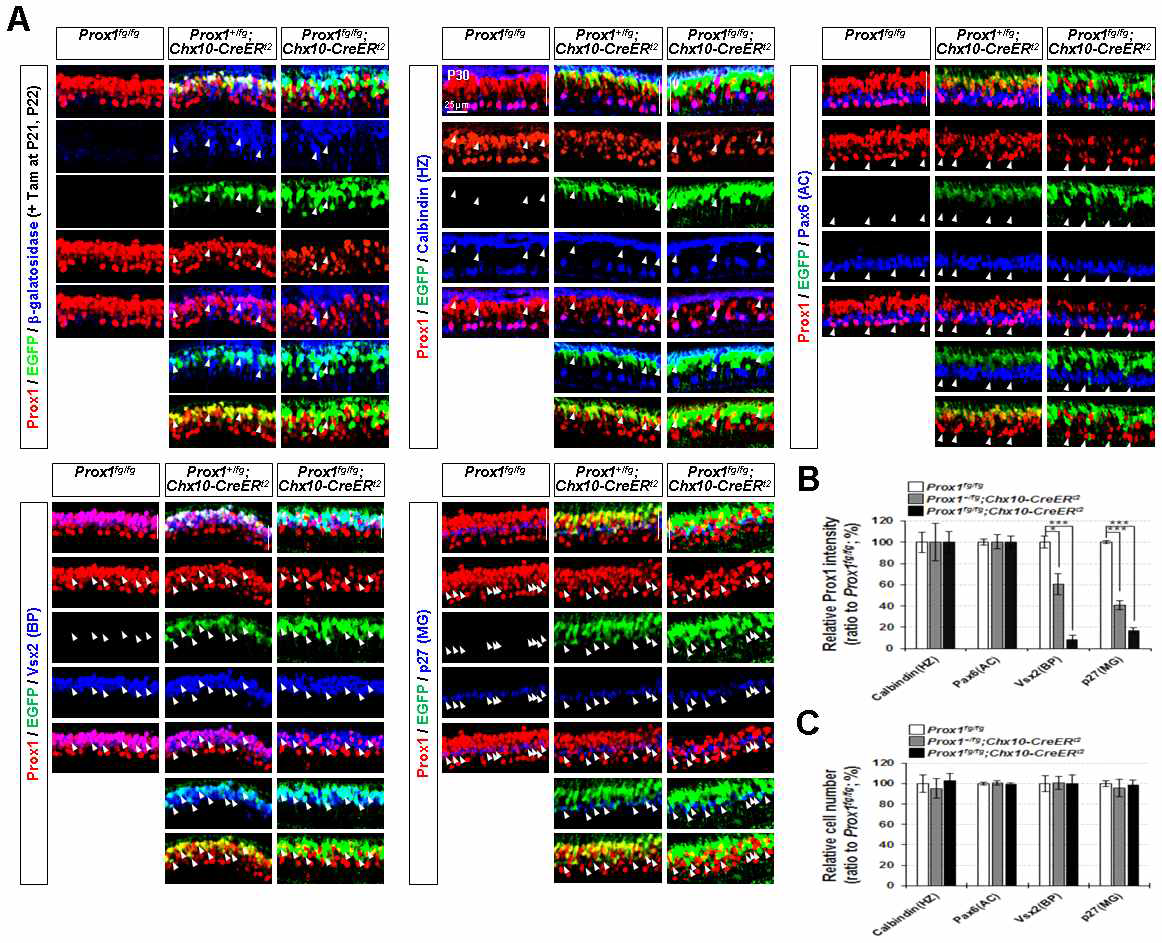 표
Muller glia 내 양극세포 유래 Prox1의 존재. (A, B) Prox1fg/fgknock-in생쥐와 양극세포에서 특이적 활성을 보이는 Chx10 유전자 부위의 발현 조절을 받는 CreERt2를 발현하는 Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐를 교배하여 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2생쥐를 제작함으로써 Prox1 단백질을 자발적으로 발현하는 BPC에서 Prox1 유전자를 한 개 혹은 두 개 모두 제거한 후, Calbindin으로 표지된 HZC와 Pax6로 표지된 ACC, 그리고 p27로 표지된 MG에 존재하는 Prox1 단백질의 양을 검사하였음. Tamoxifen을 주입한 Prox1fg/+;Chx10-CreERt2생쥐와 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2생쥐 망막 내 BPC에서 Prox1 단백질의 발현을 대신한 EGFP 신호를 관찰함으로써 BPC에서의 Prox1 유전자가 효과적으로 제거되었음을 확인함. 실제로 해당 생쥐의 BPC에 존재하는 Prox1 단백질의 양이 정상 생쥐의 57%, 11% 수준으로 유의미하게 감소되어 있었음. 이와 동시에 MG에서의 Prox1 단백질양 또한 정상 생쥐의 40%, 18% 수준으로 유의미하게 감소되었음. 그러나 MG에서 Prox1의 감소는 EGFP 신호를 동반하지 않는 현상으로, 즉 Cre recombinase에 의한 Prox1 유전자의 상실 없이 나타난 현상으로, 이는 BPC에서 Prox1의 단백질 감소로 인해 이를 받아들이는 MG내의 Prox1 역시 감소했음을 의미함. (C) BPC에서 Prox1 유전자의 제거는 생쥐 망막 조직 내 각각의 신경세포의 숫자에는 영향을 미치지 않는 것을 확인함
표
Muller glia 내 양극세포 유래 Prox1의 존재. (A, B) Prox1fg/fgknock-in생쥐와 양극세포에서 특이적 활성을 보이는 Chx10 유전자 부위의 발현 조절을 받는 CreERt2를 발현하는 Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐를 교배하여 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2생쥐를 제작함으로써 Prox1 단백질을 자발적으로 발현하는 BPC에서 Prox1 유전자를 한 개 혹은 두 개 모두 제거한 후, Calbindin으로 표지된 HZC와 Pax6로 표지된 ACC, 그리고 p27로 표지된 MG에 존재하는 Prox1 단백질의 양을 검사하였음. Tamoxifen을 주입한 Prox1fg/+;Chx10-CreERt2생쥐와 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2생쥐 망막 내 BPC에서 Prox1 단백질의 발현을 대신한 EGFP 신호를 관찰함으로써 BPC에서의 Prox1 유전자가 효과적으로 제거되었음을 확인함. 실제로 해당 생쥐의 BPC에 존재하는 Prox1 단백질의 양이 정상 생쥐의 57%, 11% 수준으로 유의미하게 감소되어 있었음. 이와 동시에 MG에서의 Prox1 단백질양 또한 정상 생쥐의 40%, 18% 수준으로 유의미하게 감소되었음. 그러나 MG에서 Prox1의 감소는 EGFP 신호를 동반하지 않는 현상으로, 즉 Cre recombinase에 의한 Prox1 유전자의 상실 없이 나타난 현상으로, 이는 BPC에서 Prox1의 단백질 감소로 인해 이를 받아들이는 MG내의 Prox1 역시 감소했음을 의미함. (C) BPC에서 Prox1 유전자의 제거는 생쥐 망막 조직 내 각각의 신경세포의 숫자에는 영향을 미치지 않는 것을 확인함
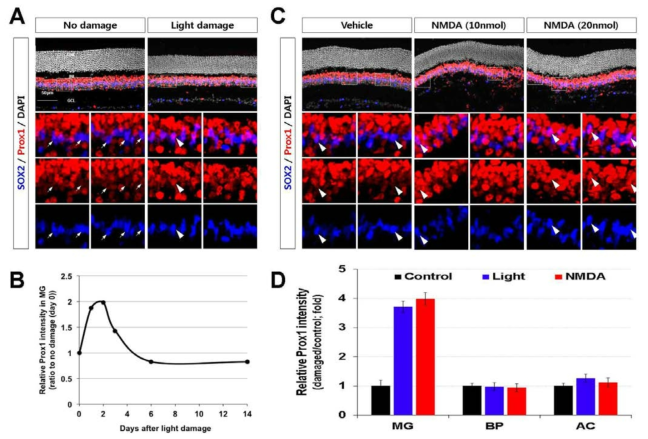 표
망막 손상 상황에서 Muller glia 세포 내 Prox1 양 증가. (A, B) 광수용세포의 광손상에 의한 MG 세포 내 Prox1 양의 증가. MG 세포는 성체 망막에서 지속적으로 퇴화되는 광수용세포의 재생을 담당하는 것으로 알려져 있음. 또한, Prox1은 배아 망막 내 망막신경전구세포의 유지에 필요한 것으로 알려져 있어, MG에 존재하는 외래 Prox1이 MG가 광수용세포 전구세포로 유지되는데 관여할 가능성이 있음. 이러한 가설은 강한 빛을 가하여 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한 생쥐 망막에서 일어나는 MG의 광수용세포 재생 과정에서 Prox1 단백질의 양이 증가하는 양상을 통해 확인하였음. (C, D) Glutamate excitotoxicity에 의해 유도된 망막 손상 상황에서 MG세포 내 Prox1 양 증가. 망막 내 glutamate를 신경전달물질로 활성화되는 AC, retinal ganglion cell (RGC) 등이 과도한 glutamate 신경전달 작용으로 인해 퇴화되면 MG 세포가 이를 부분적으로 재생하기 위해 세포 분열하여 분화한다는 것이 알려져 있음. 이러한 과정에서 주로 신경전구세포에 발현이 강한 Prox1이 역 할을 할 가능성을 확인하기 위해, glutamate의 analog인 NMDA를 생후 30일 생쥐 안구 내에 직접 주입함. 그 후 7일째 생쥐 안구를 분리 후 망막에서 Sox2로 표지되는 MG 세포 내에 존재하는 Prox1의 양을 PBS를 주입한 생쥐 망막과 비교함
표
망막 손상 상황에서 Muller glia 세포 내 Prox1 양 증가. (A, B) 광수용세포의 광손상에 의한 MG 세포 내 Prox1 양의 증가. MG 세포는 성체 망막에서 지속적으로 퇴화되는 광수용세포의 재생을 담당하는 것으로 알려져 있음. 또한, Prox1은 배아 망막 내 망막신경전구세포의 유지에 필요한 것으로 알려져 있어, MG에 존재하는 외래 Prox1이 MG가 광수용세포 전구세포로 유지되는데 관여할 가능성이 있음. 이러한 가설은 강한 빛을 가하여 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한 생쥐 망막에서 일어나는 MG의 광수용세포 재생 과정에서 Prox1 단백질의 양이 증가하는 양상을 통해 확인하였음. (C, D) Glutamate excitotoxicity에 의해 유도된 망막 손상 상황에서 MG세포 내 Prox1 양 증가. 망막 내 glutamate를 신경전달물질로 활성화되는 AC, retinal ganglion cell (RGC) 등이 과도한 glutamate 신경전달 작용으로 인해 퇴화되면 MG 세포가 이를 부분적으로 재생하기 위해 세포 분열하여 분화한다는 것이 알려져 있음. 이러한 과정에서 주로 신경전구세포에 발현이 강한 Prox1이 역 할을 할 가능성을 확인하기 위해, glutamate의 analog인 NMDA를 생후 30일 생쥐 안구 내에 직접 주입함. 그 후 7일째 생쥐 안구를 분리 후 망막에서 Sox2로 표지되는 MG 세포 내에 존재하는 Prox1의 양을 PBS를 주입한 생쥐 망막과 비교함
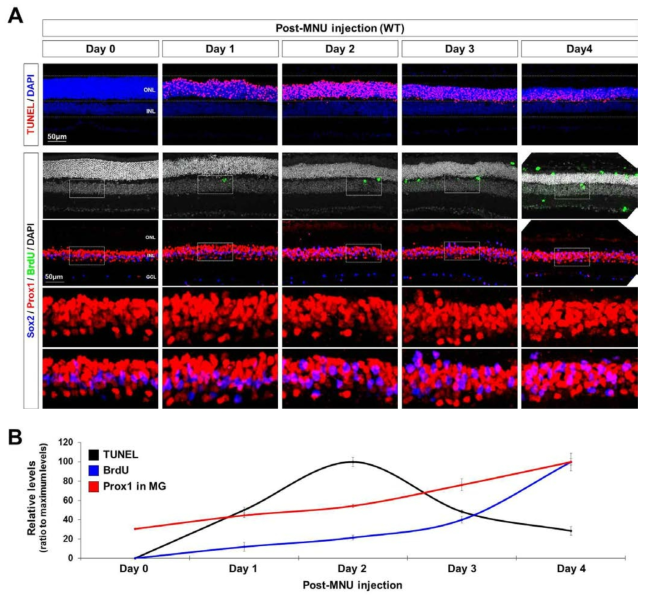 표
MNU (N-methyl-N-nitrosourea)를 이용한 광수용세포 특이적 퇴화 유도. 마우스의 복강에 MNU를 주사하여 망막내 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도했을 때, 시간의 흐름에 따라 Sox2로 표지된 MG 세포 내에서 Prox1의 양이 증가함과 동시에 BrdU로 표지된 새롭게 증식하는 세포의 수 또한 증가함을 확인함. 이러한 결과는, 광수용세포의 손상은 외부로부터 MG내로 Prox1 단백질의 유입을 촉진하고, 이로인해 MG에 축적된 과량의 외인성 Prox1이 MG의 증식을 촉진함으로써 MG가 손상된 망막신경세포로 분화하여 망막신경세포의 재생을 촉진하는데 관여할 것이라는 가능성을 시사함
표
MNU (N-methyl-N-nitrosourea)를 이용한 광수용세포 특이적 퇴화 유도. 마우스의 복강에 MNU를 주사하여 망막내 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도했을 때, 시간의 흐름에 따라 Sox2로 표지된 MG 세포 내에서 Prox1의 양이 증가함과 동시에 BrdU로 표지된 새롭게 증식하는 세포의 수 또한 증가함을 확인함. 이러한 결과는, 광수용세포의 손상은 외부로부터 MG내로 Prox1 단백질의 유입을 촉진하고, 이로인해 MG에 축적된 과량의 외인성 Prox1이 MG의 증식을 촉진함으로써 MG가 손상된 망막신경세포로 분화하여 망막신경세포의 재생을 촉진하는데 관여할 것이라는 가능성을 시사함
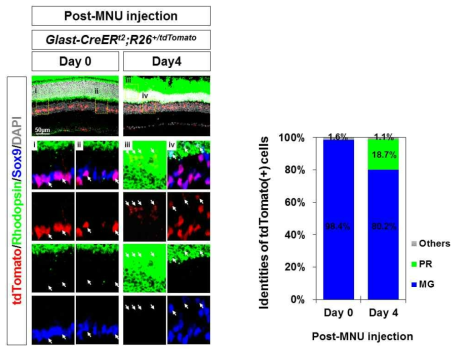 표
손상된 망망신경세포에서 Muller glia로부터 광수용세포로의 망막신경세포 재생. MNU를 주사하여 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한지 4일후에 보이는 BrdU로 표지된 세포들이 MG로부터 유래된 세포인지를 확인하고자 MG에서 특이적 활성을 보이는 Glast 유전자 부위의 발현 조절을 받는 CreERt2를 발현하는 Glast-CreERt2 생쥐를 만들었으며, 이 생쥐 망막에서 Cre recombinase 활성이 나타난 MG를 표지하기 위해 Rosa-tdTomato Cre reporter를 함께 가진 생쥐를 제작함. 광수용 세포의 퇴화를 유도한 이후에 tdTomato로 표지되는 MG의 이동을 추적해본 결과, 처음에는 tdTomato로 표지된 MG세포들이 그들의 원래 위치인 Sox9으로 표지된 MG층에서만 존재하였으나, 4일 후에는 그들중 일부가 광수용세포층으로 이동하여 rhodopsin으로 표지되는 광수용세포로 완전히 분화되어있음을 확인하였음
표
손상된 망망신경세포에서 Muller glia로부터 광수용세포로의 망막신경세포 재생. MNU를 주사하여 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한지 4일후에 보이는 BrdU로 표지된 세포들이 MG로부터 유래된 세포인지를 확인하고자 MG에서 특이적 활성을 보이는 Glast 유전자 부위의 발현 조절을 받는 CreERt2를 발현하는 Glast-CreERt2 생쥐를 만들었으며, 이 생쥐 망막에서 Cre recombinase 활성이 나타난 MG를 표지하기 위해 Rosa-tdTomato Cre reporter를 함께 가진 생쥐를 제작함. 광수용 세포의 퇴화를 유도한 이후에 tdTomato로 표지되는 MG의 이동을 추적해본 결과, 처음에는 tdTomato로 표지된 MG세포들이 그들의 원래 위치인 Sox9으로 표지된 MG층에서만 존재하였으나, 4일 후에는 그들중 일부가 광수용세포층으로 이동하여 rhodopsin으로 표지되는 광수용세포로 완전히 분화되어있음을 확인하였음
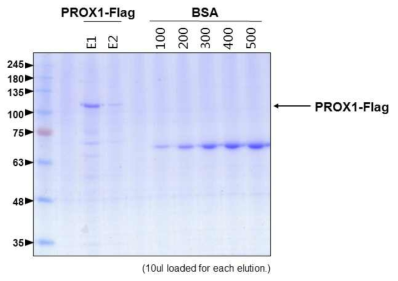 표
Prox1 재조합 단백질의 대량생산. Prox1 단백질의 망막신경세포 재생 효과를 직접적으로 검증하기 위해 flag-tag이 표지된 Prox1 재조합 단백질을 대량생산하였음. 대장균을 이용한 대량 생산 시스템에서 대부분 단백질 용해성의 문제로 분리가 어려웠던 호메오도메인 전사인자 단백질들의 대량 생산 유도를 위해 Sf9 세포에 vaculovirus를 이용한 발현 시스템을 이용하였음. Flag 표지된 Prox1 cDNA를 pFastBac vaculovirus vector에 cloning 한 후 Sf9 insect cell에 transfection 후 recombinant protein을 발현하는 vaculovirus를 분리 후 다시 Sf9 세포에 감염하여 단백질 발현을 유도함. 해당 세포에서 Flag-Prox1을 Flag antibody를 이용하여 affinity purification 후 antibody-protein complex에서 protein을 acid elution 하여 20ul elution fraction을 SDS-PAGE 후 Coommassie Blue staining으로 검출함. Flag-Prox1 단백질의 상대량 계산을 위해 특정량의 bovine serum albumin (BSA)를 함께 검출하였음
표
Prox1 재조합 단백질의 대량생산. Prox1 단백질의 망막신경세포 재생 효과를 직접적으로 검증하기 위해 flag-tag이 표지된 Prox1 재조합 단백질을 대량생산하였음. 대장균을 이용한 대량 생산 시스템에서 대부분 단백질 용해성의 문제로 분리가 어려웠던 호메오도메인 전사인자 단백질들의 대량 생산 유도를 위해 Sf9 세포에 vaculovirus를 이용한 발현 시스템을 이용하였음. Flag 표지된 Prox1 cDNA를 pFastBac vaculovirus vector에 cloning 한 후 Sf9 insect cell에 transfection 후 recombinant protein을 발현하는 vaculovirus를 분리 후 다시 Sf9 세포에 감염하여 단백질 발현을 유도함. 해당 세포에서 Flag-Prox1을 Flag antibody를 이용하여 affinity purification 후 antibody-protein complex에서 protein을 acid elution 하여 20ul elution fraction을 SDS-PAGE 후 Coommassie Blue staining으로 검출함. Flag-Prox1 단백질의 상대량 계산을 위해 특정량의 bovine serum albumin (BSA)를 함께 검출하였음
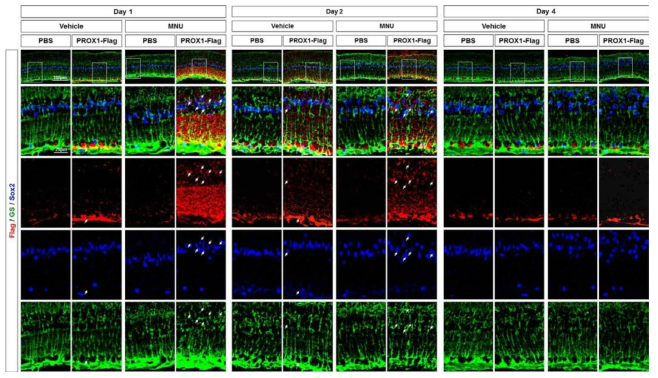 표
Prox1 재조합 단백질의 망막신경세포로의 침투능력 검증. ‘그림 141’에서 생산한 Prox1 재조합 단백질을 각각 MNU를 주사하여 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한 생쥐와 PBS를 주입한 생쥐의 안구에 주입하여 이들의 망막신경세포로의 침투능력을 검증하였음. Flag-antibody를 사용한 면역형 광염색법을 사용하여 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 망막내 존재여부를 확인하였을 때, 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한 생쥐 망막에서 더 많은 양의 Prox1 재조합 단백질이 관찰되었음. 특히 이들 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 대부분은 Sox2로 표지된 MG에 존재하고 있음을 확인함
표
Prox1 재조합 단백질의 망막신경세포로의 침투능력 검증. ‘그림 141’에서 생산한 Prox1 재조합 단백질을 각각 MNU를 주사하여 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한 생쥐와 PBS를 주입한 생쥐의 안구에 주입하여 이들의 망막신경세포로의 침투능력을 검증하였음. Flag-antibody를 사용한 면역형 광염색법을 사용하여 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 망막내 존재여부를 확인하였을 때, 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한 생쥐 망막에서 더 많은 양의 Prox1 재조합 단백질이 관찰되었음. 특히 이들 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 대부분은 Sox2로 표지된 MG에 존재하고 있음을 확인함
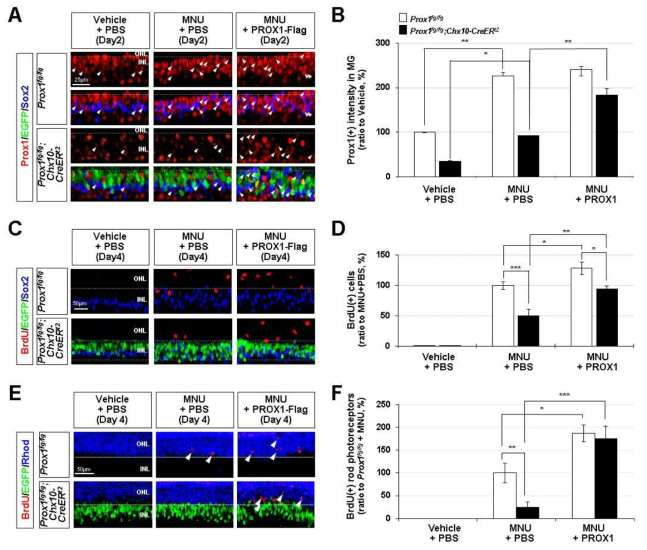 표
Prox1 재조합 단백질을 사용한 망막신경세포 재생 촉진 효과 검증. (A, B) BP에서 Prox1의 감소로 인해 이를 받아들이는 MG내의 Prox1 역시 감소되도록 만들어놓은 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐의 경우, 정상 생쥐와는 다르게 MNU를 이용하여 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한 경우에도 Sox2로 표지된 MG내에서의 Prox1 단백질의 증가가 크게 나타나지 않았음. 이것은 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 주입에 의해 다시 정상 생쥐와 비슷한 수준으로 회복됨을 확인하였음. (C, D) MG내의 Prox1이 감소되도록 만들어놓은 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐의 경우에는 MNU를 이용한 광수용세포의 퇴화조건에서 BrdU로 표지되는 MG로부터 새롭게 증식한 세포의 수 또한 정상 생쥐에서보다 크게 감소되어있었으나, 이또한 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 주입에 의해 다시 정상 생쥐와 비슷한 수준으로 회복됨을 확인하였음. (E, F) 망막신경세포 손상 후 MG에 존재하는 Prox1에 의해 유도된다고 생각되는 MG부터 광수용세포로의 망막신경세포 재생 정도 또한 정상생쥐에 비해 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐에서 크게 감소하였지만, 이 역시 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 주입에 의해 다시 정상 생쥐와 비슷한 수준으로 회복됨을 확인하였음
표
Prox1 재조합 단백질을 사용한 망막신경세포 재생 촉진 효과 검증. (A, B) BP에서 Prox1의 감소로 인해 이를 받아들이는 MG내의 Prox1 역시 감소되도록 만들어놓은 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐의 경우, 정상 생쥐와는 다르게 MNU를 이용하여 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한 경우에도 Sox2로 표지된 MG내에서의 Prox1 단백질의 증가가 크게 나타나지 않았음. 이것은 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 주입에 의해 다시 정상 생쥐와 비슷한 수준으로 회복됨을 확인하였음. (C, D) MG내의 Prox1이 감소되도록 만들어놓은 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐의 경우에는 MNU를 이용한 광수용세포의 퇴화조건에서 BrdU로 표지되는 MG로부터 새롭게 증식한 세포의 수 또한 정상 생쥐에서보다 크게 감소되어있었으나, 이또한 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 주입에 의해 다시 정상 생쥐와 비슷한 수준으로 회복됨을 확인하였음. (E, F) 망막신경세포 손상 후 MG에 존재하는 Prox1에 의해 유도된다고 생각되는 MG부터 광수용세포로의 망막신경세포 재생 정도 또한 정상생쥐에 비해 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐에서 크게 감소하였지만, 이 역시 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 주입에 의해 다시 정상 생쥐와 비슷한 수준으로 회복됨을 확인하였음
 표
Tetra-Cystein (Lumio) tag을 이용한 형광 단백질 검출법 원리. 기존 단백질 이동을 관찰하기 위해 주로 사용된 GFP tag 등은 그 자체가 이미 30 kDa에 가까운 크기를 가지는 단백질로, 자칫 호메오도메인 전사인자 자체가 가지고 있는 단백질의 3차 구조에 영향을 줄 가능성이 높아, 200여개의 각기 다른 특징을 가지는 호메오도메인 전사인자를 표지하는 과정에서 예상치 못한 실험 오류가 나올 수 있을 것으로 판단됨. 따라서 상대적으로 간단한 6개의 아미노산만으로 형광을 표지할 수 있는 Lumio tag을 이용해 호메오도메인 전사인자가 가지는 단백질 구조를 방해하지 않으면서도 효과적인 형광 검출을 통해 이동성 및 비이동성 전사인자의 발굴에 사용할 예정임. 그림에서 보는 것과 같이 Lumio tag이 포함하는 4개의 Cysteine 잔기들에 불활성 Lumio 화학물질이 반응하면 활성화되어 녹색이나 적색의 형광을 띄는 특징을 이용해 세포 외부로 분비된 단백질의 양을 형광의 intensity를 측정함으로 간접적으로 확인할 수 있다. 또한, 세포 내부에 존재하는 단백질의 양은 transfection한 세포를 형광현미경으로 측정하거나 FACS를 이용한 형광 검측법으로 확인하여 세포 내부와 세포 외부에 분포하는 호메오도메인 전사인자의 양을 조사하고자 하였다
표
Tetra-Cystein (Lumio) tag을 이용한 형광 단백질 검출법 원리. 기존 단백질 이동을 관찰하기 위해 주로 사용된 GFP tag 등은 그 자체가 이미 30 kDa에 가까운 크기를 가지는 단백질로, 자칫 호메오도메인 전사인자 자체가 가지고 있는 단백질의 3차 구조에 영향을 줄 가능성이 높아, 200여개의 각기 다른 특징을 가지는 호메오도메인 전사인자를 표지하는 과정에서 예상치 못한 실험 오류가 나올 수 있을 것으로 판단됨. 따라서 상대적으로 간단한 6개의 아미노산만으로 형광을 표지할 수 있는 Lumio tag을 이용해 호메오도메인 전사인자가 가지는 단백질 구조를 방해하지 않으면서도 효과적인 형광 검출을 통해 이동성 및 비이동성 전사인자의 발굴에 사용할 예정임. 그림에서 보는 것과 같이 Lumio tag이 포함하는 4개의 Cysteine 잔기들에 불활성 Lumio 화학물질이 반응하면 활성화되어 녹색이나 적색의 형광을 띄는 특징을 이용해 세포 외부로 분비된 단백질의 양을 형광의 intensity를 측정함으로 간접적으로 확인할 수 있다. 또한, 세포 내부에 존재하는 단백질의 양은 transfection한 세포를 형광현미경으로 측정하거나 FACS를 이용한 형광 검측법으로 확인하여 세포 내부와 세포 외부에 분포하는 호메오도메인 전사인자의 양을 조사하고자 하였다
 표
세포 내 단백질에 대한 Lumio chemical의 비특이적 반응. (A) 293T 세포에 각 호메오도메인 전사인자들을 발현한 후 세포 배양액을 10% (final) trichloroacetic acid (TCA)로 처리하여 세포 배양액 내 macromolecule의 침전을 얻고, 이 배양액 단백질 (Conc. Media) 중 호메오도메인 전사인자의 존재 여부를 V5 antibody를 이용한 Western blot으로 조사함 (A, 왼쪽). 세포에 해당 단백질이 정상적으로 발현되었는지를 조사하기 위해 cell lysate를 얻고 세포 내에 존재하는 전사인자의 양을 역시 V5 antibody를 이용한 Western blot으로 조사함. (B) 동일 세포 배양액 네 존재하는 Lumio-tag 단백질의 양을 정량하기 위해 Lumio-Green chemical을 처리한 후 Ex.508nm/Em523nm 의 조건에서 형광 강도를 측정함. 그 결과 세포에 정상적으로 발현이 되었고, 세포 외부로 일부 단백질들이 분비되었음에도 불구하고 전혀 그들 사이의 차이를 검증할 수가 없었다
표
세포 내 단백질에 대한 Lumio chemical의 비특이적 반응. (A) 293T 세포에 각 호메오도메인 전사인자들을 발현한 후 세포 배양액을 10% (final) trichloroacetic acid (TCA)로 처리하여 세포 배양액 내 macromolecule의 침전을 얻고, 이 배양액 단백질 (Conc. Media) 중 호메오도메인 전사인자의 존재 여부를 V5 antibody를 이용한 Western blot으로 조사함 (A, 왼쪽). 세포에 해당 단백질이 정상적으로 발현되었는지를 조사하기 위해 cell lysate를 얻고 세포 내에 존재하는 전사인자의 양을 역시 V5 antibody를 이용한 Western blot으로 조사함. (B) 동일 세포 배양액 네 존재하는 Lumio-tag 단백질의 양을 정량하기 위해 Lumio-Green chemical을 처리한 후 Ex.508nm/Em523nm 의 조건에서 형광 강도를 측정함. 그 결과 세포에 정상적으로 발현이 되었고, 세포 외부로 일부 단백질들이 분비되었음에도 불구하고 전혀 그들 사이의 차이를 검증할 수가 없었다
 표
분비형 전사인자에 대한 high-throughput screening을 위한 assay system 확립. (A) 단백질의 N-말단이 V5-tag으로 표지된 EN2, OTX2, PAX6, VAX1을 각각 12well culture dish에 있는 293T 세포에 발현 후 (DNA 500ng/401mm2) 해당 세포를 heparin이 10mg/ml농도로 첨가된 Freestyle 293 Expression Medium (Invitrogen, medium 양, 1ml/12well)에서 3시간동안 배양하여 세포 외부로 분비된 HP들을 포집함. 3시간 이후에 세포배양액 0.5ml을 분리하여 dot-blot kit를 이용, PVDF membrane에 결합시킨 후 각 dot에 존재하는 V5가 표지된 HP의 상대적 양을 V5 antibody를 이용한 Dot blot (DB)으로 조사함. 이와 동시에, 이들 HP의 정상적인 세포 내 발현을 V5 antibody를 이용한 Western blot (WB)으로 조사함. (B) 세포배양액에 heparin을 첨가하지 않은 경우에는, 각각의 HP들이 세포내에서 정상적으로 발현되고 있음에도 불구하고 EN2를 제외한 기존 분비 HP들을 DB을 통하여 검출할 수 없었음. (C) 세포배양액에 heparin을 첨가한 경우에는 기존 분비 HP들을 DB을 이용하여 유의한 수준으로 검출 할 수 있었음. 이를 통하여 대부분의 HP들은 세포 외부의 heparin sulfate proteoglycan에 결합되어 존재한다는 사실을 간접적으로 확인함. HP cDNA 뒤에 존재하는 internal ribosome entry site (IRES)를 통해 연결된 비분비성 enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)의 세포 배양액으로의 분비 여부를 통해 세포 사멸과 이에 의한 비특이적 HP의 배양액 노출 가능성을 확인하였을 때, EGFP가 검출된 샘플이 하나도 존재하지 않은 것을 통해 유전자 과발현에 의한 세포 독성 및 세포 사멸에 의한 비특이적 HP의 배양액 노출은 없는 것으로 확인함
표
분비형 전사인자에 대한 high-throughput screening을 위한 assay system 확립. (A) 단백질의 N-말단이 V5-tag으로 표지된 EN2, OTX2, PAX6, VAX1을 각각 12well culture dish에 있는 293T 세포에 발현 후 (DNA 500ng/401mm2) 해당 세포를 heparin이 10mg/ml농도로 첨가된 Freestyle 293 Expression Medium (Invitrogen, medium 양, 1ml/12well)에서 3시간동안 배양하여 세포 외부로 분비된 HP들을 포집함. 3시간 이후에 세포배양액 0.5ml을 분리하여 dot-blot kit를 이용, PVDF membrane에 결합시킨 후 각 dot에 존재하는 V5가 표지된 HP의 상대적 양을 V5 antibody를 이용한 Dot blot (DB)으로 조사함. 이와 동시에, 이들 HP의 정상적인 세포 내 발현을 V5 antibody를 이용한 Western blot (WB)으로 조사함. (B) 세포배양액에 heparin을 첨가하지 않은 경우에는, 각각의 HP들이 세포내에서 정상적으로 발현되고 있음에도 불구하고 EN2를 제외한 기존 분비 HP들을 DB을 통하여 검출할 수 없었음. (C) 세포배양액에 heparin을 첨가한 경우에는 기존 분비 HP들을 DB을 이용하여 유의한 수준으로 검출 할 수 있었음. 이를 통하여 대부분의 HP들은 세포 외부의 heparin sulfate proteoglycan에 결합되어 존재한다는 사실을 간접적으로 확인함. HP cDNA 뒤에 존재하는 internal ribosome entry site (IRES)를 통해 연결된 비분비성 enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)의 세포 배양액으로의 분비 여부를 통해 세포 사멸과 이에 의한 비특이적 HP의 배양액 노출 가능성을 확인하였을 때, EGFP가 검출된 샘플이 하나도 존재하지 않은 것을 통해 유전자 과발현에 의한 세포 독성 및 세포 사멸에 의한 비특이적 HP의 배양액 노출은 없는 것으로 확인함
 표
각 호메오도메인 전사인자의 상대적 분비능. ‘그림4’와 같은 결과 내 DB의 dot intensity와 WB의 밴드 intensity를 Multi Gauge V3.0 software (Fuji, Tokyo, Japan)로 측정한 후, 각 HP들의 상대적 분비 값을 측정하였음. 실험에 사용한 3개의 세포주 모두에서 유사한 정도로 분비되는 것으로 확인된 Pitx1의 ‘세포 배양액 DB의 dot intensity/세포 내 단백질 WB의 밴드 intensity’를 100으로 정하고 이에 대한 상대 값으로 해당 HP들의 분비능 (상대적 분비능, relative secretion index, RSI)을 지정하였음
표
각 호메오도메인 전사인자의 상대적 분비능. ‘그림4’와 같은 결과 내 DB의 dot intensity와 WB의 밴드 intensity를 Multi Gauge V3.0 software (Fuji, Tokyo, Japan)로 측정한 후, 각 HP들의 상대적 분비 값을 측정하였음. 실험에 사용한 3개의 세포주 모두에서 유사한 정도로 분비되는 것으로 확인된 Pitx1의 ‘세포 배양액 DB의 dot intensity/세포 내 단백질 WB의 밴드 intensity’를 100으로 정하고 이에 대한 상대 값으로 해당 HP들의 분비능 (상대적 분비능, relative secretion index, RSI)을 지정하였음
 표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 분비 여부 판별. (A) 총 170개의 HP들 중 3개의 세포주 모두에서 정상적인 발현이 관찰되지 않은 7개 HP들과 HP이 아닌 1개의 단백질을 제외한 162개 HP을 대 상으로하여 이들의 각 세포주에서의 RSI를 로그값으로 변환(Log10(RSI/100))한 후, 그 분포를 확인한 결과 양봉분포(bimodal distribution)를 나타냄. 이때, 가장 큰 분포를 나타내는 그래프의 시작점을 경계값(Cut-off, 그래프에서 점선으로 표시함)으로 설정하고 이보다 작은 RSI값을 가지는 HP들을 비분비성-HP(non secretory-HP, nsHP)으로, 이보다 큰 RSI값을 가지는 HP들을 분비성 -HP(secretory-HP, sHP)으로 분류하기로 결정함. 293T 세포주에서는 약84% (136개), GT1-7 세포주에서는 약87% (141개), MDCK 세포주에서는 약60% (98개)의 HP이 sHP으로 분류됨. (B) 피어슨상관계수(Pearson’s correlation coefficient, PCC)를 측정함으로써 서로 다른 세포주에서 나타나는 분비능의 상관관계를 조사함. 모든 경우에 약하기는 하지만 상관관계가 있음을 확인하였음
표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 분비 여부 판별. (A) 총 170개의 HP들 중 3개의 세포주 모두에서 정상적인 발현이 관찰되지 않은 7개 HP들과 HP이 아닌 1개의 단백질을 제외한 162개 HP을 대 상으로하여 이들의 각 세포주에서의 RSI를 로그값으로 변환(Log10(RSI/100))한 후, 그 분포를 확인한 결과 양봉분포(bimodal distribution)를 나타냄. 이때, 가장 큰 분포를 나타내는 그래프의 시작점을 경계값(Cut-off, 그래프에서 점선으로 표시함)으로 설정하고 이보다 작은 RSI값을 가지는 HP들을 비분비성-HP(non secretory-HP, nsHP)으로, 이보다 큰 RSI값을 가지는 HP들을 분비성 -HP(secretory-HP, sHP)으로 분류하기로 결정함. 293T 세포주에서는 약84% (136개), GT1-7 세포주에서는 약87% (141개), MDCK 세포주에서는 약60% (98개)의 HP이 sHP으로 분류됨. (B) 피어슨상관계수(Pearson’s correlation coefficient, PCC)를 측정함으로써 서로 다른 세포주에서 나타나는 분비능의 상관관계를 조사함. 모든 경우에 약하기는 하지만 상관관계가 있음을 확인하였음
 표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 서로다른 세포주에서의 분비능 비교. ‘그림 6A’의 결과를 도식화하여 나타냄. 그림에서 나타낸 서로다른 색깔은 각각의 HP이 해당하는 세포주에서 sHP 으로 분류되었음을 의미함. 전체 HP들 중94%에 해당하는 152개의 HP이 실험에 사용한 3개의 세포주들 중 적어도 한 개의 세포주에서 분비능을 가짐을 확인함. 이는 세포밖으로의 분비능은 대부분의 HP들이 가지는 일반적인 특징임을 시사함. 그러나 전체 HP들 중 52.5%에 해당하는 85개의 HP들만이 실험에 사용한 3개의 세포주 모두에서 분비능을 나타냈으며, 6.2%에 해당하는 10개의 HP은 3개의 세포주 모두에서 분비능이 없는 nsHP으로 분류되었음. 이러한 결과를 통하여 HP의 분비능은 이들의 가지는 일반적인 특징이기는 하지만 세포의 종류와 그 환경에 따라 다르게 나타날 수 있음을 확인하였음
표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 서로다른 세포주에서의 분비능 비교. ‘그림 6A’의 결과를 도식화하여 나타냄. 그림에서 나타낸 서로다른 색깔은 각각의 HP이 해당하는 세포주에서 sHP 으로 분류되었음을 의미함. 전체 HP들 중94%에 해당하는 152개의 HP이 실험에 사용한 3개의 세포주들 중 적어도 한 개의 세포주에서 분비능을 가짐을 확인함. 이는 세포밖으로의 분비능은 대부분의 HP들이 가지는 일반적인 특징임을 시사함. 그러나 전체 HP들 중 52.5%에 해당하는 85개의 HP들만이 실험에 사용한 3개의 세포주 모두에서 분비능을 나타냈으며, 6.2%에 해당하는 10개의 HP은 3개의 세포주 모두에서 분비능이 없는 nsHP으로 분류되었음. 이러한 결과를 통하여 HP의 분비능은 이들의 가지는 일반적인 특징이기는 하지만 세포의 종류와 그 환경에 따라 다르게 나타날 수 있음을 확인하였음
 표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 주변 세포 침투능력 검증. 293T, GT1-7 및 MDCK 세포들을 이용한 분비능 측정에 이용한 호메오도메인 전사인자들을 대상으로 하여 이들의 주변 세포로의 침투 능력을 조사하였음. 이를 위하여 HeLa 세포에 ‘호메오도메인 전사인자-IRES(Internal Ribosome Entry Site, 내부 리보솜 유입점)-GFP(Green Fluorescent Protein, 초록 형광 단백질)’ 시스템으로 제작된 각각의 호메오도메인 전사인자들을 과발현시킨 후 면역형광염색하여 관찰하였음. ‘호메오도 메인 전사인자-IRES-GFP’ 시스템은 ‘호메오도메인 전사인자-IRES-GFP’를 하나의 전사체로 만든 후, ‘호메오도메인 전사인자’와 ‘GFP’를 각각의 독립된 단백질로 발현시킬 수 있는 시스템으로, 형광 현미경 관찰시에 호메오도메인 전사인자의 신호와 GFP의 신호가 동시에 나타나는 세포를 조사함으로써 각각의 호메오도메인 전사인자가 과발현된 세포를 확인할 수 있으며, 호메오도메인 전사인자의 신호만 나타나는 세포를 조사함으로써 호메오도메인 전사인자의 주변 세포로의 침투능력을 확인할 수 있음
표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 주변 세포 침투능력 검증. 293T, GT1-7 및 MDCK 세포들을 이용한 분비능 측정에 이용한 호메오도메인 전사인자들을 대상으로 하여 이들의 주변 세포로의 침투 능력을 조사하였음. 이를 위하여 HeLa 세포에 ‘호메오도메인 전사인자-IRES(Internal Ribosome Entry Site, 내부 리보솜 유입점)-GFP(Green Fluorescent Protein, 초록 형광 단백질)’ 시스템으로 제작된 각각의 호메오도메인 전사인자들을 과발현시킨 후 면역형광염색하여 관찰하였음. ‘호메오도 메인 전사인자-IRES-GFP’ 시스템은 ‘호메오도메인 전사인자-IRES-GFP’를 하나의 전사체로 만든 후, ‘호메오도메인 전사인자’와 ‘GFP’를 각각의 독립된 단백질로 발현시킬 수 있는 시스템으로, 형광 현미경 관찰시에 호메오도메인 전사인자의 신호와 GFP의 신호가 동시에 나타나는 세포를 조사함으로써 각각의 호메오도메인 전사인자가 과발현된 세포를 확인할 수 있으며, 호메오도메인 전사인자의 신호만 나타나는 세포를 조사함으로써 호메오도메인 전사인자의 주변 세포로의 침투능력을 확인할 수 있음
 표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포 간 이동 정도 비교 그래프. HP의 상대적 분비능을 측정한 선행연구에서 기준으로 삼았던 Pitx1의 면역형광염색결과에서 ‘HP의 신호(red)만 나타나는 세포의 수 / HP의 신호(red)와 GFP의 신호(green)가 동시에 나타나는 세포(yellow)의 수’를 100으로 정하고 이에 대한 상대값으로 각각의 HP들의 주변세포로의 침투능 (상대적 침투능, relative transfer index, RTI)을 지정하였음. HP의 주변세포로의 침투능력(좌측 Y축)을 세포밖으로의 분비능력(우측 Y축)과 비교해보았을 때, 이들의 상관관계가 매우 높은 것으로 나타남. 이러한 결과는, HP은 일단 세포 밖으로 분비가 되면 주변 세포로의 이동은 쉽게 일어날수 있음을 시사함
표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포 간 이동 정도 비교 그래프. HP의 상대적 분비능을 측정한 선행연구에서 기준으로 삼았던 Pitx1의 면역형광염색결과에서 ‘HP의 신호(red)만 나타나는 세포의 수 / HP의 신호(red)와 GFP의 신호(green)가 동시에 나타나는 세포(yellow)의 수’를 100으로 정하고 이에 대한 상대값으로 각각의 HP들의 주변세포로의 침투능 (상대적 침투능, relative transfer index, RTI)을 지정하였음. HP의 주변세포로의 침투능력(좌측 Y축)을 세포밖으로의 분비능력(우측 Y축)과 비교해보았을 때, 이들의 상관관계가 매우 높은 것으로 나타남. 이러한 결과는, HP은 일단 세포 밖으로 분비가 되면 주변 세포로의 이동은 쉽게 일어날수 있음을 시사함
 표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 생체내에서의 세포 간 이동 현상. (A) sHP 또는 nsHP들의 세포 간 이동 현상이 생체 내에서도 동일하게 일어나는 것인지를 확인하기 위하여, HeLa 세포주를 이용한 HP의 주변 침투능 검증에 사용한것과 동일한 HP 유전자 카세트를 수정 후 13.5일된 생쥐 배아 뇌실에 elecroporation을 통해 도입함. (B) 유전자 카세트 도입 3일 후인 수정 후 16.5일에 배아 뇌를 적출하여 배아 뇌신경세포에서 HP의 신호(red)만을 나타내는 세포의 존재 여부를 V5와 EGFP에 대한 면역형광 염색을 통하여 확인함으로써 HP의 생체내에서의 세포간 이동을 조사함. (C) 그 결과, 앞선 3개의 세포주를 사용한 HP의 분비능 조사와 HeLa 세포주를 사용한 HP의 주변세포로의 침투능 조사에서 분비능 및 침투능을 모두 가진다고 검증된 OTX2, EN2, PAX6, VAX1 등의 HP 들의 결과에서는 모두 세포간 이동을 나타내는 HP의 신호(red)만을 나타내는 세포를 다수 확인 할 수 있었으나, 세포밖으로의 분비능 및 주변세포로의 침투능이 모두 없다고 검증된 SHOX2의 경우에는 세포간 이동을 나타내는 HP의 신호(red)만을 나타내는 세포 없이 EGFP를 동시에 발현하는 세포들에만 머무르고 있음을 확인함
표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 생체내에서의 세포 간 이동 현상. (A) sHP 또는 nsHP들의 세포 간 이동 현상이 생체 내에서도 동일하게 일어나는 것인지를 확인하기 위하여, HeLa 세포주를 이용한 HP의 주변 침투능 검증에 사용한것과 동일한 HP 유전자 카세트를 수정 후 13.5일된 생쥐 배아 뇌실에 elecroporation을 통해 도입함. (B) 유전자 카세트 도입 3일 후인 수정 후 16.5일에 배아 뇌를 적출하여 배아 뇌신경세포에서 HP의 신호(red)만을 나타내는 세포의 존재 여부를 V5와 EGFP에 대한 면역형광 염색을 통하여 확인함으로써 HP의 생체내에서의 세포간 이동을 조사함. (C) 그 결과, 앞선 3개의 세포주를 사용한 HP의 분비능 조사와 HeLa 세포주를 사용한 HP의 주변세포로의 침투능 조사에서 분비능 및 침투능을 모두 가진다고 검증된 OTX2, EN2, PAX6, VAX1 등의 HP 들의 결과에서는 모두 세포간 이동을 나타내는 HP의 신호(red)만을 나타내는 세포를 다수 확인 할 수 있었으나, 세포밖으로의 분비능 및 주변세포로의 침투능이 모두 없다고 검증된 SHOX2의 경우에는 세포간 이동을 나타내는 HP의 신호(red)만을 나타내는 세포 없이 EGFP를 동시에 발현하는 세포들에만 머무르고 있음을 확인함
 표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 생체 내 세포 간 이동 정도 비교. Pitx1의 면역형광염색결과에서 ‘HP의 신호(red)만 나타나는 세포의 수 / HP의 신호(red)와 GFP의 신호(green)가 동시에 나타나는 세포(yellow)의 수’를 100으로 정하고 이에 대한 상대값으로 각각의 HP들의 생체내에서의 세포간 이동 정도(RTI)를 측정하였음. HP의 생체내에서의 주변세포로의 이동정도(좌측 Y축)를 mouse 시상하부 유래 신경세포인 GT1-7 세포에서의 HP의 분비정도(우측 Y축)와 비교해보았을 때, 약한수준이기는 하지만 상관관계가 있음 확인함. 이를 통하여 HP의 세포간 이동 및 침투현상은 세포종류 및 환경조건에 따라 다르게 나타나기는 하지만 생체 조건에서도 여전히 동일하게 나타나는 현상임을 검증하였음
표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 생체 내 세포 간 이동 정도 비교. Pitx1의 면역형광염색결과에서 ‘HP의 신호(red)만 나타나는 세포의 수 / HP의 신호(red)와 GFP의 신호(green)가 동시에 나타나는 세포(yellow)의 수’를 100으로 정하고 이에 대한 상대값으로 각각의 HP들의 생체내에서의 세포간 이동 정도(RTI)를 측정하였음. HP의 생체내에서의 주변세포로의 이동정도(좌측 Y축)를 mouse 시상하부 유래 신경세포인 GT1-7 세포에서의 HP의 분비정도(우측 Y축)와 비교해보았을 때, 약한수준이기는 하지만 상관관계가 있음 확인함. 이를 통하여 HP의 세포간 이동 및 침투현상은 세포종류 및 환경조건에 따라 다르게 나타나기는 하지만 생체 조건에서도 여전히 동일하게 나타나는 현상임을 검증하였음
 표
ANTP 호메오도메인 전사인자 subclass별 분비능 비교. 호메오도메인 전사인자 중 가장 많은 수를 차지하는 ANTP family의 분비능을 각 subclass로 나누어 비교한 결과, Hox subclass보다 NKL subclass가 더 분비능이 높음을 알 수 있음. 특히, Nkx subclass member와 enrailed와 Vax1을 포함하는 Emx subclass의 분비능이 높음을 알 수 있음. 따라서, 이들 subclass가 공통적으로 가지는 호메오도메인 내의 아미노산 서열 또는 호메오도메인 외부의 특징적 아미노산 서열 및 구조를 좀 더 비교 분석해 볼 필요성이 있음
표
ANTP 호메오도메인 전사인자 subclass별 분비능 비교. 호메오도메인 전사인자 중 가장 많은 수를 차지하는 ANTP family의 분비능을 각 subclass로 나누어 비교한 결과, Hox subclass보다 NKL subclass가 더 분비능이 높음을 알 수 있음. 특히, Nkx subclass member와 enrailed와 Vax1을 포함하는 Emx subclass의 분비능이 높음을 알 수 있음. 따라서, 이들 subclass가 공통적으로 가지는 호메오도메인 내의 아미노산 서열 또는 호메오도메인 외부의 특징적 아미노산 서열 및 구조를 좀 더 비교 분석해 볼 필요성이 있음
 표
분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자와 비분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자의 호메오도메인 서열 비교. (top) 분비성 호메오도메인 (40종) 서열을 multiple alignment하고 sequence 패턴을 분석함.(bottom) 마찬가지로, 비분비성 호메오도메인 (16종) 서열을 multiple alignment하고 sequence 패턴을 분석함. 이 과정에 호메오도메인 subclass에 따른 sequence bias를 고려하기 위해서 Henikoff’s weighting scheme를 적용함. 그 결과, 분비성 호메오도메인은 비분비성 호메오도메인에 비해 N-말단 20-30번 부위에 proline (P) 선호도가 있는 반면, 비분비성 호메오도메인에는 없는 것으로 확인됨
표
분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자와 비분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자의 호메오도메인 서열 비교. (top) 분비성 호메오도메인 (40종) 서열을 multiple alignment하고 sequence 패턴을 분석함.(bottom) 마찬가지로, 비분비성 호메오도메인 (16종) 서열을 multiple alignment하고 sequence 패턴을 분석함. 이 과정에 호메오도메인 subclass에 따른 sequence bias를 고려하기 위해서 Henikoff’s weighting scheme를 적용함. 그 결과, 분비성 호메오도메인은 비분비성 호메오도메인에 비해 N-말단 20-30번 부위에 proline (P) 선호도가 있는 반면, 비분비성 호메오도메인에는 없는 것으로 확인됨
![분비성 호메오도메인과 비분비성 호메오도메인의 구조 비교. (left) 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자인 ej139의 알려진 구조. (right) 비분비성 호메오도메인인 ej042의 알려진 구조. ‘그림16’의 orange box에 해당하는 residue(red stick)와 주변 5A 이내에 인접한 ATOM을 stick으로 표시함. 해당 sequence는 ej139에서는 PLP[23-25]의 패턴을 나타내고, ej042에서는 KYL[22-24]의 패턴을 나타냄. 현재 가설(호메오도메인이 DNA에 binding되지 않은 conformation[open form]을 가질 수 있고, 이 점이 secretion에 관련이 있다)을 바탕으로 추측해 볼 때, ej139 PLP의 양쪽 proline은 open form에서 helix-turn-helix 구조 안정화와 관련있을 수 있음. ej042의 L24는 hydrophobic core를 형성하면서 현재 conformation(closed form)에서의 helix packing에 관련된다고 추측됨 분비성 호메오도메인과 비분비성 호메오도메인의 구조 비교. (left) 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자인 ej139의 알려진 구조. (right) 비분비성 호메오도메인인 ej042의 알려진 구조. ‘그림16’의 orange box에 해당하는 residue(red stick)와 주변 5A 이내에 인접한 ATOM을 stick으로 표시함. 해당 sequence는 ej139에서는 PLP[23-25]의 패턴을 나타내고, ej042에서는 KYL[22-24]의 패턴을 나타냄. 현재 가설(호메오도메인이 DNA에 binding되지 않은 conformation[open form]을 가질 수 있고, 이 점이 secretion에 관련이 있다)을 바탕으로 추측해 볼 때, ej139 PLP의 양쪽 proline은 open form에서 helix-turn-helix 구조 안정화와 관련있을 수 있음. ej042의 L24는 hydrophobic core를 형성하면서 현재 conformation(closed form)에서의 helix packing에 관련된다고 추측됨](https://nrms.kisti.re.kr/bitextimages/TRKO201900025868/TRKO201900025868_41_image_1.png) 표
분비성 호메오도메인과 비분비성 호메오도메인의 구조 비교. (left) 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자인 ej139의 알려진 구조. (right) 비분비성 호메오도메인인 ej042의 알려진 구조. ‘그림16’의 orange box에 해당하는 residue(red stick)와 주변 5A 이내에 인접한 ATOM을 stick으로 표시함. 해당 sequence는 ej139에서는 PLP[23-25]의 패턴을 나타내고, ej042에서는 KYL[22-24]의 패턴을 나타냄. 현재 가설(호메오도메인이 DNA에 binding되지 않은 conformation[open form]을 가질 수 있고, 이 점이 secretion에 관련이 있다)을 바탕으로 추측해 볼 때, ej139 PLP의 양쪽 proline은 open form에서 helix-turn-helix 구조 안정화와 관련있을 수 있음. ej042의 L24는 hydrophobic core를 형성하면서 현재 conformation(closed form)에서의 helix packing에 관련된다고 추측됨
표
분비성 호메오도메인과 비분비성 호메오도메인의 구조 비교. (left) 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자인 ej139의 알려진 구조. (right) 비분비성 호메오도메인인 ej042의 알려진 구조. ‘그림16’의 orange box에 해당하는 residue(red stick)와 주변 5A 이내에 인접한 ATOM을 stick으로 표시함. 해당 sequence는 ej139에서는 PLP[23-25]의 패턴을 나타내고, ej042에서는 KYL[22-24]의 패턴을 나타냄. 현재 가설(호메오도메인이 DNA에 binding되지 않은 conformation[open form]을 가질 수 있고, 이 점이 secretion에 관련이 있다)을 바탕으로 추측해 볼 때, ej139 PLP의 양쪽 proline은 open form에서 helix-turn-helix 구조 안정화와 관련있을 수 있음. ej042의 L24는 hydrophobic core를 형성하면서 현재 conformation(closed form)에서의 helix packing에 관련된다고 추측됨
 표
호메오도메인 비의존성 분비. (A) 각 호메오도메인 subclass에 해당하는 전사인자들로부터 호메오도메인 만을 선택적으로 분리한 후 293T 세포에 발현한 후 각 호메오도메인들의 분비능을 조사함. 모든 종류의 호메오도메인은 그 자체만으로는 분비가 일어나지 않음 . (B) 기존에 알려진 분비형 호메오도메인 전사인자들에서 호메오도메인이 선택적으로 제거되었거나 호메오도메인 만을 가지는 변이형을 293T 세포에 발현 후 정상 호메오도메인 전사인자와 분비성을 비교 조사함. 기존에 알려진 분비형 호메오도메인 전사인자들인 Otx2, Pax6와 En2 등은 호메오도메인이 제거된 상태에서도 분비가 일어남을 확인하였음. 이는 특정 호메오도메인이 세포 외부로 분비를 결정하는 중요한 motif를 가지고 있지는 않다는 것과, 호메오도메인 이외의 부분에 호메오도메인 전사인자의 분비성을 조절하는 motif가 존재할 가능성을 시사함. (위) Media에 존재하는 단백질을 검출하는 dot-blot. (아래) 세포 내부에 있는 단백질들을 조사하는 Western blot
표
호메오도메인 비의존성 분비. (A) 각 호메오도메인 subclass에 해당하는 전사인자들로부터 호메오도메인 만을 선택적으로 분리한 후 293T 세포에 발현한 후 각 호메오도메인들의 분비능을 조사함. 모든 종류의 호메오도메인은 그 자체만으로는 분비가 일어나지 않음 . (B) 기존에 알려진 분비형 호메오도메인 전사인자들에서 호메오도메인이 선택적으로 제거되었거나 호메오도메인 만을 가지는 변이형을 293T 세포에 발현 후 정상 호메오도메인 전사인자와 분비성을 비교 조사함. 기존에 알려진 분비형 호메오도메인 전사인자들인 Otx2, Pax6와 En2 등은 호메오도메인이 제거된 상태에서도 분비가 일어남을 확인하였음. 이는 특정 호메오도메인이 세포 외부로 분비를 결정하는 중요한 motif를 가지고 있지는 않다는 것과, 호메오도메인 이외의 부분에 호메오도메인 전사인자의 분비성을 조절하는 motif가 존재할 가능성을 시사함. (위) Media에 존재하는 단백질을 검출하는 dot-blot. (아래) 세포 내부에 있는 단백질들을 조사하는 Western blot
 표
비호메오도메인 전사인자들의 분비능 및 세포 간 이동 조사. (A) HeLa 세포를 이용하여 호메오도메인 전사인자들과 다른 class 전사인자들(비호메오도메인 전사인자)의 분비능을 측정함. 그 결과 이들중 일부가 호메오도메인 전사인자들처럼 세포 외부로 분비가 됨을 확인함. 이를 통하여 전사인자들의 세포 간 이동이 호메오도메인 전사인자에만 국한된 현상이 아님을 확인함. 그러나 이들은 호메오도메인 전사인자들과는 다르게 heparin의 존재 여부에 관계없이 동일한 분비능을 보이는 것으로 보아, 호메오도메인 전사인자들의 분비경로와는 다른 경로를 통하여 세포 외부로 분비될 가능성을 생각해볼 수 있었음. (B) 전사인자의 신호(Red)만 나타나는 세포가 존재함을 확인함으로써, 분비능을 가지는 비호메오도메인 전사인자들중 일부(MAX, SOX2, 그리고 FOXA1)는 주변 세포로의 침투능력 또한 가지고 있음을 확인함. 이들의 주변세포로의 침투능 또한 호메오도메인 전사인자와는 다르게 heparin의 존재 여부와는 관계없이 동일하게 나타남을 확인함
표
비호메오도메인 전사인자들의 분비능 및 세포 간 이동 조사. (A) HeLa 세포를 이용하여 호메오도메인 전사인자들과 다른 class 전사인자들(비호메오도메인 전사인자)의 분비능을 측정함. 그 결과 이들중 일부가 호메오도메인 전사인자들처럼 세포 외부로 분비가 됨을 확인함. 이를 통하여 전사인자들의 세포 간 이동이 호메오도메인 전사인자에만 국한된 현상이 아님을 확인함. 그러나 이들은 호메오도메인 전사인자들과는 다르게 heparin의 존재 여부에 관계없이 동일한 분비능을 보이는 것으로 보아, 호메오도메인 전사인자들의 분비경로와는 다른 경로를 통하여 세포 외부로 분비될 가능성을 생각해볼 수 있었음. (B) 전사인자의 신호(Red)만 나타나는 세포가 존재함을 확인함으로써, 분비능을 가지는 비호메오도메인 전사인자들중 일부(MAX, SOX2, 그리고 FOXA1)는 주변 세포로의 침투능력 또한 가지고 있음을 확인함. 이들의 주변세포로의 침투능 또한 호메오도메인 전사인자와는 다르게 heparin의 존재 여부와는 관계없이 동일하게 나타남을 확인함
 표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 선택적 특성인 세포 침투능력. (A) 선행연구를 통해 규명한 비호메오도메인 전사인자들의 분비 및 세포 간 이동 능력과 호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포 간 이동의 공통적 특징을 규명하고자 비호메오도메인 전사인자들 중 분비능을 가지는 동시에 세포간 이동성을 보인 SOX2, FOXA1과, 분비능은 있지만 세포간 이동성이 없는 FOXP3, 비분비성 E2F6 단백질을 293T 세포에 발현 후 핵 추출물을 분리하여 해당 단백질들의 상대적 농도를 확인함. (B) 이들 전사인자들을 포함한 핵추출물을 HeLa 세포 배양액에 처리한 결과 이들 비호메오도메인 전사인자들은 모두가 HeLa 세포에 침투하지 못하고 세포 외부에 있음을 확인함. 이와 대조적으로 비분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자인 SHOX2의 경우는 HeLa 세포에 처리 시 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자인 EN2, OTX2와 마찬가지로 세포 내부로 침투하였음을 확인함. 이러한 결과를 통하여 비호메오도메인 전사인자들의 세포 간 이동은 호메오도메인 전사인자들처럼 단백질 자체로 이루어지는 것이 아니라 exosome과 같은 막구조를 통한 간접적인 현상일 가능성을 확인할 수 있었음. 또한 세포 외부로의 분비는 다양한 전사인자들의 특징이지만, 주변 세포막을 직접 침투할 수 있는 능력은 호메오도메인 전사인자들만의 선택적 특성이라는 점을 확인하였음
표
호메오도메인 전사인자의 선택적 특성인 세포 침투능력. (A) 선행연구를 통해 규명한 비호메오도메인 전사인자들의 분비 및 세포 간 이동 능력과 호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포 간 이동의 공통적 특징을 규명하고자 비호메오도메인 전사인자들 중 분비능을 가지는 동시에 세포간 이동성을 보인 SOX2, FOXA1과, 분비능은 있지만 세포간 이동성이 없는 FOXP3, 비분비성 E2F6 단백질을 293T 세포에 발현 후 핵 추출물을 분리하여 해당 단백질들의 상대적 농도를 확인함. (B) 이들 전사인자들을 포함한 핵추출물을 HeLa 세포 배양액에 처리한 결과 이들 비호메오도메인 전사인자들은 모두가 HeLa 세포에 침투하지 못하고 세포 외부에 있음을 확인함. 이와 대조적으로 비분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자인 SHOX2의 경우는 HeLa 세포에 처리 시 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자인 EN2, OTX2와 마찬가지로 세포 내부로 침투하였음을 확인함. 이러한 결과를 통하여 비호메오도메인 전사인자들의 세포 간 이동은 호메오도메인 전사인자들처럼 단백질 자체로 이루어지는 것이 아니라 exosome과 같은 막구조를 통한 간접적인 현상일 가능성을 확인할 수 있었음. 또한 세포 외부로의 분비는 다양한 전사인자들의 특징이지만, 주변 세포막을 직접 침투할 수 있는 능력은 호메오도메인 전사인자들만의 선택적 특성이라는 점을 확인하였음
 표
분비형 호메오도메인 전사인자의 구조적 특징. 91개 중 발현이 확인된 81개의 호메오도메인 전사인자들은 50% 이상 32개, 11-50%가 6개, 10% 이하가 43개임. 이들을 다시 50% 이상을 분비성, 50% 이하를 비분비성으로 분류하여 그들 사이의 아미노산 배열의 상호 연관성을 MEME 프로그램으로 분석한 후 3개 이상의 전사인자에서 공통적으로 나타난 6개 이상 20개 이하의 아미노산 서열로 이루어진 motif들 만을 다시 분석함. 분비성 전사인자들에서는 호메오도메인 내부의 여러 motif가 가장 연관성이 높게 나왔고, 그 다음으로 paired domain, LIM domain 등이 그다음 특징으로 나옴. 비분비성에서도 마찬가지로 호메오도메인 내부의 motif와 POU domain 등이 높은 연관성을 가지는 것으로 나타남. 이들 중 유일하게 분비성 전사인자의 Motif 7이 호메오도메인 외부 아미노산 서열들로 총 6개의 전사인자에서 관찰되었으며, 이는 반복된 Histidine을 가지고 있음
표
분비형 호메오도메인 전사인자의 구조적 특징. 91개 중 발현이 확인된 81개의 호메오도메인 전사인자들은 50% 이상 32개, 11-50%가 6개, 10% 이하가 43개임. 이들을 다시 50% 이상을 분비성, 50% 이하를 비분비성으로 분류하여 그들 사이의 아미노산 배열의 상호 연관성을 MEME 프로그램으로 분석한 후 3개 이상의 전사인자에서 공통적으로 나타난 6개 이상 20개 이하의 아미노산 서열로 이루어진 motif들 만을 다시 분석함. 분비성 전사인자들에서는 호메오도메인 내부의 여러 motif가 가장 연관성이 높게 나왔고, 그 다음으로 paired domain, LIM domain 등이 그다음 특징으로 나옴. 비분비성에서도 마찬가지로 호메오도메인 내부의 motif와 POU domain 등이 높은 연관성을 가지는 것으로 나타남. 이들 중 유일하게 분비성 전사인자의 Motif 7이 호메오도메인 외부 아미노산 서열들로 총 6개의 전사인자에서 관찰되었으며, 이는 반복된 Histidine을 가지고 있음
 표
분비성 및 비분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자들의 아미노산 배열 비교. (A) 분비성 (sHP, 푸른색) 및 비분비성 (ns-HP, 붉은색) 호메오도메인 전사인자의 아미노산 서열을 MUSCLE multiple alignment software를 이용하여 align 한 후 특정 부위에서 반복되어 나타나는 유사한 특징의 아미노산의 숫자를 Y-축으로 나타냄. 분비성 판별 기준을 증감하면서 이 과정에서도 peak 크기가 변하지 않는 부분을 분비성 또는 비분비성 전사인자들에 공통적으로 보존되어 있는 부위로 잠정 판정함. (B) 그 결과 호메오도메인 (약 600-800번에 걸쳐서 분포) 앞쪽의 133번과 348번, 그리고 호메오도메인 뒤쪽으로 1207번 위치에 분포하는 아미노산 서열이 분비성과 비분비성에 다른 특징을 가짐을 확인함. 해당 부위를 화살표로 표시함. 왼쪽은 호메오도메인의 분포만을 별도로 나타낸 그림
표
분비성 및 비분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자들의 아미노산 배열 비교. (A) 분비성 (sHP, 푸른색) 및 비분비성 (ns-HP, 붉은색) 호메오도메인 전사인자의 아미노산 서열을 MUSCLE multiple alignment software를 이용하여 align 한 후 특정 부위에서 반복되어 나타나는 유사한 특징의 아미노산의 숫자를 Y-축으로 나타냄. 분비성 판별 기준을 증감하면서 이 과정에서도 peak 크기가 변하지 않는 부분을 분비성 또는 비분비성 전사인자들에 공통적으로 보존되어 있는 부위로 잠정 판정함. (B) 그 결과 호메오도메인 (약 600-800번에 걸쳐서 분포) 앞쪽의 133번과 348번, 그리고 호메오도메인 뒤쪽으로 1207번 위치에 분포하는 아미노산 서열이 분비성과 비분비성에 다른 특징을 가짐을 확인함. 해당 부위를 화살표로 표시함. 왼쪽은 호메오도메인의 분포만을 별도로 나타낸 그림
 표
변이형 호메오도메인 전사인자의 주변 세포 침투능력 검증. ‘그림 24’에서 분비능 측정에 이용한 변이형 호메오도메인 전사인자들을 대상으로 하여 이들의 주변 세포로의 침투 능력을 조사하였음. 분비능을 가지는 소수성 아미노산 대신 극성 아미노산을 가지도록 만든 호메오도메인 전사인자-변이형인 EN2-L191E, OTX2-F258E, PAX6-L130E, 그리고 VAX1-L305E의 경우 의 경우, 호메오도메인 전사인자의 신호(Red)만 나타나는 세포의 수가 현저히 감소하였음. 반면 비분비성 특징을 나타내는 극성 아미노산 대신 소수성 아미노산을 가지도록 만든 호메오도메인 전사인자-변이형인 HOXD4-S233L과 SHOX2-P305L의 경우에는 호메오도메인 전사인자의 신호(Red)만 나타나는 세포의 수가 크게 증가하였음. (A) HeLa 세포를 이용한 변이형 호메오도메인 전사인자의 침투능력 검증. (B) 생쥐 배아 뇌실을 이용한 변이형 호메오도메인 전사인자의 생체내에서의 세포 간이동 검증
표
변이형 호메오도메인 전사인자의 주변 세포 침투능력 검증. ‘그림 24’에서 분비능 측정에 이용한 변이형 호메오도메인 전사인자들을 대상으로 하여 이들의 주변 세포로의 침투 능력을 조사하였음. 분비능을 가지는 소수성 아미노산 대신 극성 아미노산을 가지도록 만든 호메오도메인 전사인자-변이형인 EN2-L191E, OTX2-F258E, PAX6-L130E, 그리고 VAX1-L305E의 경우 의 경우, 호메오도메인 전사인자의 신호(Red)만 나타나는 세포의 수가 현저히 감소하였음. 반면 비분비성 특징을 나타내는 극성 아미노산 대신 소수성 아미노산을 가지도록 만든 호메오도메인 전사인자-변이형인 HOXD4-S233L과 SHOX2-P305L의 경우에는 호메오도메인 전사인자의 신호(Red)만 나타나는 세포의 수가 크게 증가하였음. (A) HeLa 세포를 이용한 변이형 호메오도메인 전사인자의 침투능력 검증. (B) 생쥐 배아 뇌실을 이용한 변이형 호메오도메인 전사인자의 생체내에서의 세포 간이동 검증
 표
Vax1의 세포 내 소기관 내의 위치. Vax1의 subcellular organelle marker와의 co-staining을 통해 Vax1은 핵에 주로 분포하며 세포질에서는 응집된 형태로 나타남을 알 수 있음. 이러한 응집된 Vax1 분포는 핵막 및 ER과는 중복되어 있지만, Golgi와는 중복되어 있지 않음. 이는 일반적인 분비단백질이 거치는 ER-Golgi를 통한 분비를 따르지는 않음을 시사함. 그 외 mitochondria, lysosome 등의 세포 소기관과 endosome, autophagosome 등 단백질의 세포 내 이동에 관여하는 이동낭 (trafficking vesicle) 등과도 겹치지 않음. 이는 Vax1이 세포 핵 내에서 출발하여 세포 외부로 특수한 수송 과정을 통해 분비됨을 시사함
표
Vax1의 세포 내 소기관 내의 위치. Vax1의 subcellular organelle marker와의 co-staining을 통해 Vax1은 핵에 주로 분포하며 세포질에서는 응집된 형태로 나타남을 알 수 있음. 이러한 응집된 Vax1 분포는 핵막 및 ER과는 중복되어 있지만, Golgi와는 중복되어 있지 않음. 이는 일반적인 분비단백질이 거치는 ER-Golgi를 통한 분비를 따르지는 않음을 시사함. 그 외 mitochondria, lysosome 등의 세포 소기관과 endosome, autophagosome 등 단백질의 세포 내 이동에 관여하는 이동낭 (trafficking vesicle) 등과도 겹치지 않음. 이는 Vax1이 세포 핵 내에서 출발하여 세포 외부로 특수한 수송 과정을 통해 분비됨을 시사함
 표
Vax1 분비에 미치는 세포 내 단백질 이동 억제 약물의 효과. Vax1의 분비가 기존 알려진 정형적인 ER-Golgi 경로에 대한 억제 약물인 brefeldinA(12시간); 핵공을 통한 핵->세포질로의 단백질 이동을 억제하는 leptomycinB(4시간); 리소좀에서의 단백질 분해를 억제하는 bafilomycinA1(24시간); proteasome을 통한 단백질 분해를 억제하는 MG132(4시간); PI3K의 활성 억제를 통해 autophagy를 저해하는 3-MA(12시간) 후 세포 배양액에 분비된 Vax1 단백질의 양을 비교함. 그 결과, Vax1의 분비는 ER-Golgi를 매개하지 않으며, 핵공을 통한 세포질로의 이동도 필요하지 않음을 확인함. 또한, Vax1은 proteasome을 통한 분해보다는 리소좀을 통해 분해될 가능성이 높고, 이 과정은 세포질에서 단백질을 리소좀으로 이동하는 autophagy를 매개하지는 않을 것이라는 가능성을 시사함
표
Vax1 분비에 미치는 세포 내 단백질 이동 억제 약물의 효과. Vax1의 분비가 기존 알려진 정형적인 ER-Golgi 경로에 대한 억제 약물인 brefeldinA(12시간); 핵공을 통한 핵->세포질로의 단백질 이동을 억제하는 leptomycinB(4시간); 리소좀에서의 단백질 분해를 억제하는 bafilomycinA1(24시간); proteasome을 통한 단백질 분해를 억제하는 MG132(4시간); PI3K의 활성 억제를 통해 autophagy를 저해하는 3-MA(12시간) 후 세포 배양액에 분비된 Vax1 단백질의 양을 비교함. 그 결과, Vax1의 분비는 ER-Golgi를 매개하지 않으며, 핵공을 통한 세포질로의 이동도 필요하지 않음을 확인함. 또한, Vax1은 proteasome을 통한 분해보다는 리소좀을 통해 분해될 가능성이 높고, 이 과정은 세포질에서 단백질을 리소좀으로 이동하는 autophagy를 매개하지는 않을 것이라는 가능성을 시사함
 표
Vax1의 분비에 미치는 소포체 위치화의 조사. (A) HeLa 세포에 Vax1 일반형과 소포체 위치화 신호 (KDEL: Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu) 추가 돌연변이를 각각 과발현 후 배양액에 분비된 Vax1의 양과 세포 내 Vax1의 양을 Dot-Blot (DB)과 WB으로 조사하여 상대적 분비 계수를 측정함. (B) HeLa 세포에 Vax1-KDEL-V5-IRES-EGFP를 발현하고 세포 내 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. GFP (회색)는 Vax1 단백질 (붉은색)들과 동일한 DNA construct에 encoding 되어 있으며 독립적으로 번역이 되므로 Vax1을 발현하는 세포를 표지함. 소포체 (녹색)는 소포체 단백질 중의 하나인 Calnexin 단백질을 항원으로 인식하는 항체를 사용하여 표지함
표
Vax1의 분비에 미치는 소포체 위치화의 조사. (A) HeLa 세포에 Vax1 일반형과 소포체 위치화 신호 (KDEL: Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu) 추가 돌연변이를 각각 과발현 후 배양액에 분비된 Vax1의 양과 세포 내 Vax1의 양을 Dot-Blot (DB)과 WB으로 조사하여 상대적 분비 계수를 측정함. (B) HeLa 세포에 Vax1-KDEL-V5-IRES-EGFP를 발현하고 세포 내 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. GFP (회색)는 Vax1 단백질 (붉은색)들과 동일한 DNA construct에 encoding 되어 있으며 독립적으로 번역이 되므로 Vax1을 발현하는 세포를 표지함. 소포체 (녹색)는 소포체 단백질 중의 하나인 Calnexin 단백질을 항원으로 인식하는 항체를 사용하여 표지함
 표
Vax1 단백질의 핵막 구조 매개 분비. Vax1 단백질의 비정형적 이동이 핵막에서 유래한 vesicle을 매개할 가능성을 확인하기 위해 endosome 막에서 small vesicle을 형성하는 정상 Vps4와 autophagy 과정에서 유비퀴틴화된 단백질을 막구조로 이동하는 역할을 하는 p62를 HeLa Vax1과 함께 발현한 후 Vax1의 분비(A)와 세포 내 분포(B)를 조사함. 그 결과 Vps4는 Vax1의 분비를 증진하는 것을 알 수 있음. 반대로 p62는 Vax1의 분비를 억제함. 이 결과들은 Vax1의 분비에 Vps4가 관여하는 MVB는 긍정적 연관성을 가지고 있으며, autophagy는 부정적 연관성을 가지고 있음을 시사함
표
Vax1 단백질의 핵막 구조 매개 분비. Vax1 단백질의 비정형적 이동이 핵막에서 유래한 vesicle을 매개할 가능성을 확인하기 위해 endosome 막에서 small vesicle을 형성하는 정상 Vps4와 autophagy 과정에서 유비퀴틴화된 단백질을 막구조로 이동하는 역할을 하는 p62를 HeLa Vax1과 함께 발현한 후 Vax1의 분비(A)와 세포 내 분포(B)를 조사함. 그 결과 Vps4는 Vax1의 분비를 증진하는 것을 알 수 있음. 반대로 p62는 Vax1의 분비를 억제함. 이 결과들은 Vax1의 분비에 Vps4가 관여하는 MVB는 긍정적 연관성을 가지고 있으며, autophagy는 부정적 연관성을 가지고 있음을 시사함
 표
효모 vacuole을 매개로 한 Vax1의 수송. 그림 8에서 제시된 lysosome을 매개로한 Vax1의 분비 과정은 효모의 vacuole을 통한 세포내 단백질의 분비 과정과 유사점이 있다. 이를 증명하기 위해 Vax1을 효모에 발현 후 Vax1의 분비와 이동을 검증함. Vax1-GFP 단백질을 정상 (wt) 및 vacuole로의 소포 이동이 저해된 ypt7d 효모에 발현 한 후 세포 내 분포 (왼쪽 그림)와 세포 배양액으로의 분비를 각각 면역형광염색과 Western blotting으로 조사함. 그 결과 Vax1은 정상 효모 배양액에서는 관찰이 되지만 ypt7d 효모에서는 관찰이 되지 않음. 이는 Vax1이 세포 내 막구조 소포에 의해 vaculoe로 이동한 후 분비가 된다는 것을 의미한다. 이를 좀 더 명확히 증명하기 위해 wt과 ypt7d 효모에서 vaculoe을 분리한 후 vacuole에 포함된 Vax1을 관찰한 결과, wt에 비해 ypt7d 효모의 vacuole에 있는 Vax1 단백질의 양이 현저히 적음을 알 수 있었음
표
효모 vacuole을 매개로 한 Vax1의 수송. 그림 8에서 제시된 lysosome을 매개로한 Vax1의 분비 과정은 효모의 vacuole을 통한 세포내 단백질의 분비 과정과 유사점이 있다. 이를 증명하기 위해 Vax1을 효모에 발현 후 Vax1의 분비와 이동을 검증함. Vax1-GFP 단백질을 정상 (wt) 및 vacuole로의 소포 이동이 저해된 ypt7d 효모에 발현 한 후 세포 내 분포 (왼쪽 그림)와 세포 배양액으로의 분비를 각각 면역형광염색과 Western blotting으로 조사함. 그 결과 Vax1은 정상 효모 배양액에서는 관찰이 되지만 ypt7d 효모에서는 관찰이 되지 않음. 이는 Vax1이 세포 내 막구조 소포에 의해 vaculoe로 이동한 후 분비가 된다는 것을 의미한다. 이를 좀 더 명확히 증명하기 위해 wt과 ypt7d 효모에서 vaculoe을 분리한 후 vacuole에 포함된 Vax1을 관찰한 결과, wt에 비해 ypt7d 효모의 vacuole에 있는 Vax1 단백질의 양이 현저히 적음을 알 수 있었음
 표
분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자의 가능한 세포 내 이동 경로. 호메오도메인 전사인자가 세포 외부로 방출되는 과정은 세포질에서 세포막을 직접 투과하는 과정이나 세포질에 분비과립 내에 위치하여 세포막과 융합 후 분비되는 방식이 가능함. 세포질 내 단백질 형태나 분비과립 형태로 존재하기 위해서 호메오도메인 전사인자들은 핵에서 핵공을 통해 외부로 나오거나 핵 탈출 중간체를 이용해 분비 과립 형태로 세포질로 이동함. 이러한 과정은 직접 핵막이 세포질로 바로 노출되거나 핵외막과 연결된 소포체를 매개하는 방식이 가능함. 이러한 다양한 가능성을 염두에 두고 향후 호메오도메인 전사인자 단백질들의 분비 과정을 규명하는 연구를 계획할 예정임
표
분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자의 가능한 세포 내 이동 경로. 호메오도메인 전사인자가 세포 외부로 방출되는 과정은 세포질에서 세포막을 직접 투과하는 과정이나 세포질에 분비과립 내에 위치하여 세포막과 융합 후 분비되는 방식이 가능함. 세포질 내 단백질 형태나 분비과립 형태로 존재하기 위해서 호메오도메인 전사인자들은 핵에서 핵공을 통해 외부로 나오거나 핵 탈출 중간체를 이용해 분비 과립 형태로 세포질로 이동함. 이러한 과정은 직접 핵막이 세포질로 바로 노출되거나 핵외막과 연결된 소포체를 매개하는 방식이 가능함. 이러한 다양한 가능성을 염두에 두고 향후 호메오도메인 전사인자 단백질들의 분비 과정을 규명하는 연구를 계획할 예정임
 표
핵 탈출 비의존성 Vax1 분비. HeLa 세포에 Vax1-V5-IRES-EGFP를 발현하고 해당 세포를 12시간 동안 MeOH 또는 핵공 의존성 핵 탈출을 억제하는 leptomycin B (LMB)를 처리 후 세포 배양액에 존재하는 Vax1을 검출함. LMB 처리는 Vax1의 세포 배양액으로 분비된 Vax1의 양을 증가시킴. 해당 세포들에서 Vax1과 동시에 발현된 EGFP의 경우는 어떤 조건에서도 세포 배양액으로 분비가 되지 않는 것으로 보아, LMB 처리에 의한 Vax1의 분비 증가는 Vax1의 분비가 핵공에 의한 것이 아님을 시사함
표
핵 탈출 비의존성 Vax1 분비. HeLa 세포에 Vax1-V5-IRES-EGFP를 발현하고 해당 세포를 12시간 동안 MeOH 또는 핵공 의존성 핵 탈출을 억제하는 leptomycin B (LMB)를 처리 후 세포 배양액에 존재하는 Vax1을 검출함. LMB 처리는 Vax1의 세포 배양액으로 분비된 Vax1의 양을 증가시킴. 해당 세포들에서 Vax1과 동시에 발현된 EGFP의 경우는 어떤 조건에서도 세포 배양액으로 분비가 되지 않는 것으로 보아, LMB 처리에 의한 Vax1의 분비 증가는 Vax1의 분비가 핵공에 의한 것이 아님을 시사함
 표
Vax1 핵 위치 돌연변이의 조사. (A) Vax1의 호메오도메인 상에 존재하는 핵 위치신호(nuclear localization signal, NLS)에 해당하는 151번과 152번 위치에 있는 arginine(R) 아미노산을 alanine(A)으로 변경함. 정상 Vax1과 Vax1의 NLS 변이형 Vax1(RR/AA)를 HeLa 세포에 과발현한 후 해당 단백질들의 분비를 DB로 조사하고 (B), 이들 단백질들의 세포 내 상대량을 RIPA buffer로 추출한 세포 내 단백질들을 WB로 조사함. Vax1(RR/AA)는 정상 Vax1에 비해 RIPA에 의해 추출되는 분획(soluble, S)에 양이 줄어들어 있었으며, RIPA에 의해 추출되지 않은 분획(precipitate, P)에 집중되어 있음. 이는 Vax1(RR/AA)가 세포 내에서 응집체를 만들 가능성을 시사함. (D) 정상 Vax1과 Vax1의 NLS 변이형 Vax1(RR/AA)의 세포 내 위치를 핵과 세포질 나눈 세포 분획의 WB를 통해 조사함. 또한, 각 분획에서 Vax1의 응집 여부를 RIPA 추출 여부를 통해 조사함. (E) 정상 Vax1과 Vax1의 NLS 변이형 Vax1(RR/AA)의 세포 내 위치를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. DAPI는 핵내 DNA를 표지하며, GFP는 Vax1 단백질들과 동일한 DNA construct에 encoding 되어 있으며 독립적으로 번역이 되므로 Vax1을 발현하는 세포를 표지함. GFP는 주로 세포질에 분포하며 일부는 핵에도 존재함
표
Vax1 핵 위치 돌연변이의 조사. (A) Vax1의 호메오도메인 상에 존재하는 핵 위치신호(nuclear localization signal, NLS)에 해당하는 151번과 152번 위치에 있는 arginine(R) 아미노산을 alanine(A)으로 변경함. 정상 Vax1과 Vax1의 NLS 변이형 Vax1(RR/AA)를 HeLa 세포에 과발현한 후 해당 단백질들의 분비를 DB로 조사하고 (B), 이들 단백질들의 세포 내 상대량을 RIPA buffer로 추출한 세포 내 단백질들을 WB로 조사함. Vax1(RR/AA)는 정상 Vax1에 비해 RIPA에 의해 추출되는 분획(soluble, S)에 양이 줄어들어 있었으며, RIPA에 의해 추출되지 않은 분획(precipitate, P)에 집중되어 있음. 이는 Vax1(RR/AA)가 세포 내에서 응집체를 만들 가능성을 시사함. (D) 정상 Vax1과 Vax1의 NLS 변이형 Vax1(RR/AA)의 세포 내 위치를 핵과 세포질 나눈 세포 분획의 WB를 통해 조사함. 또한, 각 분획에서 Vax1의 응집 여부를 RIPA 추출 여부를 통해 조사함. (E) 정상 Vax1과 Vax1의 NLS 변이형 Vax1(RR/AA)의 세포 내 위치를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. DAPI는 핵내 DNA를 표지하며, GFP는 Vax1 단백질들과 동일한 DNA construct에 encoding 되어 있으며 독립적으로 번역이 되므로 Vax1을 발현하는 세포를 표지함. GFP는 주로 세포질에 분포하며 일부는 핵에도 존재함
 표
분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자의 핵 탈출 중간체 발견. 분비능을 가지는 호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포내에서의 분포 형태를 면역형광염색법으로 관찰하는 과정에서 그들이 세포핵 내부에 존재하고 있음은 물론 세포핵에서 가까운 부위에서 작은 소낭(small vesicle)의 형태로도 존재하고 있음을 확인하였음. 또한 이들 중의 일부는 세포핵에서 곧바로 나오는듯한 모습을 하고 있음을 확인할 수 있었으며, 이들을 감싸고 있는 소낭이 모두 핵막에 존재하는 핵막 단백질인 LaminB로 구성되어 있음을 확인할 수 있었음. 이러한 사실은 세포핵 안에 존재하던 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자들이 세포핵 바깥으로 배출되는 과정에서 그것이 직접 핵막을 통과하여 분비될 가능성을 제시함
표
분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자의 핵 탈출 중간체 발견. 분비능을 가지는 호메오도메인 전사인자의 세포내에서의 분포 형태를 면역형광염색법으로 관찰하는 과정에서 그들이 세포핵 내부에 존재하고 있음은 물론 세포핵에서 가까운 부위에서 작은 소낭(small vesicle)의 형태로도 존재하고 있음을 확인하였음. 또한 이들 중의 일부는 세포핵에서 곧바로 나오는듯한 모습을 하고 있음을 확인할 수 있었으며, 이들을 감싸고 있는 소낭이 모두 핵막에 존재하는 핵막 단백질인 LaminB로 구성되어 있음을 확인할 수 있었음. 이러한 사실은 세포핵 안에 존재하던 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자들이 세포핵 바깥으로 배출되는 과정에서 그것이 직접 핵막을 통과하여 분비될 가능성을 제시함
 표
Vax1의 핵 탈출 중간체 위치. (A) Vax1 호메오도메인 전사인자를 HeLa 세포에 발현 시 핵 내 뿐만 아니 라 핵 주변 구조에도 위치함을 알 수 있음. 이러한 핵 주변 구조체는 핵 내막 단백질인 laminB와 소포체 막단백질인 ER-dsRed 단백질을 함께 포함함을 알 수 있음. (B) 이러한 Vax1의 핵막 유래 구조체 내 위치는 생쥐 시신경 신경조세포 전구세포 (optic stalk astrocyte precursor (OS-APC))에서도 관찰됨. 특히 Vax1을 포함하는 구조체는 단일막구조 뿐만 아니라 이중막구조까지 관찰되며 일부는 핵막에서 돌출된 형태를 보임
표
Vax1의 핵 탈출 중간체 위치. (A) Vax1 호메오도메인 전사인자를 HeLa 세포에 발현 시 핵 내 뿐만 아니 라 핵 주변 구조에도 위치함을 알 수 있음. 이러한 핵 주변 구조체는 핵 내막 단백질인 laminB와 소포체 막단백질인 ER-dsRed 단백질을 함께 포함함을 알 수 있음. (B) 이러한 Vax1의 핵막 유래 구조체 내 위치는 생쥐 시신경 신경조세포 전구세포 (optic stalk astrocyte precursor (OS-APC))에서도 관찰됨. 특히 Vax1을 포함하는 구조체는 단일막구조 뿐만 아니라 이중막구조까지 관찰되며 일부는 핵막에서 돌출된 형태를 보임
 표
TorsinA에 의한 Vax1 분비 조절. (A) HeLa 세포에 TorsinA-WT과 ATPase inactive TorsinA-ΔE를 V5-Vax1과 함께 과발현 후 배양액에 분비된 Vax1의 양과 세포 내 Vax1의 양을 Dot-Blot (DB)과 WB으로 조사함. (B) TorsinA의 Vax1의 세포 내 분포에 미치는 영향을 면역형 광염색으로 조사함. (C) Vax1과 TorsinA를 각각 표지한 입자가 핵막으로부터 돌출된 부분에 함께 위치하는 것을 면역투과전자현미경 기법으로 확인함. (D) Human TorsinA에 대한 siRNA를 2종 합성하여 Vax1을 과발현하는 HeLa 세포에 처리 후 Vax1의 분비를 조사함. (E) TorsinA siRNA를 처리한 세포에서 Vax1의 세포 내 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사함
표
TorsinA에 의한 Vax1 분비 조절. (A) HeLa 세포에 TorsinA-WT과 ATPase inactive TorsinA-ΔE를 V5-Vax1과 함께 과발현 후 배양액에 분비된 Vax1의 양과 세포 내 Vax1의 양을 Dot-Blot (DB)과 WB으로 조사함. (B) TorsinA의 Vax1의 세포 내 분포에 미치는 영향을 면역형 광염색으로 조사함. (C) Vax1과 TorsinA를 각각 표지한 입자가 핵막으로부터 돌출된 부분에 함께 위치하는 것을 면역투과전자현미경 기법으로 확인함. (D) Human TorsinA에 대한 siRNA를 2종 합성하여 Vax1을 과발현하는 HeLa 세포에 처리 후 Vax1의 분비를 조사함. (E) TorsinA siRNA를 처리한 세포에서 Vax1의 세포 내 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사함
 표
Torsin에 의한 호메오도메인 단백질 분비 조절. 선행연구를 통해 VAX1 단백질의 분비가 ER 내부/핵막 간 단백질인 Torsin에 의해 조절됨을 증명한 바 있다. 이러한 Torsin의 기능이 다른 호메오도메인 전사인자의 분비에도 관련되어 있는지를 증명하고자 정상 (WT)과 비활성화 (dE) Torsin을 각 분비성 호메오도메인 단백질과 함께 HeLa 세포에 발현 후 세포 외부로 분비된 호메오도메인 단백질을 dot blot으로 검증하였다. 그 결과 Torsin WT은 분비를 촉진하는 반면 dE 변이형은 이들 단백질의 분비를 공통적으로 억제하였다. 또한 dE가 함께 발현된 세포에서 호메오도메인 단백질은 정상 세포에서 발현시 관찰되는 핵 돌출구조가 관찰되지 않음을 알 수 있다. 이는 Torsin에 의해 유도되는 핵 내막 유래 소포에 의해 호메오도메인 전사인자 단백질들의 분비가 매개된다는 것을 간접적으로 제시한다
표
Torsin에 의한 호메오도메인 단백질 분비 조절. 선행연구를 통해 VAX1 단백질의 분비가 ER 내부/핵막 간 단백질인 Torsin에 의해 조절됨을 증명한 바 있다. 이러한 Torsin의 기능이 다른 호메오도메인 전사인자의 분비에도 관련되어 있는지를 증명하고자 정상 (WT)과 비활성화 (dE) Torsin을 각 분비성 호메오도메인 단백질과 함께 HeLa 세포에 발현 후 세포 외부로 분비된 호메오도메인 단백질을 dot blot으로 검증하였다. 그 결과 Torsin WT은 분비를 촉진하는 반면 dE 변이형은 이들 단백질의 분비를 공통적으로 억제하였다. 또한 dE가 함께 발현된 세포에서 호메오도메인 단백질은 정상 세포에서 발현시 관찰되는 핵 돌출구조가 관찰되지 않음을 알 수 있다. 이는 Torsin에 의해 유도되는 핵 내막 유래 소포에 의해 호메오도메인 전사인자 단백질들의 분비가 매개된다는 것을 간접적으로 제시한다
 표
세포 내 Vax1 농도 구배를 통한 BafilomycinA1의 작용 역추론. Vax1의 분비를 극적으로 증가시키는 bafilomycinA1의 적용 범위를 추론하기 위해 Vax1의 세포 내 농도를 조절하여 세포 분획 별로 조사함. BafilomycinA1의 첨가로 인해 Vax1의 세포 외 분비 (Media)가 증가하며, 동시에 세포 내 (WCE; whole cell extract) Vax1의 양적인 증가를 확인함. 세포 분획법을 통해 세포질 (Cyto; cytoplasm)과 세포핵 (Nuc; nucleus)을 분리하여 각각의 분획에 존재하는 Vax1의 양을 비교하여 세포 내 Vax1의 양적인 증가가 세포질에서의 Vax1 증가에서 기인한 것임을 확인함
표
세포 내 Vax1 농도 구배를 통한 BafilomycinA1의 작용 역추론. Vax1의 분비를 극적으로 증가시키는 bafilomycinA1의 적용 범위를 추론하기 위해 Vax1의 세포 내 농도를 조절하여 세포 분획 별로 조사함. BafilomycinA1의 첨가로 인해 Vax1의 세포 외 분비 (Media)가 증가하며, 동시에 세포 내 (WCE; whole cell extract) Vax1의 양적인 증가를 확인함. 세포 분획법을 통해 세포질 (Cyto; cytoplasm)과 세포핵 (Nuc; nucleus)을 분리하여 각각의 분획에 존재하는 Vax1의 양을 비교하여 세포 내 Vax1의 양적인 증가가 세포질에서의 Vax1 증가에서 기인한 것임을 확인함
 표
Hsp70에 의한 Vax1 분비 조절. Vax1과 상호작용하는 것으로 확인된 단백질들 중 세포 내 단백질들의 용해도와 관련이 있는 후보를 검색한 결과 heat-shock protein 70 (Hsp70)과 Hsp28이 확인됨 (Kim et al. (2014)). 이 중 Hsp70이 Vax1의 세포 내 용해도를 조절하여 Vax1 단백질의 분비를 조절할 가능성을 확인하기 위해 Vax1을 Hsp70이 과발현된 상태에서 함께 발현하거나, siRNA를 이용하여 Hsp70의 양을 줄인 세포에 Vax1을 발현하고 Vax1의 세포 외 분비를 DB로 조사함. 세포 내 Vax1 양은 WB로 조사함. Vax1은 Hsp70 양이 증가된 세포에서 분비가 촉진되고, Hsp70 양이 감소된 세포에서는 분비가 감소함을 확인함. 이는 Hsp70이 Vax1의 세포 내 용해도를 증가시켜 분비를 촉진할 것이라는 가설을 지지함
표
Hsp70에 의한 Vax1 분비 조절. Vax1과 상호작용하는 것으로 확인된 단백질들 중 세포 내 단백질들의 용해도와 관련이 있는 후보를 검색한 결과 heat-shock protein 70 (Hsp70)과 Hsp28이 확인됨 (Kim et al. (2014)). 이 중 Hsp70이 Vax1의 세포 내 용해도를 조절하여 Vax1 단백질의 분비를 조절할 가능성을 확인하기 위해 Vax1을 Hsp70이 과발현된 상태에서 함께 발현하거나, siRNA를 이용하여 Hsp70의 양을 줄인 세포에 Vax1을 발현하고 Vax1의 세포 외 분비를 DB로 조사함. 세포 내 Vax1 양은 WB로 조사함. Vax1은 Hsp70 양이 증가된 세포에서 분비가 촉진되고, Hsp70 양이 감소된 세포에서는 분비가 감소함을 확인함. 이는 Hsp70이 Vax1의 세포 내 용해도를 증가시켜 분비를 촉진할 것이라는 가설을 지지함
 표
Vax1과 Hsp70 사이의 세포 내 관계 조사. (A) Vax1과 Hsp70의 독립적 세포 내 분포와 공동으로 발현된 세포에서의 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. Vax1의 경우는 Hsp70 존재 여부와 상관없이 지속적으로 세포핵 내에 존재함. Hsp70은 그 자체로는 주로 세포질에 존재하지만, Vax1과 함께 발현되면 세포핵 내에서도 일부가 관찰됨. (B) Vax1과 Hsp70 사이의 세포 내 분포를 세포 분획별 웨스턴 블롯 (WB)으로 조사함. (A)의 결과와 유사하게 Hsp70은 Vax1과 함께 발현된 상황에서는 세포핵에서도 관찰이 됨. 이 경과들은 Vax1이 Hsp70과 결합하여 세포핵 내부로 끌고 갈 가능성을 의미한다. (C) Vax1과 Hsp70 사이의 상호작용을 co-IP를 이용하여 직접 조사함. 그 결과 HA-Hsp70이 V5 항체를 이용하여 V5-Vax1을 IP하면 함께 분리됨을 알 수 있음
표
Vax1과 Hsp70 사이의 세포 내 관계 조사. (A) Vax1과 Hsp70의 독립적 세포 내 분포와 공동으로 발현된 세포에서의 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. Vax1의 경우는 Hsp70 존재 여부와 상관없이 지속적으로 세포핵 내에 존재함. Hsp70은 그 자체로는 주로 세포질에 존재하지만, Vax1과 함께 발현되면 세포핵 내에서도 일부가 관찰됨. (B) Vax1과 Hsp70 사이의 세포 내 분포를 세포 분획별 웨스턴 블롯 (WB)으로 조사함. (A)의 결과와 유사하게 Hsp70은 Vax1과 함께 발현된 상황에서는 세포핵에서도 관찰이 됨. 이 경과들은 Vax1이 Hsp70과 결합하여 세포핵 내부로 끌고 갈 가능성을 의미한다. (C) Vax1과 Hsp70 사이의 상호작용을 co-IP를 이용하여 직접 조사함. 그 결과 HA-Hsp70이 V5 항체를 이용하여 V5-Vax1을 IP하면 함께 분리됨을 알 수 있음
 표
Vax1 막소포와 핵막 구조체, 그리고 Hsp70의 관계 조사. (A) Vax1의 막소포와 Hsp70의 세포 내 상호 분포를 핵막 구조체 표시자인 LaminB, LaminC 단백질과 함께 면역형광염색으로 조사함. (화살표 머리) Vax1, Hsp70, 핵막 구조체가 하나의 신호로 겹쳐지는 것으로 보아 Vax1의 막소포는 핵막에서 유래되었으며, Vax1에 의해 세포핵으로 내제화된 Hsp70이 Vax1의 막소포 형성에 참여하고 있음을 유추할 수 있음. (B) 핵막 구조체 단백질 lamin과 Vax1 사이의 상호작용을 면역침강반응으로 조사함
표
Vax1 막소포와 핵막 구조체, 그리고 Hsp70의 관계 조사. (A) Vax1의 막소포와 Hsp70의 세포 내 상호 분포를 핵막 구조체 표시자인 LaminB, LaminC 단백질과 함께 면역형광염색으로 조사함. (화살표 머리) Vax1, Hsp70, 핵막 구조체가 하나의 신호로 겹쳐지는 것으로 보아 Vax1의 막소포는 핵막에서 유래되었으며, Vax1에 의해 세포핵으로 내제화된 Hsp70이 Vax1의 막소포 형성에 참여하고 있음을 유추할 수 있음. (B) 핵막 구조체 단백질 lamin과 Vax1 사이의 상호작용을 면역침강반응으로 조사함
 표
Vax1의 비자가성 망막 신경 축삭 성장 촉진 효과. 수정 후 13일째 정상 생쥐 망막과 ventral hypothalamus (vHT), 그리고, Vax1 결핍 생쥐 망막과 vHT를 각각 분리한 후 교차 상호 배양을 통해 Vax1의 존재 여부가 망막 신경의 성장에 미치는 영향을 조사함. Vax1이 결핍된 망막은 정상 vHT와 Vax1 결핍 vHT와 배양시 정상적인 축삭의 성장을 보인 반면, 정상 망막과 Vax1 결핍 망막 모두 Vax1 결핍 vHT와 공동 배양 시는 축삭 성장이 억제되는 양상을 나타냄. 이는 Vax1의 망막 내부 발현 보다는 vHT에서의 발현이 망막 신경 축삭의 성장에 필수적임을 시사함
표
Vax1의 비자가성 망막 신경 축삭 성장 촉진 효과. 수정 후 13일째 정상 생쥐 망막과 ventral hypothalamus (vHT), 그리고, Vax1 결핍 생쥐 망막과 vHT를 각각 분리한 후 교차 상호 배양을 통해 Vax1의 존재 여부가 망막 신경의 성장에 미치는 영향을 조사함. Vax1이 결핍된 망막은 정상 vHT와 Vax1 결핍 vHT와 배양시 정상적인 축삭의 성장을 보인 반면, 정상 망막과 Vax1 결핍 망막 모두 Vax1 결핍 vHT와 공동 배양 시는 축삭 성장이 억제되는 양상을 나타냄. 이는 Vax1의 망막 내부 발현 보다는 vHT에서의 발현이 망막 신경 축삭의 성장에 필수적임을 시사함
 표
Vax1 전사인자활성 비의존적 망막 신경 축삭 촉진 효과. 정상 Vax1과 전사인자 활성이 결핍된 Vax1(R152S), 또는 Vax2를 COS7 세포에 발현 한 후 수정후 13일째 생쥐 망막과 공동 배양하여 이들 세포가 Vax1이 생체 내에서 기능을 하는 vHT를 대체할 수 있는지를 조사함. 생쥐 망막 신경 축삭은 Vax1을 발현하는 COS7 세포와 Vax1(R152S)를 발현하는 COS7 세포에는 선택적 성장을 하지만, 일반 COS7과 Vax2를 발현하는 COS7 세포로는 선택적 성장을 하지 않는 것으로 나타남. 이는 Vax1 전사인자 활성이 아니라 Vax1 단백질 자체가 망막 신경 축삭의 성장에 필요함을 시사함. 흥미롭게, 망막 신경 축삭 성장을 유도한 Vax1과 Vax1(R152S)의 경우는 망막 신경 유전자를 발현한 COS7 세포뿐만 아니라 유전자를 발현해 주지 않은 망막 신경 축삭에서도 면역형광염색시 검출이 되는 것으로 확인됨. 이와 달리 망막 신경 축삭 성장을 유도하지 않은 Vax2의 경우는 망막 신경 축삭에는 전혀 검출이되지 않음. 이는 Vax1 및 Vax1(R152S) 단백질이 망막 신경 축삭으로 이동을 하였음을 의미하는 결과로 판단됨
표
Vax1 전사인자활성 비의존적 망막 신경 축삭 촉진 효과. 정상 Vax1과 전사인자 활성이 결핍된 Vax1(R152S), 또는 Vax2를 COS7 세포에 발현 한 후 수정후 13일째 생쥐 망막과 공동 배양하여 이들 세포가 Vax1이 생체 내에서 기능을 하는 vHT를 대체할 수 있는지를 조사함. 생쥐 망막 신경 축삭은 Vax1을 발현하는 COS7 세포와 Vax1(R152S)를 발현하는 COS7 세포에는 선택적 성장을 하지만, 일반 COS7과 Vax2를 발현하는 COS7 세포로는 선택적 성장을 하지 않는 것으로 나타남. 이는 Vax1 전사인자 활성이 아니라 Vax1 단백질 자체가 망막 신경 축삭의 성장에 필요함을 시사함. 흥미롭게, 망막 신경 축삭 성장을 유도한 Vax1과 Vax1(R152S)의 경우는 망막 신경 유전자를 발현한 COS7 세포뿐만 아니라 유전자를 발현해 주지 않은 망막 신경 축삭에서도 면역형광염색시 검출이 되는 것으로 확인됨. 이와 달리 망막 신경 축삭 성장을 유도하지 않은 Vax2의 경우는 망막 신경 축삭에는 전혀 검출이되지 않음. 이는 Vax1 및 Vax1(R152S) 단백질이 망막 신경 축삭으로 이동을 하였음을 의미하는 결과로 판단됨
 표
생쥐 망막에서 Vax1 mRNA 발현 검사. 수정 후 14.5일 정상 (wt), Vax1 결핍 (vax1-ko), Vax2 결핍 (vax2-ko), Vax1과 Vax2 공동 결핍 (vax-dko) 생쥐 망막에서 RNA를 분리 후 RT-qPCR을 통해 Vax1, Vax2, Pax6, Pax6, Pax2 mRNA의 양을 측정 후 이 값을 GAPDH PCR product에 대한 상대적 양으로 변환 후 상호 비교함. 그 결과 정상 망막에서의 Vax1 양이 Vax1이 결핍된 망막에서의 Vax1 양과 비교해 거의 차이가 없는 것으로 보아, 망막 내 미세한 양의 Vax1 mRNA에서 합성된 Vax1이 단백질이 그림 7에서 면역형광 염색에서 나타난 결과가 아님을 증명함
표
생쥐 망막에서 Vax1 mRNA 발현 검사. 수정 후 14.5일 정상 (wt), Vax1 결핍 (vax1-ko), Vax2 결핍 (vax2-ko), Vax1과 Vax2 공동 결핍 (vax-dko) 생쥐 망막에서 RNA를 분리 후 RT-qPCR을 통해 Vax1, Vax2, Pax6, Pax6, Pax2 mRNA의 양을 측정 후 이 값을 GAPDH PCR product에 대한 상대적 양으로 변환 후 상호 비교함. 그 결과 정상 망막에서의 Vax1 양이 Vax1이 결핍된 망막에서의 Vax1 양과 비교해 거의 차이가 없는 것으로 보아, 망막 내 미세한 양의 Vax1 mRNA에서 합성된 Vax1이 단백질이 그림 7에서 면역형광 염색에서 나타난 결과가 아님을 증명함
 표
생체 내 Vax1 단백질의 세포 간 이동 증거. Vax1의 mRNA의 발현을 in situ RNA hybridization을 통하여 조사한 결과 Vax1은 optic stalk에서만 발현이 되고 망막에는 전혀 발현이 되지 않지만 (A), 면역형광염색을 통해 Vax1 단백질의 분포를 조사한 결과 Vax1 단백질은 망막에서도 발현이 되는 것으로 검출이 됨 (B, 녹색). 하지만, 망막에서 Vax1이 검출된 망막 갱글리온세포는 optic stalk의 경우와 달리 Vax1 유전자 부위에서 발현되는 lacZ에 의해 생성된 b-galactosidase (b-Gal) 단백질이 전혀 검출이 되지 않음. 이는 망막 갱글리온세포내에 존재하는 Vax1 단백질은 세포 내부에서 생성된 것이 아니라 세포 외부에서 이동된 것임을 시사함
표
생체 내 Vax1 단백질의 세포 간 이동 증거. Vax1의 mRNA의 발현을 in situ RNA hybridization을 통하여 조사한 결과 Vax1은 optic stalk에서만 발현이 되고 망막에는 전혀 발현이 되지 않지만 (A), 면역형광염색을 통해 Vax1 단백질의 분포를 조사한 결과 Vax1 단백질은 망막에서도 발현이 되는 것으로 검출이 됨 (B, 녹색). 하지만, 망막에서 Vax1이 검출된 망막 갱글리온세포는 optic stalk의 경우와 달리 Vax1 유전자 부위에서 발현되는 lacZ에 의해 생성된 b-galactosidase (b-Gal) 단백질이 전혀 검출이 되지 않음. 이는 망막 갱글리온세포내에 존재하는 Vax1 단백질은 세포 내부에서 생성된 것이 아니라 세포 외부에서 이동된 것임을 시사함
 표
Vax1의 세포 간 이동. Myc-Vax1 또는 Myc-Vax2를 각각 COS7 세포에 발현하고 이 세포들을 Actin-EGFP를 발현하는 COS7 세포와 섞어서 24시간 동안 배양 후 Actin-EGFP를 발현하는 세포에 Vax1 또는 Vax2의 존재 여부를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. Vax1을 발현하는 세포와 공동 배양한 Actin-EGFP COS7 세포들 중 일부는 Vax1을 포함하고 있는 반면, Vax2를 발현하는 세포와 공동 배양한 Actin-EGFP COS7 세포들은 전혀 Vax2를 포함하고 있지 않았다. 이 결과는 Vax1이 특이적으로 주변 세포로 이동할 수 있는 특징을 가지고 있음을 시사한다
표
Vax1의 세포 간 이동. Myc-Vax1 또는 Myc-Vax2를 각각 COS7 세포에 발현하고 이 세포들을 Actin-EGFP를 발현하는 COS7 세포와 섞어서 24시간 동안 배양 후 Actin-EGFP를 발현하는 세포에 Vax1 또는 Vax2의 존재 여부를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. Vax1을 발현하는 세포와 공동 배양한 Actin-EGFP COS7 세포들 중 일부는 Vax1을 포함하고 있는 반면, Vax2를 발현하는 세포와 공동 배양한 Actin-EGFP COS7 세포들은 전혀 Vax2를 포함하고 있지 않았다. 이 결과는 Vax1이 특이적으로 주변 세포로 이동할 수 있는 특징을 가지고 있음을 시사한다
 표
Vax1 단백질의 망막조직 내부로의 이동과 및 망막 신경세포 외부에의 집중적 분포. 그림 17의 배양 세포주를 이용한 실험과 마찬가지로 EGFP 또는 Vax1-EGFP를 발현하는 세포의 배양액을 P0 생쥐 망막조직에 3 시간 동안 처리한 후 망막세포 내부로 이동한 EGFP 단백질 (A)과 세포 외부에 남아 있는 EGFP 단백질 (B)을 differential fixing & staining method를 통해 조사함. 그 결과 Vax1 단백질은 망막조직 외부에 다량 결합하고 있으며 (B), 일부는 세포 내부에까지 이동할 수 있음 (A)을 알 수 있다
표
Vax1 단백질의 망막조직 내부로의 이동과 및 망막 신경세포 외부에의 집중적 분포. 그림 17의 배양 세포주를 이용한 실험과 마찬가지로 EGFP 또는 Vax1-EGFP를 발현하는 세포의 배양액을 P0 생쥐 망막조직에 3 시간 동안 처리한 후 망막세포 내부로 이동한 EGFP 단백질 (A)과 세포 외부에 남아 있는 EGFP 단백질 (B)을 differential fixing & staining method를 통해 조사함. 그 결과 Vax1 단백질은 망막조직 외부에 다량 결합하고 있으며 (B), 일부는 세포 내부에까지 이동할 수 있음 (A)을 알 수 있다
 표
Vax1 단백질의 뇌 조직 침투. Myc-Vax1을 발현하는 293T 세포 배양액을 수정 후 14일 된 생쥐 배아 뇌실에 미세주입 후 12 시간 후 생쥐 전뇌 세포에 도입된 Vax1 단백질을 Myc을 이용한 면역형광염색으로 확인함. 그 결과 Myc 만을 발현하는 293T 세포 배양액을 주입한 뇌에서는 Myc 면역 형광 염색이 검출되지 않은 반면, Myc-Vax1 배양액을 주입한 전뇌 뇌실 근처의 세포들은 Myc-Vax1 면역형광 신호를 나타내었다. 이는 Myc-Vax1-293T 배양액 내 존재하던 Myc-Vax1 단백질이 뇌세포로 이동함을 시사하는 결과로 해석된다
표
Vax1 단백질의 뇌 조직 침투. Myc-Vax1을 발현하는 293T 세포 배양액을 수정 후 14일 된 생쥐 배아 뇌실에 미세주입 후 12 시간 후 생쥐 전뇌 세포에 도입된 Vax1 단백질을 Myc을 이용한 면역형광염색으로 확인함. 그 결과 Myc 만을 발현하는 293T 세포 배양액을 주입한 뇌에서는 Myc 면역 형광 염색이 검출되지 않은 반면, Myc-Vax1 배양액을 주입한 전뇌 뇌실 근처의 세포들은 Myc-Vax1 면역형광 신호를 나타내었다. 이는 Myc-Vax1-293T 배양액 내 존재하던 Myc-Vax1 단백질이 뇌세포로 이동함을 시사하는 결과로 해석된다
 표
Vax1 단일항체 제작을 위한 생쥐 혈청 테스트 결과. (A) Vax1 N-말단을 항원을 주입한 생쥐에서 분리한 생쥐 백혈구에서 유도된 hybridoma 세포 배양액을 Western blot의 항체로 사용하여 Vax1과 Vax2를 발현하는 cell lysate 내에 존재하는 Vax1 단백질에 대한 특이성을 조사함. Positive control인 rabbit polyclonal antibody에 비해 상대적으로 낮은 titer 때문에 약하게 10번 클론에서 신호가 확인됨. (B) Western blot에서 신호가 확인된 10번 클론이 denature된 단백질 보다 정상적 구조의 Vax1 단백질에 대한 특이성이 높은지를 확인하기 위해 면역형광염색을 통해 조사한 결과 rabbit polyclonal antibody 보다도 더 높은 신호를 보였다. 이를 통해 10번 클론은 정상 구조의 Vax1 단백질을 인식하는 특징이 있으므로, 향후 생체 내에서 정상적 구조의 Vax1 단백질의 작용을 저해할 목적으로 사용이 가능하다는 결론을 얻었음. 현재 FRL에서 Vax1-mAb10 clone을 이용하여 single chain IgG (scIgG) 유전자를 cloning 하려고 함. Vax1-scIgG 유전자가 확보되면 이를 생쥐에 RGC에 발현하여 RGC 외부에 분포하는 Vax1 단백질의 기능을 저하하여 RGC 성장 이상 여부를 관찰할 예정임
표
Vax1 단일항체 제작을 위한 생쥐 혈청 테스트 결과. (A) Vax1 N-말단을 항원을 주입한 생쥐에서 분리한 생쥐 백혈구에서 유도된 hybridoma 세포 배양액을 Western blot의 항체로 사용하여 Vax1과 Vax2를 발현하는 cell lysate 내에 존재하는 Vax1 단백질에 대한 특이성을 조사함. Positive control인 rabbit polyclonal antibody에 비해 상대적으로 낮은 titer 때문에 약하게 10번 클론에서 신호가 확인됨. (B) Western blot에서 신호가 확인된 10번 클론이 denature된 단백질 보다 정상적 구조의 Vax1 단백질에 대한 특이성이 높은지를 확인하기 위해 면역형광염색을 통해 조사한 결과 rabbit polyclonal antibody 보다도 더 높은 신호를 보였다. 이를 통해 10번 클론은 정상 구조의 Vax1 단백질을 인식하는 특징이 있으므로, 향후 생체 내에서 정상적 구조의 Vax1 단백질의 작용을 저해할 목적으로 사용이 가능하다는 결론을 얻었음. 현재 FRL에서 Vax1-mAb10 clone을 이용하여 single chain IgG (scIgG) 유전자를 cloning 하려고 함. Vax1-scIgG 유전자가 확보되면 이를 생쥐에 RGC에 발현하여 RGC 외부에 분포하는 Vax1 단백질의 기능을 저하하여 RGC 성장 이상 여부를 관찰할 예정임
 표
vHT에서 발현되며 각각 Vax1의 upstream과 downstream에 위치하며, 망막 RGC 성장 촉진 효과가 있는 것으로 알려진 Shh와 Netrin이 실재로 vHT로의 RGC axon 성장에 어떤 기여를 하는지를 조사하기 위하여, vHT와 망막 공동배양액에 Shh 항체 (a-Shh)와 Netrin 수용체인 Dcc의 extracellular domain에 human immunoglobulin 유전자의 Fc 부위를 연결하여 제작한 DCC-FC를 각각 처리하여 RGC axon에 존재하는 Shh 수용체와 Netrin 수용체가 Shh 및 Netrin과 결합을 하지 못하도록 유도함. 그 결과, Shh 항체나 DCC-FC 모두 vHT에 대한 RGC axon의 성장을 저해하지 못함. 따라서, Shh나 Netrin이 vHT에 대한 RGC axon 성장에 필수적인 역할을 하는 인자는 아님을 확인함
표
vHT에서 발현되며 각각 Vax1의 upstream과 downstream에 위치하며, 망막 RGC 성장 촉진 효과가 있는 것으로 알려진 Shh와 Netrin이 실재로 vHT로의 RGC axon 성장에 어떤 기여를 하는지를 조사하기 위하여, vHT와 망막 공동배양액에 Shh 항체 (a-Shh)와 Netrin 수용체인 Dcc의 extracellular domain에 human immunoglobulin 유전자의 Fc 부위를 연결하여 제작한 DCC-FC를 각각 처리하여 RGC axon에 존재하는 Shh 수용체와 Netrin 수용체가 Shh 및 Netrin과 결합을 하지 못하도록 유도함. 그 결과, Shh 항체나 DCC-FC 모두 vHT에 대한 RGC axon의 성장을 저해하지 못함. 따라서, Shh나 Netrin이 vHT에 대한 RGC axon 성장에 필수적인 역할을 하는 인자는 아님을 확인함
 표
세포 외부 Vax1 단백질의 망막 신경 축삭 성장 유도 효과. (A,B) 기존 연구를 통해 확인한 세포 외부로 분비되는 Vax1 단백질이 망막 신경 성장 작용을 유도할 수 있는지를 직접 확인하기 위해 GST-표지가 된 Vax1 단백질을 생쥐 망막 배양액에 처리한 후 망막 축삭의 성장을 조사함. 그 결과 외부에서 추가한 Vax1 단백질은 망막 신경 축삭 내부로 침투할 수 있음을 면역형광염색으로 확인함. 이러한 Vax1의 망막 신경 축삭으로의 이동은 Vax1 항체를 이용해 Vax1을 항체와 복합체로 만든 경우는 억제가 되는 것으로 보아 Vax1의 망막 신경 침투는 Vax1 단백질 자체의 효과이며, 특정 Vax1 단백질의 3차원적 구조가 필요한 것으로 이에 필요한 것으로 확인됨. (C,D) 이러한 Vax1 단백질의 망막 신경 축삭으로의 이동과 축삭 성장 유도 효과는 재조합 단백질만이 가지는 기능이 아니라 vHT에서 발현되는 생체 내 Vax1 단백질 또한 동일한 활성이 있음을 증명하기 위해 vHT와 망막의 공동 배양액에 Vax1 항체를 추가한 결과 Vax1의 망막 신경 축삭으로의 이동과 축삭의 성장 모두 억제됨을 알 수 있음
표
세포 외부 Vax1 단백질의 망막 신경 축삭 성장 유도 효과. (A,B) 기존 연구를 통해 확인한 세포 외부로 분비되는 Vax1 단백질이 망막 신경 성장 작용을 유도할 수 있는지를 직접 확인하기 위해 GST-표지가 된 Vax1 단백질을 생쥐 망막 배양액에 처리한 후 망막 축삭의 성장을 조사함. 그 결과 외부에서 추가한 Vax1 단백질은 망막 신경 축삭 내부로 침투할 수 있음을 면역형광염색으로 확인함. 이러한 Vax1의 망막 신경 축삭으로의 이동은 Vax1 항체를 이용해 Vax1을 항체와 복합체로 만든 경우는 억제가 되는 것으로 보아 Vax1의 망막 신경 침투는 Vax1 단백질 자체의 효과이며, 특정 Vax1 단백질의 3차원적 구조가 필요한 것으로 이에 필요한 것으로 확인됨. (C,D) 이러한 Vax1 단백질의 망막 신경 축삭으로의 이동과 축삭 성장 유도 효과는 재조합 단백질만이 가지는 기능이 아니라 vHT에서 발현되는 생체 내 Vax1 단백질 또한 동일한 활성이 있음을 증명하기 위해 vHT와 망막의 공동 배양액에 Vax1 항체를 추가한 결과 Vax1의 망막 신경 축삭으로의 이동과 축삭의 성장 모두 억제됨을 알 수 있음
 표
시신경 교차점 형성을 위한 세포 외부 Vax1의 역할. 배측 시상하부 (ventral hypothalamus)에서 분비되는 Vax1 단백질의 생체 내 역할을 규명하기 위해 시상하부와 인접한 수정 후 13일 생쥐 배아 제3뇌실 (third ventricle) 내에 비면역항체 또는 Vax1을 인식하는 항체를 분비하는 콜라겐 구조체를 이식함. 구조체를 이식한 생쥐 배아 안구에 세포막을 표지하는 형광시약인 DiI를 주입하여 해당 안구에서 유래하는 시신경의 분포를 추적함. 24시간 후 해당 배아의 절편을 획득하여 DiI에 의해 표지된 왼쪽 안구에서 유래한 시신경의 분포를 조사한 결과 비면역항체를 이식한 생쥐 배아는 정상적인 중심선으로의 성장을 보인 반면, Vax1 항체를 이식한 생쥐 배아에서는 시신경의 성장이 저하되어 중심선으로의 접근이 억제됨. 중심선으로의 성장이 억제된 시신경은 시신경 축삭 내 Vax1의 분포가 줄어들어 있음
표
시신경 교차점 형성을 위한 세포 외부 Vax1의 역할. 배측 시상하부 (ventral hypothalamus)에서 분비되는 Vax1 단백질의 생체 내 역할을 규명하기 위해 시상하부와 인접한 수정 후 13일 생쥐 배아 제3뇌실 (third ventricle) 내에 비면역항체 또는 Vax1을 인식하는 항체를 분비하는 콜라겐 구조체를 이식함. 구조체를 이식한 생쥐 배아 안구에 세포막을 표지하는 형광시약인 DiI를 주입하여 해당 안구에서 유래하는 시신경의 분포를 추적함. 24시간 후 해당 배아의 절편을 획득하여 DiI에 의해 표지된 왼쪽 안구에서 유래한 시신경의 분포를 조사한 결과 비면역항체를 이식한 생쥐 배아는 정상적인 중심선으로의 성장을 보인 반면, Vax1 항체를 이식한 생쥐 배아에서는 시신경의 성장이 저하되어 중심선으로의 접근이 억제됨. 중심선으로의 성장이 억제된 시신경은 시신경 축삭 내 Vax1의 분포가 줄어들어 있음
 표
Vax1 단백질의 생체 내 세포 간 이동. Vax1-GFP를 GAL4 전사촉진인자의 존재 하에 발현할 수 있는 UAS-Vax1-GFP 형질전환 초파리를 제작한 후, 이 초파리를 wing imaginal disc의 중심축 부위에서 GAL4가 특이적으로 발현되는 Ptc-Gal4 초파리와 교배해서 Vax1-GFP 단백질을 wing imaginal disc 중심부에서 발현하였다. 또한, Ptc-Gal4에 의해 Vax1-GFP와 마찬가지로 UAS-RFP에서 RFP 단백질이 발현이 되도록 만들어 주어 Vax1-GFP의 분포와 상호 비교하였다. 아래쪽 확대 그림에서 보듯이, Vax1-GFP 단백질은 RFP와 마찬가지로 원래 발현이 되는 지역인 wing imaginal disc 중심축 세포들뿐만 아니라 anterior (A) part에 RFP를 발현하지 않는 세포들에서도 관찰이 되었다. 이는 Vax1-GFP 단백질이 주변 세포들로 이동을 할 수 있음을 알 수 있었다
표
Vax1 단백질의 생체 내 세포 간 이동. Vax1-GFP를 GAL4 전사촉진인자의 존재 하에 발현할 수 있는 UAS-Vax1-GFP 형질전환 초파리를 제작한 후, 이 초파리를 wing imaginal disc의 중심축 부위에서 GAL4가 특이적으로 발현되는 Ptc-Gal4 초파리와 교배해서 Vax1-GFP 단백질을 wing imaginal disc 중심부에서 발현하였다. 또한, Ptc-Gal4에 의해 Vax1-GFP와 마찬가지로 UAS-RFP에서 RFP 단백질이 발현이 되도록 만들어 주어 Vax1-GFP의 분포와 상호 비교하였다. 아래쪽 확대 그림에서 보듯이, Vax1-GFP 단백질은 RFP와 마찬가지로 원래 발현이 되는 지역인 wing imaginal disc 중심축 세포들뿐만 아니라 anterior (A) part에 RFP를 발현하지 않는 세포들에서도 관찰이 되었다. 이는 Vax1-GFP 단백질이 주변 세포들로 이동을 할 수 있음을 알 수 있었다
 표
Heparin sulfate proteoglycan 분포 조절을 통한 생체 내 Vax1 이동 변화. Heparin sulfate proteoglycan에 의한 Vax1의 세포 간 이동을 생체 내에서 검증하기 위해, transmembrane heparin sulfate proteoglycan인 syndecan (Sdc)과 GPI-anchoring proteoglycan인 glypican의 초파리 homolog dally-like protein (Dlp)의 mutant와 overexpression line들을 확보함. 이들 중 dally와 dlp는 hedgehog, wingless, dpp 등의 필수적인 발달 조절인자들의 분포를 조절하는 유전자이므로 mutant들은 대부분 초기 발달에서 성장을 멈추어 Vax1 분비에 대한 조사를 하기가 불가능함. 따라서, 비교적 초기 발달 이상이 미약한 Sdc mutant인 Sdc23 line에서의 Vax1 이동과 UAS-Dlp 초파리를 이용하여 Vax1을 발현하는 세포에서 함께 Dlp를 과발현하여 local heparin sulfate proteoglycan 농도를 높이는 방식으로 Vax1의 세포 간 이동에 미치는 heparin sulfate proteoglycan들의 효과를 조사함. 그림에 보는 것처럼 Vax1을 Ds-Red와 동시에 Ptc-gal4를 이용하여 wing imaginal disc의 중간에서 발현하면, 발현하는 세포뿐만 아니라 posterior part의 Ptc-negative 세포들에까지 이동하여 분포함을 이미 증명한 바 있다. 하지만, Ptc-gal4를 발현하는 세포에 Vax1, Ds-Red를 Dlp와 함께 발현하면, Vax1이 이동하지 못하고 발현하는 세포에만 머무는 것을 알 수 있다. 따라서, 세포 외부로 분비된 Vax1 단백질이 과발현된 Dlp glypican heparin sulfate proteoglycan에 포집되어 주변으로의 이동이 저해되었다고 유추할 수 있다
표
Heparin sulfate proteoglycan 분포 조절을 통한 생체 내 Vax1 이동 변화. Heparin sulfate proteoglycan에 의한 Vax1의 세포 간 이동을 생체 내에서 검증하기 위해, transmembrane heparin sulfate proteoglycan인 syndecan (Sdc)과 GPI-anchoring proteoglycan인 glypican의 초파리 homolog dally-like protein (Dlp)의 mutant와 overexpression line들을 확보함. 이들 중 dally와 dlp는 hedgehog, wingless, dpp 등의 필수적인 발달 조절인자들의 분포를 조절하는 유전자이므로 mutant들은 대부분 초기 발달에서 성장을 멈추어 Vax1 분비에 대한 조사를 하기가 불가능함. 따라서, 비교적 초기 발달 이상이 미약한 Sdc mutant인 Sdc23 line에서의 Vax1 이동과 UAS-Dlp 초파리를 이용하여 Vax1을 발현하는 세포에서 함께 Dlp를 과발현하여 local heparin sulfate proteoglycan 농도를 높이는 방식으로 Vax1의 세포 간 이동에 미치는 heparin sulfate proteoglycan들의 효과를 조사함. 그림에 보는 것처럼 Vax1을 Ds-Red와 동시에 Ptc-gal4를 이용하여 wing imaginal disc의 중간에서 발현하면, 발현하는 세포뿐만 아니라 posterior part의 Ptc-negative 세포들에까지 이동하여 분포함을 이미 증명한 바 있다. 하지만, Ptc-gal4를 발현하는 세포에 Vax1, Ds-Red를 Dlp와 함께 발현하면, Vax1이 이동하지 못하고 발현하는 세포에만 머무는 것을 알 수 있다. 따라서, 세포 외부로 분비된 Vax1 단백질이 과발현된 Dlp glypican heparin sulfate proteoglycan에 포집되어 주변으로의 이동이 저해되었다고 유추할 수 있다
 표
Sdc N-말단 특이적 Vax1의 결합. (A) HEK293T 세포에 Vax1과 GFP-Sdc1, GFP-Sdc2를 발현하고 GFP에 대한 항체를 이용하여 Sdc 단백질을 면역침강하였다. 침강된 면역복합체에 Vax1 단백질이 함께 존재하는지를 Vax1에 대한 항체를 이용하여 Western blot으로 확인하였다. (B) Vax1 대신 Vax2를 GFP-Sdc와 발현 후 동일한 방법으로 Vax2의 Sdc에 대한 상호작용을 조사하였다. (C) Vax1의 Sdc2의 N-말단 부위 (GFP-Sdc2-N) 또는 C-말단 (GFP-Sdc2-C) 에 대한 선택적 결합을 Vax1 면역침강법으로 조사하였다
표
Sdc N-말단 특이적 Vax1의 결합. (A) HEK293T 세포에 Vax1과 GFP-Sdc1, GFP-Sdc2를 발현하고 GFP에 대한 항체를 이용하여 Sdc 단백질을 면역침강하였다. 침강된 면역복합체에 Vax1 단백질이 함께 존재하는지를 Vax1에 대한 항체를 이용하여 Western blot으로 확인하였다. (B) Vax1 대신 Vax2를 GFP-Sdc와 발현 후 동일한 방법으로 Vax2의 Sdc에 대한 상호작용을 조사하였다. (C) Vax1의 Sdc2의 N-말단 부위 (GFP-Sdc2-N) 또는 C-말단 (GFP-Sdc2-C) 에 대한 선택적 결합을 Vax1 면역침강법으로 조사하였다
 표
Vax1의 세포 외부 분비 및 당 결합에 관여하는 부위 검증. 앞의 결과들에 의하면 분비된 Vax1은 주변 세포의 proteoglycan의 당 사슬에 결합을 한 후 주변세포로의 이동 및 해당 세포에 신호를 전달할 가능성이 있다. 이러한 Vax1의 분비와 주변세포의 proteoglycan 당 사슬에 결합하는 부위에 대한 정보를 얻고자 Vax1 단백질의 절편을 293T 세포에 발현 한 후 배양액 내 Vax1 절편의 양과 heparin에 의해 증가되는 배양액 내 Vax1 절편의 양을 조사함으로써 세포 외부로의 분비에 관여하는 Vax1 부위와 당사슬에 결합하는 부위를 검증하려고 함 (A&B). 그 결과 Vax1의 N-말단이 없는 경우 세포 외부로 분비는 가능하나 수용성으로 있지 못하고 당사슬을 포함한 proteoglycan에 결합하여 있는 것으로 나타남 (heparin 처리 시에만 확인된 C1, C2, C3 절편들). 이와는 반대로 homeodomain이 없는 경우는 그림 24와 마찬가지로 세포 외부에서 대부분 수용성으로 존재함을 알 수 있음. 따라서, 세포외부로의 분비 이후 Vax1은 homeodomain과 C-말단을 통해 세포막 및 proteoglycan에 결합함을 알 수 있음
표
Vax1의 세포 외부 분비 및 당 결합에 관여하는 부위 검증. 앞의 결과들에 의하면 분비된 Vax1은 주변 세포의 proteoglycan의 당 사슬에 결합을 한 후 주변세포로의 이동 및 해당 세포에 신호를 전달할 가능성이 있다. 이러한 Vax1의 분비와 주변세포의 proteoglycan 당 사슬에 결합하는 부위에 대한 정보를 얻고자 Vax1 단백질의 절편을 293T 세포에 발현 한 후 배양액 내 Vax1 절편의 양과 heparin에 의해 증가되는 배양액 내 Vax1 절편의 양을 조사함으로써 세포 외부로의 분비에 관여하는 Vax1 부위와 당사슬에 결합하는 부위를 검증하려고 함 (A&B). 그 결과 Vax1의 N-말단이 없는 경우 세포 외부로 분비는 가능하나 수용성으로 있지 못하고 당사슬을 포함한 proteoglycan에 결합하여 있는 것으로 나타남 (heparin 처리 시에만 확인된 C1, C2, C3 절편들). 이와는 반대로 homeodomain이 없는 경우는 그림 24와 마찬가지로 세포 외부에서 대부분 수용성으로 존재함을 알 수 있음. 따라서, 세포외부로의 분비 이후 Vax1은 homeodomain과 C-말단을 통해 세포막 및 proteoglycan에 결합함을 알 수 있음
 표
시신경에서 Vax1과 Sdc2 사이의 상호 작용. (A) Vax1과 Sdc 단백질 간 상호작용을 P0 생쥐 시신경 cell lysate를 Vax1 단백질에 대한 항체로 면역침강한 후 Vax1과 결합하여 함께 분리된 Sdc2, Sdc3, Glp1 등의 HSPG 단백질을 WB로 검출함. (B) 또한, 이 과정 중 면역침강 용액에 heparin을 추가하여 HSPG 단백질의 heparin 당 부위에 결합된 단백질들을 해리 시킨 경우 Vax1과 Sdc2, Sdc3, Glp1 등 HSPG 단백질과의 결합이 억제되었지만, 세포 핵 내에서 Vax1과 상호결합하는 것으로 확인된 Pax2의 경우는 heparin의 존재 유무에 상관 없이 결합을 하고 있음을 알 수 있다. 이는 Vax1이 HSPG의 heparin 당 부위와 특이적 결합을 함을 시사함
표
시신경에서 Vax1과 Sdc2 사이의 상호 작용. (A) Vax1과 Sdc 단백질 간 상호작용을 P0 생쥐 시신경 cell lysate를 Vax1 단백질에 대한 항체로 면역침강한 후 Vax1과 결합하여 함께 분리된 Sdc2, Sdc3, Glp1 등의 HSPG 단백질을 WB로 검출함. (B) 또한, 이 과정 중 면역침강 용액에 heparin을 추가하여 HSPG 단백질의 heparin 당 부위에 결합된 단백질들을 해리 시킨 경우 Vax1과 Sdc2, Sdc3, Glp1 등 HSPG 단백질과의 결합이 억제되었지만, 세포 핵 내에서 Vax1과 상호결합하는 것으로 확인된 Pax2의 경우는 heparin의 존재 유무에 상관 없이 결합을 하고 있음을 알 수 있다. 이는 Vax1이 HSPG의 heparin 당 부위와 특이적 결합을 함을 시사함
 표
시신경 내 Vax1 단백질의 heparin 민감성 분포. Heparin에 민감하게 Sdc3 등의 HSPG와 면역침강되었던 Vax1 단백질이 실재로 시신경 내에서 망막 신경 축삭 부위에 존재하는 Sdc3와 같이 위치를 하는지를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. 그 결과 Sdc3와 Vax1은 망막 신경 축삭에서만 특이적으로 공통의 분포를 나타 내었으며, 이러한 면역형광염색 신호는 heparin 당을 분해하는 heparitinase의 처리에 의해 사라졌다. 하지만, chondroitinase처럼 heparin 당을 분해하지 못하는 효소에 의해서는 영향을 받지 않음
표
시신경 내 Vax1 단백질의 heparin 민감성 분포. Heparin에 민감하게 Sdc3 등의 HSPG와 면역침강되었던 Vax1 단백질이 실재로 시신경 내에서 망막 신경 축삭 부위에 존재하는 Sdc3와 같이 위치를 하는지를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. 그 결과 Sdc3와 Vax1은 망막 신경 축삭에서만 특이적으로 공통의 분포를 나타 내었으며, 이러한 면역형광염색 신호는 heparin 당을 분해하는 heparitinase의 처리에 의해 사라졌다. 하지만, chondroitinase처럼 heparin 당을 분해하지 못하는 효소에 의해서는 영향을 받지 않음
 표
Vax1에 의한 망막 신경 축삭 성장 유도에 세포막 투과가 필요함. Vax1의 경우 망막 신경 축삭 세포막 외부 뿐만 아니라 세포 내부에서도 관찰이 되었으므로, Vax1의 작용점이 세포막에서 Sdc2와의 결합을 통해 축삭의 성장을 유도할 수도 있고 세포 내부로 이동하여 세포 내부에 존재하는 단백질들을 통해 축삭 성장을 유도할 가능성도 있다. 이를 증명하기 위해 세포막 투과성이 떨어진 Vax1(WF/SR) 변이 단백질을 발현하는 COS7 세포의 망막 신경 축삭 성장 유도 효과를 정상 Vax1을 발현하는 COS7 세포와 비교하였다. 그 결과 Vax1(WF/SR) 단백질은 Vax1과 달리 선택적 망막 신경 성장 유도를 하지 못하는 것을 확인되었다. 이는 Vax1의 Sdc를 비롯한 HSPG에의 결합뿐만 아니라 축삭 세포 내로의 이동이 중요하다는 사실을 시사함
표
Vax1에 의한 망막 신경 축삭 성장 유도에 세포막 투과가 필요함. Vax1의 경우 망막 신경 축삭 세포막 외부 뿐만 아니라 세포 내부에서도 관찰이 되었으므로, Vax1의 작용점이 세포막에서 Sdc2와의 결합을 통해 축삭의 성장을 유도할 수도 있고 세포 내부로 이동하여 세포 내부에 존재하는 단백질들을 통해 축삭 성장을 유도할 가능성도 있다. 이를 증명하기 위해 세포막 투과성이 떨어진 Vax1(WF/SR) 변이 단백질을 발현하는 COS7 세포의 망막 신경 축삭 성장 유도 효과를 정상 Vax1을 발현하는 COS7 세포와 비교하였다. 그 결과 Vax1(WF/SR) 단백질은 Vax1과 달리 선택적 망막 신경 성장 유도를 하지 못하는 것을 확인되었다. 이는 Vax1의 Sdc를 비롯한 HSPG에의 결합뿐만 아니라 축삭 세포 내로의 이동이 중요하다는 사실을 시사함
 표
Vax1의 세포질 내 결합단백질 발굴. Vax1의 세포질 내로의 이동이 망막 신경 축삭 성장에 필요하다는 사실에 기반하여, GST-Vax1이 과발현된 293T 세포의 세포질에서 Vax1의 세포질 내 작용 단백질을 GST full-down을 통해 포집하고, 이를 MALDI-TOF를 이용하여 분석하였다. 그 결과 대부분의 세포질 내 Vax1 결합단백질들이 리보좀에 존재하는 단백질들 (ribosomal protein S (RPS) 또는 RPL)이나 단백질 합성에 관여하는 단백질 (eIF3B/C, Hsp70)로 확인되었다. 이는 Vax1이 세포질에서 단백질 합성에 관여할 것이라는 것을 의미하는 결과로 해석된다
표
Vax1의 세포질 내 결합단백질 발굴. Vax1의 세포질 내로의 이동이 망막 신경 축삭 성장에 필요하다는 사실에 기반하여, GST-Vax1이 과발현된 293T 세포의 세포질에서 Vax1의 세포질 내 작용 단백질을 GST full-down을 통해 포집하고, 이를 MALDI-TOF를 이용하여 분석하였다. 그 결과 대부분의 세포질 내 Vax1 결합단백질들이 리보좀에 존재하는 단백질들 (ribosomal protein S (RPS) 또는 RPL)이나 단백질 합성에 관여하는 단백질 (eIF3B/C, Hsp70)로 확인되었다. 이는 Vax1이 세포질에서 단백질 합성에 관여할 것이라는 것을 의미하는 결과로 해석된다
 표
Vax1의 망막 신경 축삭 내 단백질 생합성 촉진 효과. Vax1의 리보좀 및 단백질 생합성 조절 단백질과의 상호작용이 가지는 의미를 확인하기 위해, metionine이 제거된 망막 배양액에 L-azidohonoalanine (AHA)를 첨가한 후 Vax1을 6시간 동안 첨가하여 Vax1이 작용하는 망막 신경 축삭과 망막 신경 세포에서 생합성되는 단백질들에 AHA가 들어가도록 하였다. 그 후 망막조직을 고정한 후 세포 내부에 생성된 AHA를 포함한 단백질을 DIBO-fluor Alexa488과의 Click chemistry를 통해 형광 표지한 후 현미경 하에서 관찰함. 그 결과, Vax1이 처리된 망막 신경 축삭 부위에 단백질 생합성이 비처리 망막 신경이나 세포막 비투과 Vax1(WF/SR) 단백질과 비교해서 급격하게 증가한 것을 알 수 있음. 하지만, 이러한 증가는 세포 본체에서는 두드러지지 않는 것으로 보아 Vax1의 타겟이 축삭에 집중되어 있음을 알 수 있음
표
Vax1의 망막 신경 축삭 내 단백질 생합성 촉진 효과. Vax1의 리보좀 및 단백질 생합성 조절 단백질과의 상호작용이 가지는 의미를 확인하기 위해, metionine이 제거된 망막 배양액에 L-azidohonoalanine (AHA)를 첨가한 후 Vax1을 6시간 동안 첨가하여 Vax1이 작용하는 망막 신경 축삭과 망막 신경 세포에서 생합성되는 단백질들에 AHA가 들어가도록 하였다. 그 후 망막조직을 고정한 후 세포 내부에 생성된 AHA를 포함한 단백질을 DIBO-fluor Alexa488과의 Click chemistry를 통해 형광 표지한 후 현미경 하에서 관찰함. 그 결과, Vax1이 처리된 망막 신경 축삭 부위에 단백질 생합성이 비처리 망막 신경이나 세포막 비투과 Vax1(WF/SR) 단백질과 비교해서 급격하게 증가한 것을 알 수 있음. 하지만, 이러한 증가는 세포 본체에서는 두드러지지 않는 것으로 보아 Vax1의 타겟이 축삭에 집중되어 있음을 알 수 있음
 표
Vax1에 의한 시신경 축삭 특이적 단백질 합성 촉진 효과 검증. 세포 내 단백질 합성 촉진을 통해 시신경 축삭 성장을 유도하는 Vax1의 효과가 세포핵과 세포 본체 (cell body)에서 일어나는 현상인지 실재 성장이 일어나는 축삭에서 나타나는 현상인지를 검증하기 위해 세포 본체가 포함된 망막 이식체와 축삭을 분리 후 축삭 부위에만 Vax1 단백질을 처리하고 새롭게 합성되는 단백질들을 AHA-Alexa488을 이용해 표지함. 그 결과 축삭 부위에만 Vax1을 처리해도 축삭 성장과 신규 단백질 합성이 촉진되는 것을 통해 Vax1은 축삭 특이적 단백질 합성 유도를 통해 축삭 성장을 유도함을 알 수 있음
표
Vax1에 의한 시신경 축삭 특이적 단백질 합성 촉진 효과 검증. 세포 내 단백질 합성 촉진을 통해 시신경 축삭 성장을 유도하는 Vax1의 효과가 세포핵과 세포 본체 (cell body)에서 일어나는 현상인지 실재 성장이 일어나는 축삭에서 나타나는 현상인지를 검증하기 위해 세포 본체가 포함된 망막 이식체와 축삭을 분리 후 축삭 부위에만 Vax1 단백질을 처리하고 새롭게 합성되는 단백질들을 AHA-Alexa488을 이용해 표지함. 그 결과 축삭 부위에만 Vax1을 처리해도 축삭 성장과 신규 단백질 합성이 촉진되는 것을 통해 Vax1은 축삭 특이적 단백질 합성 유도를 통해 축삭 성장을 유도함을 알 수 있음
 표
단백질 생합성 의존적 Vax1에 의한 망막 신경 축삭 성장 촉진 효과. Vax1에 의한 축삭 내 단백질 생합성 촉진이 실재 Vax1에 의한 망막 신경 축삭 성장과 어떤 연관성이 있는지를 조사하기 위해, 망막 배양액에 Vax1을 처리 시 유전자 발현 억제제인 alpha-amanitin과 단백질 생합성 억제제인 anisomycin을 각각 처리하고 축삭 내 Vax1의 침투와 축삭의 성장 정도를 측정함. 그 결과 Vax1의 침투에는 이상이 없지만 Vax1에 의해 촉진되는 축삭 성장은 anisomycin 처리 시에 억제됨을 관찰함. 따라서 Vax1이 세포 내로 이동 후 세포 내 단백질 생합성을 통해 망막 신경 축삭 성장을 유도하는 것으로 결론을 내릴 수 있었음
표
단백질 생합성 의존적 Vax1에 의한 망막 신경 축삭 성장 촉진 효과. Vax1에 의한 축삭 내 단백질 생합성 촉진이 실재 Vax1에 의한 망막 신경 축삭 성장과 어떤 연관성이 있는지를 조사하기 위해, 망막 배양액에 Vax1을 처리 시 유전자 발현 억제제인 alpha-amanitin과 단백질 생합성 억제제인 anisomycin을 각각 처리하고 축삭 내 Vax1의 침투와 축삭의 성장 정도를 측정함. 그 결과 Vax1의 침투에는 이상이 없지만 Vax1에 의해 촉진되는 축삭 성장은 anisomycin 처리 시에 억제됨을 관찰함. 따라서 Vax1이 세포 내로 이동 후 세포 내 단백질 생합성을 통해 망막 신경 축삭 성장을 유도하는 것으로 결론을 내릴 수 있었음
 표
Vax1 이식을 통한 Vax1-ko 생쥐의 시신경 재성장 유도. (A&B) 시상하부 배측 중심선으로의 시신경 성장이 저해된 Vax1-ko 생쥐 배아 제3뇌실 내에 6X-His 펩티드, Vax1-His 단백질, 세포 침투능이 상실된 Vax1(WF/SR)-His 단백질을 분비하는 콜라겐 구조체를 이식하고 시신경의 성장을 우측 안구에 주입한 DiI 형광 염색시약에 의해 표지된 시신경의 분포를 통해 조사함. 이 중 Vax1-His 단백질만이 Vax1-ko 생쥐 시신경의 재성장을 유도할 수 있음. Vax1-ko 생쥐 배아 시 신경 성장 이상이 시상하부 측면에 발현되어 시신경 축삭 성장을 억제하는 Slit에 의한 것인지를 확인하기 위해 Slit 단백질의 수용체인 Robo1의 Slit 결합부위를 포함하는 Robo1-Fc 단백질 분비하는 콜라겐 구조체를 제3뇌실에 이식함. 그 결과 부분적인 시신경의 재성장이 일어났고, 이러한 효과는 Vax1과 Robo1-Fc를 함께 분비하는 콜라겐 구조체의 이식 시에 극대화되었음. (C) 이를 통해 시신경의 시상하부 중심축으로의 성장이 성장 촉진인자인 Vax1과 성장 억제인자인 Slit 사이의 상호 견재를 통해 일어난다는 모델을 구축하였음
표
Vax1 이식을 통한 Vax1-ko 생쥐의 시신경 재성장 유도. (A&B) 시상하부 배측 중심선으로의 시신경 성장이 저해된 Vax1-ko 생쥐 배아 제3뇌실 내에 6X-His 펩티드, Vax1-His 단백질, 세포 침투능이 상실된 Vax1(WF/SR)-His 단백질을 분비하는 콜라겐 구조체를 이식하고 시신경의 성장을 우측 안구에 주입한 DiI 형광 염색시약에 의해 표지된 시신경의 분포를 통해 조사함. 이 중 Vax1-His 단백질만이 Vax1-ko 생쥐 시신경의 재성장을 유도할 수 있음. Vax1-ko 생쥐 배아 시 신경 성장 이상이 시상하부 측면에 발현되어 시신경 축삭 성장을 억제하는 Slit에 의한 것인지를 확인하기 위해 Slit 단백질의 수용체인 Robo1의 Slit 결합부위를 포함하는 Robo1-Fc 단백질 분비하는 콜라겐 구조체를 제3뇌실에 이식함. 그 결과 부분적인 시신경의 재성장이 일어났고, 이러한 효과는 Vax1과 Robo1-Fc를 함께 분비하는 콜라겐 구조체의 이식 시에 극대화되었음. (C) 이를 통해 시신경의 시상하부 중심축으로의 성장이 성장 촉진인자인 Vax1과 성장 억제인자인 Slit 사이의 상호 견재를 통해 일어난다는 모델을 구축하였음
 표
Vax1에 의한 시신경 축삭 성장 조절 모식도. (A) Vax1(붉은색)은 전뇌 배부위 중심부에서 강하게 발현되고 외곽으로 갈수록 그 농도가 줄어드는 반면, Slit은 전뇌 등부위에서 높고 배부위에서는 낮은 발현 양상을 보인다. (B) 시신경 축삭이 안구를 나와서 뇌 중심선을 향하여 성장하는 동안 시신경 성장부 주변에서 분비된 Vax1이 지속적으로 시신경 축삭의 성장을 유도한다. (C) 시신경이 전뇌 배부위 주변에 접근하면 이곳에 높은 농도로 존재하는 Slit의 작용으로 등부위로의 성장은 억제되는 반면 배부위 중심부에서 분비되는 Vax1에 의해 배부위 중심부로의 성장은 지속된다. 하지만 Vax1이 없는 생쥐의 경우는 배부위 중심부로의 이동이 저하되어 뇌 주변부에서 시신경이 성장을 멈춘다. (D) 뇌 중심선까지 성장한 시신경 축삭은 그곳에 특이적으로 발현된 ephrinB2에 시신경 축삭에 EphB1이 반응하여 시신경 축삭 성장을 멈추고 되돌아 온다. 하지만, EphB1이 없는 시신경 축삭은 그대로 그 부위를 통과하여 반대편 뇌로 성장을 하게 된다. 이 모든 과정에서 Vax1은 시 신경 축삭의 방향과는 상관 없이 축삭 내 단백질 합성 촉진을 통해 시신경 축삭의 성장 속도를 높이는 역할을 한다
표
Vax1에 의한 시신경 축삭 성장 조절 모식도. (A) Vax1(붉은색)은 전뇌 배부위 중심부에서 강하게 발현되고 외곽으로 갈수록 그 농도가 줄어드는 반면, Slit은 전뇌 등부위에서 높고 배부위에서는 낮은 발현 양상을 보인다. (B) 시신경 축삭이 안구를 나와서 뇌 중심선을 향하여 성장하는 동안 시신경 성장부 주변에서 분비된 Vax1이 지속적으로 시신경 축삭의 성장을 유도한다. (C) 시신경이 전뇌 배부위 주변에 접근하면 이곳에 높은 농도로 존재하는 Slit의 작용으로 등부위로의 성장은 억제되는 반면 배부위 중심부에서 분비되는 Vax1에 의해 배부위 중심부로의 성장은 지속된다. 하지만 Vax1이 없는 생쥐의 경우는 배부위 중심부로의 이동이 저하되어 뇌 주변부에서 시신경이 성장을 멈춘다. (D) 뇌 중심선까지 성장한 시신경 축삭은 그곳에 특이적으로 발현된 ephrinB2에 시신경 축삭에 EphB1이 반응하여 시신경 축삭 성장을 멈추고 되돌아 온다. 하지만, EphB1이 없는 시신경 축삭은 그대로 그 부위를 통과하여 반대편 뇌로 성장을 하게 된다. 이 모든 과정에서 Vax1은 시 신경 축삭의 방향과는 상관 없이 축삭 내 단백질 합성 촉진을 통해 시신경 축삭의 성장 속도를 높이는 역할을 한다
 표
세포 표면 부착 이상 Vax1(KR/AA) 변이형. (A) (위) Otx2와 Vax1의 당사슬 결합 부위. (아래)293T 세포에 정상 Vax1, 전사활성 저하형 Vax1(R152S), Vax1(RK/AA) 변이형을 발현 후 함께 발현한 Vax1 타겟인 Tcf7l1-luciferase 활성을 조사하여 Vax1 비발현 세포 (Mock)의 luciferase 값과 비교함. (B) 293T 세포에 Vax1 또는 Vax1(KR/AA)를 발현 후 세포 배양액에 10% heparin을 3시간 동안 처리하여 세포막의 HS에 결합한 Vax1 단백질을 배양액으로 이동시킨 다음 배양액 단백질을 WB로 분석하여 배양액에 존재하는 Vax1 단백질의 상대량을 heparin 비처리군과 상호 비교함. (C) 293T 세포에 Vax1과 GFP-Sdc2를 함께 발현 후 GFP에 대한 항체로 면역침강 후 함께 분리된 Vax1의 양을 WB으로 조사함. (D) COS7 세포에 Myc/His 표지된 Vax1 또는 Vax1(KR/AA) 재조합단백질을 처리하고 12시간 이후에 세포에 존재하는 Vax1 단백질들을 Myc 항체를 이용한 면역염색으로 조사함
표
세포 표면 부착 이상 Vax1(KR/AA) 변이형. (A) (위) Otx2와 Vax1의 당사슬 결합 부위. (아래)293T 세포에 정상 Vax1, 전사활성 저하형 Vax1(R152S), Vax1(RK/AA) 변이형을 발현 후 함께 발현한 Vax1 타겟인 Tcf7l1-luciferase 활성을 조사하여 Vax1 비발현 세포 (Mock)의 luciferase 값과 비교함. (B) 293T 세포에 Vax1 또는 Vax1(KR/AA)를 발현 후 세포 배양액에 10% heparin을 3시간 동안 처리하여 세포막의 HS에 결합한 Vax1 단백질을 배양액으로 이동시킨 다음 배양액 단백질을 WB로 분석하여 배양액에 존재하는 Vax1 단백질의 상대량을 heparin 비처리군과 상호 비교함. (C) 293T 세포에 Vax1과 GFP-Sdc2를 함께 발현 후 GFP에 대한 항체로 면역침강 후 함께 분리된 Vax1의 양을 WB으로 조사함. (D) COS7 세포에 Myc/His 표지된 Vax1 또는 Vax1(KR/AA) 재조합단백질을 처리하고 12시간 이후에 세포에 존재하는 Vax1 단백질들을 Myc 항체를 이용한 면역염색으로 조사함
 표
Vax1(KR/AA) 생쥐 제작을 위한 CRISPR/Cas9 실험. (위) 생쥐 Vax1 유전자 구성도 및 genotyping PCR primer 위치 표시. Vax1 exon 2번에 해당하는 DNA 염기서열 내 K101, R102 부위가 A101, A102로 변환한 ssDNA를 합성하여 (오렌지색) K101 부위 DNA 앞 17bp 부위를 타겟으로 하는 gRNA와 함께 생쥐 수정란에 주입함. (아래 왼쪽) mVax1-F/Vax1-KI_R primer로 KI Vax1 부위를 증폭하고, mVax1-GT_F/mVax1-GT_R primer로 WT Vax1 부위를 증폭함. 그 결과 6마리의 배아 중 총 5마리에서 KI Vax1이 관찰이 되었고, 이들 유전자 Vax1 exon2 부위를 분리하여 유전자 염기서열을 분석한 결과 3마리는 KI/KI homozygote, 2마리는 KI/del로 확인되었다
표
Vax1(KR/AA) 생쥐 제작을 위한 CRISPR/Cas9 실험. (위) 생쥐 Vax1 유전자 구성도 및 genotyping PCR primer 위치 표시. Vax1 exon 2번에 해당하는 DNA 염기서열 내 K101, R102 부위가 A101, A102로 변환한 ssDNA를 합성하여 (오렌지색) K101 부위 DNA 앞 17bp 부위를 타겟으로 하는 gRNA와 함께 생쥐 수정란에 주입함. (아래 왼쪽) mVax1-F/Vax1-KI_R primer로 KI Vax1 부위를 증폭하고, mVax1-GT_F/mVax1-GT_R primer로 WT Vax1 부위를 증폭함. 그 결과 6마리의 배아 중 총 5마리에서 KI Vax1이 관찰이 되었고, 이들 유전자 Vax1 exon2 부위를 분리하여 유전자 염기서열을 분석한 결과 3마리는 KI/KI homozygote, 2마리는 KI/del로 확인되었다
 표
변이형 Vax1 생쥐의 성체시기 해부학적 뇌 분석. (A) 생후 30일 된 생쥐에 뇌를 위쪽(왼쪽)과 아래쪽(오른쪽)에서 바라본 모습. 정상 Vax1 생쥐에 뇌에서는 시신경 교차가 일어나나, 변이형 Vax1 생쥐에 뇌에서는 시신경 교차가 일어나지 않음 (오른쪽). (B) 동결절편기를 이용하여 뇌를 절단 한 후, H&E 염색을 통해 해부학적 구조 관철 결과함. 태아시기와 마찬가지고 변이형에서 뇌교 (corpus callosum, 중간의 백색질) 가 형성되지 않았으며, septum 부위에 비정상적 구조로 인해 뇌실(ventricle) 부위가 확장된 모습도 보임. septum 부위에서 변이형 Vax1 의 전사 활성 이상으로 구조적 변화를 일으킨 것으로 예상됨. (C) 면역 형광 염색법을 이용하여 뇌교를 관찰 한 결과, 정상 Vax1 생쥐의 뇌교에서는 Vax1 단백질의 염색과 신경축삭 표지자인 NF160 이 함께 관찰 되었으나 변이형에서는 뇌교가 형성되지 않았으며, NF160 의 표지 및 Vax1 이 관찰되지 않았음
표
변이형 Vax1 생쥐의 성체시기 해부학적 뇌 분석. (A) 생후 30일 된 생쥐에 뇌를 위쪽(왼쪽)과 아래쪽(오른쪽)에서 바라본 모습. 정상 Vax1 생쥐에 뇌에서는 시신경 교차가 일어나나, 변이형 Vax1 생쥐에 뇌에서는 시신경 교차가 일어나지 않음 (오른쪽). (B) 동결절편기를 이용하여 뇌를 절단 한 후, H&E 염색을 통해 해부학적 구조 관철 결과함. 태아시기와 마찬가지고 변이형에서 뇌교 (corpus callosum, 중간의 백색질) 가 형성되지 않았으며, septum 부위에 비정상적 구조로 인해 뇌실(ventricle) 부위가 확장된 모습도 보임. septum 부위에서 변이형 Vax1 의 전사 활성 이상으로 구조적 변화를 일으킨 것으로 예상됨. (C) 면역 형광 염색법을 이용하여 뇌교를 관찰 한 결과, 정상 Vax1 생쥐의 뇌교에서는 Vax1 단백질의 염색과 신경축삭 표지자인 NF160 이 함께 관찰 되었으나 변이형에서는 뇌교가 형성되지 않았으며, NF160 의 표지 및 Vax1 이 관찰되지 않았음
 표
Vax1 (KR/AA) 생쥐에서 나타나는 시신경 교차 장애. 앞의 그림 ?에 따르면 정상 Vax1 유전자를 발현하는 생쥐에서는 시신경교차가 정상적인 구조인 반면, 변이형 Vax1 (AA) 유전자를 발현하는 생쥐에서는 시신경 교차의 구조가 나타나지 않음. (A) 생쥐 시각계에서 시신경의 95% 이상은 눈과 반대쪽에 위치한 뇌 부위로 연결되고 5% 이내의 시신경이 동일한 쪽의 뇌 부위로 연결이 됨. 특히, 이 중 측시상핵(lateral geniculate nucleus, LGN)으로 연결된 시신경은 망막의 이미지를 전달하고 이 정보가 대뇌의 시각중추 (visual cortex 1, V1) 영역으로 전달되는 특징이 있음. (B) 이러한 시신경 교차 여부를 확인하는 방법은 생쥐의 좌우측 눈에 각각 다른 색깔을 나타내는 시신경 염색 형광물질을 주입한 후 이들 형광물질이 좌우측 LGN에 분포하는 양상을 통해 알 수 있음. 즉, 오른쪽 눈(right eye, RE)에 주입한 녹색 형광물질에 염색된 시신경의 대부분은 왼쪽 LGN에서 검출되고, 왼쪽 눈(left eye, LR)에 주입한 적색 형광물질에 염색된 시신영은 오른쪽 LGN에서 주로 검출됨. (C) 생후 60일 된 생쥐에 눈에 각각 녹색과 붉은색 형광을 나타내는 Cholera Toxin B (CTB)를 주입함. Vax1(+/AA) 생쥐에서는 시신경교차로 인해 CTB를 주입한 대부분 반대쪽 뇌의 LGN 영역에서 염색되었으나, Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐에서는 시신경 교차의 상실로 인해 CTB가 주입한 눈과 같은 쪽 뇌 영역에서 염색되었음. 이는 Vax1의 세포 간 이동이 저해되면 시신경이 뇌 중간선 부위를 통과하지 못하고 같은 쪽 뇌로 진행을 함을 의미함
표
Vax1 (KR/AA) 생쥐에서 나타나는 시신경 교차 장애. 앞의 그림 ?에 따르면 정상 Vax1 유전자를 발현하는 생쥐에서는 시신경교차가 정상적인 구조인 반면, 변이형 Vax1 (AA) 유전자를 발현하는 생쥐에서는 시신경 교차의 구조가 나타나지 않음. (A) 생쥐 시각계에서 시신경의 95% 이상은 눈과 반대쪽에 위치한 뇌 부위로 연결되고 5% 이내의 시신경이 동일한 쪽의 뇌 부위로 연결이 됨. 특히, 이 중 측시상핵(lateral geniculate nucleus, LGN)으로 연결된 시신경은 망막의 이미지를 전달하고 이 정보가 대뇌의 시각중추 (visual cortex 1, V1) 영역으로 전달되는 특징이 있음. (B) 이러한 시신경 교차 여부를 확인하는 방법은 생쥐의 좌우측 눈에 각각 다른 색깔을 나타내는 시신경 염색 형광물질을 주입한 후 이들 형광물질이 좌우측 LGN에 분포하는 양상을 통해 알 수 있음. 즉, 오른쪽 눈(right eye, RE)에 주입한 녹색 형광물질에 염색된 시신경의 대부분은 왼쪽 LGN에서 검출되고, 왼쪽 눈(left eye, LR)에 주입한 적색 형광물질에 염색된 시신영은 오른쪽 LGN에서 주로 검출됨. (C) 생후 60일 된 생쥐에 눈에 각각 녹색과 붉은색 형광을 나타내는 Cholera Toxin B (CTB)를 주입함. Vax1(+/AA) 생쥐에서는 시신경교차로 인해 CTB를 주입한 대부분 반대쪽 뇌의 LGN 영역에서 염색되었으나, Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐에서는 시신경 교차의 상실로 인해 CTB가 주입한 눈과 같은 쪽 뇌 영역에서 염색되었음. 이는 Vax1의 세포 간 이동이 저해되면 시신경이 뇌 중간선 부위를 통과하지 못하고 같은 쪽 뇌로 진행을 함을 의미함
 표
Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 시신경 분석. (A) 생후 60일 생쥐 안구의 정면 사진(왼쪽)과 측면 사진(오른쪽). Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 경우 정상 Vax1(+/+) 생쥐와 비교해 안구의 형태와 크기가 크게 다르지 않음. (B) 생후 60일 Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐와 정상 Vax1(+/+) 생쥐의 시신경 절편을 H&E 염색하여 축삭(옅은 부위)과 시신경을 구성하는 다양한 세포들의 핵(진한 부위)을 염색함. 그 결과 축삭 주변에 시신경 세포들이 흩어져 분포하고 있음을 알 수 있음. 이는 Vax1(-/-) 생쥐에서 보고된 축삭과 시신경세포들의 상호작용 실패에 따른 망막 신경 축삭 노출 현상(defasciclation)과 차이가 있는 결과임. 시신경 내 성상세포(astrocyte) 핵를 표지하는 Pax2와 세포질을 표시하는 Gfap 역시 시신경에 골고루 분포함. 또한, 시신경을 통해 망막으로 연결된 혈관세포를 표지하는 CD31 역시 시신경에 정상적으로 분포함. 시신경 축삭을 둘러싸는 oligodendrocyte의 백색질에 집중된 지질을 Oil-Red O 염색으로 조사한 결과 백색질의 분포도 정상으로 판별됨
표
Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 시신경 분석. (A) 생후 60일 생쥐 안구의 정면 사진(왼쪽)과 측면 사진(오른쪽). Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 경우 정상 Vax1(+/+) 생쥐와 비교해 안구의 형태와 크기가 크게 다르지 않음. (B) 생후 60일 Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐와 정상 Vax1(+/+) 생쥐의 시신경 절편을 H&E 염색하여 축삭(옅은 부위)과 시신경을 구성하는 다양한 세포들의 핵(진한 부위)을 염색함. 그 결과 축삭 주변에 시신경 세포들이 흩어져 분포하고 있음을 알 수 있음. 이는 Vax1(-/-) 생쥐에서 보고된 축삭과 시신경세포들의 상호작용 실패에 따른 망막 신경 축삭 노출 현상(defasciclation)과 차이가 있는 결과임. 시신경 내 성상세포(astrocyte) 핵를 표지하는 Pax2와 세포질을 표시하는 Gfap 역시 시신경에 골고루 분포함. 또한, 시신경을 통해 망막으로 연결된 혈관세포를 표지하는 CD31 역시 시신경에 정상적으로 분포함. 시신경 축삭을 둘러싸는 oligodendrocyte의 백색질에 집중된 지질을 Oil-Red O 염색으로 조사한 결과 백색질의 분포도 정상으로 판별됨
 표
Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐 망막의 해부학적 분석. 생후 30일 된 생쥐 망막에 해부학적 분석. 생후 30일 된 Vax1 생쥐와 Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 망막세포를 면역형광염색법을 이용하여 망막을 구성하는 각각의 세포를 확인함. 광수용체 세포(photoreceptor)를 표지하는 Rhod,,M-cone 과 수평세포(horizontal cell)를 표지하는 Calbindin, 무축삭세포(amacrine cell)을 표지하는 Chx10, Pax6, 신경결세포(ganglion cell)을 표지하는 Brn3b 등을 이용하여 확인한 결과, 정상 생쥐와 Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐에서 망막에서 발현되는 단백질의 큰 변화는 보이지 않음. 이는 Vax1 단백질이 망막구조의 발생에는 직접적인 영향을 미치지 않음을 의미함
표
Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐 망막의 해부학적 분석. 생후 30일 된 생쥐 망막에 해부학적 분석. 생후 30일 된 Vax1 생쥐와 Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 망막세포를 면역형광염색법을 이용하여 망막을 구성하는 각각의 세포를 확인함. 광수용체 세포(photoreceptor)를 표지하는 Rhod,,M-cone 과 수평세포(horizontal cell)를 표지하는 Calbindin, 무축삭세포(amacrine cell)을 표지하는 Chx10, Pax6, 신경결세포(ganglion cell)을 표지하는 Brn3b 등을 이용하여 확인한 결과, 정상 생쥐와 Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐에서 망막에서 발현되는 단백질의 큰 변화는 보이지 않음. 이는 Vax1 단백질이 망막구조의 발생에는 직접적인 영향을 미치지 않음을 의미함
 표
Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 시각 기능 검사. (A) 시신경 교차가 일어나지 못한 Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐는 정상 생쥐와 비교해 눈에서 뇌로의 시신경 연결은 반전이 된 반면, 뇌에서 다양한 운동 신경들로 전달되는 경로는 정상과 유사하게 되어 있을 가능성이 높음. 이는 눈에서 감지한 이미지가 뇌로 전달이 되더라도 해당 이미지를 인식한 뇌가 운동을 유도하는 과정에서 방향성이 반전될 가능성이 있음 (모식도로 그리기). (B) 이러한 시각 정보와 운동의 반전 여부를 확인하기 위해, 시각운동 반응(optokinetic response, OKR)을 Optomotry를 이용하여 조사함. Vax1(+/AA) 생쥐는 좌우 방향으로 움직이는 세로축 선들에 반응해 머리를 같은 방향으로 움직이며, 그 정확도가 약 0.4로 정상 생쥐와 유사한 반면, Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐는 거의 반응을 하지 못하는 것을 알 수 있음 (n=3). (C) Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 비정상적 시각 반응이 망막 기능의 이상에서 나타나는지를 망막전위도 (electroretinogram, ERG) 측정을 통해 조사함. Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐는 정상 Vax1(+/+) 생쥐에 비해 명반응 자극에 대한 망막 전위도 (photopic ERG)의 a-wave에는 큰 차이를 나타내지 않았지만 b-wave는 정상보다 지연된 반응 양상을 보임
표
Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 시각 기능 검사. (A) 시신경 교차가 일어나지 못한 Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐는 정상 생쥐와 비교해 눈에서 뇌로의 시신경 연결은 반전이 된 반면, 뇌에서 다양한 운동 신경들로 전달되는 경로는 정상과 유사하게 되어 있을 가능성이 높음. 이는 눈에서 감지한 이미지가 뇌로 전달이 되더라도 해당 이미지를 인식한 뇌가 운동을 유도하는 과정에서 방향성이 반전될 가능성이 있음 (모식도로 그리기). (B) 이러한 시각 정보와 운동의 반전 여부를 확인하기 위해, 시각운동 반응(optokinetic response, OKR)을 Optomotry를 이용하여 조사함. Vax1(+/AA) 생쥐는 좌우 방향으로 움직이는 세로축 선들에 반응해 머리를 같은 방향으로 움직이며, 그 정확도가 약 0.4로 정상 생쥐와 유사한 반면, Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐는 거의 반응을 하지 못하는 것을 알 수 있음 (n=3). (C) Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐의 비정상적 시각 반응이 망막 기능의 이상에서 나타나는지를 망막전위도 (electroretinogram, ERG) 측정을 통해 조사함. Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐는 정상 Vax1(+/+) 생쥐에 비해 명반응 자극에 대한 망막 전위도 (photopic ERG)의 a-wave에는 큰 차이를 나타내지 않았지만 b-wave는 정상보다 지연된 반응 양상을 보임
 표
Vax1(KR/AA) 생쥐의 해부학적 분석. (위) 수정 후 15일 생쥐 배아 사진. 정상 및 Vax1(+/-) 생쥐와 달리 나머지 생쥐들에서는 안구 하부에 틈이 생기는 coloboma가 관찰됨. 해당 생쥐 뇌 절편을 조사한 결과 해당 생쥐의 optic stalk의 하부가 완전히 닫히지 않아 시신경 성장이 정상적으로 일어나지 못해 optic chiasm 형성이 일어나지 않음. ON, optic nerve. 다만, 변이형 Vax1 단백질만을 가지는 Vax1 AA/AA 생쥐에서는 입 천장이 열리는 구개열이 나타나지는 않음. 입천장 뼈를 만드는 신경능세포(Neural crest cell) 에서는 Vax1에 역할에 대한 규명이 필요함
표
Vax1(KR/AA) 생쥐의 해부학적 분석. (위) 수정 후 15일 생쥐 배아 사진. 정상 및 Vax1(+/-) 생쥐와 달리 나머지 생쥐들에서는 안구 하부에 틈이 생기는 coloboma가 관찰됨. 해당 생쥐 뇌 절편을 조사한 결과 해당 생쥐의 optic stalk의 하부가 완전히 닫히지 않아 시신경 성장이 정상적으로 일어나지 못해 optic chiasm 형성이 일어나지 않음. ON, optic nerve. 다만, 변이형 Vax1 단백질만을 가지는 Vax1 AA/AA 생쥐에서는 입 천장이 열리는 구개열이 나타나지는 않음. 입천장 뼈를 만드는 신경능세포(Neural crest cell) 에서는 Vax1에 역할에 대한 규명이 필요함
 표
Vax1(AA) 단백질의 세포 간 이동 저하. 1차년도에 제작 완료한 Vax1(AA) 단백질을 발현하는 생쥐 시신경에서 세포 간 이동을 검증하기 위하여 각기 정상 Vax1 및 변이형 Vax1(AA) 유전자를 0, 1, 2개 씩 발현하는 수정 후 14.5일 생쥐 시신경 내 Vax1을 시신경축삭 표지자인 Nf160 과의 면역형광염색을 통해 조사함. 그 결과, 정상 생쥐 시신경 축삭에서 관찰되던 Vax1 단백질이 Vax1(AA)만을 발현하는 생쥐 시신경축삭에서는 관찰되지 않음. 이는 시신경을 둘러싸고 있는 astrocyte precursor cell (APC)에서 발현된 Vax1이 시신경축삭으로 이동이 되지 못했음을 의미함
표
Vax1(AA) 단백질의 세포 간 이동 저하. 1차년도에 제작 완료한 Vax1(AA) 단백질을 발현하는 생쥐 시신경에서 세포 간 이동을 검증하기 위하여 각기 정상 Vax1 및 변이형 Vax1(AA) 유전자를 0, 1, 2개 씩 발현하는 수정 후 14.5일 생쥐 시신경 내 Vax1을 시신경축삭 표지자인 Nf160 과의 면역형광염색을 통해 조사함. 그 결과, 정상 생쥐 시신경 축삭에서 관찰되던 Vax1 단백질이 Vax1(AA)만을 발현하는 생쥐 시신경축삭에서는 관찰되지 않음. 이는 시신경을 둘러싸고 있는 astrocyte precursor cell (APC)에서 발현된 Vax1이 시신경축삭으로 이동이 되지 못했음을 의미함
 표
Vax1(AA) 생쥐에서 관찰된 hypomorphic phenotype. 선행연구를 통해 Vax1(AA) 변이 단백질은 세포 간 이동 뿐만 아니라 Vax1 타겟 유전자에 대한 전사 활성 역시 정상의 80% 정도로 감소함을 발견하였다. 이는 Vax1(AA) 생쥐에서 나타난 변화들이 단백질이 세포 간 이동 실패로 인해 나타나는 것과 동시에 Vax1 타겟 유전자 발현의 저하에 의해서도 나타날 가능성이 있다. 이를 확인하기 위해 Vax1 전사 기능에 의존적인 것으로 알려진 망막과 시축(optic stalk) 사이의 경계 형성을 망막과 시축의 마커인 Pax6와 Pax2의 분포를 통해 조사하였다. Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐에서 망막 부위가 시축 영역으로 확장되어 있으며, 이 부위는 두 영역의 세포들이 섞여 있는 특징을 보인다. 다만, 이 현상은 Vax1(-/-) 생쥐에서 보이는 망막 영역의 전반적 확장 현상 보다는 다소 약한 특징을 보임
표
Vax1(AA) 생쥐에서 관찰된 hypomorphic phenotype. 선행연구를 통해 Vax1(AA) 변이 단백질은 세포 간 이동 뿐만 아니라 Vax1 타겟 유전자에 대한 전사 활성 역시 정상의 80% 정도로 감소함을 발견하였다. 이는 Vax1(AA) 생쥐에서 나타난 변화들이 단백질이 세포 간 이동 실패로 인해 나타나는 것과 동시에 Vax1 타겟 유전자 발현의 저하에 의해서도 나타날 가능성이 있다. 이를 확인하기 위해 Vax1 전사 기능에 의존적인 것으로 알려진 망막과 시축(optic stalk) 사이의 경계 형성을 망막과 시축의 마커인 Pax6와 Pax2의 분포를 통해 조사하였다. Vax1(AA/AA) 생쥐에서 망막 부위가 시축 영역으로 확장되어 있으며, 이 부위는 두 영역의 세포들이 섞여 있는 특징을 보인다. 다만, 이 현상은 Vax1(-/-) 생쥐에서 보이는 망막 영역의 전반적 확장 현상 보다는 다소 약한 특징을 보임
 표
Otx2-AA 단백질의 세포 간 이동 능력 측정. 1단계 연구를 통해 cortical PV cell 외부의 perineural network (PNN)의 chondroitin sulfate (CS)에 결합하는 부위로 판명된 Otx2의 44-45번에 있는 Arg-Lys (RK) 부위를 Alanine으로 치환한 Otx2-AA 단백질의 세포 간 이동 능력을 배양세포에서 조사함. (A) Otx2를 과발현하는 293T 세포의 배양액 (growth medium (GM))을 heparin 존재 여부에 따라 분리한 후 각 배양액에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질의 양을 조사함. 그 결과 정상 Otx2 단백질은 heparin 처리 없이는 배양액에서 거의 검출이 되지 않았지만, Otx2-AA는 heparin 처리 없이도 정상보다 3배 이상의 단백질이 배양액에 존재함. 이는 Otx2-AA 단백질의 세포막 부착력이 약화되었음을 의미함. (B) Otx2-AA 단백질의 세포 간 이동을 조사하기 위해 Otx2-myc/His 재조합단백질을 COS7 세포에 처리 후 세포 배양액을 포집하여 세포에 결합하지 못하고 배양액에 남은 단백질과 넣어 준 단백질 양을 상호 비교함. 그 결과, Otx2의 경우는 약 60% 단백질이 세포로 이동하지 못하고 남아 있지만 Otx2-AA는 거의 대부분 단백질이 세포로 이동하지 못하고 배양액에 남아 있음을 확인함. (C) 마찬가지로 COS7 세포 내부로 이동한 Otx2 단백질의 양을 면역형광염색으로 조사한 결과 세포의 핵까지 이동한 정상 Otx2보다 Otx2-AA 단백질은 세포막에만 일부 검출될 뿐 세포 내부로 이동이 거의 이루어지지 않음
표
Otx2-AA 단백질의 세포 간 이동 능력 측정. 1단계 연구를 통해 cortical PV cell 외부의 perineural network (PNN)의 chondroitin sulfate (CS)에 결합하는 부위로 판명된 Otx2의 44-45번에 있는 Arg-Lys (RK) 부위를 Alanine으로 치환한 Otx2-AA 단백질의 세포 간 이동 능력을 배양세포에서 조사함. (A) Otx2를 과발현하는 293T 세포의 배양액 (growth medium (GM))을 heparin 존재 여부에 따라 분리한 후 각 배양액에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질의 양을 조사함. 그 결과 정상 Otx2 단백질은 heparin 처리 없이는 배양액에서 거의 검출이 되지 않았지만, Otx2-AA는 heparin 처리 없이도 정상보다 3배 이상의 단백질이 배양액에 존재함. 이는 Otx2-AA 단백질의 세포막 부착력이 약화되었음을 의미함. (B) Otx2-AA 단백질의 세포 간 이동을 조사하기 위해 Otx2-myc/His 재조합단백질을 COS7 세포에 처리 후 세포 배양액을 포집하여 세포에 결합하지 못하고 배양액에 남은 단백질과 넣어 준 단백질 양을 상호 비교함. 그 결과, Otx2의 경우는 약 60% 단백질이 세포로 이동하지 못하고 남아 있지만 Otx2-AA는 거의 대부분 단백질이 세포로 이동하지 못하고 배양액에 남아 있음을 확인함. (C) 마찬가지로 COS7 세포 내부로 이동한 Otx2 단백질의 양을 면역형광염색으로 조사한 결과 세포의 핵까지 이동한 정상 Otx2보다 Otx2-AA 단백질은 세포막에만 일부 검출될 뿐 세포 내부로 이동이 거의 이루어지지 않음
 표
Otx2-AA 단백질의 생화학적 활성 검증. (A) Otx2와 Otx2-AA 단백질을 각각 Otx2의 타겟 유전자인 IRBP의 promoter 부위에 해당되는 DNA oligomer probe와 섞어서 타겟 DNA 서열에 대한 결합력을 측정함. 그 결과 Otx2-AA는 Otx2와 비교해 약간 감소하였지만 여전히 정상적인 DNA 결합능력을 가지고 있음을 확인함. (B) DNA에 정상적 결합을 하는 Otx2-AA의 전사촉진 활성을 망막 내 Otx2 타겟 유전자인 Crx와 PKCalpha promoter에 의해 발현되는 luciferase의 활성을 조사함으로써 확인함. 그 결과 Otx2-AA는 Otx2에 비해 약 70~80% 정도의 전사활성을 가지는 것으로 확인됨
표
Otx2-AA 단백질의 생화학적 활성 검증. (A) Otx2와 Otx2-AA 단백질을 각각 Otx2의 타겟 유전자인 IRBP의 promoter 부위에 해당되는 DNA oligomer probe와 섞어서 타겟 DNA 서열에 대한 결합력을 측정함. 그 결과 Otx2-AA는 Otx2와 비교해 약간 감소하였지만 여전히 정상적인 DNA 결합능력을 가지고 있음을 확인함. (B) DNA에 정상적 결합을 하는 Otx2-AA의 전사촉진 활성을 망막 내 Otx2 타겟 유전자인 Crx와 PKCalpha promoter에 의해 발현되는 luciferase의 활성을 조사함으로써 확인함. 그 결과 Otx2-AA는 Otx2에 비해 약 70~80% 정도의 전사활성을 가지는 것으로 확인됨
 표
Otx2-AA 생쥐의 뇌 발달 유지 효과. Otx2의 활성이 정상에 비해 약 70% 정도인 Otx2-AA의 기능이 실재로 생체 내에서 어떤 발달 이상을 가지고 올지를 조사하기 위해, Otx2가 2개 모두 정상인 경우 (Otx2+/+), 하나의 정상 Otx2와 하나의 Otx2-AA를 가지는 경우 (Otx2+/AA), Otx2-AA만 두 개 가지는 경우 (Otx2AA/AA), Otx2 하나만 가지는 경우 (Otx2+/GFP), Otx2-AA만 하나 가지는 경우 (Otx2AA/GFP)로 나누어 뇌와 안구 발달을 조사함. 그 결과, Otx2가 하나만 있을 때는 뇌와 안구 발달 모두 정상이지만, Otx2-AA만 하나 가진 경우는 안구 발달이 전혀 이루어지지 않고 뇌의 크기도 줄어들어 있음을 알 수 있다. 이는 Otx2-AA가 정 상적인 Otx2에 비해 그 기능이 심각히 약함을 알 수 있음. 또한, Otx2-AA만 두 개 있는 경우, 뇌 발달은 정상이지만 안구의 발달에 약한 이상이 있는 것을 알 수 있음. 이는 Otx2-AA 두 개가 Otx2하나보다 그 활성이 부족함을 시사함. 따라서, 정상 Otx2 하나만 가질 경우 생체는 최소 70% 이상의 전사활성을 가지거나, 70% 이하의 전사활성을 가지더라도 세포 간 이동을 함으로써 이를 보정할 수 있다고 판단할 수 있음
표
Otx2-AA 생쥐의 뇌 발달 유지 효과. Otx2의 활성이 정상에 비해 약 70% 정도인 Otx2-AA의 기능이 실재로 생체 내에서 어떤 발달 이상을 가지고 올지를 조사하기 위해, Otx2가 2개 모두 정상인 경우 (Otx2+/+), 하나의 정상 Otx2와 하나의 Otx2-AA를 가지는 경우 (Otx2+/AA), Otx2-AA만 두 개 가지는 경우 (Otx2AA/AA), Otx2 하나만 가지는 경우 (Otx2+/GFP), Otx2-AA만 하나 가지는 경우 (Otx2AA/GFP)로 나누어 뇌와 안구 발달을 조사함. 그 결과, Otx2가 하나만 있을 때는 뇌와 안구 발달 모두 정상이지만, Otx2-AA만 하나 가진 경우는 안구 발달이 전혀 이루어지지 않고 뇌의 크기도 줄어들어 있음을 알 수 있다. 이는 Otx2-AA가 정 상적인 Otx2에 비해 그 기능이 심각히 약함을 알 수 있음. 또한, Otx2-AA만 두 개 있는 경우, 뇌 발달은 정상이지만 안구의 발달에 약한 이상이 있는 것을 알 수 있음. 이는 Otx2-AA 두 개가 Otx2하나보다 그 활성이 부족함을 시사함. 따라서, 정상 Otx2 하나만 가질 경우 생체는 최소 70% 이상의 전사활성을 가지거나, 70% 이하의 전사활성을 가지더라도 세포 간 이동을 함으로써 이를 보정할 수 있다고 판단할 수 있음
 표
Otx2-AA 생쥐의 시력 테스트. 각기 다른 Otx2 유전자의 변이를 가진 생쥐들의 시력을 검증하기 위하여 생후 60일 생쥐들을 Optomotry를 이용하여 생쥐 정면에 각기 흑백의 세로띠를 반시계 방향으로 속도를 변화시키며 이동할 때 (cyc/deg) 나타나는 생쥐의 머리 돌림 반응도 (head turns) 측정으로 시력을 검증함. 그 결과 Otx2(+/AA) 생쥐는 정상과 비교하여 약간 감소한 시력이지만 여전히 정상 수준의 시각을 가지고 있었지만, Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐는 시력이 심각한 정도로 손상되어 있었고, Otx2(AA/AA) 생쥐는 시력이 거의 존재하지 않는 상태로 판명됨
표
Otx2-AA 생쥐의 시력 테스트. 각기 다른 Otx2 유전자의 변이를 가진 생쥐들의 시력을 검증하기 위하여 생후 60일 생쥐들을 Optomotry를 이용하여 생쥐 정면에 각기 흑백의 세로띠를 반시계 방향으로 속도를 변화시키며 이동할 때 (cyc/deg) 나타나는 생쥐의 머리 돌림 반응도 (head turns) 측정으로 시력을 검증함. 그 결과 Otx2(+/AA) 생쥐는 정상과 비교하여 약간 감소한 시력이지만 여전히 정상 수준의 시각을 가지고 있었지만, Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐는 시력이 심각한 정도로 손상되어 있었고, Otx2(AA/AA) 생쥐는 시력이 거의 존재하지 않는 상태로 판명됨
 표
Otx2-AA 생쥐 망막의 시각 반응도 테스트. 그림 92에서 확인한 Otx2(+/GFP) 및 Otx2(AA/AA) 생쥐의 시력 상실의 원인이 망막 수준의 활성도 감소에서 나타나는지를 검증하기 위하여 생후 30일 및 60일 생쥐 망막의 빛에 대한 반응도를 electroretinogram (ERG)를 이용하여 측정하였다. 그 결과 약한 빛에 반응하는 관상세포 (rod photoreceptor)와 이와 연결된 양극세포의 반응을 측정하는 scotopic ERG 반응에서 관상세포 반응도를 나타내는 a-wave의 경우 Otx2(+/GFP)와 Otx2(AA/AA) 생쥐가 정상에 비해 약 70% 수준의 반응도를 나타내는 반면 (A), b-wave 반응은 거의 30% 이하로 나타나 (C) 이들 생쥐 시력 약화의 원인은 양극세포의 수준에서 주로 나타남을 확인함
표
Otx2-AA 생쥐 망막의 시각 반응도 테스트. 그림 92에서 확인한 Otx2(+/GFP) 및 Otx2(AA/AA) 생쥐의 시력 상실의 원인이 망막 수준의 활성도 감소에서 나타나는지를 검증하기 위하여 생후 30일 및 60일 생쥐 망막의 빛에 대한 반응도를 electroretinogram (ERG)를 이용하여 측정하였다. 그 결과 약한 빛에 반응하는 관상세포 (rod photoreceptor)와 이와 연결된 양극세포의 반응을 측정하는 scotopic ERG 반응에서 관상세포 반응도를 나타내는 a-wave의 경우 Otx2(+/GFP)와 Otx2(AA/AA) 생쥐가 정상에 비해 약 70% 수준의 반응도를 나타내는 반면 (A), b-wave 반응은 거의 30% 이하로 나타나 (C) 이들 생쥐 시력 약화의 원인은 양극세포의 수준에서 주로 나타남을 확인함
 표
Otx2 활성에 따른 망막신경 발달 및 퇴화. (A) 뇌와 안구발달을 통해 추정한 Otx2와 Otx2-AA의 상대적 활성을 안구 발달이 정상인 생쥐 망막에서 추가로 검증함. 안구 크기가 정상인 Otx2+/GFP와 Otx2AA/AA의 경우 생후 2주 (P14)부터 이미 INL을 구성하는 세포의 수가 감소되어 있음을 보아, Otx2가 하나만 있거나 활성이 떨어진 Otx2-AA 두 개를 가지는 경우는 망막 신경 발달이 정상적으로 이루어 질 수 없음을 증명함. 또한, 더 나아가 이 망막조직들은 시간이 지남에 따라 망막신경들의 퇴화가 일어나는 것으로 보아 Otx2의 기능이 망막발달 뿐만 아니라 망막신경세포의 유지에도 중요함을 알 수 있음. (B) 구조적으로 정상인 Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막의 경우도 두께가 정상에 비해 약 20% 이상 감소해 있었으며, 광수용세포가 위치한 outer nuclear layer (ONL) 뿐만 아니라 interneuron들이 위치한 inner nuclear layer (INL)에 걸쳐 광범위한 세포의 감소가 나타났다
표
Otx2 활성에 따른 망막신경 발달 및 퇴화. (A) 뇌와 안구발달을 통해 추정한 Otx2와 Otx2-AA의 상대적 활성을 안구 발달이 정상인 생쥐 망막에서 추가로 검증함. 안구 크기가 정상인 Otx2+/GFP와 Otx2AA/AA의 경우 생후 2주 (P14)부터 이미 INL을 구성하는 세포의 수가 감소되어 있음을 보아, Otx2가 하나만 있거나 활성이 떨어진 Otx2-AA 두 개를 가지는 경우는 망막 신경 발달이 정상적으로 이루어 질 수 없음을 증명함. 또한, 더 나아가 이 망막조직들은 시간이 지남에 따라 망막신경들의 퇴화가 일어나는 것으로 보아 Otx2의 기능이 망막발달 뿐만 아니라 망막신경세포의 유지에도 중요함을 알 수 있음. (B) 구조적으로 정상인 Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막의 경우도 두께가 정상에 비해 약 20% 이상 감소해 있었으며, 광수용세포가 위치한 outer nuclear layer (ONL) 뿐만 아니라 interneuron들이 위치한 inner nuclear layer (INL)에 걸쳐 광범위한 세포의 감소가 나타났다
 표
Otx2-AA/AA 망막에서 줄어든 INL과 ONL의 두께가 세포의 발달 이상인지 아니면 세포의 과도한 사멸 때문에 일어나는지를 검증하기 위해 4주령 정상 생쥐 (WT)와 Otx2-AA/+ (Ht), Otx2-AA/AA (Ho) 망막에서 apoptosis로 죽어가는 세포의 분포를 TUNEL 염색으로 조사함. 그 결과 Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막 내 ONL 및 INL 상층부 세포에서 TUNEL에 의해 염색되는 세포의 수가 증가되어 있음을 알 수 있다. Otx2-AA/+ 생쥐 망막에도 일부 ONL 세포에서 TUNEL 신호가 관찰된 것으로 보아 Otx2의 세포 간 이동이 광수용세포의 생존에 중요할 것으로 예측함
표
Otx2-AA/AA 망막에서 줄어든 INL과 ONL의 두께가 세포의 발달 이상인지 아니면 세포의 과도한 사멸 때문에 일어나는지를 검증하기 위해 4주령 정상 생쥐 (WT)와 Otx2-AA/+ (Ht), Otx2-AA/AA (Ho) 망막에서 apoptosis로 죽어가는 세포의 분포를 TUNEL 염색으로 조사함. 그 결과 Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막 내 ONL 및 INL 상층부 세포에서 TUNEL에 의해 염색되는 세포의 수가 증가되어 있음을 알 수 있다. Otx2-AA/+ 생쥐 망막에도 일부 ONL 세포에서 TUNEL 신호가 관찰된 것으로 보아 Otx2의 세포 간 이동이 광수용세포의 생존에 중요할 것으로 예측함
 표
망막 내 Otx2-AA 발현양 저하와 양극세포 감소. 6주령 Otx2-AA/AA 망막에서 Otx2를 발현하는 INL 내 세포의 수가 정상의 30% 수준으로 급감한 것을 알 수 있다. 이는 Otx2를 발현하는 INL 세포 수의 감소와 일치하는 것으로 세포 간 이동 기능이 저하된 Otx2-AA는 Otx2 발달 및 유지를 지원하지 못하는 것으로 판명됨. 양극세포에서 발현된 Otx2가 이동하여 분포하는 RGC에도 Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막에서는 Otx2가 거의 상실이 되어, Otx2-AA 단백질은 세포 간 이동이 결여되었음을 다시 한 번 증명함. 또한, ONL의 광수용세포 세포질과 inner segment에서 관찰되던 Otx2 단백질 역시 거의 사라짐을 알 수 있다. 그 결과 ONL에 위치하는 광수용세포의 전체 숫자도 정상의 60% 정도로 줄어들어 있음을 알 수 있다
표
망막 내 Otx2-AA 발현양 저하와 양극세포 감소. 6주령 Otx2-AA/AA 망막에서 Otx2를 발현하는 INL 내 세포의 수가 정상의 30% 수준으로 급감한 것을 알 수 있다. 이는 Otx2를 발현하는 INL 세포 수의 감소와 일치하는 것으로 세포 간 이동 기능이 저하된 Otx2-AA는 Otx2 발달 및 유지를 지원하지 못하는 것으로 판명됨. 양극세포에서 발현된 Otx2가 이동하여 분포하는 RGC에도 Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막에서는 Otx2가 거의 상실이 되어, Otx2-AA 단백질은 세포 간 이동이 결여되었음을 다시 한 번 증명함. 또한, ONL의 광수용세포 세포질과 inner segment에서 관찰되던 Otx2 단백질 역시 거의 사라짐을 알 수 있다. 그 결과 ONL에 위치하는 광수용세포의 전체 숫자도 정상의 60% 정도로 줄어들어 있음을 알 수 있다
 표
Otx2-AA/AA 망막 내 원추세포 특이적 광수용세포 사멸. Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막에서 INL과 더불어 ONL에서도 세포의 유실이 일어났으므로, ONL 세포 유실이 관상세포 (rod photoreceptor)와 원추세포 (cone photoreceptor) 중 어느 세포 군에서 주로 일어났는지를 조사하기 위하여, 6주령의 WT 생쥐와 Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막을 관상세포 특이적 rodopsin과 원추세포 특이적 G/R opsin을 이용하여 면역형광염색을 수행함. 그 결과 관상세포의 수에는 큰 차이가 없었지만, 원추세포의 경우는 심각한 세포수의 감소가 나타남. 따라서, Otx2-AA/AA 망막 ONL에서의 세포 유실은 주로 원추세포의 유실에 의한 것인 것으로 예측함
표
Otx2-AA/AA 망막 내 원추세포 특이적 광수용세포 사멸. Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막에서 INL과 더불어 ONL에서도 세포의 유실이 일어났으므로, ONL 세포 유실이 관상세포 (rod photoreceptor)와 원추세포 (cone photoreceptor) 중 어느 세포 군에서 주로 일어났는지를 조사하기 위하여, 6주령의 WT 생쥐와 Otx2-AA/AA 생쥐 망막을 관상세포 특이적 rodopsin과 원추세포 특이적 G/R opsin을 이용하여 면역형광염색을 수행함. 그 결과 관상세포의 수에는 큰 차이가 없었지만, 원추세포의 경우는 심각한 세포수의 감소가 나타남. 따라서, Otx2-AA/AA 망막 ONL에서의 세포 유실은 주로 원추세포의 유실에 의한 것인 것으로 예측함
 표
내부 Otx2와 외부 Otx2의 기능 예측. 위의 결과들을 기반으로 각 신경 조직의 정상적 발달 및 유지에 필요한 Otx2 활성을 도식화 함. 결과에 의하면 Otx2의 기능은 세포 내부에서 발현되어 작용하는 내부 Otx2 단백질과 외부로부터 이동하여 세포 내 기능에 참여하는 외부 Otx2 단백질로 나누어 볼 수 있다. 이들 두 종류의 Otx2 단백질 기능의 총합이 세포가 가지는 Otx2 활성이 총합이라고 볼 수 있다. 정상적 뇌의 발달을 위해서는 최소한 정상에 비해 38%의 Otx2 기능이 요구됨을 알 수 있고, 이는 Otx2AA/GFP에서 처럼 주로 세포 내부에서 작용하는 Otx2의 활성과 유사한 양상을 보인다. 망막 발달을 위한 최소의 Otx2 활성은 약 51%이며 이는 세포 내부의 기능 뿐만 아니라 세포 외부에서 영입되는 단백질 또한 필요로 함을 알 수 있다. 즉, 세포 내부 단백질의 총량이 정상에 비해 약 63%이지만 세포 외부로부터 영입되는 단백질의 양이 정상의 39% 밖에 되지 않는 Otx2AA/AA의 경우에는 약한 눈 발생의 이상과 더불어 망막 내 양극세포의 발달 이상을 나타낸다. Otx2+/GFP의 경우는 세포 내부 단백질 총량은 Otx2AA/AA에 비해 오히려 약간 낮지만 세포 간이동에 의해 획득한 외부 단백질이 오히려 높아 총량 역시 61% 정도가 되어 안구 발달은 정상이고 약한 양극세포의 발달 이상만 보인다
표
내부 Otx2와 외부 Otx2의 기능 예측. 위의 결과들을 기반으로 각 신경 조직의 정상적 발달 및 유지에 필요한 Otx2 활성을 도식화 함. 결과에 의하면 Otx2의 기능은 세포 내부에서 발현되어 작용하는 내부 Otx2 단백질과 외부로부터 이동하여 세포 내 기능에 참여하는 외부 Otx2 단백질로 나누어 볼 수 있다. 이들 두 종류의 Otx2 단백질 기능의 총합이 세포가 가지는 Otx2 활성이 총합이라고 볼 수 있다. 정상적 뇌의 발달을 위해서는 최소한 정상에 비해 38%의 Otx2 기능이 요구됨을 알 수 있고, 이는 Otx2AA/GFP에서 처럼 주로 세포 내부에서 작용하는 Otx2의 활성과 유사한 양상을 보인다. 망막 발달을 위한 최소의 Otx2 활성은 약 51%이며 이는 세포 내부의 기능 뿐만 아니라 세포 외부에서 영입되는 단백질 또한 필요로 함을 알 수 있다. 즉, 세포 내부 단백질의 총량이 정상에 비해 약 63%이지만 세포 외부로부터 영입되는 단백질의 양이 정상의 39% 밖에 되지 않는 Otx2AA/AA의 경우에는 약한 눈 발생의 이상과 더불어 망막 내 양극세포의 발달 이상을 나타낸다. Otx2+/GFP의 경우는 세포 내부 단백질 총량은 Otx2AA/AA에 비해 오히려 약간 낮지만 세포 간이동에 의해 획득한 외부 단백질이 오히려 높아 총량 역시 61% 정도가 되어 안구 발달은 정상이고 약한 양극세포의 발달 이상만 보인다
 표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 Otx2의 양적 변화. 망막의 발달 및 퇴화가 관찰된 P90 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막 내 Otx2 단백질과 mRNA 양을 정상생쥐와 Western blot (WB)와 RT-qPCR을 통해 비교함. 그 결과 단백질의 경우 정상에 비해 약 44.5%, mRNA는 정상에 비해 약 48.5% 수준을 나타냄. 이 값이 전체 망막 세포 중 Otx2 발현 세포의 수의 감소에 의한 것인지 아니면 전체 Otx2 발현 세포 수의 변화는 없이 단위세포 당 양적 변화에 의한 것인지를 조사하기 위해 P90 Otx2(+/GFP) 망막 내 Otx2 발현 세포를 면역형광염색을 통해 조사함. 그 결과 Otx2를 발현하는 ONL 세포 수는 정상의 94.5%로 큰 변화가 없지만 Otx2를 발현하는 INL 세포 수는 정상의 40.3% 정도 밖에 되지 않았다. 이와는 달리 ONL과 INL 단위세포 당 Otx2 면역형광염색 강도는 61%와 58%로 좀 더 높았다. 이는 WB와 RT-qPCR에서 확인된 Otx2의 양의 감소는 단위세포 당발현량 감소와 INL의 Otx2 발현 세포 수의 감소의 복합적 요인으로 나타난 것으로 파악됨
표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 Otx2의 양적 변화. 망막의 발달 및 퇴화가 관찰된 P90 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막 내 Otx2 단백질과 mRNA 양을 정상생쥐와 Western blot (WB)와 RT-qPCR을 통해 비교함. 그 결과 단백질의 경우 정상에 비해 약 44.5%, mRNA는 정상에 비해 약 48.5% 수준을 나타냄. 이 값이 전체 망막 세포 중 Otx2 발현 세포의 수의 감소에 의한 것인지 아니면 전체 Otx2 발현 세포 수의 변화는 없이 단위세포 당 양적 변화에 의한 것인지를 조사하기 위해 P90 Otx2(+/GFP) 망막 내 Otx2 발현 세포를 면역형광염색을 통해 조사함. 그 결과 Otx2를 발현하는 ONL 세포 수는 정상의 94.5%로 큰 변화가 없지만 Otx2를 발현하는 INL 세포 수는 정상의 40.3% 정도 밖에 되지 않았다. 이와는 달리 ONL과 INL 단위세포 당 Otx2 면역형광염색 강도는 61%와 58%로 좀 더 높았다. 이는 WB와 RT-qPCR에서 확인된 Otx2의 양의 감소는 단위세포 당발현량 감소와 INL의 Otx2 발현 세포 수의 감소의 복합적 요인으로 나타난 것으로 파악됨
 표
Otx2 heterozygote 생쥐의 시각 이상. 위의 결과들에 따르면 Otx2의 양적, 질적 감소는 생쥐 망막 발달 및 유지에 심각한 영향을 주는 것으로 파악됨. 따라서, Otx2 유전자를 하나만 가지는 3개월령 (P90) Otx2 heterozygote (Otx2(+/GFP); 검은색 막대) 생쥐의 시력 (visual acuity; A)와 망막의 빛에 의한 반응을 측정하는 electroretinogram (ERG; B-E)를 통해 검증함. 그 결과 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐는 시력이 약화되어 있으며 망막의 강한 빛 반응도가 심각하게 약화되어 있음을 알 수 있음
표
Otx2 heterozygote 생쥐의 시각 이상. 위의 결과들에 따르면 Otx2의 양적, 질적 감소는 생쥐 망막 발달 및 유지에 심각한 영향을 주는 것으로 파악됨. 따라서, Otx2 유전자를 하나만 가지는 3개월령 (P90) Otx2 heterozygote (Otx2(+/GFP); 검은색 막대) 생쥐의 시력 (visual acuity; A)와 망막의 빛에 의한 반응을 측정하는 electroretinogram (ERG; B-E)를 통해 검증함. 그 결과 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐는 시력이 약화되어 있으며 망막의 강한 빛 반응도가 심각하게 약화되어 있음을 알 수 있음
 표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막의 점진적 퇴화. 시력과 시각반응의 이상을 보인 P90 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막의 이상이 망막의 퇴화에 의한 것인지를 조사하기 위해 각 시기별로 생쥐 망막절편을 분리하여 H&E 염색으로 망막 내 신경세포 수를 조사함 (A). 그 결과, Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐의 광수용세포가 위치한 ONL은 큰 변화가 없는 반면, 시신경을 이루는 갱글리온세포가 위치한 GCL의 경우는 발달이 완료되는 생후 2주 시점에는 큰 이상이 없다가 갱글리온세포는 시간이 지남에 따라 퇴화함을 알 수 있음. 또한, 이들 두 세포들을 연결하는 세포들이 집중적으로 위치한 INL의 수는 이미 발달과정에도 감소를 하였고, 시간이 지남에 따라 역시 심각한 퇴화를 나타냄. 이 결과를 통해, Otx2 유전자 하나 만으로 INL 세포의 발달이 온전하게 이루어지지 못하고, 갱글리온세포의 유지가 정상적이지 못함을 확인함
표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막의 점진적 퇴화. 시력과 시각반응의 이상을 보인 P90 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막의 이상이 망막의 퇴화에 의한 것인지를 조사하기 위해 각 시기별로 생쥐 망막절편을 분리하여 H&E 염색으로 망막 내 신경세포 수를 조사함 (A). 그 결과, Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐의 광수용세포가 위치한 ONL은 큰 변화가 없는 반면, 시신경을 이루는 갱글리온세포가 위치한 GCL의 경우는 발달이 완료되는 생후 2주 시점에는 큰 이상이 없다가 갱글리온세포는 시간이 지남에 따라 퇴화함을 알 수 있음. 또한, 이들 두 세포들을 연결하는 세포들이 집중적으로 위치한 INL의 수는 이미 발달과정에도 감소를 하였고, 시간이 지남에 따라 역시 심각한 퇴화를 나타냄. 이 결과를 통해, Otx2 유전자 하나 만으로 INL 세포의 발달이 온전하게 이루어지지 못하고, 갱글리온세포의 유지가 정상적이지 못함을 확인함
 표
Otx2(+/GFP) 망막에서 양극세포와 평행세포의 감소. Otx2 발현 세포 수의 감소가 나타난 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 감소한 INL 세포의 정체를 규명하기 위해, 각 INL 신경세포 특이적 마커의 분포를 통해 조사함. 그 결과 양극세포에서 발현되는 Vsx2를 가지는 세포의 수가 Otx2 경우처럼 정상의 40% 수준으로 감소 함. 특히, Vsx2는 Otx2 유전자 부위에서 발현되는 GFP와 동일한 세포에서 나타나는 것으로 보아, Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐에서 감소한 Otx2 발현 세포는 양극세포로 추정됨. Calbinin에 의해 표지되는 INL 상부의 평행세포도 그 수가 감소하였으나, 이 세포는 Otx2 및 GFP를 발현하지 않는 것으로 보아 2차적 결과로 판단됨
표
Otx2(+/GFP) 망막에서 양극세포와 평행세포의 감소. Otx2 발현 세포 수의 감소가 나타난 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 감소한 INL 세포의 정체를 규명하기 위해, 각 INL 신경세포 특이적 마커의 분포를 통해 조사함. 그 결과 양극세포에서 발현되는 Vsx2를 가지는 세포의 수가 Otx2 경우처럼 정상의 40% 수준으로 감소 함. 특히, Vsx2는 Otx2 유전자 부위에서 발현되는 GFP와 동일한 세포에서 나타나는 것으로 보아, Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐에서 감소한 Otx2 발현 세포는 양극세포로 추정됨. Calbinin에 의해 표지되는 INL 상부의 평행세포도 그 수가 감소하였으나, 이 세포는 Otx2 및 GFP를 발현하지 않는 것으로 보아 2차적 결과로 판단됨
 표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막 내 ON 및 OFF 신경세포 분포 및 반응도. (A) 생후 90일의 정상 생쥐와 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막의 망막 갱글리온세포에 64개에 전극을 비선택적으로 위치한 후 망막에 2초간 빛을 점멸하면서 각 신경 세포들의 전기적 활성도를 측정하였다. 이들 중 빛이 켜졌을때와 빛이 꺼졌을 때 모두 반응하는 ON/OFF 갱글리온세포들의 반응만을 별도로 분리한 후 이들을 반응도 그래프를 하나로 나타냄. 이 과정에서 초기 측정 후 해당 망막에 ON 양극세포에서만 발현되는 mGluR의 억제제인 L-AP4를 처리하면 ON/OFF 갱글리온세포의 ON 반응만이 선택적으로 사라져 OFF 반응의 정도만 측정할 수 있다. 이 조건에서 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막의 상당수 ON/OFF 갱글리온세포는 OFF 반응이 측정이 되지 않는 것을 보아 해당 세포들의 OFF 반응에 이상이 있음을 알 수 있음. (B) 위의 측정 결과들을 도표로 나타내었다. (C,D) 이들 중 일부는 빛이 켜지면 빛이 없을 때 활성화된 OFF 회로의 ON 회로 억제의 결과로 ON 반응의 급격한 감소가 동반되는 효과가 정상 생쥐에서는 나오는 반면 Otx(+/GFP) 생쥐에서는 나오지 않는 것으로 보아 해당 생쥐에서 OFF 양극세포의 활성도가 감소됨을 알 수 있음
표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막 내 ON 및 OFF 신경세포 분포 및 반응도. (A) 생후 90일의 정상 생쥐와 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막의 망막 갱글리온세포에 64개에 전극을 비선택적으로 위치한 후 망막에 2초간 빛을 점멸하면서 각 신경 세포들의 전기적 활성도를 측정하였다. 이들 중 빛이 켜졌을때와 빛이 꺼졌을 때 모두 반응하는 ON/OFF 갱글리온세포들의 반응만을 별도로 분리한 후 이들을 반응도 그래프를 하나로 나타냄. 이 과정에서 초기 측정 후 해당 망막에 ON 양극세포에서만 발현되는 mGluR의 억제제인 L-AP4를 처리하면 ON/OFF 갱글리온세포의 ON 반응만이 선택적으로 사라져 OFF 반응의 정도만 측정할 수 있다. 이 조건에서 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막의 상당수 ON/OFF 갱글리온세포는 OFF 반응이 측정이 되지 않는 것을 보아 해당 세포들의 OFF 반응에 이상이 있음을 알 수 있음. (B) 위의 측정 결과들을 도표로 나타내었다. (C,D) 이들 중 일부는 빛이 켜지면 빛이 없을 때 활성화된 OFF 회로의 ON 회로 억제의 결과로 ON 반응의 급격한 감소가 동반되는 효과가 정상 생쥐에서는 나오는 반면 Otx(+/GFP) 생쥐에서는 나오지 않는 것으로 보아 해당 생쥐에서 OFF 양극세포의 활성도가 감소됨을 알 수 있음
 표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 양극세포 발달 이상. P90 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 나타난 Otx2 발현 양극세포의 감소 원인이 발달의 문제인지 아니면 퇴화에 의한 것인지를 규명하기위해 망막발달이 완성되는 생후 2주 (P13) 망막 절편에서 Otx2 발현 세포와 전체 양극세포를 표지하는 Vsx2, rod 양극세포를 표지하는 PKCalpha, ON-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 G0alpha, OFF-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 Vsx1, 제 2형 (Type-2; T2) OFF-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 Recoverin 등의 분포를 조사함 (A). 그 결과 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포를 제외한 전체 양극세포의 수와 rod, ON-cone, OFF-cone 양극세포 수가 모두가 Otx2 수의 감소와 유사하게 정상 망막에 비해 약 20-30% 정도 감소한 것으로 나타남 (B). 이는 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 양극세포의 발달이 감소함을 시사함. 이들 다양한 양극세포들 중 Otx2를 발현하는 세포를 간접적으로 Otx2 부위에서 발현되는 GFP의 분포와 비교하여 조사한 결과, rod와 ON-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 PKCalpha와 G0alpha는 100% GFP를 발현하고 있지만, OFF-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 Vsx1의 경우는 약 22% 정도만 GFP와 공동발현되고 있었고, T2 OFF-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 Recoverin은 전혀 GFP와 겹치지 않음. 흥미로운 것은 이론적으로 GFP와 완벽하게 겹쳐야하는 Otx2 조차도 약 24%는 GFP와 겹치지 않고 있는 것으로 보아 이들 GFP(-) 세포들에 존재하는 Otx2와 이들의 기능에 대한 의문점이 들었다
표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 양극세포 발달 이상. P90 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 나타난 Otx2 발현 양극세포의 감소 원인이 발달의 문제인지 아니면 퇴화에 의한 것인지를 규명하기위해 망막발달이 완성되는 생후 2주 (P13) 망막 절편에서 Otx2 발현 세포와 전체 양극세포를 표지하는 Vsx2, rod 양극세포를 표지하는 PKCalpha, ON-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 G0alpha, OFF-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 Vsx1, 제 2형 (Type-2; T2) OFF-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 Recoverin 등의 분포를 조사함 (A). 그 결과 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포를 제외한 전체 양극세포의 수와 rod, ON-cone, OFF-cone 양극세포 수가 모두가 Otx2 수의 감소와 유사하게 정상 망막에 비해 약 20-30% 정도 감소한 것으로 나타남 (B). 이는 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서 양극세포의 발달이 감소함을 시사함. 이들 다양한 양극세포들 중 Otx2를 발현하는 세포를 간접적으로 Otx2 부위에서 발현되는 GFP의 분포와 비교하여 조사한 결과, rod와 ON-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 PKCalpha와 G0alpha는 100% GFP를 발현하고 있지만, OFF-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 Vsx1의 경우는 약 22% 정도만 GFP와 공동발현되고 있었고, T2 OFF-cone 양극세포를 표지하는 Recoverin은 전혀 GFP와 겹치지 않음. 흥미로운 것은 이론적으로 GFP와 완벽하게 겹쳐야하는 Otx2 조차도 약 24%는 GFP와 겹치지 않고 있는 것으로 보아 이들 GFP(-) 세포들에 존재하는 Otx2와 이들의 기능에 대한 의문점이 들었다
 표
T2 OFF-cone 양극세포의 외부 Otx2 발현. Otx2 유전자 부위에서 발현되는 GFP와 전혀 겹치지 않는 Recoverin 발현 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포의 발달과 유지에 대한 Otx2의 기능을 조사하기 위해 Otx2(푸른색), Recoverin (붉은색), GFP (녹색)을 동시에 면역형광염색을 통해 검출하였다. 그 결과 흥미롭게 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포는 GFP가 없음에도 불구하고 Otx2 단백질은 포함하고 있었다. 이는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포에 분포하는 Otx2 단백질은 세포 내부에서 발현되었다기 보다는 세포 외부로부터 이동되어 왔음을 시사한다
표
T2 OFF-cone 양극세포의 외부 Otx2 발현. Otx2 유전자 부위에서 발현되는 GFP와 전혀 겹치지 않는 Recoverin 발현 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포의 발달과 유지에 대한 Otx2의 기능을 조사하기 위해 Otx2(푸른색), Recoverin (붉은색), GFP (녹색)을 동시에 면역형광염색을 통해 검출하였다. 그 결과 흥미롭게 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포는 GFP가 없음에도 불구하고 Otx2 단백질은 포함하고 있었다. 이는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포에 분포하는 Otx2 단백질은 세포 내부에서 발현되었다기 보다는 세포 외부로부터 이동되어 왔음을 시사한다
 표
제 2형 양극세포 내 Otx2 유전자 발현의 부재. (A) 앞의 그림에서 Otx2 유전자 부위에서 발현되는 GFP 존재 없이 Otx2 단백질만을 포함하는 제 2형 양극세포 내 Otx2가 외부에서 유래한 것인지를 증명하기 위하여 Otx2 mRNA 발현을 직접 조사함. Otx2 mRNA와 동일한 염기서열 (sense) 또는 상보적 염기서열 (antisense, Otx2)을 가지는 RNA를 합성 후 DIG로 표지하고 이를 생후 30일 생쥐 망막에 hybridization 후 이들 RNA들과 상보 결합을 하는 mRNA를 포함하는 세포의 위치를 형광표지된 anti-DIG 항체를 이용하여 조사함. 그 결과 sense RNA는 전혀 망막에 특이적 신호를 제공하지 않았지만, Otx2는 Otx2 단백질이 나타났던 INL과 ONL 위치에 특이적 신호를 보임. (B) Otx2 유전자의 제2형 양극세포 내 발현 여부를 조사하기 위하여 제2형 양극세포 표지자인 Recoverin에 대한 면역형광염색을 Otx2 ISH와 동시에 수행한 결과 제2형 양극세포는 Otx2 유전자 발현이 거의 검출되지 않음. (C) 이와는 반대로 관상 양극세포 표지자인 PKCalpha에 대한 면역 형광염색을 동시에 수행하였을 때는 Otx2 mRNA와 Otx2 단백질 모두 이들 세포에서 발현됨을 알수 있음. (D) 이를 통하여 관상 양극세포는 Otx2 mRNA를 통해 Otx2 단백질을 발현하고, 제2형 양극세포는 Otx2 mRNA 발현 없이 Otx2 단백질을 발현함을 알 수 있음
표
제 2형 양극세포 내 Otx2 유전자 발현의 부재. (A) 앞의 그림에서 Otx2 유전자 부위에서 발현되는 GFP 존재 없이 Otx2 단백질만을 포함하는 제 2형 양극세포 내 Otx2가 외부에서 유래한 것인지를 증명하기 위하여 Otx2 mRNA 발현을 직접 조사함. Otx2 mRNA와 동일한 염기서열 (sense) 또는 상보적 염기서열 (antisense, Otx2)을 가지는 RNA를 합성 후 DIG로 표지하고 이를 생후 30일 생쥐 망막에 hybridization 후 이들 RNA들과 상보 결합을 하는 mRNA를 포함하는 세포의 위치를 형광표지된 anti-DIG 항체를 이용하여 조사함. 그 결과 sense RNA는 전혀 망막에 특이적 신호를 제공하지 않았지만, Otx2는 Otx2 단백질이 나타났던 INL과 ONL 위치에 특이적 신호를 보임. (B) Otx2 유전자의 제2형 양극세포 내 발현 여부를 조사하기 위하여 제2형 양극세포 표지자인 Recoverin에 대한 면역형광염색을 Otx2 ISH와 동시에 수행한 결과 제2형 양극세포는 Otx2 유전자 발현이 거의 검출되지 않음. (C) 이와는 반대로 관상 양극세포 표지자인 PKCalpha에 대한 면역 형광염색을 동시에 수행하였을 때는 Otx2 mRNA와 Otx2 단백질 모두 이들 세포에서 발현됨을 알수 있음. (D) 이를 통하여 관상 양극세포는 Otx2 mRNA를 통해 Otx2 단백질을 발현하고, 제2형 양극세포는 Otx2 mRNA 발현 없이 Otx2 단백질을 발현함을 알 수 있음
 표
T2 OFF-cone 양극세포에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질의 유래 검증. T2 OFF-cone 양극세포에서 존재하는 Otx2가 실재로 세포 간 이동을 통해 획득한 것인지를 증명하기 위해 생후 13일째 생쥐 안구 내에 일반 생쥐 항체 (preimmune IgG) 또는 Otx2에 대한 단일항체 (anti-Otx2 IgG)를 주입하여 세포 외부에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질과 결합하여 Otx2 단백질의 세포 간 이동을 억제함. 2일후인 생후 15일에 해당 생쥐들의 안구를 적출하여 망막 절편 내 Recovrin-positive T2 OFF-cone 양극세포에서 Otx2 단백질의 존재 여부를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. 그 결고, Otx2에 대한 단일항체를 주사한 안구 내 망막의 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포 내 Otx2 단백질의 양이 급격히 감소함을 알 수 있음. 이는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포 내에 존재하는 Otx2가 세포 간 이동을 통해 획득된 것이라는 사실을 반증함
표
T2 OFF-cone 양극세포에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질의 유래 검증. T2 OFF-cone 양극세포에서 존재하는 Otx2가 실재로 세포 간 이동을 통해 획득한 것인지를 증명하기 위해 생후 13일째 생쥐 안구 내에 일반 생쥐 항체 (preimmune IgG) 또는 Otx2에 대한 단일항체 (anti-Otx2 IgG)를 주입하여 세포 외부에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질과 결합하여 Otx2 단백질의 세포 간 이동을 억제함. 2일후인 생후 15일에 해당 생쥐들의 안구를 적출하여 망막 절편 내 Recovrin-positive T2 OFF-cone 양극세포에서 Otx2 단백질의 존재 여부를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. 그 결고, Otx2에 대한 단일항체를 주사한 안구 내 망막의 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포 내 Otx2 단백질의 양이 급격히 감소함을 알 수 있음. 이는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포 내에 존재하는 Otx2가 세포 간 이동을 통해 획득된 것이라는 사실을 반증함
 표
Otx2 항체 주입에 의한 제2형 양극세포의 퇴화. 그림 59에서와 마찬가지로 Otx2에 대한 항체를 생후 13일 정상 생쥐 또는 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에 투여 후 2주 후인 생후 30일에 해당 생쥐 망막을 포집 후 그 안에 존재하는 제2형 양극세포(A,B) 및 관상 양극세포(C,D)의 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. 그 결과 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에 Otx2 항체를 투여한 결과 제2형 양극 세포의 수가 감소함을 알 수 있음. 이는 해당 생쥐 망막의 세포 외부에 존재하는 Otx2가 제2형 양극세포의 유지에 필요함을 시사함
표
Otx2 항체 주입에 의한 제2형 양극세포의 퇴화. 그림 59에서와 마찬가지로 Otx2에 대한 항체를 생후 13일 정상 생쥐 또는 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에 투여 후 2주 후인 생후 30일에 해당 생쥐 망막을 포집 후 그 안에 존재하는 제2형 양극세포(A,B) 및 관상 양극세포(C,D)의 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사함. 그 결과 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에 Otx2 항체를 투여한 결과 제2형 양극 세포의 수가 감소함을 알 수 있음. 이는 해당 생쥐 망막의 세포 외부에 존재하는 Otx2가 제2형 양극세포의 유지에 필요함을 시사함
 표
Otx2 단백질의 망막 신경 내 침투. 생후 13일 생쥐 안구 내에 Otx2-myc 단백질을 200ng 주입 후 각 시간에 따른 망막 내 단백질 분포를 Myc tag에 대한 항체를 이용하여 조사함. 그 결과 주입 후 하루 후부터 Otx2-myc 단백질이 주로 망막갱글리온세포에서 관찰되다 이틀 후부터는 INL, 3일후부터는 ONL까지 침투하였음. 하지만, 주입 후 7일 이후에는 해당 단백질들이 망막에 거의 존재하지 않는 것으로 보아, Otx2-myc 단백질은 주입 후 2일 이후 망막 양극세포들에 침투하고 1주일 이내에 소멸됨을 알 수 있음
표
Otx2 단백질의 망막 신경 내 침투. 생후 13일 생쥐 안구 내에 Otx2-myc 단백질을 200ng 주입 후 각 시간에 따른 망막 내 단백질 분포를 Myc tag에 대한 항체를 이용하여 조사함. 그 결과 주입 후 하루 후부터 Otx2-myc 단백질이 주로 망막갱글리온세포에서 관찰되다 이틀 후부터는 INL, 3일후부터는 ONL까지 침투하였음. 하지만, 주입 후 7일 이후에는 해당 단백질들이 망막에 거의 존재하지 않는 것으로 보아, Otx2-myc 단백질은 주입 후 2일 이후 망막 양극세포들에 침투하고 1주일 이내에 소멸됨을 알 수 있음
 표
Otx2 투여를 통한 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막퇴화 억제. (A) Otx2 단백질을 생후 13일째 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐의 우측 안구 내에 투여한 후 2주 후인 생후 28일에 생쥐의 ERG 반응을 조사 함. (B) Otx2를 투여한 생쥐의 경우 주로 광수용세포의 반응에 의해 나타나는 a-wave와 rod 또는 ON-cone 양극세포에 의해 나타나는 b-wave의 크기가 비투여한 왼쪽 안구에 비해 확연하게 차이 를 보이는 것을 알 수 있음. (C) 위의 PBS를 투여한 정상 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막과 Otx2를 투여 한 생쥐 망막 내 신경세포의 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사한 결과, PBS 투여 생쥐보다 Otx2 투여 생쥐 망막 내 Otx2 및 GFP 발현 세포 수가 급격하게 늘어나 있음을 알 수 있음. 이는 외부에서 투 여한 Otx2가 Otx2를 발현하는 세포의 퇴화를 억제할 수 있음을 시사함. 또한, 양극세포를 표지하는 Vsx2 수 역시 증가한 것을 알 수 있음. PKCalpha를 발현하는 rod 양극세포의 수도 비록 Otx2나 Chx10 발현 세포보다 낮기는 하지만 유의미한 증가를 보였다. 특히, Recoverin을 발현하는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포의 경우는 PBS 투여 망막에서는 완전히 퇴화가 되었지만, Otx2 투여 망막에서 는 여전히 많은 수의 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포가 남아 있음. 이는 Vsx1을 발현하는 전체 OFF-cone 양극세포에도 적용되는 사실이었다. 실재로 a-wave의 증가는 hyperpolarization에 의해 나타나는 것으로 일반적으로 빛에 의해 hyperpolarization 되는 photoreceptor의 활성 증가 뿐만 아니라 OFF cone 양극세포의 활성 강화에 의해서도 나타날 가능성이 높은 것으로 알려져 있다. 따라서, rod 및 cone 광수용세포의 수는 크게 변화가 없는 반면 T2 OFF-cone을 포함한 전체적인 OFF cone 양극세포 수의 증가가 Otx2 투여 망막에서 그 퇴화가 억제되었음을 알 수 있다
표
Otx2 투여를 통한 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막퇴화 억제. (A) Otx2 단백질을 생후 13일째 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐의 우측 안구 내에 투여한 후 2주 후인 생후 28일에 생쥐의 ERG 반응을 조사 함. (B) Otx2를 투여한 생쥐의 경우 주로 광수용세포의 반응에 의해 나타나는 a-wave와 rod 또는 ON-cone 양극세포에 의해 나타나는 b-wave의 크기가 비투여한 왼쪽 안구에 비해 확연하게 차이 를 보이는 것을 알 수 있음. (C) 위의 PBS를 투여한 정상 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막과 Otx2를 투여 한 생쥐 망막 내 신경세포의 분포를 면역형광염색으로 조사한 결과, PBS 투여 생쥐보다 Otx2 투여 생쥐 망막 내 Otx2 및 GFP 발현 세포 수가 급격하게 늘어나 있음을 알 수 있음. 이는 외부에서 투 여한 Otx2가 Otx2를 발현하는 세포의 퇴화를 억제할 수 있음을 시사함. 또한, 양극세포를 표지하는 Vsx2 수 역시 증가한 것을 알 수 있음. PKCalpha를 발현하는 rod 양극세포의 수도 비록 Otx2나 Chx10 발현 세포보다 낮기는 하지만 유의미한 증가를 보였다. 특히, Recoverin을 발현하는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포의 경우는 PBS 투여 망막에서는 완전히 퇴화가 되었지만, Otx2 투여 망막에서 는 여전히 많은 수의 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포가 남아 있음. 이는 Vsx1을 발현하는 전체 OFF-cone 양극세포에도 적용되는 사실이었다. 실재로 a-wave의 증가는 hyperpolarization에 의해 나타나는 것으로 일반적으로 빛에 의해 hyperpolarization 되는 photoreceptor의 활성 증가 뿐만 아니라 OFF cone 양극세포의 활성 강화에 의해서도 나타날 가능성이 높은 것으로 알려져 있다. 따라서, rod 및 cone 광수용세포의 수는 크게 변화가 없는 반면 T2 OFF-cone을 포함한 전체적인 OFF cone 양극세포 수의 증가가 Otx2 투여 망막에서 그 퇴화가 억제되었음을 알 수 있다
 표
외래 Otx2 단백질의 미토콘드리아 침투. 세포 외부에서 세포 내부로 침투한 Otx2 단백질의 세포 내 작용 위치를 세포 소기관의 표지자들의 분포와 비교하여 조사함. 망막세포인 RGC5 세포의 배양액에 순수 분리한 Otx2 단백질 (200 ng/ml)을 첨가하고 4시간 후 세포를 고정 후 미토콘드리아 단백질인 Tom20, 리소좀 단백질인 Lamp2, 골지체 단백질인 GM130과 Otx2와의 공동 면역 형광염색을 통해 비교함. 그 결과 Otx2 단백질은 미토콘드리아 단백질인 Tom20와 같은 위치에 발견되지만, 리소좀이나 골지체에는 위치하지 않음
표
외래 Otx2 단백질의 미토콘드리아 침투. 세포 외부에서 세포 내부로 침투한 Otx2 단백질의 세포 내 작용 위치를 세포 소기관의 표지자들의 분포와 비교하여 조사함. 망막세포인 RGC5 세포의 배양액에 순수 분리한 Otx2 단백질 (200 ng/ml)을 첨가하고 4시간 후 세포를 고정 후 미토콘드리아 단백질인 Tom20, 리소좀 단백질인 Lamp2, 골지체 단백질인 GM130과 Otx2와의 공동 면역 형광염색을 통해 비교함. 그 결과 Otx2 단백질은 미토콘드리아 단백질인 Tom20와 같은 위치에 발견되지만, 리소좀이나 골지체에는 위치하지 않음
 표
Otx2 단백질의 망막 신경 세포 내 미토콘드리아로의 이동. (A) 생후 13일째 생쥐 안구내에 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질 (200 ng)을 주입하고 24시간 후 생쥐 안구를 적출 후 안구 절편을 Myc에 대한 항체와 미토콘드리아 단백질인 Tom20에 대한 항체를 이용하여 면역형광염색을 수행함. 그 결과 외부에서 주입한 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질은 망막갱글리온세포와 INL 내의 신경세포에서 관찰이 되었으며 이들 세포 내에 있는 미토콘드리아에서도 관찰됨. (B) 외부에서 주입한 Otx2 단백질뿐만 아니라 생체 내에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질 역시 미토콘드리아에서 관찰이 됨
표
Otx2 단백질의 망막 신경 세포 내 미토콘드리아로의 이동. (A) 생후 13일째 생쥐 안구내에 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질 (200 ng)을 주입하고 24시간 후 생쥐 안구를 적출 후 안구 절편을 Myc에 대한 항체와 미토콘드리아 단백질인 Tom20에 대한 항체를 이용하여 면역형광염색을 수행함. 그 결과 외부에서 주입한 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질은 망막갱글리온세포와 INL 내의 신경세포에서 관찰이 되었으며 이들 세포 내에 있는 미토콘드리아에서도 관찰됨. (B) 외부에서 주입한 Otx2 단백질뿐만 아니라 생체 내에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질 역시 미토콘드리아에서 관찰이 됨
 표
망막 신경 미토콘드리아 내 Otx2의 존재 규명. 생후 13일 생쥐 안구 내에 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질 (100ng)을 주입하고 24시간 후 안구를 적출하여 망막 절편을 토끼 Myc 항체를 이용하여 면역염색 후 금입자가 표지된 토끼항체에 대한 2차항체를 이용해 Myc 항체의 분포를 전자현미경으로 검출함. 단백질을 투여하지 않은 안구의 망막신경세포 미토콘드리아에는 금입자가 검출되지 않지만 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질을 투여한 안구의 신경세포 미토콘드리아에서는 금입자가 검출됨. 이는 외부에서 주입한 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질이 망막신경 내 미토콘드리아로 이동하였음을 증명하는 결과임
표
망막 신경 미토콘드리아 내 Otx2의 존재 규명. 생후 13일 생쥐 안구 내에 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질 (100ng)을 주입하고 24시간 후 안구를 적출하여 망막 절편을 토끼 Myc 항체를 이용하여 면역염색 후 금입자가 표지된 토끼항체에 대한 2차항체를 이용해 Myc 항체의 분포를 전자현미경으로 검출함. 단백질을 투여하지 않은 안구의 망막신경세포 미토콘드리아에는 금입자가 검출되지 않지만 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질을 투여한 안구의 신경세포 미토콘드리아에서는 금입자가 검출됨. 이는 외부에서 주입한 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질이 망막신경 내 미토콘드리아로 이동하였음을 증명하는 결과임
 표
망막신경 세포 내 미토콘드리아에 있는 Otx2의 특징. 생후 14일 생쥐 망막을 적출 후 세포 내 미토콘드리아를 분리하고 (mito) 이를 0.5M NaCl이 포함된 PBS 또는 proteinase-K (1U/ul)이 포함된 PBS에 30분 동안 보관하여 미토콘드리아 외막 지질 또는 단백질과 Otx2 단백질과의 상호작용을 파괴함. 그 결과 미처리 미토콘드리아에 비해 NaCl 처리군은 약 40% 정도만 Otx2 단백질이 남아 있었고, 27%만이 proteinase-K 처리 이후에 남아 있었음. 이는 대부분의 미토콘드리아 Otx2 단백질은 미토콘드리아 외막에 있고 1/3 정도만 내부에 존재함을 알 수 있음
표
망막신경 세포 내 미토콘드리아에 있는 Otx2의 특징. 생후 14일 생쥐 망막을 적출 후 세포 내 미토콘드리아를 분리하고 (mito) 이를 0.5M NaCl이 포함된 PBS 또는 proteinase-K (1U/ul)이 포함된 PBS에 30분 동안 보관하여 미토콘드리아 외막 지질 또는 단백질과 Otx2 단백질과의 상호작용을 파괴함. 그 결과 미처리 미토콘드리아에 비해 NaCl 처리군은 약 40% 정도만 Otx2 단백질이 남아 있었고, 27%만이 proteinase-K 처리 이후에 남아 있었음. 이는 대부분의 미토콘드리아 Otx2 단백질은 미토콘드리아 외막에 있고 1/3 정도만 내부에 존재함을 알 수 있음
 표
Otx2와 미토콘드리아 ATP 합성효소 ATP5A1과의 상호작용. (A) 미토콘드리아에 분포하는 Otx2 단백질의 기능을 검증하기 위해 망막신경세포에서 세포질을 미토콘드리아를 분리하고 이들 분획에 존재하는 Otx2를 Otx2 항체를 이용하여 분리함. 분리된 면역복합체에 함께 분리된 단백질체를 MALDI-TOF MS/MS를 이용해 검증한 결과 미토콘드리아 ATP 합성효소인 ATP5A1과 미토콘드리아에서 합성된 ATP를 미토콘드리아 외부로 수송하는 solute carrier 25a31 (Slc25a31)가 검출됨. (B) 이를 추가로 검증하기 위해 망막신경세포 및 순수 분리된 생쥐 망막 신경 미토콘드리아에 Otx2 또는 ATP5A1에 대한 항체를 투여하여 Otx2 및 ATP5A1를 면역침강 후 함께 분리된 ATP5A1과 Otx2를 Western blot으로 확인함. 이 결과들은 미토콘드리아 내 Otx2가 미토콘드리아 ATP5A1 등과의 상호작용을 통해 ATP 합성에 관여하고 있다는 것을 시사함
표
Otx2와 미토콘드리아 ATP 합성효소 ATP5A1과의 상호작용. (A) 미토콘드리아에 분포하는 Otx2 단백질의 기능을 검증하기 위해 망막신경세포에서 세포질을 미토콘드리아를 분리하고 이들 분획에 존재하는 Otx2를 Otx2 항체를 이용하여 분리함. 분리된 면역복합체에 함께 분리된 단백질체를 MALDI-TOF MS/MS를 이용해 검증한 결과 미토콘드리아 ATP 합성효소인 ATP5A1과 미토콘드리아에서 합성된 ATP를 미토콘드리아 외부로 수송하는 solute carrier 25a31 (Slc25a31)가 검출됨. (B) 이를 추가로 검증하기 위해 망막신경세포 및 순수 분리된 생쥐 망막 신경 미토콘드리아에 Otx2 또는 ATP5A1에 대한 항체를 투여하여 Otx2 및 ATP5A1를 면역침강 후 함께 분리된 ATP5A1과 Otx2를 Western blot으로 확인함. 이 결과들은 미토콘드리아 내 Otx2가 미토콘드리아 ATP5A1 등과의 상호작용을 통해 ATP 합성에 관여하고 있다는 것을 시사함
 표
생쥐 망막 신경 미토콘드리아의 ATP 합성복합체 구성체로의 Otx2. Otx2가 ATP5A1과 상호작용을 통하여 미토콘드리아 ATP 합성복합체에 참여할 가능성을 확인하기 위해 생후 15일 생쥐 망막 미토콘드리아를 분리 후 이를 blue native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (BN-PAGE) 및 Otx2 항체를 이용한 Western blot을 이용하여 Otx2가 포함된 미토콘드리아의 단백질 복합체의 크기를 측정함. 그 결과 Otx2는 약 700kDa 근방에서 관찰되고, 이는 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서는 감소하고, Otx2-Myc/His를 투여한 생쥐 망막에서는 그 양이 증가함. 이는 Otx2가 결합하는 ATP5A1이 포함된 ATP 합성복합체인 전자전달 복합체 V와 크기가 유사함. 따라서 Otx2는 ATP5A1과 직,간접적으로 결합하여 미토콘드리아 ATP 합성복합체에 참여함을 의미함
표
생쥐 망막 신경 미토콘드리아의 ATP 합성복합체 구성체로의 Otx2. Otx2가 ATP5A1과 상호작용을 통하여 미토콘드리아 ATP 합성복합체에 참여할 가능성을 확인하기 위해 생후 15일 생쥐 망막 미토콘드리아를 분리 후 이를 blue native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (BN-PAGE) 및 Otx2 항체를 이용한 Western blot을 이용하여 Otx2가 포함된 미토콘드리아의 단백질 복합체의 크기를 측정함. 그 결과 Otx2는 약 700kDa 근방에서 관찰되고, 이는 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막에서는 감소하고, Otx2-Myc/His를 투여한 생쥐 망막에서는 그 양이 증가함. 이는 Otx2가 결합하는 ATP5A1이 포함된 ATP 합성복합체인 전자전달 복합체 V와 크기가 유사함. 따라서 Otx2는 ATP5A1과 직,간접적으로 결합하여 미토콘드리아 ATP 합성복합체에 참여함을 의미함
 표
Otx2 투여에 의한 망막신경 내 ATP 합성 촉진. (A) Otx2의 ATP 합성복합체의 구성인자로써 기능을 확인하기 위해, 생후 15일 정상 생쥐 또는 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐와 생후 13일에 Otx2 단백질을 투여한 생쥐 망막 신경 미토콘드리아를 분리 후 in gel ATP synthase assay를 통하여 해당 미토콘드리아의 활성을 조사함. Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐는 정상 생쥐 망막에 비해 분석에 이용한 미토콘드리아 전자전달계 V의 양적인 변화는 크지 않으나 ATP 합성 복합체의 ATP 합성 능력은 정상의 1/4로 줄어들어 있음. 이와는 달리 Otx2를 투여한 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막 미토콘드리아의 활성도는 정상의 1/2 수준으로 복구가 됨. 이는 세포 내 ATP 농도의 변화로 나타남 (B)
표
Otx2 투여에 의한 망막신경 내 ATP 합성 촉진. (A) Otx2의 ATP 합성복합체의 구성인자로써 기능을 확인하기 위해, 생후 15일 정상 생쥐 또는 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐와 생후 13일에 Otx2 단백질을 투여한 생쥐 망막 신경 미토콘드리아를 분리 후 in gel ATP synthase assay를 통하여 해당 미토콘드리아의 활성을 조사함. Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐는 정상 생쥐 망막에 비해 분석에 이용한 미토콘드리아 전자전달계 V의 양적인 변화는 크지 않으나 ATP 합성 복합체의 ATP 합성 능력은 정상의 1/4로 줄어들어 있음. 이와는 달리 Otx2를 투여한 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막 미토콘드리아의 활성도는 정상의 1/2 수준으로 복구가 됨. 이는 세포 내 ATP 농도의 변화로 나타남 (B)
 표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막 내 미토콘드리아 구조 이상 (P15). (A) 생후 15일 정상 망막 및 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막과 생후 13일에 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질을 투여한 안구 내 망막 신경세포 내 미토콘드리아의 구조를 전자현미경으로 조사함. 정상 망막신경세포 내 미토콘드리아는 내막이 겹으로 접힌 cristae 구조를 잘 유지하고 있는 반면, Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막신경세포 내 미토콘드리아는 cristae 겹의 수가 적고 풀린 구조를 가지는 경우가 많음. 이에 반해 Otx2를 주입한 안구 내 망막 신경 미토콘드리아는 cristae 접힘 구조가 회복되는 경향을 보임. (B) 이러한 미토콘드리아의 특징을 정량화하여 그래프로 나타냄
표
Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막 내 미토콘드리아 구조 이상 (P15). (A) 생후 15일 정상 망막 및 Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막과 생후 13일에 Otx2-Myc/His 단백질을 투여한 안구 내 망막 신경세포 내 미토콘드리아의 구조를 전자현미경으로 조사함. 정상 망막신경세포 내 미토콘드리아는 내막이 겹으로 접힌 cristae 구조를 잘 유지하고 있는 반면, Otx2(+/GFP) 생쥐 망막신경세포 내 미토콘드리아는 cristae 겹의 수가 적고 풀린 구조를 가지는 경우가 많음. 이에 반해 Otx2를 주입한 안구 내 망막 신경 미토콘드리아는 cristae 접힘 구조가 회복되는 경향을 보임. (B) 이러한 미토콘드리아의 특징을 정량화하여 그래프로 나타냄
 표
Otx2 단백질의 세포 간 이동에 의한 망막신경퇴화 억제 기전. 정상 망막조직에서 Otx2 유전자를 발현하는 photoreceptor나 rod/ON-cone 양극세포는 해당 세포의 발달과 유지를 위해 Otx2를 사용할 뿐만 아니라 세포 외부로 Otx2 단백질을 분비함. 따라서 이들 세포의 주변에 존재하는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포나 RGC등은 세포 외부에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질을 획득하여 해당 세포 내부로 이동 후 세포의 유지에 사용하게 됨. 따라서, Otx2 유전자 하나의 결실은 Otx2를 발현하는 rod/ON-cone 양극세포의 발달 저하 뿐만 아니라 이들 세포에서 분비되는 Otx2의 양적 저하로 인해 세포 외부로부터 Otx2를 공급받는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포와 RGC 등에 Otx2의 양적 감소를 유도함. 따라서, 이들 세포는 외부에서 공급되는 Otx2가 담당하는 세포 유지의 기능이 약화되어 망막 신경퇴화로 이어지고, 이것은 결국 ERG b-wave 반응 저하를 동반한 시력 저하를 유도함
표
Otx2 단백질의 세포 간 이동에 의한 망막신경퇴화 억제 기전. 정상 망막조직에서 Otx2 유전자를 발현하는 photoreceptor나 rod/ON-cone 양극세포는 해당 세포의 발달과 유지를 위해 Otx2를 사용할 뿐만 아니라 세포 외부로 Otx2 단백질을 분비함. 따라서 이들 세포의 주변에 존재하는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포나 RGC등은 세포 외부에 존재하는 Otx2 단백질을 획득하여 해당 세포 내부로 이동 후 세포의 유지에 사용하게 됨. 따라서, Otx2 유전자 하나의 결실은 Otx2를 발현하는 rod/ON-cone 양극세포의 발달 저하 뿐만 아니라 이들 세포에서 분비되는 Otx2의 양적 저하로 인해 세포 외부로부터 Otx2를 공급받는 T2 OFF-cone 양극세포와 RGC 등에 Otx2의 양적 감소를 유도함. 따라서, 이들 세포는 외부에서 공급되는 Otx2가 담당하는 세포 유지의 기능이 약화되어 망막 신경퇴화로 이어지고, 이것은 결국 ERG b-wave 반응 저하를 동반한 시력 저하를 유도함
 표
Keton body 투여를 통한 망막 퇴화 억제 시도. 생후 13일부터 29일까지 매일 sodium β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB, 72.8 mg/kg)를 복강으로 주사하였다. (A) 생후 30일째 생쥐의 모습과 혈관 이상을 보이는 BHB 투여 생쥐 내장. (B) 매일 생쥐들의 몸무게를 측정한 결과 BHB를 투여한 생쥐 그룹들은 현저한 체중 감소를 동반함을 알 수 있음. (C & D) 이들 생쥐의 망막 내에 존재하는 Otx2 발현 세포의 수와 Recoverin 발현 제2형 양극세포의 수를 측정한 결과 BHB 투여에 의한 뚜렷한 차이를 관찰하기는 어려움
표
Keton body 투여를 통한 망막 퇴화 억제 시도. 생후 13일부터 29일까지 매일 sodium β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB, 72.8 mg/kg)를 복강으로 주사하였다. (A) 생후 30일째 생쥐의 모습과 혈관 이상을 보이는 BHB 투여 생쥐 내장. (B) 매일 생쥐들의 몸무게를 측정한 결과 BHB를 투여한 생쥐 그룹들은 현저한 체중 감소를 동반함을 알 수 있음. (C & D) 이들 생쥐의 망막 내에 존재하는 Otx2 발현 세포의 수와 Recoverin 발현 제2형 양극세포의 수를 측정한 결과 BHB 투여에 의한 뚜렷한 차이를 관찰하기는 어려움
 표
EGFP-BAC 생쥐 망막에서 호메오도메인 전사인자와 EGFP 분포 비교. 기존 논문과 데이터베이스를 기반으로 생쥐 망막에서 발현이 되는 것으로 알려진 HP들 중 BAC-EGFP 생쥐로 제작된 16종을 도입한 후, 이들 중 성공적으로 GFP 형광을 보이는 것으로 확인된 9종의 생쥐를 분석에 이용함. 이들 생쥐들이 생후 30일 망막 절편을 각각의 HP에 대한 항체와 GFP에 대한 항체로 면역형광염색을 수행함. 해당 조직에서 GFP 형광을 동반하지 않고 HP만을 발현하는 세포들을 화살표로 표시함. 위의 BAC-EGFP 생쥐 망막을 이용한 면역형광염색을 통해 세포 간 이동을 할 것으로 예측된 호메오도메인 전사인자들 중 Prox1에 집중하여 이의 유의성 검증을 하였다. 이론적으로 단백질은 mRNA과 동일한 세포에서 발현이 되어야 하고, 생쥐 Prox1은 alternative spliced varient나 isotype이 발견이 되지 않았기 때문에 Prox1 단백질과 Prox1 mRNA는 동일한 세포에서 관찰이 되어야 한다. 하지만, 생쥐 망막에서 Prox1 mRNA는 주로 INL의 윗부분에 집중되어 분포하는 반면, Prox1 단백질은 이 부분 이외에 INL의 아랫부분에도 존재하였다
표
EGFP-BAC 생쥐 망막에서 호메오도메인 전사인자와 EGFP 분포 비교. 기존 논문과 데이터베이스를 기반으로 생쥐 망막에서 발현이 되는 것으로 알려진 HP들 중 BAC-EGFP 생쥐로 제작된 16종을 도입한 후, 이들 중 성공적으로 GFP 형광을 보이는 것으로 확인된 9종의 생쥐를 분석에 이용함. 이들 생쥐들이 생후 30일 망막 절편을 각각의 HP에 대한 항체와 GFP에 대한 항체로 면역형광염색을 수행함. 해당 조직에서 GFP 형광을 동반하지 않고 HP만을 발현하는 세포들을 화살표로 표시함. 위의 BAC-EGFP 생쥐 망막을 이용한 면역형광염색을 통해 세포 간 이동을 할 것으로 예측된 호메오도메인 전사인자들 중 Prox1에 집중하여 이의 유의성 검증을 하였다. 이론적으로 단백질은 mRNA과 동일한 세포에서 발현이 되어야 하고, 생쥐 Prox1은 alternative spliced varient나 isotype이 발견이 되지 않았기 때문에 Prox1 단백질과 Prox1 mRNA는 동일한 세포에서 관찰이 되어야 한다. 하지만, 생쥐 망막에서 Prox1 mRNA는 주로 INL의 윗부분에 집중되어 분포하는 반면, Prox1 단백질은 이 부분 이외에 INL의 아랫부분에도 존재하였다
 표
분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1의 생체 내 세포간 이동 검증. (A) 세포 외부로의 분비능 및 주변세포로의 침투능이 검증된 호메오도메인 전사인자인 Prox1이 발현되는 곳에서 그와 동시에 GFP가 발현되도록 만든 Prox1-GFP 유전자변형마우스를 이용하여 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자의 생체 내에서의 세포간 이동을 검증하였음. (B) 생후 30일 된 Prox1-GFP 유전자변형 마우스의 망막절편을 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1에 특이적인 항체를 이용하여 면역형광염색하고 형광현미경하에서 관찰한 결과, Calbindin으로 표지된 망막 수평 세포(Horizontal cell, HZC)와 Vsx2로 표지된 망막 양극 세포(bipolar cell, BPC)에서는 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1과 GFP가 같은 위치에 존재하고 있는 반면, Pax6로 표지된 망막 무축색 세포(amacrine cell, ACC)와 p27로 표지된 뮬러 세포(Muller cell, MC)에서는 오로지 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1만 홀로 존재하고 있음을 확인할 수 있었음. 이는 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1의 세포외부로의 분비능 및 주변세포로의 침투능에 의한 BPC로부터 ACC와 MC로의 이동 가능성을 시사함. (C) FITC-labeled Prox1 RNA probe를 이용한 in situ hybridization (ISH) 후 Prox1에 대한 항체를 이용한 면역형광염색을 통해 생쥐 망막 절편에서의 Prox1 단백질과 mRNA의 분포를 조사함으로써 endogenous Prox1의 망막 신경 세포에서의 세포간 이동을 검증함
표
분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1의 생체 내 세포간 이동 검증. (A) 세포 외부로의 분비능 및 주변세포로의 침투능이 검증된 호메오도메인 전사인자인 Prox1이 발현되는 곳에서 그와 동시에 GFP가 발현되도록 만든 Prox1-GFP 유전자변형마우스를 이용하여 분비성 호메오도메인 전사인자의 생체 내에서의 세포간 이동을 검증하였음. (B) 생후 30일 된 Prox1-GFP 유전자변형 마우스의 망막절편을 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1에 특이적인 항체를 이용하여 면역형광염색하고 형광현미경하에서 관찰한 결과, Calbindin으로 표지된 망막 수평 세포(Horizontal cell, HZC)와 Vsx2로 표지된 망막 양극 세포(bipolar cell, BPC)에서는 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1과 GFP가 같은 위치에 존재하고 있는 반면, Pax6로 표지된 망막 무축색 세포(amacrine cell, ACC)와 p27로 표지된 뮬러 세포(Muller cell, MC)에서는 오로지 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1만 홀로 존재하고 있음을 확인할 수 있었음. 이는 호메오도메인 전사인자 Prox1의 세포외부로의 분비능 및 주변세포로의 침투능에 의한 BPC로부터 ACC와 MC로의 이동 가능성을 시사함. (C) FITC-labeled Prox1 RNA probe를 이용한 in situ hybridization (ISH) 후 Prox1에 대한 항체를 이용한 면역형광염색을 통해 생쥐 망막 절편에서의 Prox1 단백질과 mRNA의 분포를 조사함으로써 endogenous Prox1의 망막 신경 세포에서의 세포간 이동을 검증함
 표
망막 특이적 Prox1-cko 마우스 제작. (A) MC에 존재하는 Prox1 단백질이 세포자체 내 전사를 동반하지 않고 외부에서 유입된 것인지를 확인하기 위해 Prox1 유전자 부위에 EGFP가 Cre recombinase에 의존적으로 발현되는 Prox1-floxed GFP (Prox1fg/fg) knock-in 생쥐와, 망막 전체 세포에서 Cre recombinase 활성이 나타나는 Dkk3-Cre 생쥐를 교배하여 Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐를 제작함. 이 생쥐 망막에서 Cre recombinase 활성이 나타난 세포를 표지하기 위해 R26R Cre reporter를 함께 가진 생쥐를 제작함. (B) 그 결과, 망막 전체에서 Cre recombinase의 활성에 의해 β-galactosidase가 발현됨과 동시에 망막내에서 Prox1 유전자 부위의 전사 활성을 나타내는 부위에서 EGFP 신호가 나타남을 확인함. (C) Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐 망막 내 Prox1 단백질의 양을 Western blot (WB)을 통해 비교함. 그 결과 정상 생쥐에 비해 Prox1단백질의 양이 현저히 줄어들어 있음을 확인하였으며, Prox1 단백질을 대신해서 EGFP 단백질이 발현되었음을 확인함
표
망막 특이적 Prox1-cko 마우스 제작. (A) MC에 존재하는 Prox1 단백질이 세포자체 내 전사를 동반하지 않고 외부에서 유입된 것인지를 확인하기 위해 Prox1 유전자 부위에 EGFP가 Cre recombinase에 의존적으로 발현되는 Prox1-floxed GFP (Prox1fg/fg) knock-in 생쥐와, 망막 전체 세포에서 Cre recombinase 활성이 나타나는 Dkk3-Cre 생쥐를 교배하여 Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐를 제작함. 이 생쥐 망막에서 Cre recombinase 활성이 나타난 세포를 표지하기 위해 R26R Cre reporter를 함께 가진 생쥐를 제작함. (B) 그 결과, 망막 전체에서 Cre recombinase의 활성에 의해 β-galactosidase가 발현됨과 동시에 망막내에서 Prox1 유전자 부위의 전사 활성을 나타내는 부위에서 EGFP 신호가 나타남을 확인함. (C) Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐 망막 내 Prox1 단백질의 양을 Western blot (WB)을 통해 비교함. 그 결과 정상 생쥐에 비해 Prox1단백질의 양이 현저히 줄어들어 있음을 확인하였으며, Prox1 단백질을 대신해서 EGFP 단백질이 발현되었음을 확인함
 표
Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐를 이용한 망막 세포 내 Prox1 단백질의 자발적 비자발적 발현 판명. (A, B) Prox1 BAX TG 생쥐 망막에서 Prox1 유전자를 발현할 것으로 예상된 Calbindin으로 표지된 HZC과 Vsx2로 표지된 BPC는 물론, Prox1 유전자를 발현하지 않을 것으로 예측되었던 Pax6로 표지된 ACC에서 역시 Prox1 유전자 부위의 전사 활성을 나타내는 EGFP 신호가 관찰됨. 이를 통하여 ACC에서 관찰된 Prox1 단백질 역시 자체 내 Prox1 전사를 통해 생성된 것임을 확인 하였음. 그러나 p27과 Sox2에 의해 표지되는 MC은 EGFP의 발현 없이 Prox1 단백질을 나타냄을 확인함. 이는 MC에 존재하는 Prox1이 외부에서 유입되었을 가능성을 시사함. (C) Prox1 단백질을 자발적으로 발현하는 것으로 검증된 HZC, BPC, 그리고 AC의 경우에는 Prox1 유전자가 하나 제거된 Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐의 망막에서 그 수가 현저히 줄어들었으나, Prox1단백질이 외부에서 유입되었을것이라 판단되는 MC의 경우에는 그 수의 변화가 나타나지 않았음. (D) Prox1 유전자가 하나 제거된 경우에 MC의 전체 세포의 숫자는 변하지 않았지만, MC내에 존재하는 Prox1의 양은 Prox1 유전자의 제거에 동반되어 감소하는 특징을 보임. 이는 Prox1을 발현하는 세포에서 Prox1의 생산량이 감소하면 Prox1을 받아들이는 MC내의 Prox1 단백질의 양 또한 감소하였을 가능성을 시사함
표
Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐를 이용한 망막 세포 내 Prox1 단백질의 자발적 비자발적 발현 판명. (A, B) Prox1 BAX TG 생쥐 망막에서 Prox1 유전자를 발현할 것으로 예상된 Calbindin으로 표지된 HZC과 Vsx2로 표지된 BPC는 물론, Prox1 유전자를 발현하지 않을 것으로 예측되었던 Pax6로 표지된 ACC에서 역시 Prox1 유전자 부위의 전사 활성을 나타내는 EGFP 신호가 관찰됨. 이를 통하여 ACC에서 관찰된 Prox1 단백질 역시 자체 내 Prox1 전사를 통해 생성된 것임을 확인 하였음. 그러나 p27과 Sox2에 의해 표지되는 MC은 EGFP의 발현 없이 Prox1 단백질을 나타냄을 확인함. 이는 MC에 존재하는 Prox1이 외부에서 유입되었을 가능성을 시사함. (C) Prox1 단백질을 자발적으로 발현하는 것으로 검증된 HZC, BPC, 그리고 AC의 경우에는 Prox1 유전자가 하나 제거된 Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐의 망막에서 그 수가 현저히 줄어들었으나, Prox1단백질이 외부에서 유입되었을것이라 판단되는 MC의 경우에는 그 수의 변화가 나타나지 않았음. (D) Prox1 유전자가 하나 제거된 경우에 MC의 전체 세포의 숫자는 변하지 않았지만, MC내에 존재하는 Prox1의 양은 Prox1 유전자의 제거에 동반되어 감소하는 특징을 보임. 이는 Prox1을 발현하는 세포에서 Prox1의 생산량이 감소하면 Prox1을 받아들이는 MC내의 Prox1 단백질의 양 또한 감소하였을 가능성을 시사함
 표
Prox1 유전자를 제거한 Muller glia 세포에서 외부 유래 Prox1 단백질의 검출. (A) MG 내에 존재하는 Prox1 단백질의 비자발적 발현을 다시한번 검증하기 위하여 Prox1fg/fg knock-in 생 쥐와 MG에서 특이적 활성을 보이는 Glast 유전자 부위의 발현 조절을 받는 CreERt2를 발현하는 Glast-CreERt2 생쥐를 교배하여 Prox1fg/+;Glast-CreERt2 생쥐를 제작함. 이 생쥐에서 CreERt2 단 백질은 estrogen analog인 tamoxifen에 의해 활성화 되는 특징이 있으므로, 생후 21일과 22일 양일 간에 걸쳐 생쥐 복강 내 10mg/kg으로 tamoxifen을 주입 후 생후 30일에 생쥐 안구를 적출하여 Cre recombinase에 의해 유전자 재조합이 일어나 Prox1 대신 EGFP를 발현한 망막 세포의 존재 여부를 확인함. 그 결과 생쥐의 망막내 MG에서 Prox1 유전자 부위의 전사 활성을 나타내는 EGFP 신호가 검출되지 않았음. 그러나 Prox1fg/fg knock-in 생쥐와 BPC에서 특이적 활성을 보이는 Chx10 유전자 부위의 발현 조절을 받는 CreERt2를 발현하는 Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐를 교배하여 제작한 Prox1fg/+;Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐의 망막에서는 BPC에서 Prox1 유전자 부위의 전사 활성을 나타내는 EGFP 신호가 검출되었음. 이는 Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐를 통해 확인한바와 일치하는 결과임. (B) 앞서 제작한 Prox1fg/+;Glast-CreERt2 생쥐 망막의 MG에서 Prox1 유전자가 확실하게 제거되었음 을 검증하기위해 Cre recombinase 활성이 나타난 세포를 표지하는 Rosa-tdTomato Cre reporter를 함께 가진 Prox1fg/+;Glast-CreERt2;Rosa-tdTomato생쥐를 제작하고, 이 생쥐의 MG에 여전히 Prox1 단백질이 존재하는지의 여부를 검사함
표
Prox1 유전자를 제거한 Muller glia 세포에서 외부 유래 Prox1 단백질의 검출. (A) MG 내에 존재하는 Prox1 단백질의 비자발적 발현을 다시한번 검증하기 위하여 Prox1fg/fg knock-in 생 쥐와 MG에서 특이적 활성을 보이는 Glast 유전자 부위의 발현 조절을 받는 CreERt2를 발현하는 Glast-CreERt2 생쥐를 교배하여 Prox1fg/+;Glast-CreERt2 생쥐를 제작함. 이 생쥐에서 CreERt2 단 백질은 estrogen analog인 tamoxifen에 의해 활성화 되는 특징이 있으므로, 생후 21일과 22일 양일 간에 걸쳐 생쥐 복강 내 10mg/kg으로 tamoxifen을 주입 후 생후 30일에 생쥐 안구를 적출하여 Cre recombinase에 의해 유전자 재조합이 일어나 Prox1 대신 EGFP를 발현한 망막 세포의 존재 여부를 확인함. 그 결과 생쥐의 망막내 MG에서 Prox1 유전자 부위의 전사 활성을 나타내는 EGFP 신호가 검출되지 않았음. 그러나 Prox1fg/fg knock-in 생쥐와 BPC에서 특이적 활성을 보이는 Chx10 유전자 부위의 발현 조절을 받는 CreERt2를 발현하는 Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐를 교배하여 제작한 Prox1fg/+;Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐의 망막에서는 BPC에서 Prox1 유전자 부위의 전사 활성을 나타내는 EGFP 신호가 검출되었음. 이는 Prox1fg/+;Dkk3-Cre 생쥐를 통해 확인한바와 일치하는 결과임. (B) 앞서 제작한 Prox1fg/+;Glast-CreERt2 생쥐 망막의 MG에서 Prox1 유전자가 확실하게 제거되었음 을 검증하기위해 Cre recombinase 활성이 나타난 세포를 표지하는 Rosa-tdTomato Cre reporter를 함께 가진 Prox1fg/+;Glast-CreERt2;Rosa-tdTomato생쥐를 제작하고, 이 생쥐의 MG에 여전히 Prox1 단백질이 존재하는지의 여부를 검사함
 표
Muller glia 내 양극세포 유래 Prox1의 존재. (A, B) Prox1fg/fgknock-in생쥐와 양극세포에서 특이적 활성을 보이는 Chx10 유전자 부위의 발현 조절을 받는 CreERt2를 발현하는 Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐를 교배하여 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2생쥐를 제작함으로써 Prox1 단백질을 자발적으로 발현하는 BPC에서 Prox1 유전자를 한 개 혹은 두 개 모두 제거한 후, Calbindin으로 표지된 HZC와 Pax6로 표지된 ACC, 그리고 p27로 표지된 MG에 존재하는 Prox1 단백질의 양을 검사하였음. Tamoxifen을 주입한 Prox1fg/+;Chx10-CreERt2생쥐와 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2생쥐 망막 내 BPC에서 Prox1 단백질의 발현을 대신한 EGFP 신호를 관찰함으로써 BPC에서의 Prox1 유전자가 효과적으로 제거되었음을 확인함. 실제로 해당 생쥐의 BPC에 존재하는 Prox1 단백질의 양이 정상 생쥐의 57%, 11% 수준으로 유의미하게 감소되어 있었음. 이와 동시에 MG에서의 Prox1 단백질양 또한 정상 생쥐의 40%, 18% 수준으로 유의미하게 감소되었음. 그러나 MG에서 Prox1의 감소는 EGFP 신호를 동반하지 않는 현상으로, 즉 Cre recombinase에 의한 Prox1 유전자의 상실 없이 나타난 현상으로, 이는 BPC에서 Prox1의 단백질 감소로 인해 이를 받아들이는 MG내의 Prox1 역시 감소했음을 의미함. (C) BPC에서 Prox1 유전자의 제거는 생쥐 망막 조직 내 각각의 신경세포의 숫자에는 영향을 미치지 않는 것을 확인함
표
Muller glia 내 양극세포 유래 Prox1의 존재. (A, B) Prox1fg/fgknock-in생쥐와 양극세포에서 특이적 활성을 보이는 Chx10 유전자 부위의 발현 조절을 받는 CreERt2를 발현하는 Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐를 교배하여 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2생쥐를 제작함으로써 Prox1 단백질을 자발적으로 발현하는 BPC에서 Prox1 유전자를 한 개 혹은 두 개 모두 제거한 후, Calbindin으로 표지된 HZC와 Pax6로 표지된 ACC, 그리고 p27로 표지된 MG에 존재하는 Prox1 단백질의 양을 검사하였음. Tamoxifen을 주입한 Prox1fg/+;Chx10-CreERt2생쥐와 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2생쥐 망막 내 BPC에서 Prox1 단백질의 발현을 대신한 EGFP 신호를 관찰함으로써 BPC에서의 Prox1 유전자가 효과적으로 제거되었음을 확인함. 실제로 해당 생쥐의 BPC에 존재하는 Prox1 단백질의 양이 정상 생쥐의 57%, 11% 수준으로 유의미하게 감소되어 있었음. 이와 동시에 MG에서의 Prox1 단백질양 또한 정상 생쥐의 40%, 18% 수준으로 유의미하게 감소되었음. 그러나 MG에서 Prox1의 감소는 EGFP 신호를 동반하지 않는 현상으로, 즉 Cre recombinase에 의한 Prox1 유전자의 상실 없이 나타난 현상으로, 이는 BPC에서 Prox1의 단백질 감소로 인해 이를 받아들이는 MG내의 Prox1 역시 감소했음을 의미함. (C) BPC에서 Prox1 유전자의 제거는 생쥐 망막 조직 내 각각의 신경세포의 숫자에는 영향을 미치지 않는 것을 확인함
 표
망막 손상 상황에서 Muller glia 세포 내 Prox1 양 증가. (A, B) 광수용세포의 광손상에 의한 MG 세포 내 Prox1 양의 증가. MG 세포는 성체 망막에서 지속적으로 퇴화되는 광수용세포의 재생을 담당하는 것으로 알려져 있음. 또한, Prox1은 배아 망막 내 망막신경전구세포의 유지에 필요한 것으로 알려져 있어, MG에 존재하는 외래 Prox1이 MG가 광수용세포 전구세포로 유지되는데 관여할 가능성이 있음. 이러한 가설은 강한 빛을 가하여 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한 생쥐 망막에서 일어나는 MG의 광수용세포 재생 과정에서 Prox1 단백질의 양이 증가하는 양상을 통해 확인하였음. (C, D) Glutamate excitotoxicity에 의해 유도된 망막 손상 상황에서 MG세포 내 Prox1 양 증가. 망막 내 glutamate를 신경전달물질로 활성화되는 AC, retinal ganglion cell (RGC) 등이 과도한 glutamate 신경전달 작용으로 인해 퇴화되면 MG 세포가 이를 부분적으로 재생하기 위해 세포 분열하여 분화한다는 것이 알려져 있음. 이러한 과정에서 주로 신경전구세포에 발현이 강한 Prox1이 역 할을 할 가능성을 확인하기 위해, glutamate의 analog인 NMDA를 생후 30일 생쥐 안구 내에 직접 주입함. 그 후 7일째 생쥐 안구를 분리 후 망막에서 Sox2로 표지되는 MG 세포 내에 존재하는 Prox1의 양을 PBS를 주입한 생쥐 망막과 비교함
표
망막 손상 상황에서 Muller glia 세포 내 Prox1 양 증가. (A, B) 광수용세포의 광손상에 의한 MG 세포 내 Prox1 양의 증가. MG 세포는 성체 망막에서 지속적으로 퇴화되는 광수용세포의 재생을 담당하는 것으로 알려져 있음. 또한, Prox1은 배아 망막 내 망막신경전구세포의 유지에 필요한 것으로 알려져 있어, MG에 존재하는 외래 Prox1이 MG가 광수용세포 전구세포로 유지되는데 관여할 가능성이 있음. 이러한 가설은 강한 빛을 가하여 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한 생쥐 망막에서 일어나는 MG의 광수용세포 재생 과정에서 Prox1 단백질의 양이 증가하는 양상을 통해 확인하였음. (C, D) Glutamate excitotoxicity에 의해 유도된 망막 손상 상황에서 MG세포 내 Prox1 양 증가. 망막 내 glutamate를 신경전달물질로 활성화되는 AC, retinal ganglion cell (RGC) 등이 과도한 glutamate 신경전달 작용으로 인해 퇴화되면 MG 세포가 이를 부분적으로 재생하기 위해 세포 분열하여 분화한다는 것이 알려져 있음. 이러한 과정에서 주로 신경전구세포에 발현이 강한 Prox1이 역 할을 할 가능성을 확인하기 위해, glutamate의 analog인 NMDA를 생후 30일 생쥐 안구 내에 직접 주입함. 그 후 7일째 생쥐 안구를 분리 후 망막에서 Sox2로 표지되는 MG 세포 내에 존재하는 Prox1의 양을 PBS를 주입한 생쥐 망막과 비교함
 표
MNU (N-methyl-N-nitrosourea)를 이용한 광수용세포 특이적 퇴화 유도. 마우스의 복강에 MNU를 주사하여 망막내 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도했을 때, 시간의 흐름에 따라 Sox2로 표지된 MG 세포 내에서 Prox1의 양이 증가함과 동시에 BrdU로 표지된 새롭게 증식하는 세포의 수 또한 증가함을 확인함. 이러한 결과는, 광수용세포의 손상은 외부로부터 MG내로 Prox1 단백질의 유입을 촉진하고, 이로인해 MG에 축적된 과량의 외인성 Prox1이 MG의 증식을 촉진함으로써 MG가 손상된 망막신경세포로 분화하여 망막신경세포의 재생을 촉진하는데 관여할 것이라는 가능성을 시사함
표
MNU (N-methyl-N-nitrosourea)를 이용한 광수용세포 특이적 퇴화 유도. 마우스의 복강에 MNU를 주사하여 망막내 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도했을 때, 시간의 흐름에 따라 Sox2로 표지된 MG 세포 내에서 Prox1의 양이 증가함과 동시에 BrdU로 표지된 새롭게 증식하는 세포의 수 또한 증가함을 확인함. 이러한 결과는, 광수용세포의 손상은 외부로부터 MG내로 Prox1 단백질의 유입을 촉진하고, 이로인해 MG에 축적된 과량의 외인성 Prox1이 MG의 증식을 촉진함으로써 MG가 손상된 망막신경세포로 분화하여 망막신경세포의 재생을 촉진하는데 관여할 것이라는 가능성을 시사함
 표
손상된 망망신경세포에서 Muller glia로부터 광수용세포로의 망막신경세포 재생. MNU를 주사하여 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한지 4일후에 보이는 BrdU로 표지된 세포들이 MG로부터 유래된 세포인지를 확인하고자 MG에서 특이적 활성을 보이는 Glast 유전자 부위의 발현 조절을 받는 CreERt2를 발현하는 Glast-CreERt2 생쥐를 만들었으며, 이 생쥐 망막에서 Cre recombinase 활성이 나타난 MG를 표지하기 위해 Rosa-tdTomato Cre reporter를 함께 가진 생쥐를 제작함. 광수용 세포의 퇴화를 유도한 이후에 tdTomato로 표지되는 MG의 이동을 추적해본 결과, 처음에는 tdTomato로 표지된 MG세포들이 그들의 원래 위치인 Sox9으로 표지된 MG층에서만 존재하였으나, 4일 후에는 그들중 일부가 광수용세포층으로 이동하여 rhodopsin으로 표지되는 광수용세포로 완전히 분화되어있음을 확인하였음
표
손상된 망망신경세포에서 Muller glia로부터 광수용세포로의 망막신경세포 재생. MNU를 주사하여 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한지 4일후에 보이는 BrdU로 표지된 세포들이 MG로부터 유래된 세포인지를 확인하고자 MG에서 특이적 활성을 보이는 Glast 유전자 부위의 발현 조절을 받는 CreERt2를 발현하는 Glast-CreERt2 생쥐를 만들었으며, 이 생쥐 망막에서 Cre recombinase 활성이 나타난 MG를 표지하기 위해 Rosa-tdTomato Cre reporter를 함께 가진 생쥐를 제작함. 광수용 세포의 퇴화를 유도한 이후에 tdTomato로 표지되는 MG의 이동을 추적해본 결과, 처음에는 tdTomato로 표지된 MG세포들이 그들의 원래 위치인 Sox9으로 표지된 MG층에서만 존재하였으나, 4일 후에는 그들중 일부가 광수용세포층으로 이동하여 rhodopsin으로 표지되는 광수용세포로 완전히 분화되어있음을 확인하였음
 표
Prox1 재조합 단백질의 대량생산. Prox1 단백질의 망막신경세포 재생 효과를 직접적으로 검증하기 위해 flag-tag이 표지된 Prox1 재조합 단백질을 대량생산하였음. 대장균을 이용한 대량 생산 시스템에서 대부분 단백질 용해성의 문제로 분리가 어려웠던 호메오도메인 전사인자 단백질들의 대량 생산 유도를 위해 Sf9 세포에 vaculovirus를 이용한 발현 시스템을 이용하였음. Flag 표지된 Prox1 cDNA를 pFastBac vaculovirus vector에 cloning 한 후 Sf9 insect cell에 transfection 후 recombinant protein을 발현하는 vaculovirus를 분리 후 다시 Sf9 세포에 감염하여 단백질 발현을 유도함. 해당 세포에서 Flag-Prox1을 Flag antibody를 이용하여 affinity purification 후 antibody-protein complex에서 protein을 acid elution 하여 20ul elution fraction을 SDS-PAGE 후 Coommassie Blue staining으로 검출함. Flag-Prox1 단백질의 상대량 계산을 위해 특정량의 bovine serum albumin (BSA)를 함께 검출하였음
표
Prox1 재조합 단백질의 대량생산. Prox1 단백질의 망막신경세포 재생 효과를 직접적으로 검증하기 위해 flag-tag이 표지된 Prox1 재조합 단백질을 대량생산하였음. 대장균을 이용한 대량 생산 시스템에서 대부분 단백질 용해성의 문제로 분리가 어려웠던 호메오도메인 전사인자 단백질들의 대량 생산 유도를 위해 Sf9 세포에 vaculovirus를 이용한 발현 시스템을 이용하였음. Flag 표지된 Prox1 cDNA를 pFastBac vaculovirus vector에 cloning 한 후 Sf9 insect cell에 transfection 후 recombinant protein을 발현하는 vaculovirus를 분리 후 다시 Sf9 세포에 감염하여 단백질 발현을 유도함. 해당 세포에서 Flag-Prox1을 Flag antibody를 이용하여 affinity purification 후 antibody-protein complex에서 protein을 acid elution 하여 20ul elution fraction을 SDS-PAGE 후 Coommassie Blue staining으로 검출함. Flag-Prox1 단백질의 상대량 계산을 위해 특정량의 bovine serum albumin (BSA)를 함께 검출하였음
 표
Prox1 재조합 단백질의 망막신경세포로의 침투능력 검증. ‘그림 141’에서 생산한 Prox1 재조합 단백질을 각각 MNU를 주사하여 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한 생쥐와 PBS를 주입한 생쥐의 안구에 주입하여 이들의 망막신경세포로의 침투능력을 검증하였음. Flag-antibody를 사용한 면역형 광염색법을 사용하여 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 망막내 존재여부를 확인하였을 때, 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한 생쥐 망막에서 더 많은 양의 Prox1 재조합 단백질이 관찰되었음. 특히 이들 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 대부분은 Sox2로 표지된 MG에 존재하고 있음을 확인함
표
Prox1 재조합 단백질의 망막신경세포로의 침투능력 검증. ‘그림 141’에서 생산한 Prox1 재조합 단백질을 각각 MNU를 주사하여 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한 생쥐와 PBS를 주입한 생쥐의 안구에 주입하여 이들의 망막신경세포로의 침투능력을 검증하였음. Flag-antibody를 사용한 면역형 광염색법을 사용하여 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 망막내 존재여부를 확인하였을 때, 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한 생쥐 망막에서 더 많은 양의 Prox1 재조합 단백질이 관찰되었음. 특히 이들 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 대부분은 Sox2로 표지된 MG에 존재하고 있음을 확인함
 표
Prox1 재조합 단백질을 사용한 망막신경세포 재생 촉진 효과 검증. (A, B) BP에서 Prox1의 감소로 인해 이를 받아들이는 MG내의 Prox1 역시 감소되도록 만들어놓은 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐의 경우, 정상 생쥐와는 다르게 MNU를 이용하여 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한 경우에도 Sox2로 표지된 MG내에서의 Prox1 단백질의 증가가 크게 나타나지 않았음. 이것은 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 주입에 의해 다시 정상 생쥐와 비슷한 수준으로 회복됨을 확인하였음. (C, D) MG내의 Prox1이 감소되도록 만들어놓은 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐의 경우에는 MNU를 이용한 광수용세포의 퇴화조건에서 BrdU로 표지되는 MG로부터 새롭게 증식한 세포의 수 또한 정상 생쥐에서보다 크게 감소되어있었으나, 이또한 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 주입에 의해 다시 정상 생쥐와 비슷한 수준으로 회복됨을 확인하였음. (E, F) 망막신경세포 손상 후 MG에 존재하는 Prox1에 의해 유도된다고 생각되는 MG부터 광수용세포로의 망막신경세포 재생 정도 또한 정상생쥐에 비해 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐에서 크게 감소하였지만, 이 역시 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 주입에 의해 다시 정상 생쥐와 비슷한 수준으로 회복됨을 확인하였음
표
Prox1 재조합 단백질을 사용한 망막신경세포 재생 촉진 효과 검증. (A, B) BP에서 Prox1의 감소로 인해 이를 받아들이는 MG내의 Prox1 역시 감소되도록 만들어놓은 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐의 경우, 정상 생쥐와는 다르게 MNU를 이용하여 광수용세포의 퇴화를 유도한 경우에도 Sox2로 표지된 MG내에서의 Prox1 단백질의 증가가 크게 나타나지 않았음. 이것은 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 주입에 의해 다시 정상 생쥐와 비슷한 수준으로 회복됨을 확인하였음. (C, D) MG내의 Prox1이 감소되도록 만들어놓은 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐의 경우에는 MNU를 이용한 광수용세포의 퇴화조건에서 BrdU로 표지되는 MG로부터 새롭게 증식한 세포의 수 또한 정상 생쥐에서보다 크게 감소되어있었으나, 이또한 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 주입에 의해 다시 정상 생쥐와 비슷한 수준으로 회복됨을 확인하였음. (E, F) 망막신경세포 손상 후 MG에 존재하는 Prox1에 의해 유도된다고 생각되는 MG부터 광수용세포로의 망막신경세포 재생 정도 또한 정상생쥐에 비해 Prox1fg/fg;Chx10-CreERt2 생쥐에서 크게 감소하였지만, 이 역시 Prox1 재조합 단백질의 주입에 의해 다시 정상 생쥐와 비슷한 수준으로 회복됨을 확인하였음
해당 보고서가 속한 카테고리에서 활용도가 높은 상위 5개 콘텐츠를 보여줍니다.
더보기 버튼을 클릭하시면 더 많은 관련자료를 살펴볼 수 있습니다.
| 과제명(ProjectTitle) : | - |
|---|---|
| 연구책임자(Manager) : | - |
| 과제기간(DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 총연구비 (DetailSeriesProject) : | - |
| 키워드(keyword) : | - |
| 과제수행기간(LeadAgency) : | - |
| 연구목표(Goal) : | - |
| 연구내용(Abstract) : | - |
| 기대효과(Effect) : | - |
| 내보내기 구분 |
|
|---|---|
| 구성항목 |
관리번호, 제목(한글), 저자명(한글), 발행일자, 전자원문, 초록(한글), 초록(영문) 관리번호, 제목(한글), 제목(영문), 저자명(한글), 저자명(영문), 주관연구기관(한글), 주관연구기관(영문), 발행일자, 총페이지수, 주관부처명, 과제시작일, 보고서번호, 과제종료일, 주제분류, 키워드(한글), 전자원문, 키워드(영문), 입수제어번호, 초록(한글), 초록(영문), 목차 |
| 저장형식 |
|
| 메일정보 |
|
| 안내 |
총 건의 자료가 검색되었습니다. 다운받으실 자료의 인덱스를 입력하세요. (1-10,000) 검색결과의 순서대로 최대 10,000건 까지 다운로드가 가능합니다. 데이타가 많을 경우 속도가 느려질 수 있습니다.(최대 2~3분 소요) 다운로드 파일은 UTF-8 형태로 저장됩니다. ~ |
Copyright KISTI. All Rights Reserved.
AI-Helper는 오픈소스 모델을 사용합니다. 사용하고 있는 오픈소스 모델과 라이센스는 아래에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
AI-Helper uses Open Source Models. You can find the source code of these open source models, along with applicable license information below. (helpdesk@kisti.re.kr)
OpenAI의 API Key를 브라우저에 등록하여야 ChatGPT 모델을 사용할 수 있습니다.
등록키는 삭제 버튼을 누르거나, PDF 창을 닫으면 삭제됩니다.

※ AI-Helper는 부적절한 답변을 할 수 있습니다.